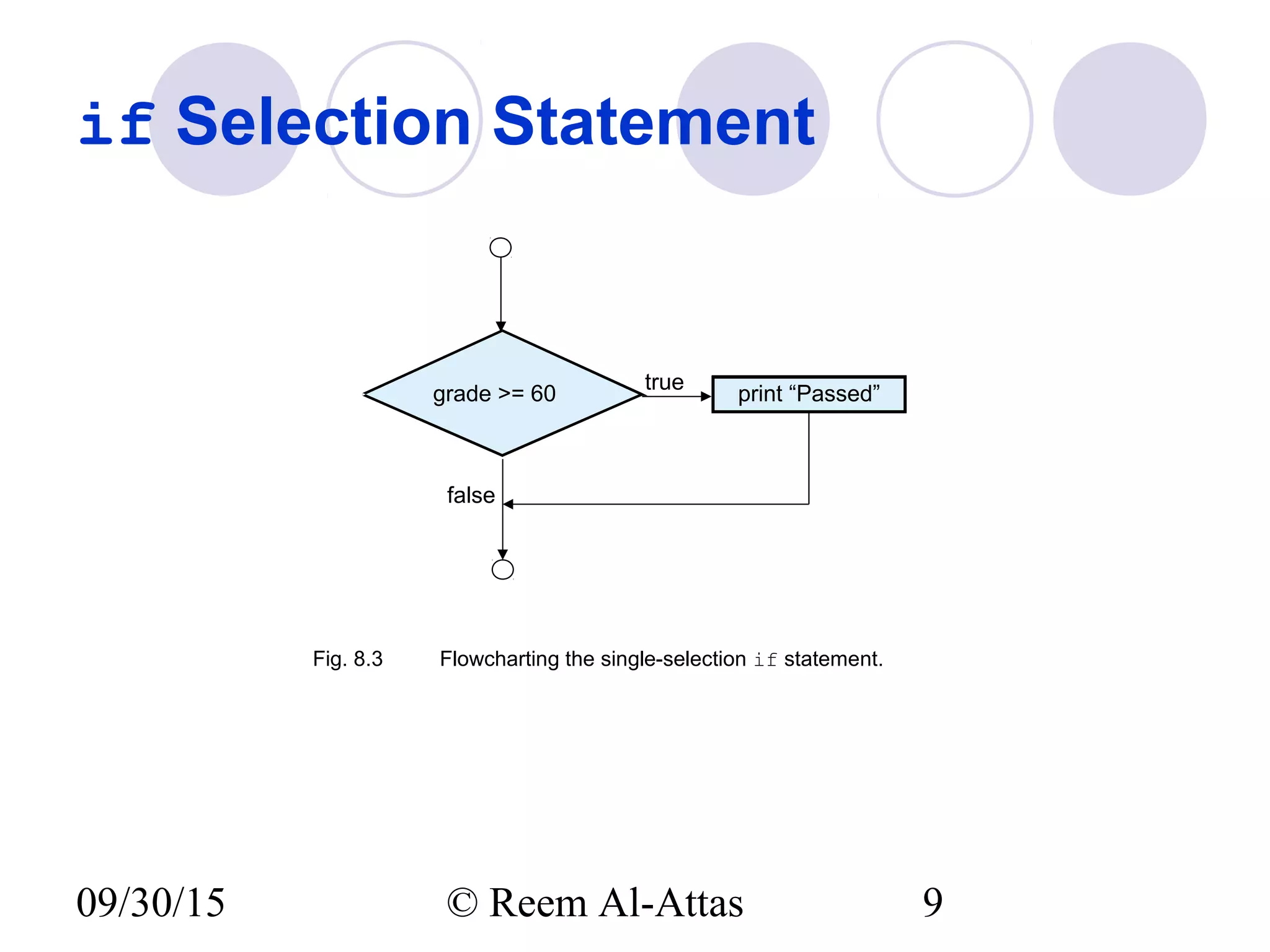
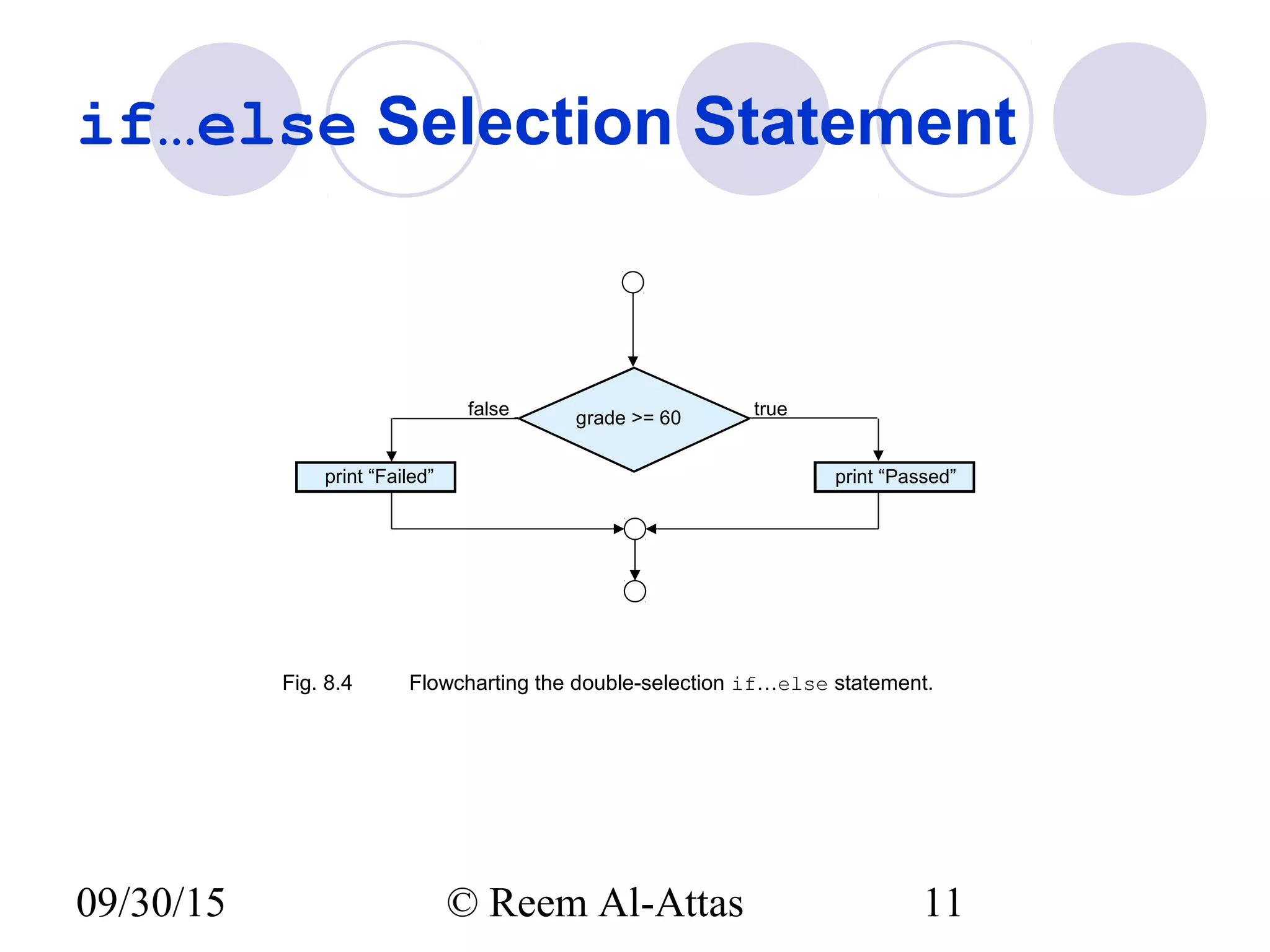
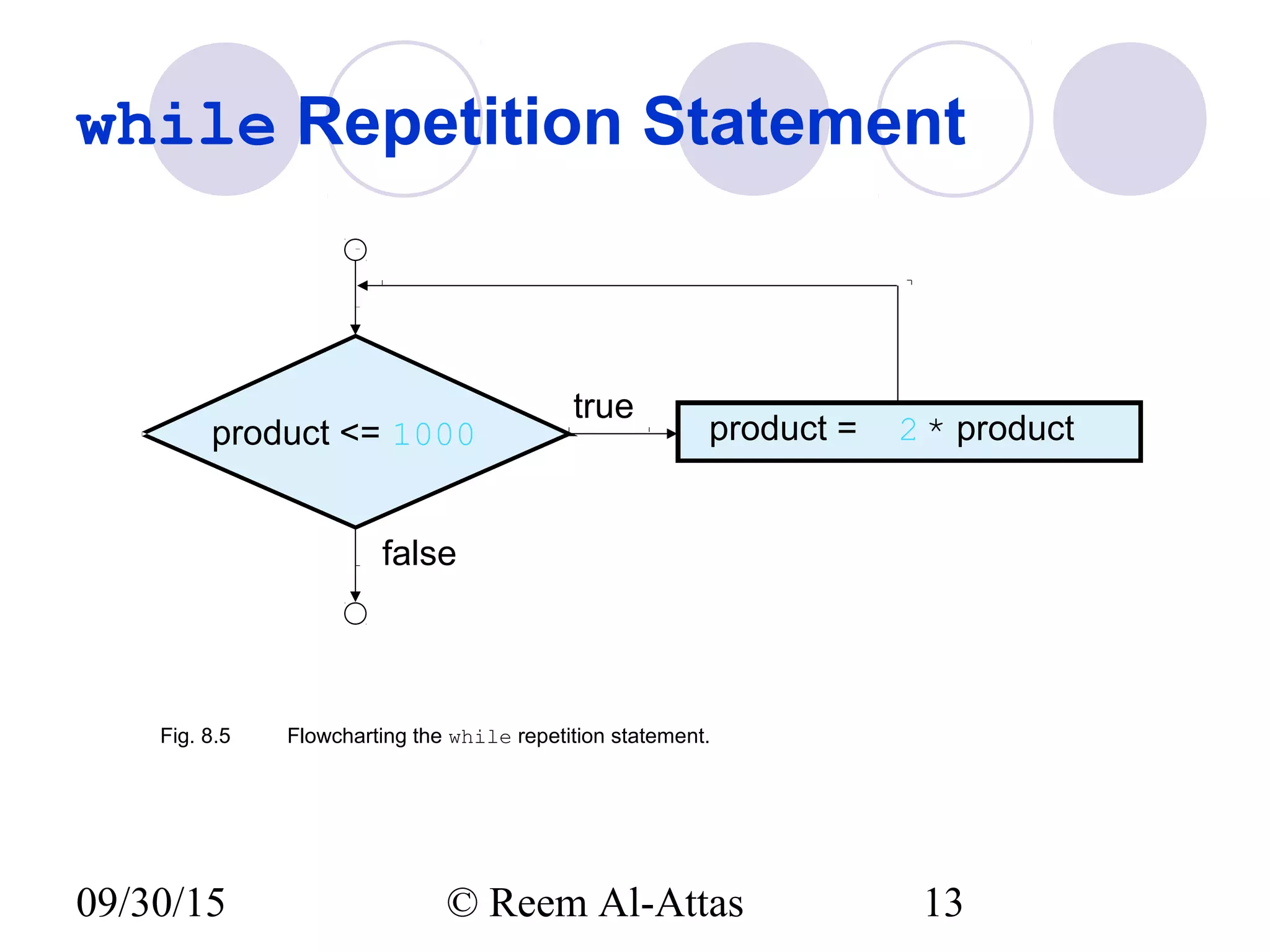
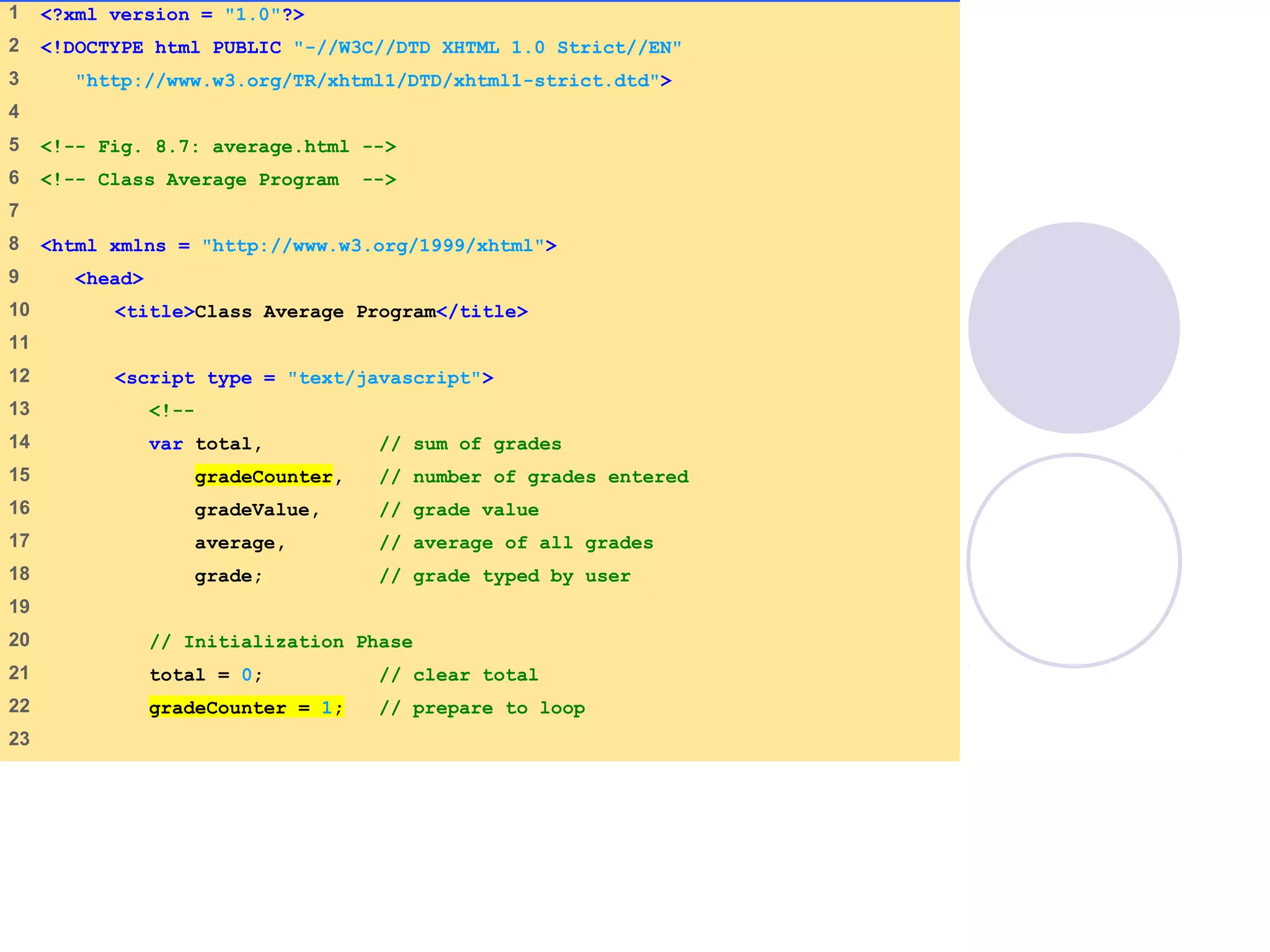
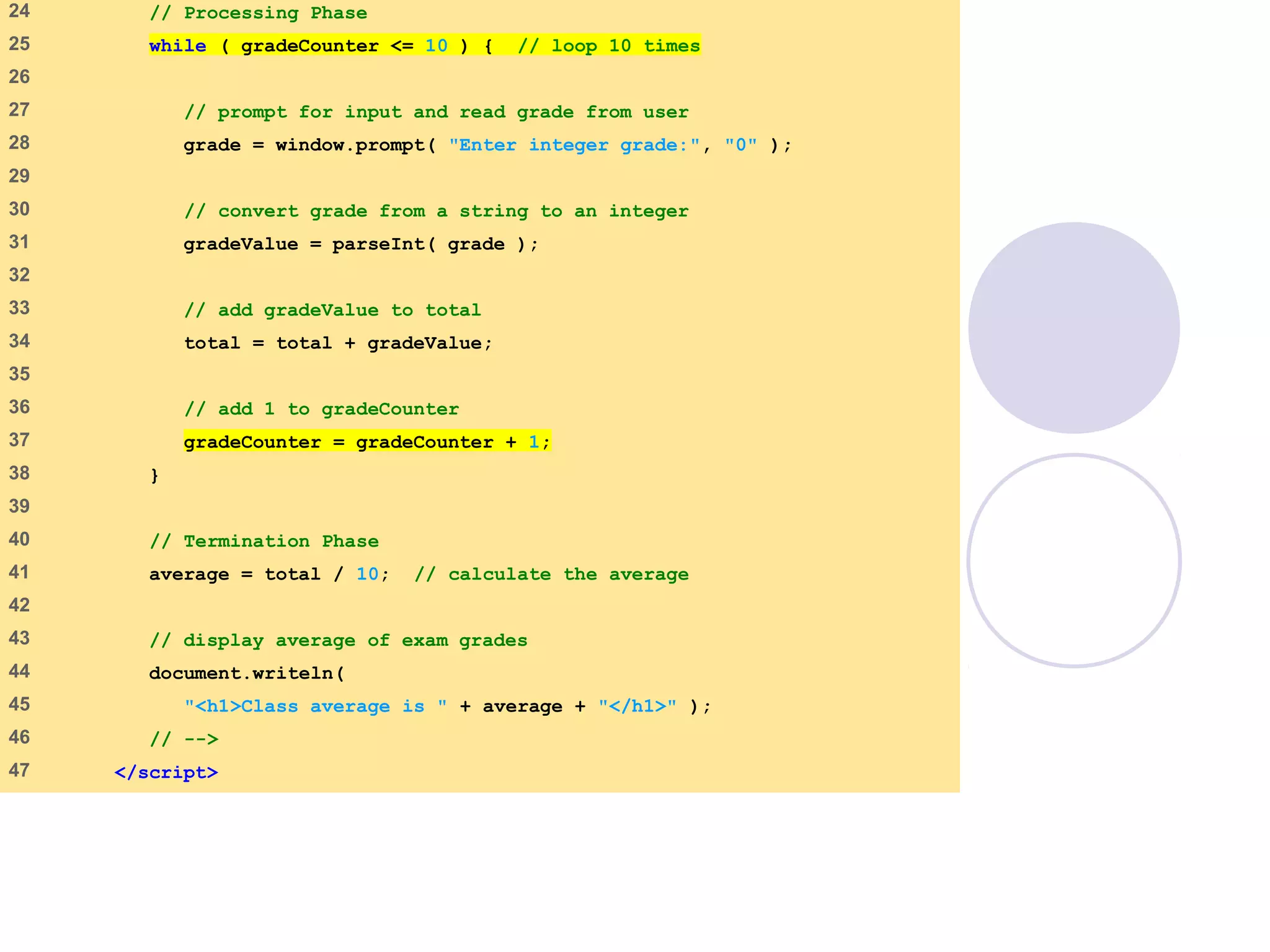
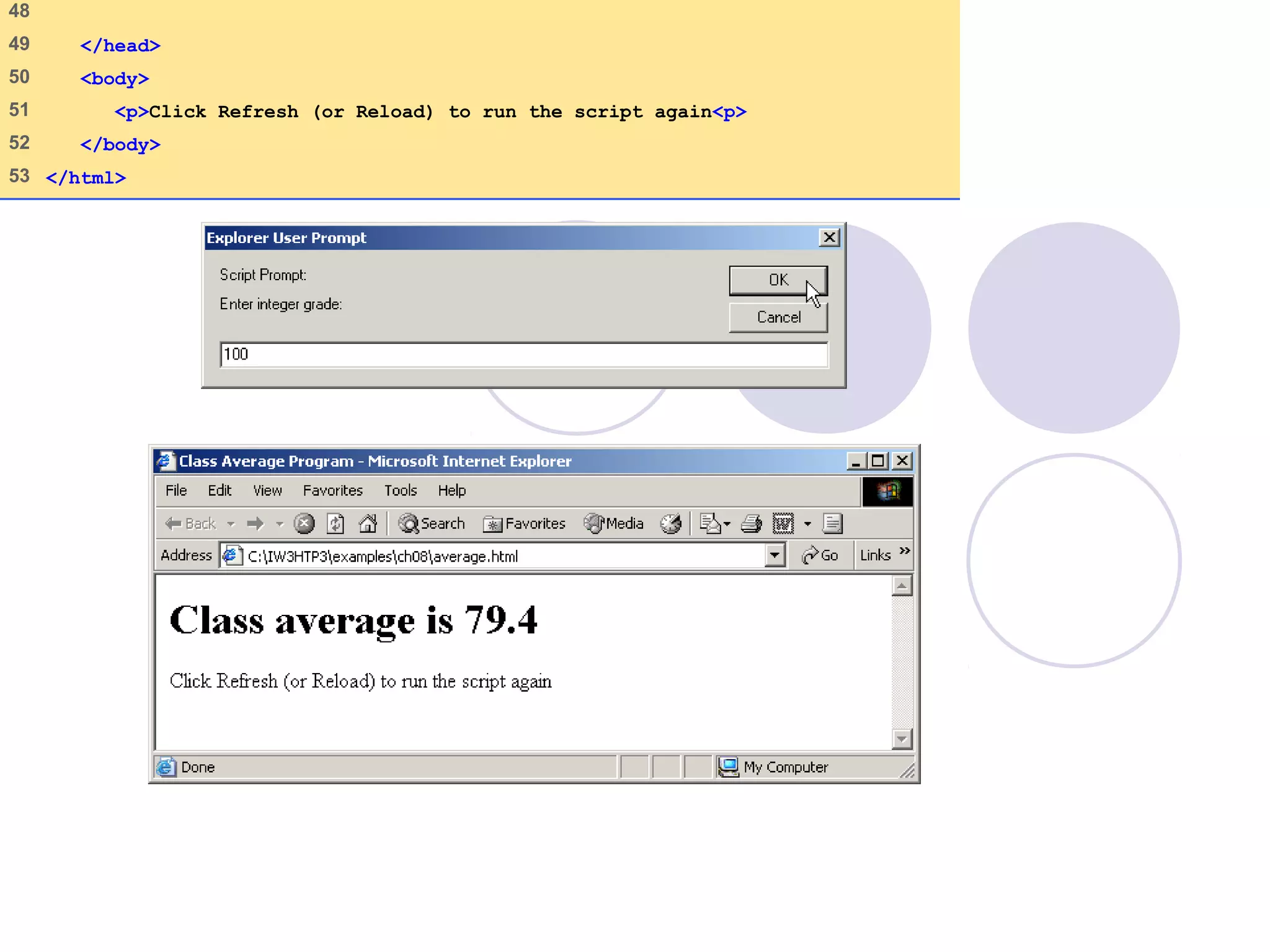
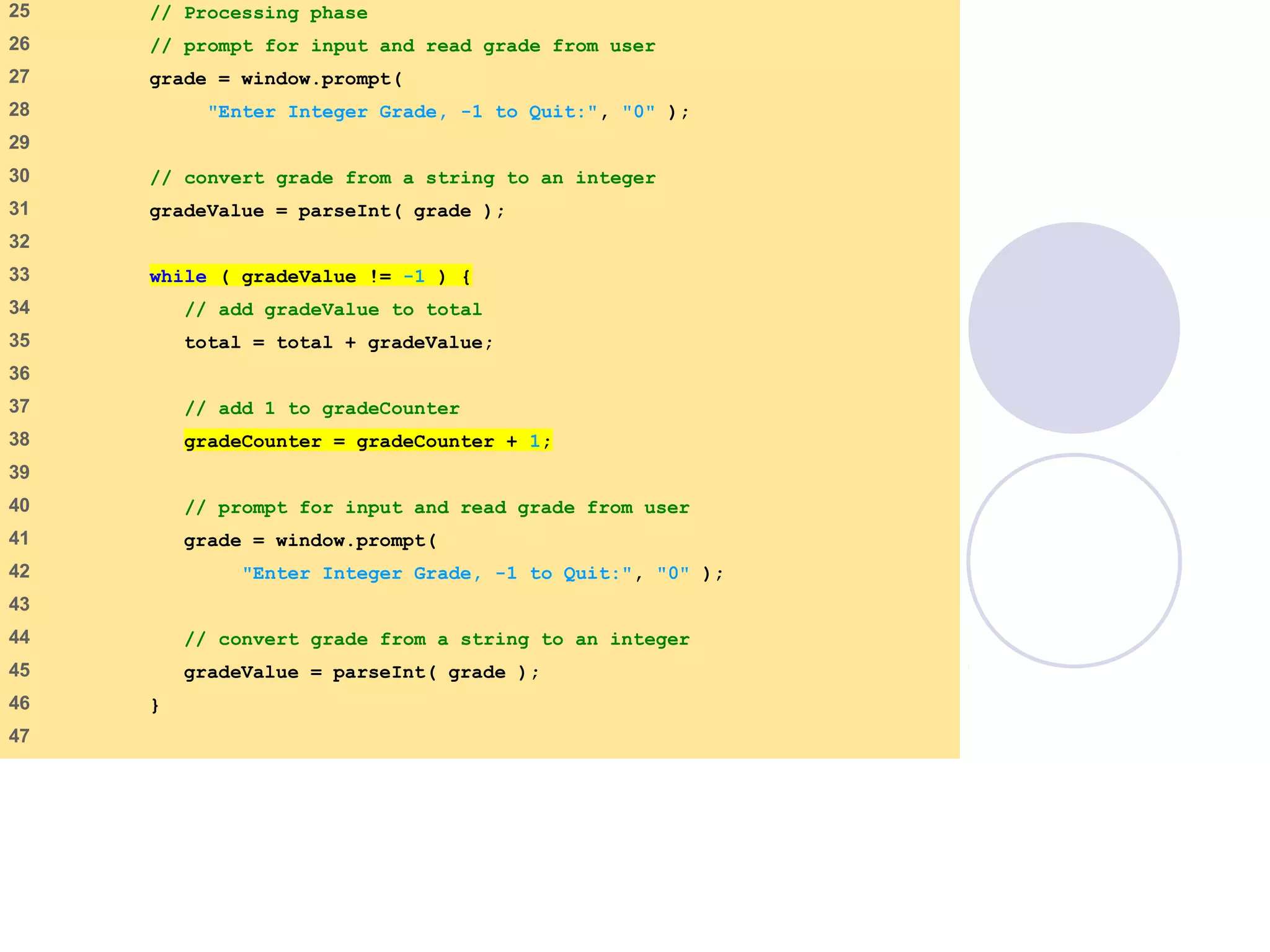
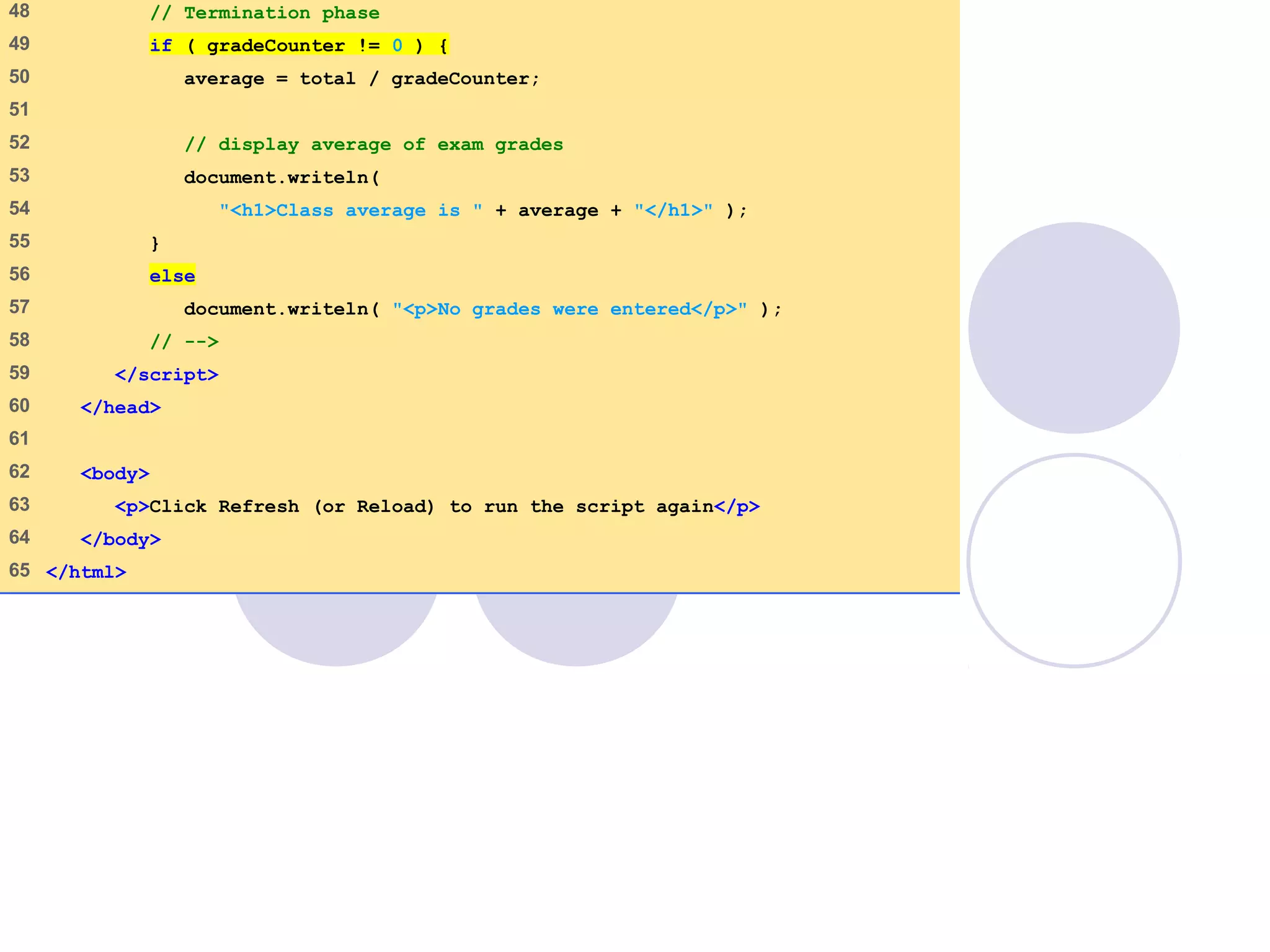
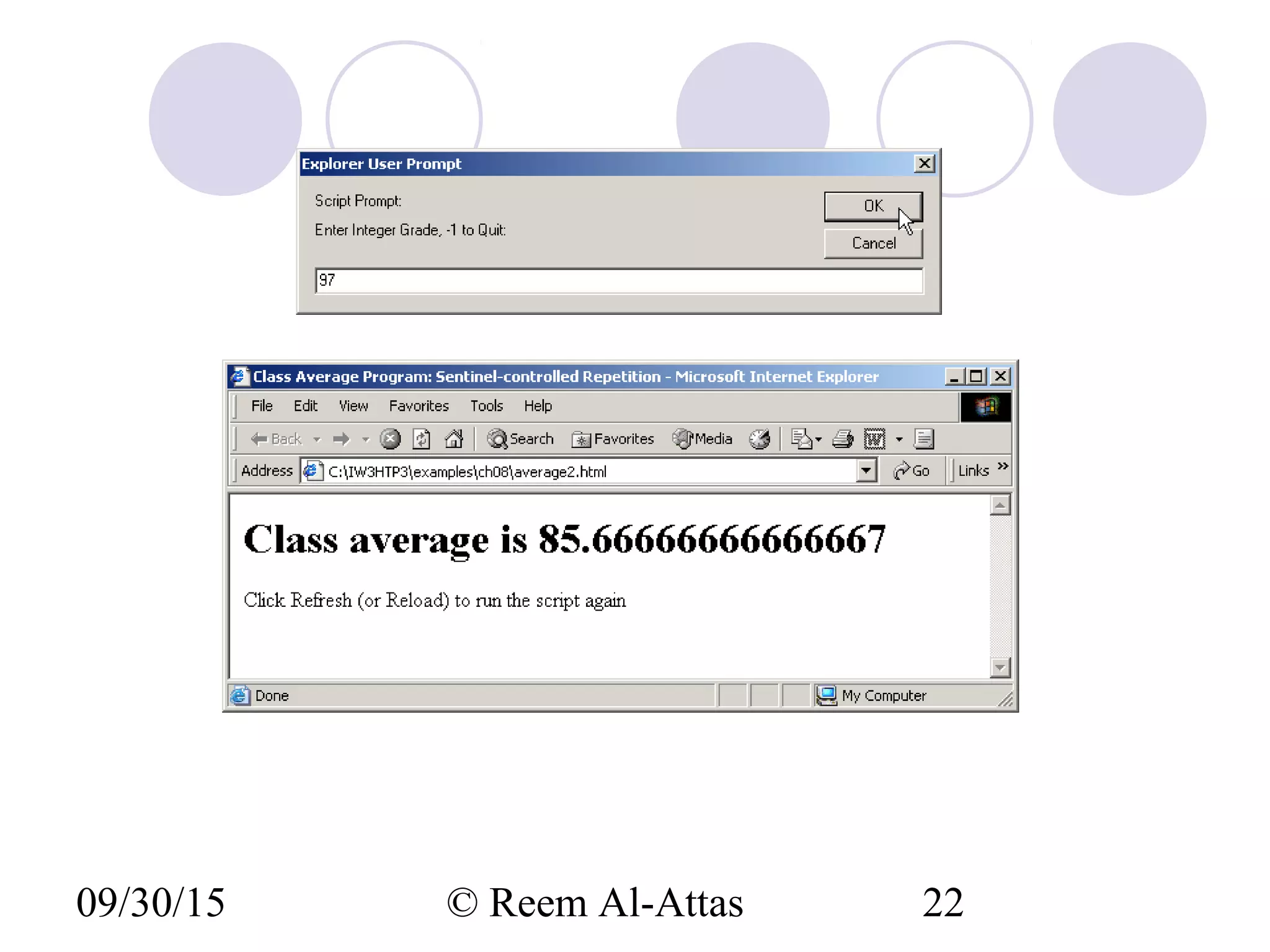
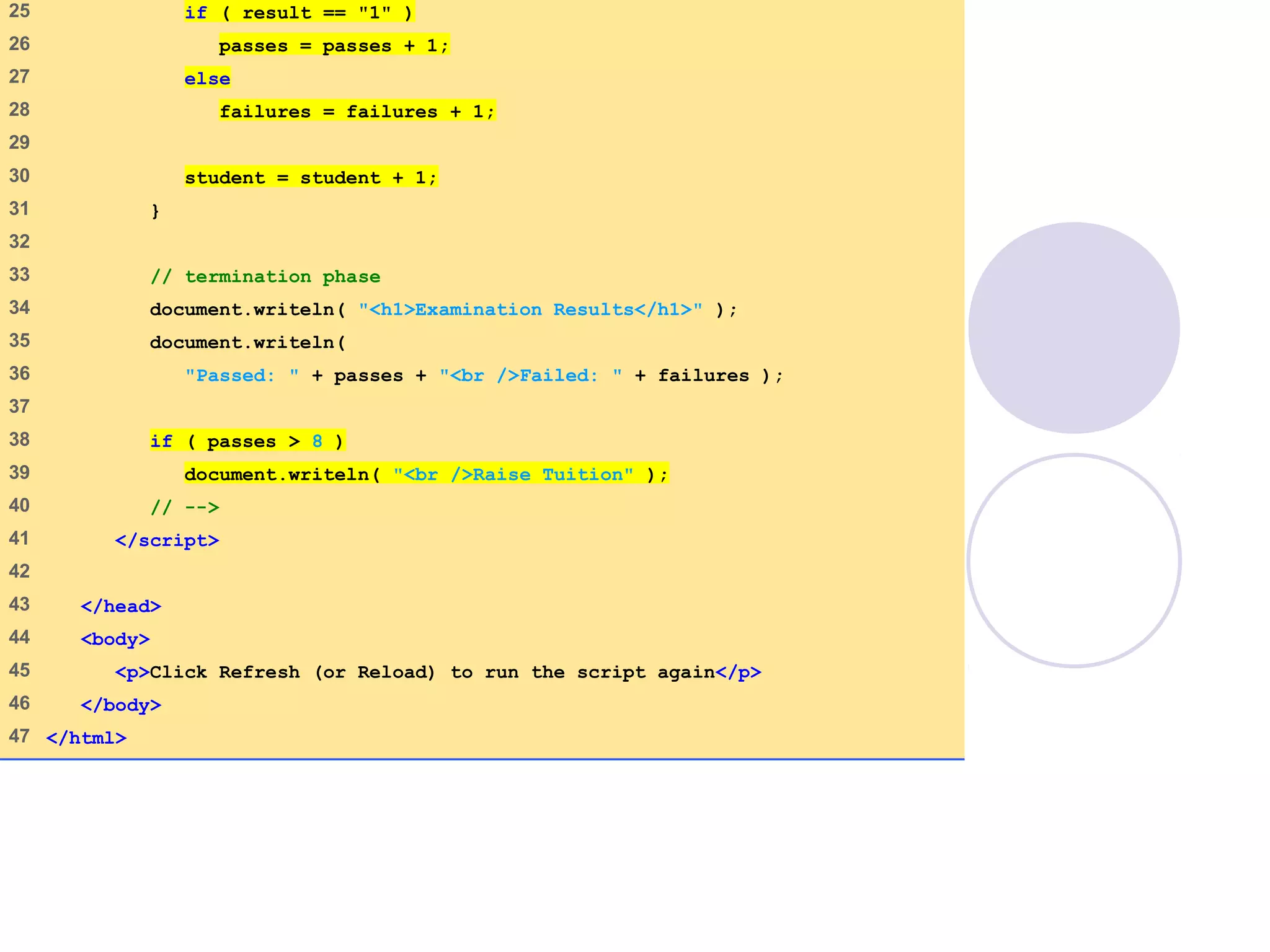
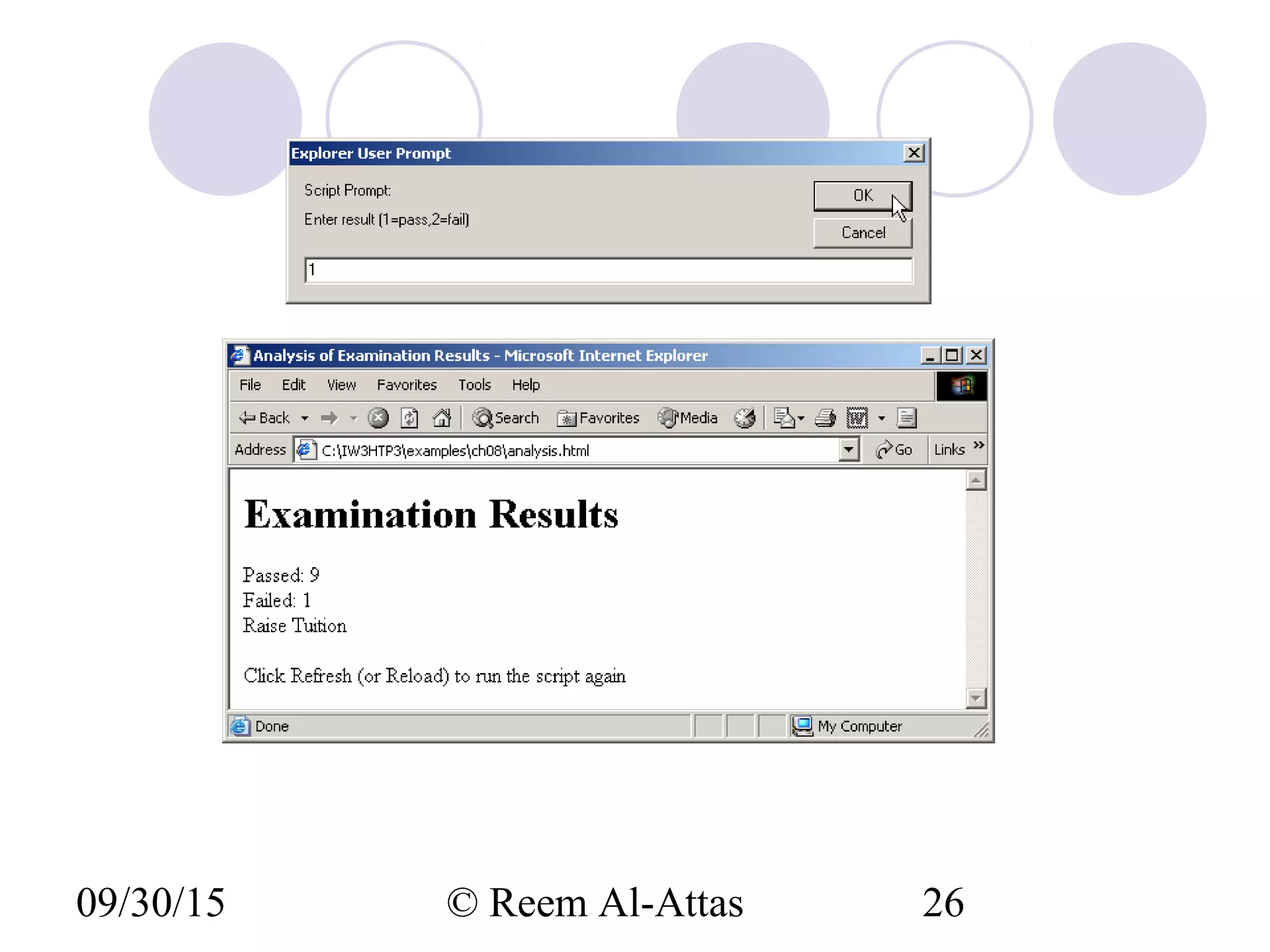
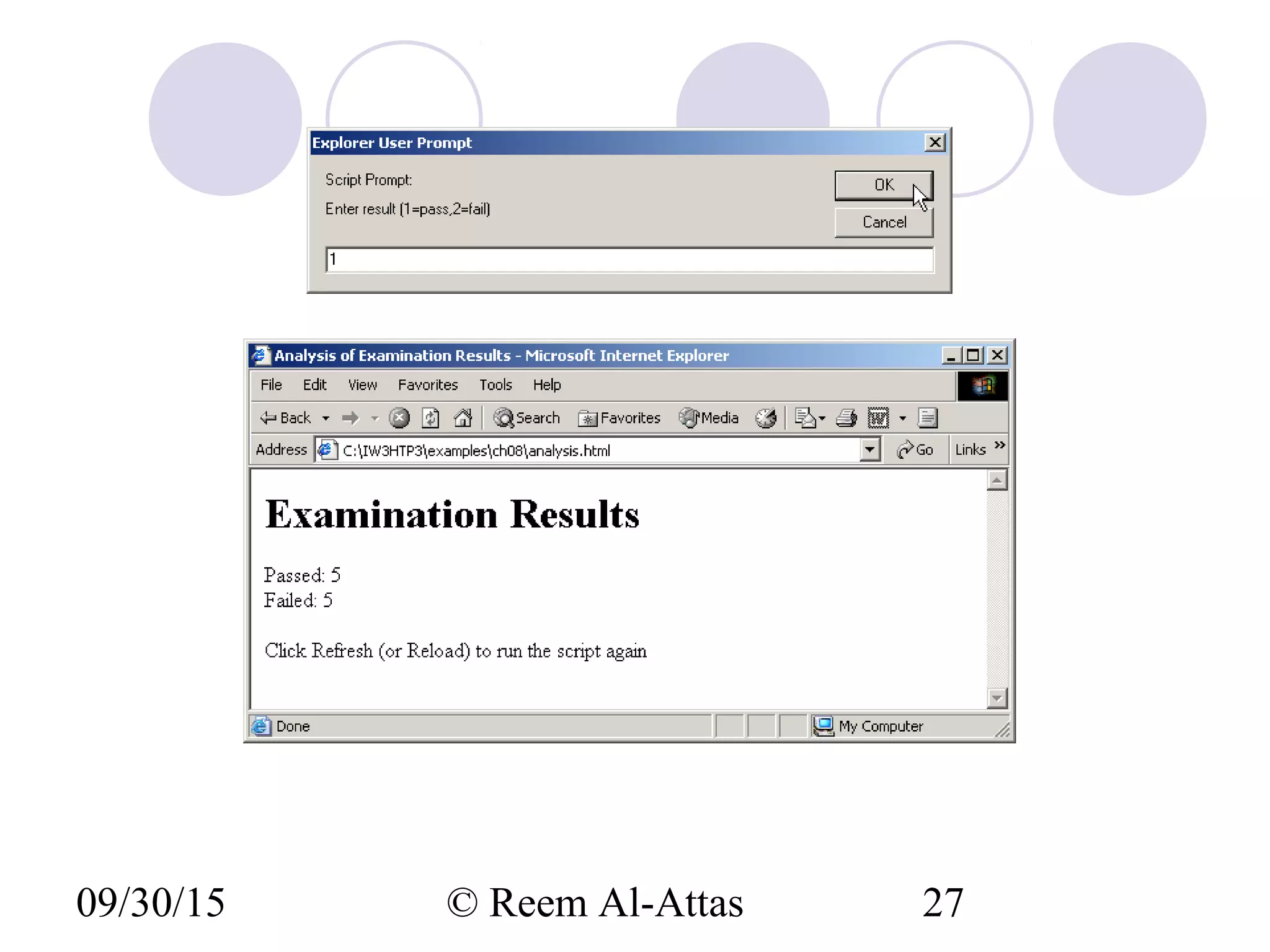
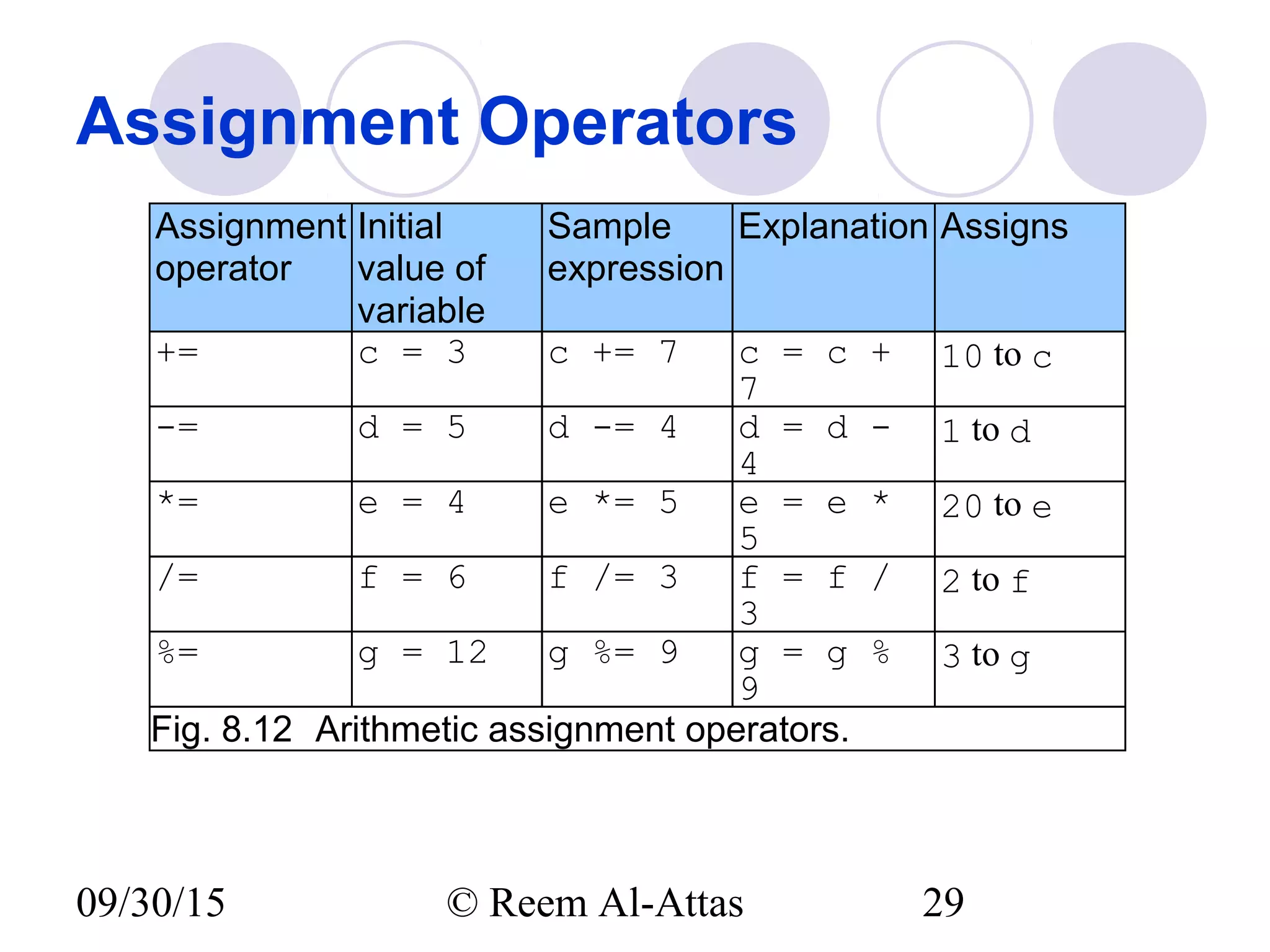
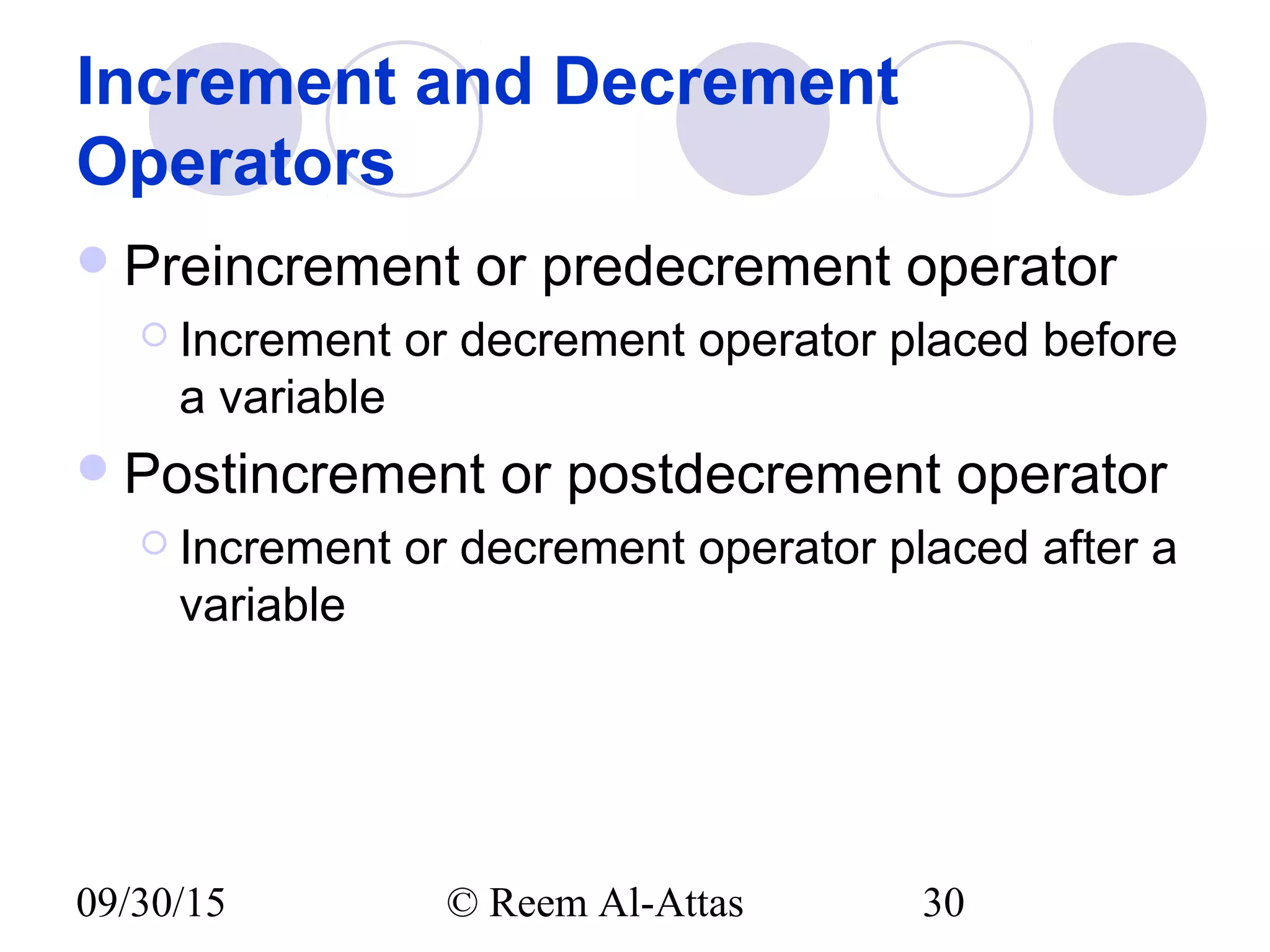
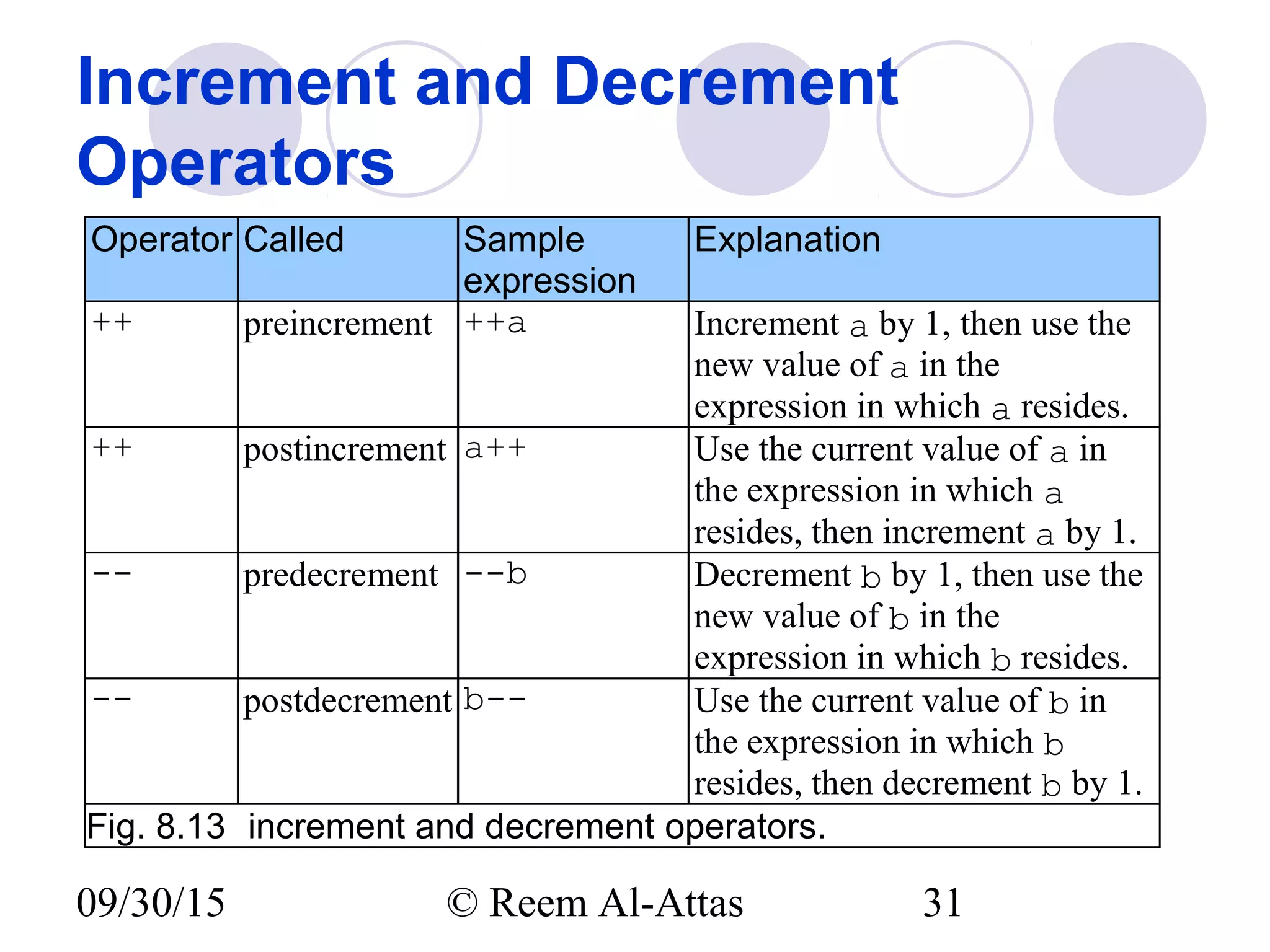
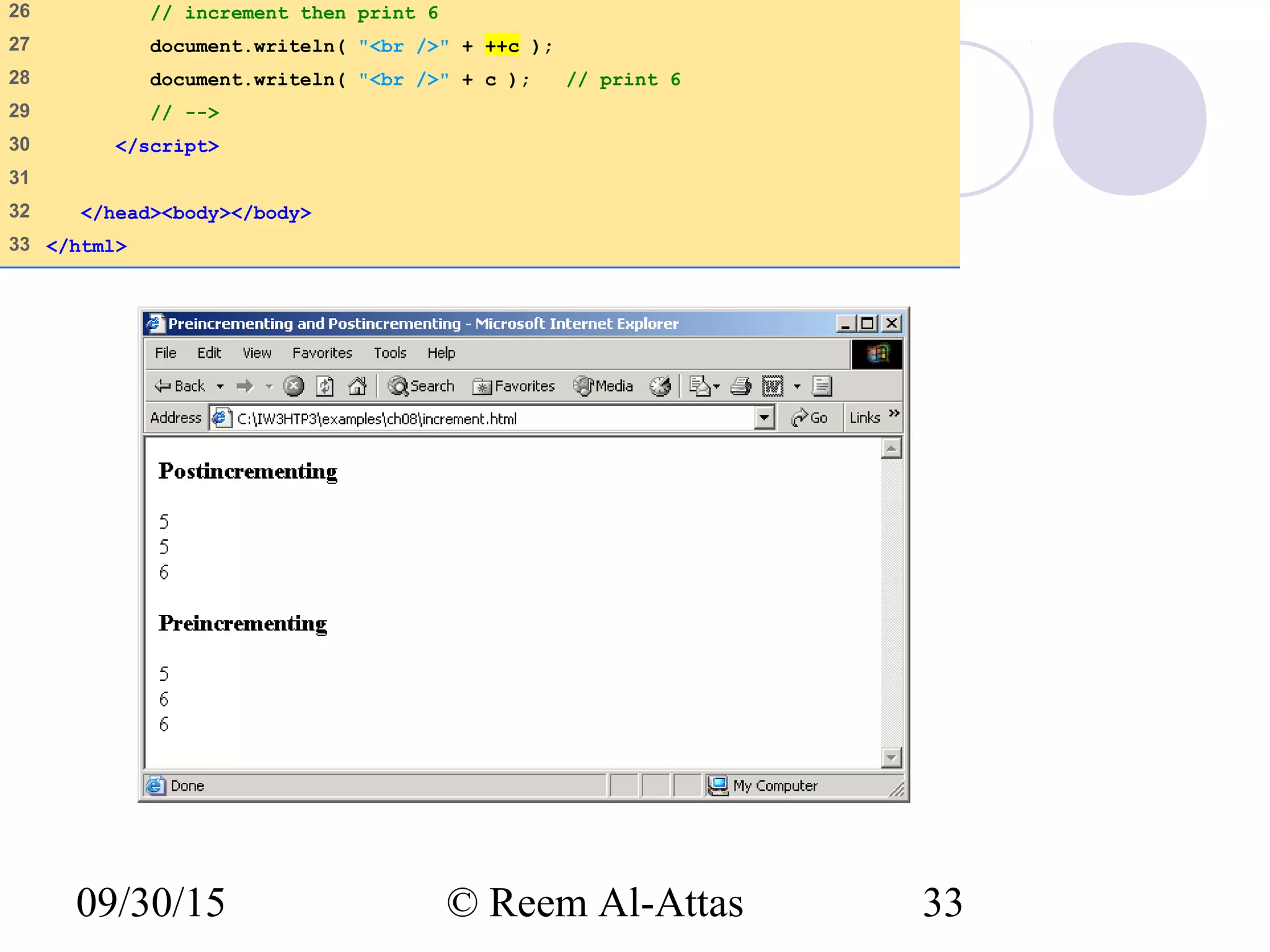
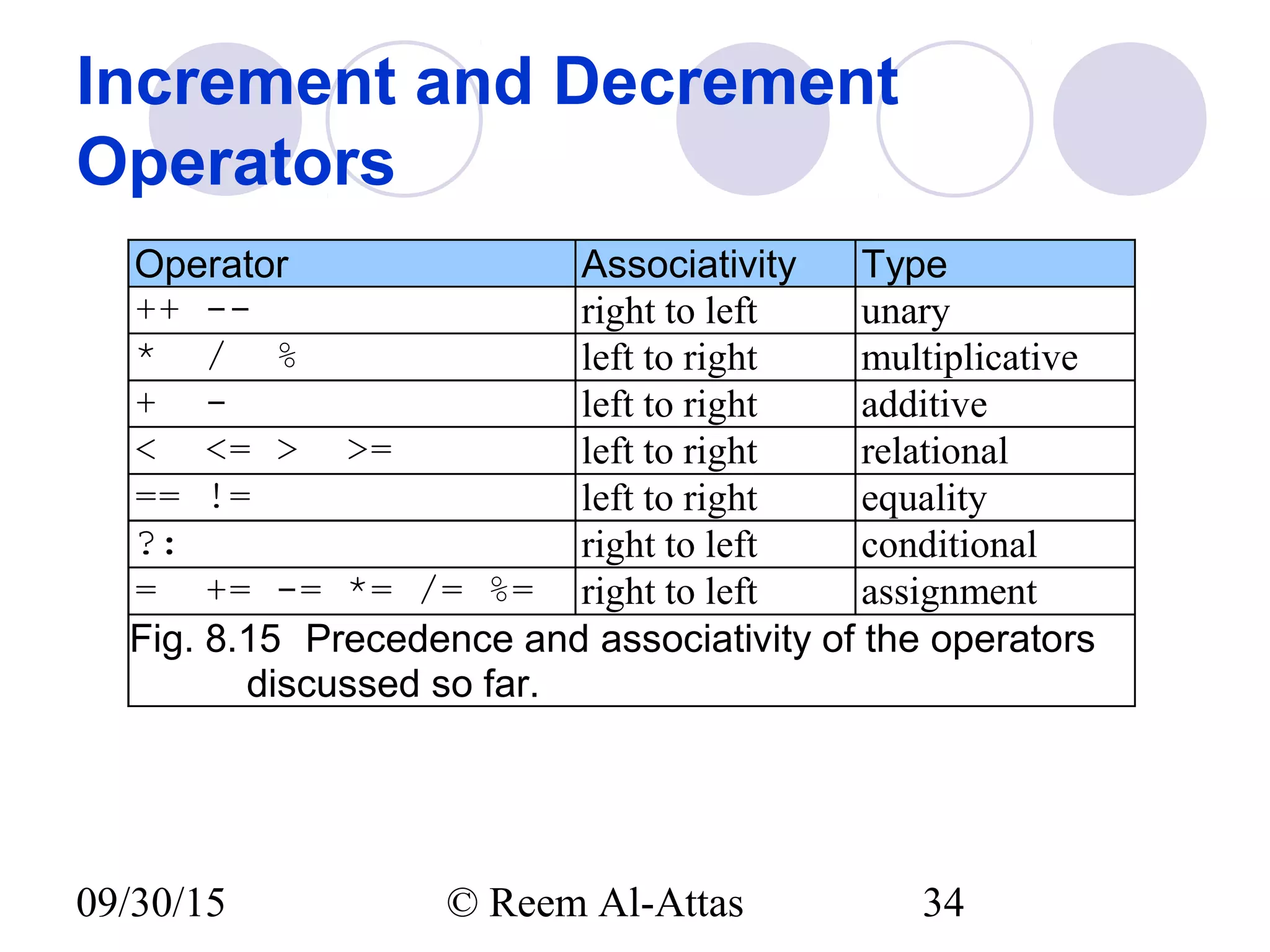
This document discusses JavaScript control structures and operators. It begins by introducing algorithms, pseudocode, and flowcharts for representing program logic. It then covers different control structures in JavaScript like if/else statements, while loops, and for loops. Various assignment operators and increment/decrement operators are also explained. Examples are provided to demonstrate counter-controlled and sentinel-controlled loop structures as well as preincrementing, postincrementing, and nested control structures.