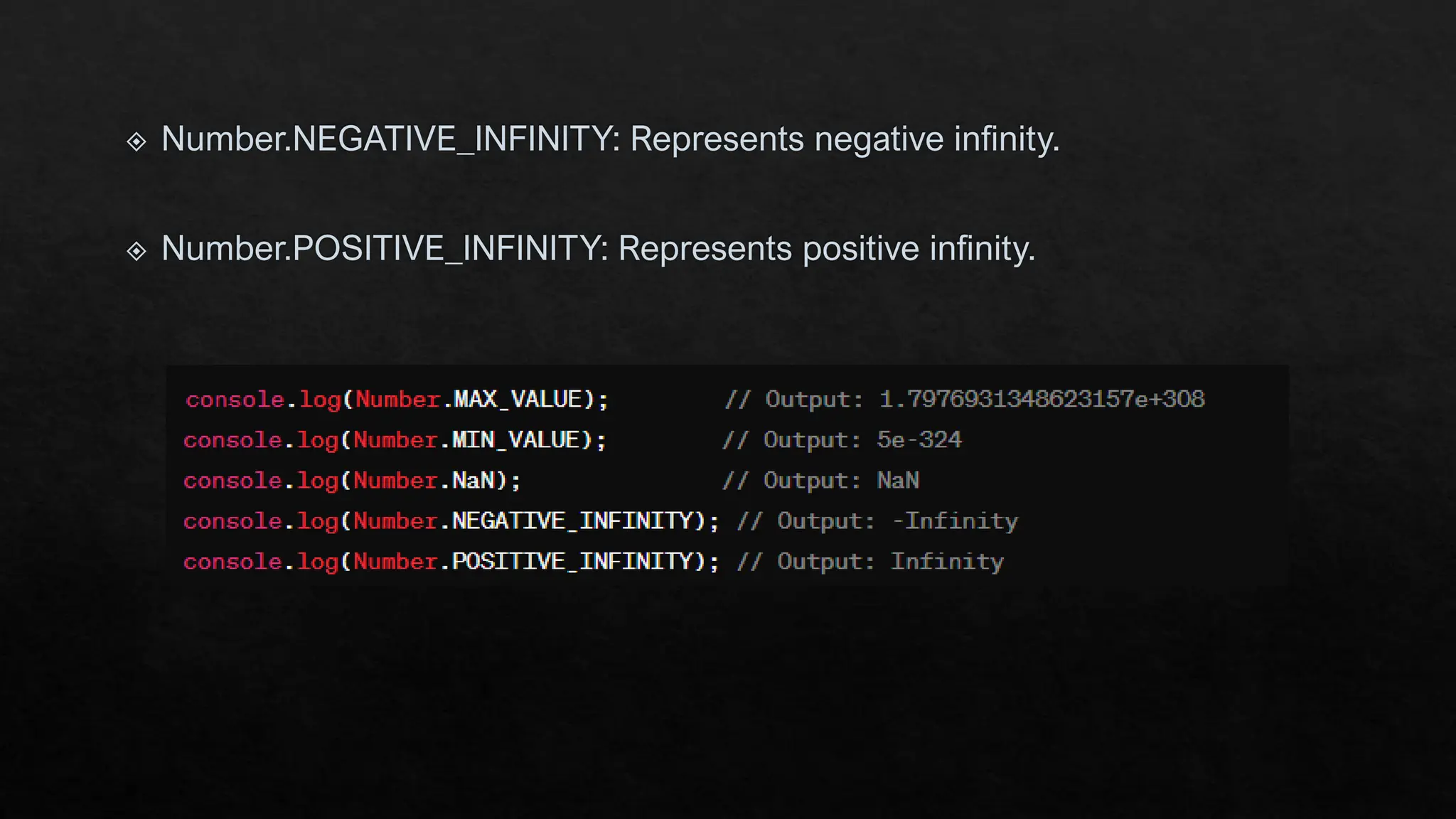
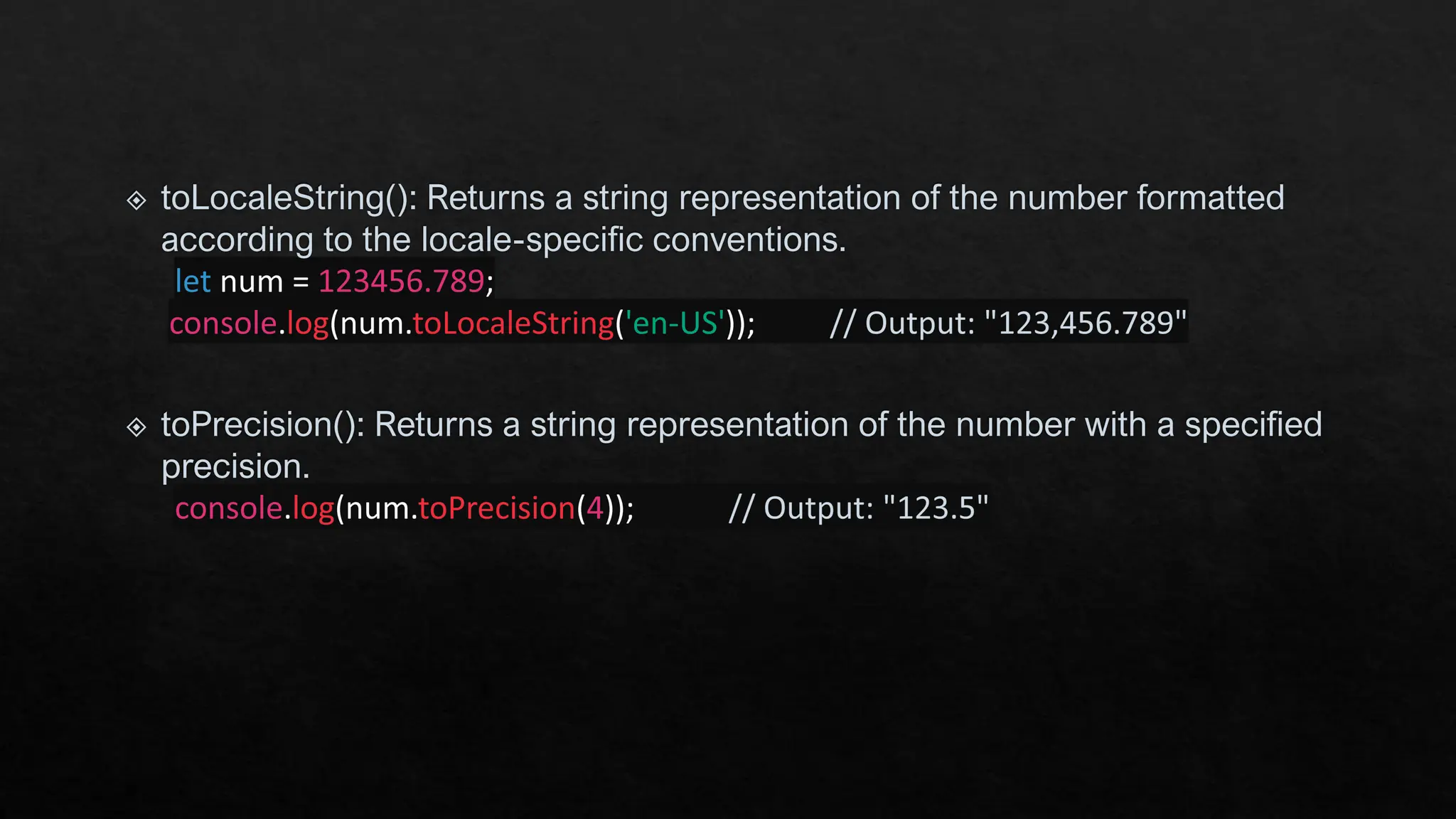
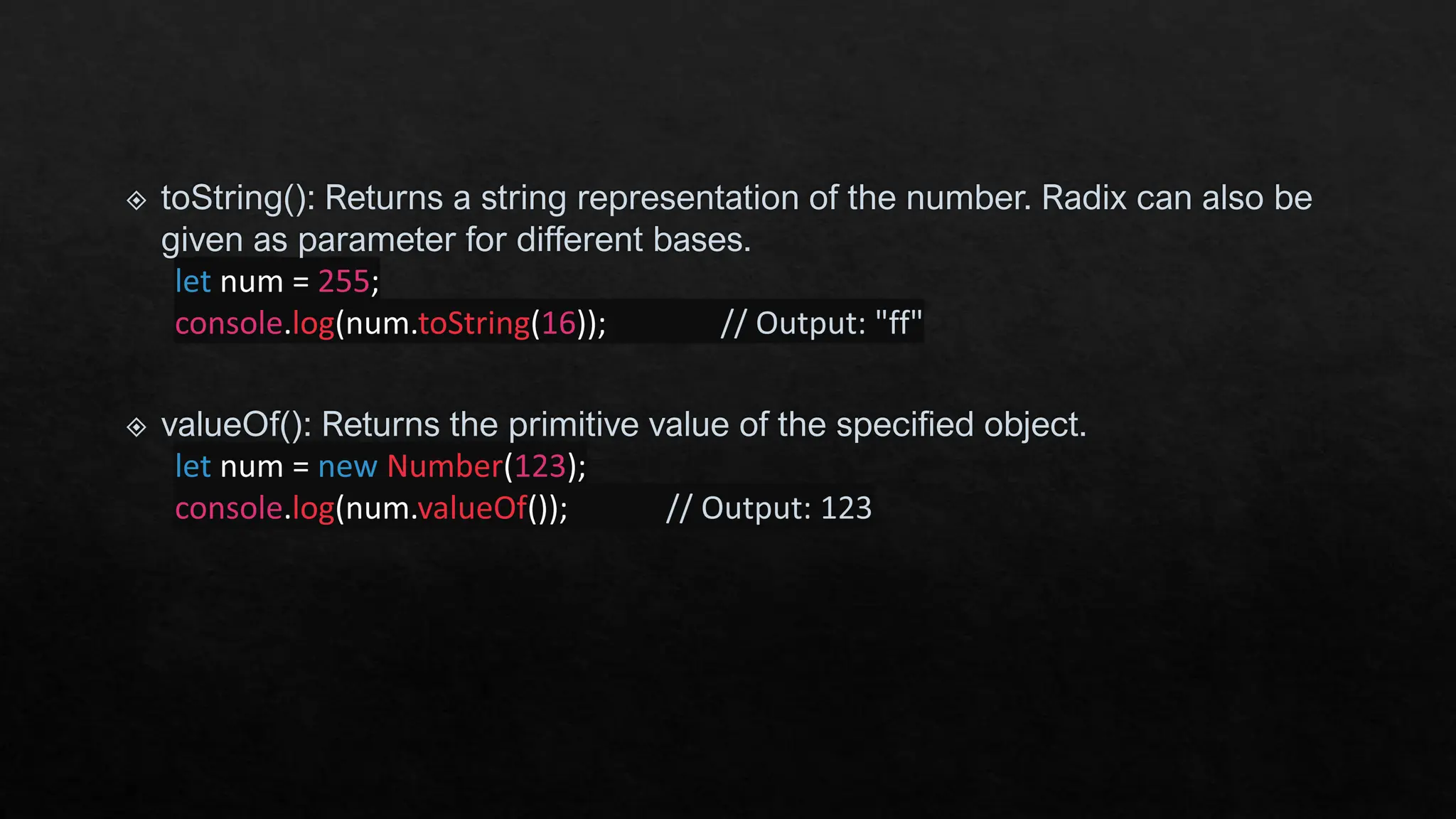
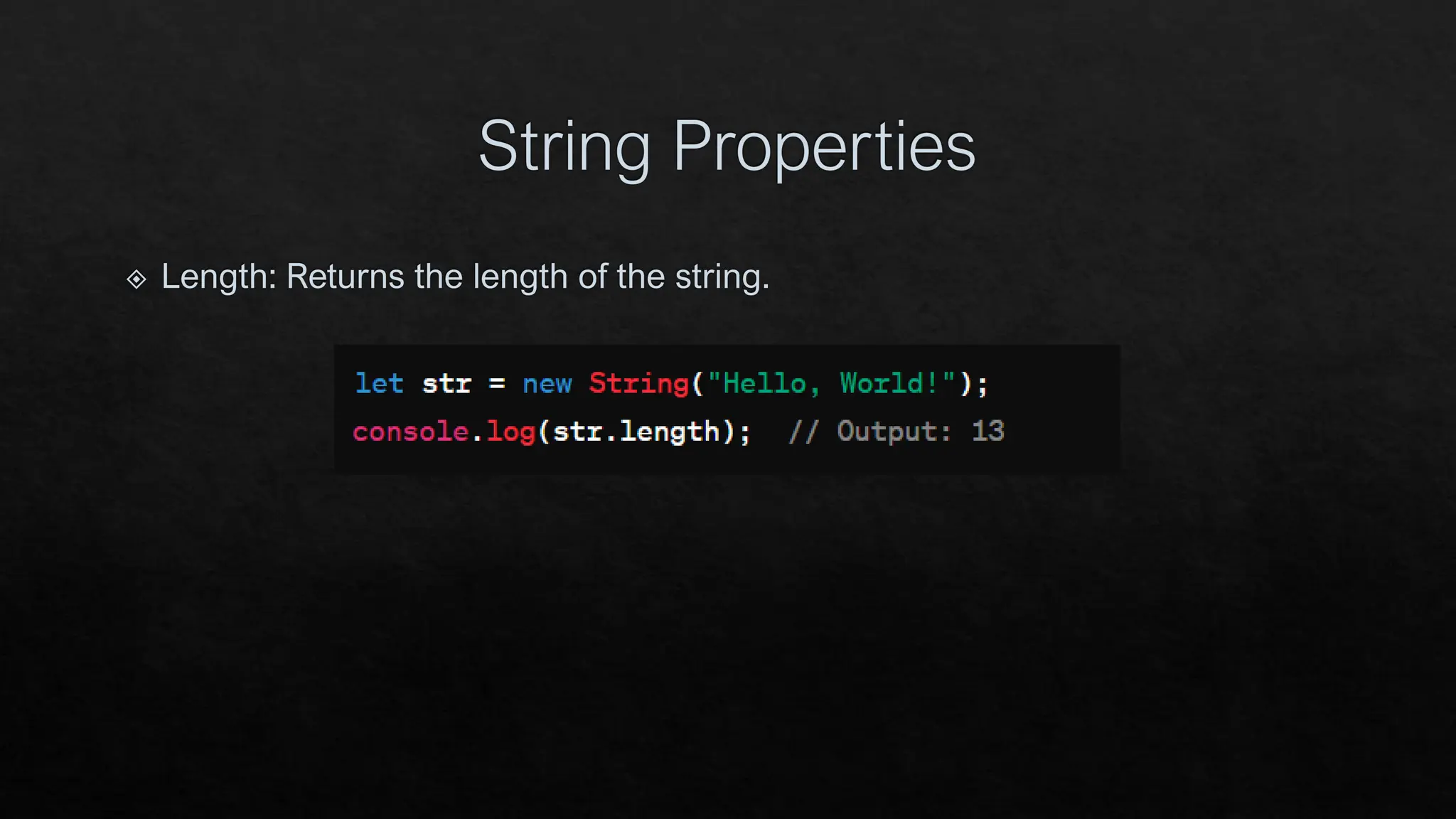
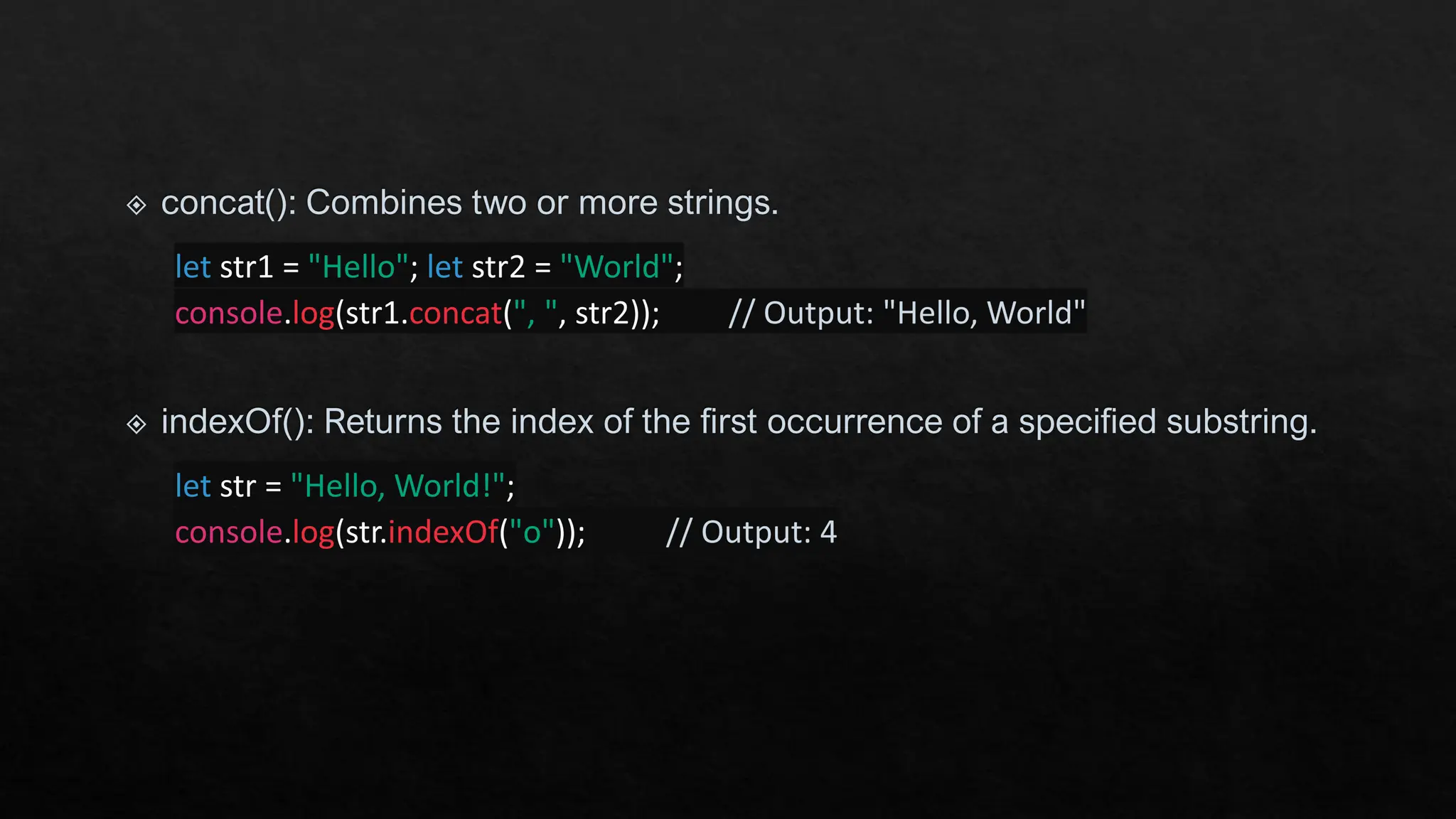
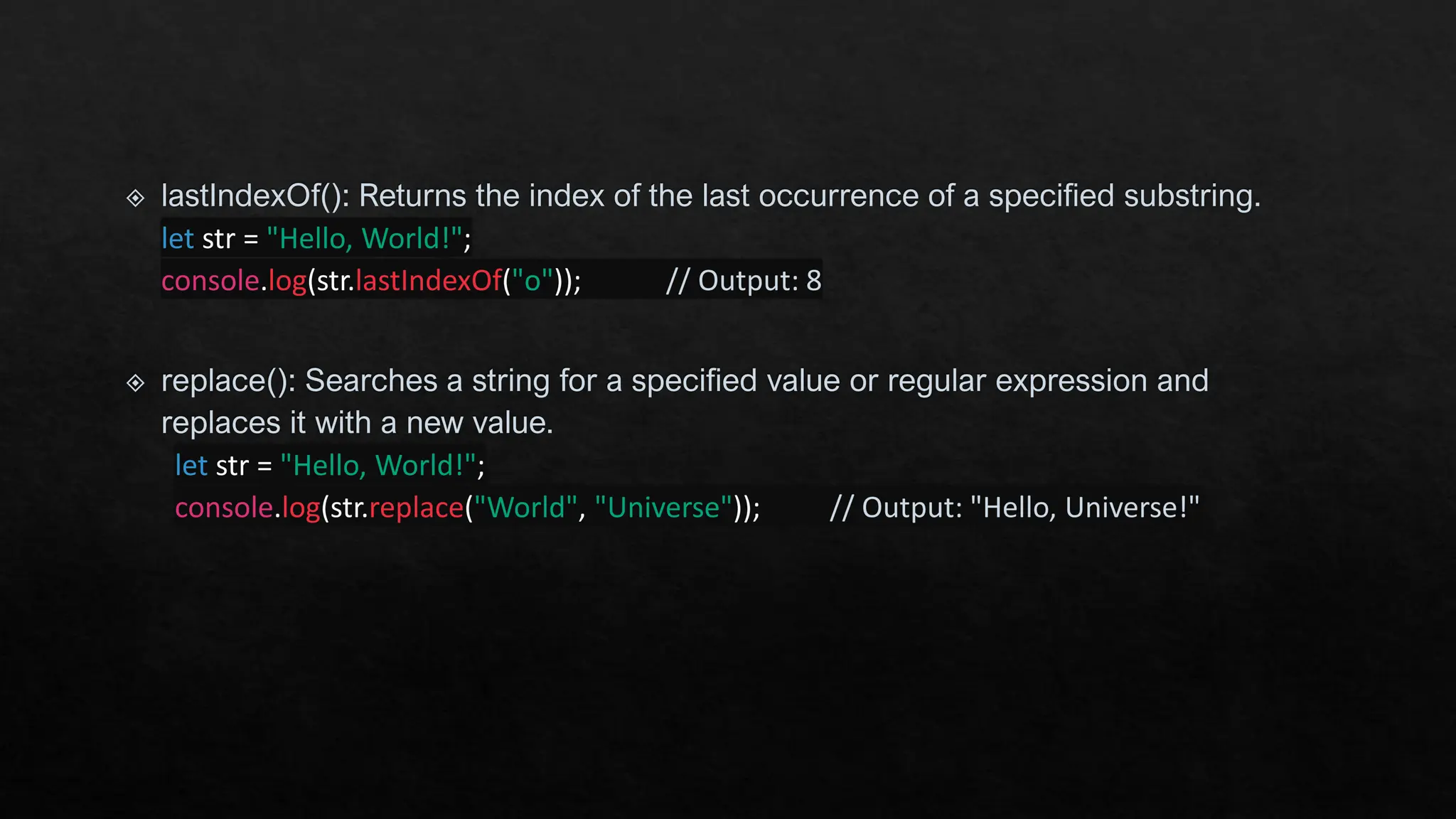
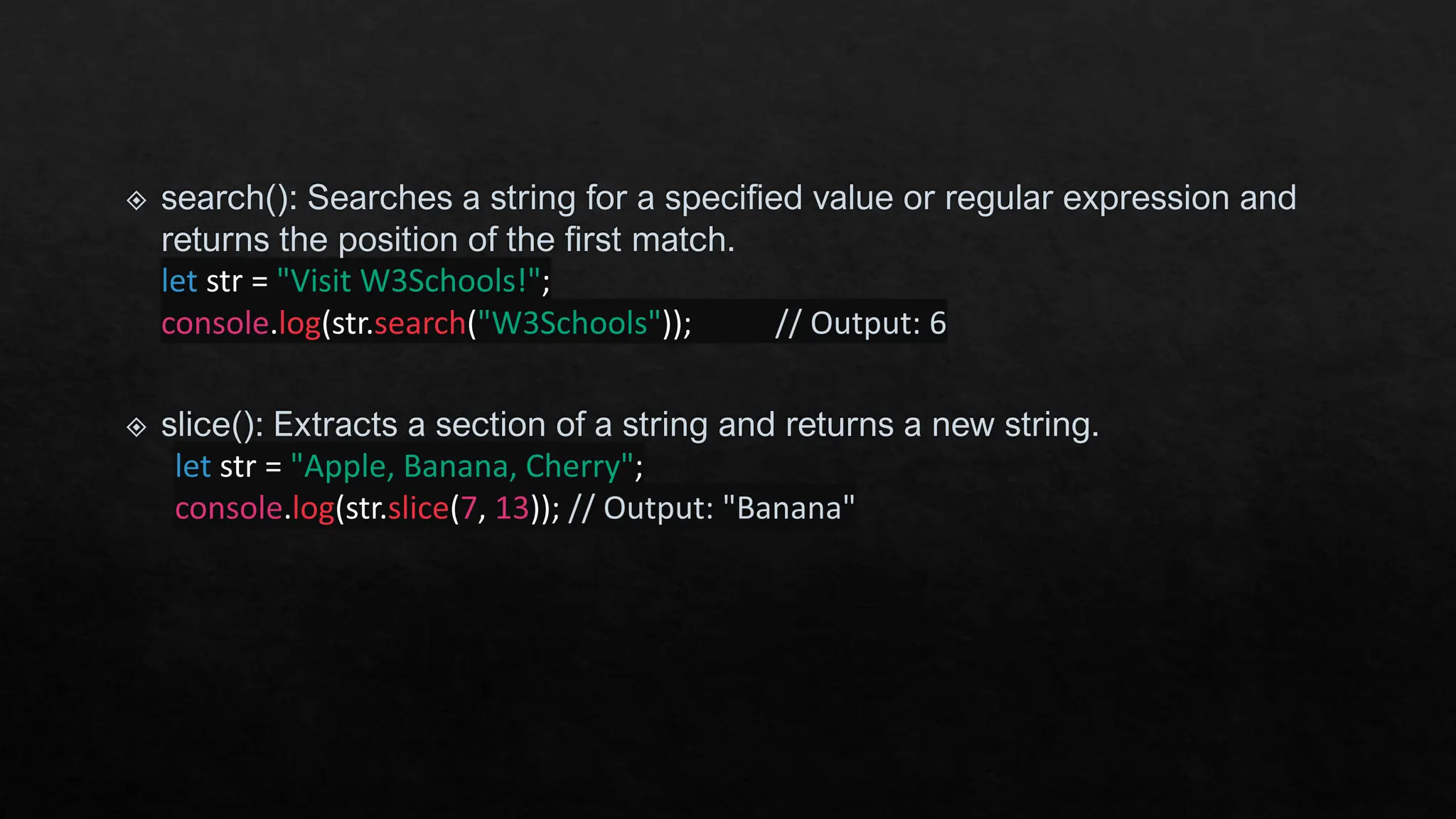
The document provides an overview of JavaScript's built-in objects for handling numbers, booleans, and strings, detailing their properties and methods. It explains number-related functions like toExponential, toFixed, and toLocaleString, as well as boolean methods like toString and valueOf. Additionally, it covers string methods such as concat, indexOf, and replace for manipulating string data.









![split(): Splits a string into an array of substrings based on a specified separator.
let str = "Apple, Banana, Cherry";
console.log(str.split(", ")); // Output: ["Apple", "Banana", "Cherry"]
substr(): Extracts a portion of a string, starting from a specified index, and returns a
new string.
let str = "Hello, World!";
console.log(str.substr(7, 5)); // Output: "World"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/js21-25ppt05816404523-240531171843-06e212bf/75/Javascript-objects-properties-and-methods-pdf-17-2048.jpg)