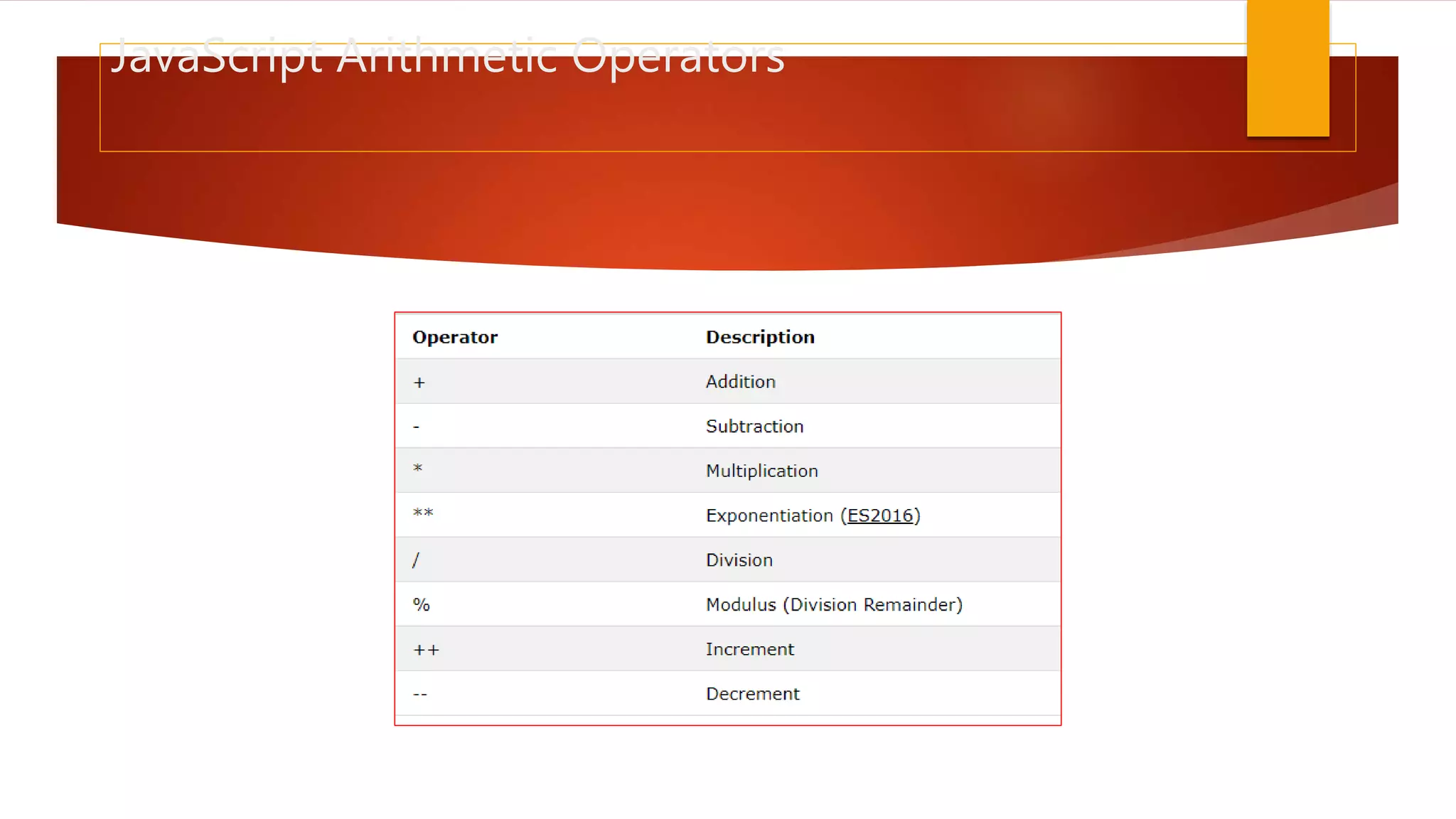
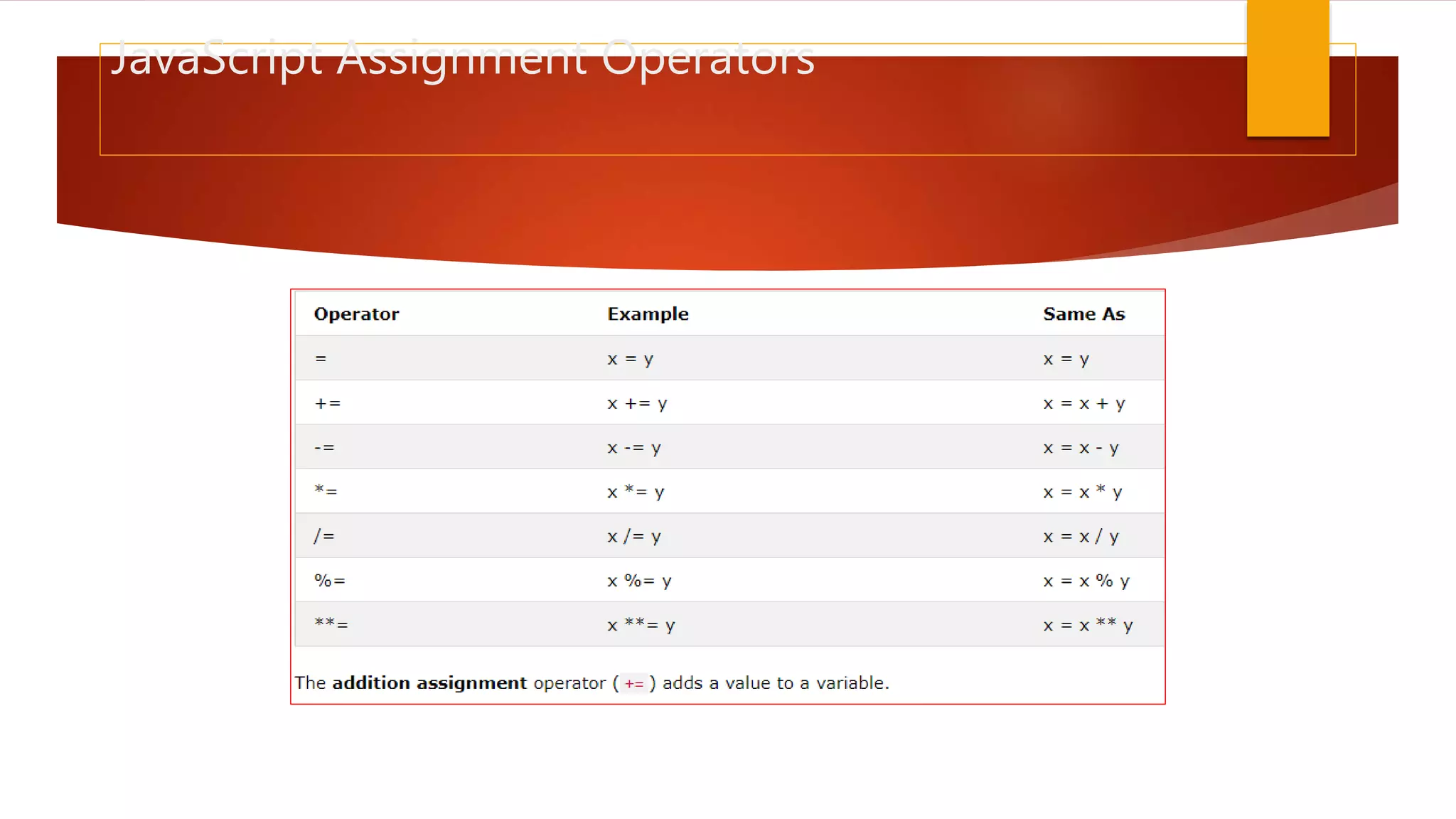
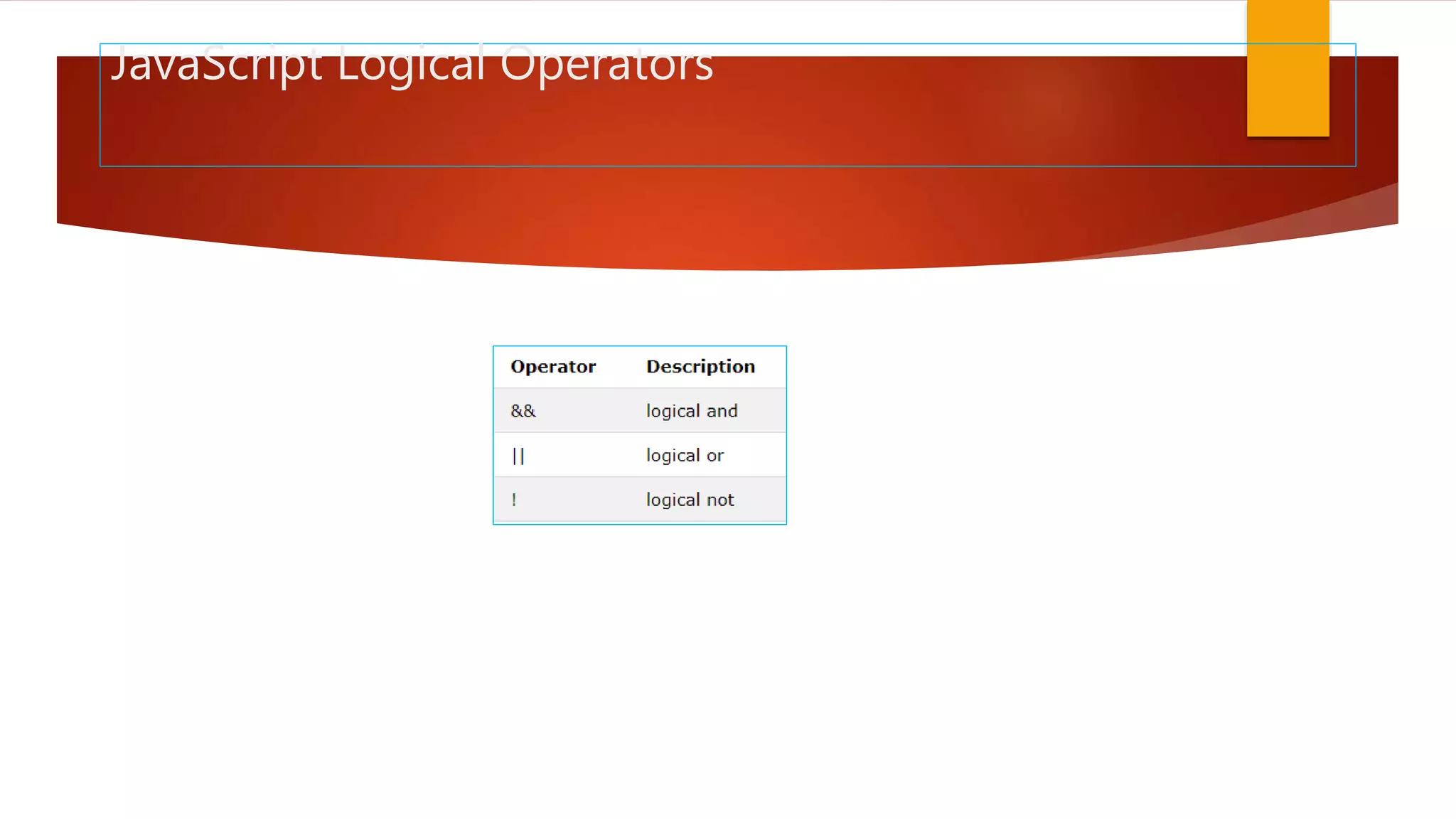
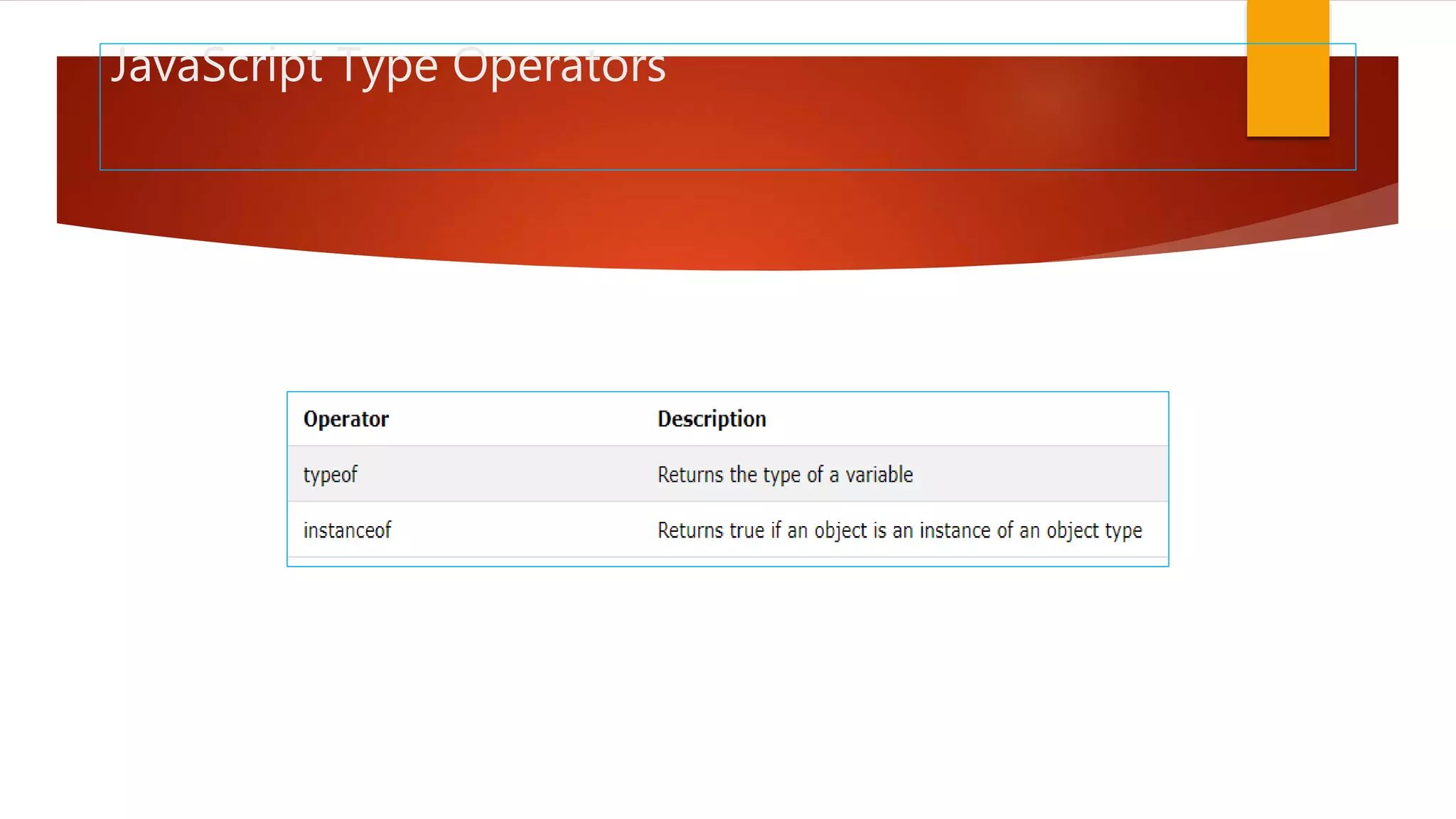
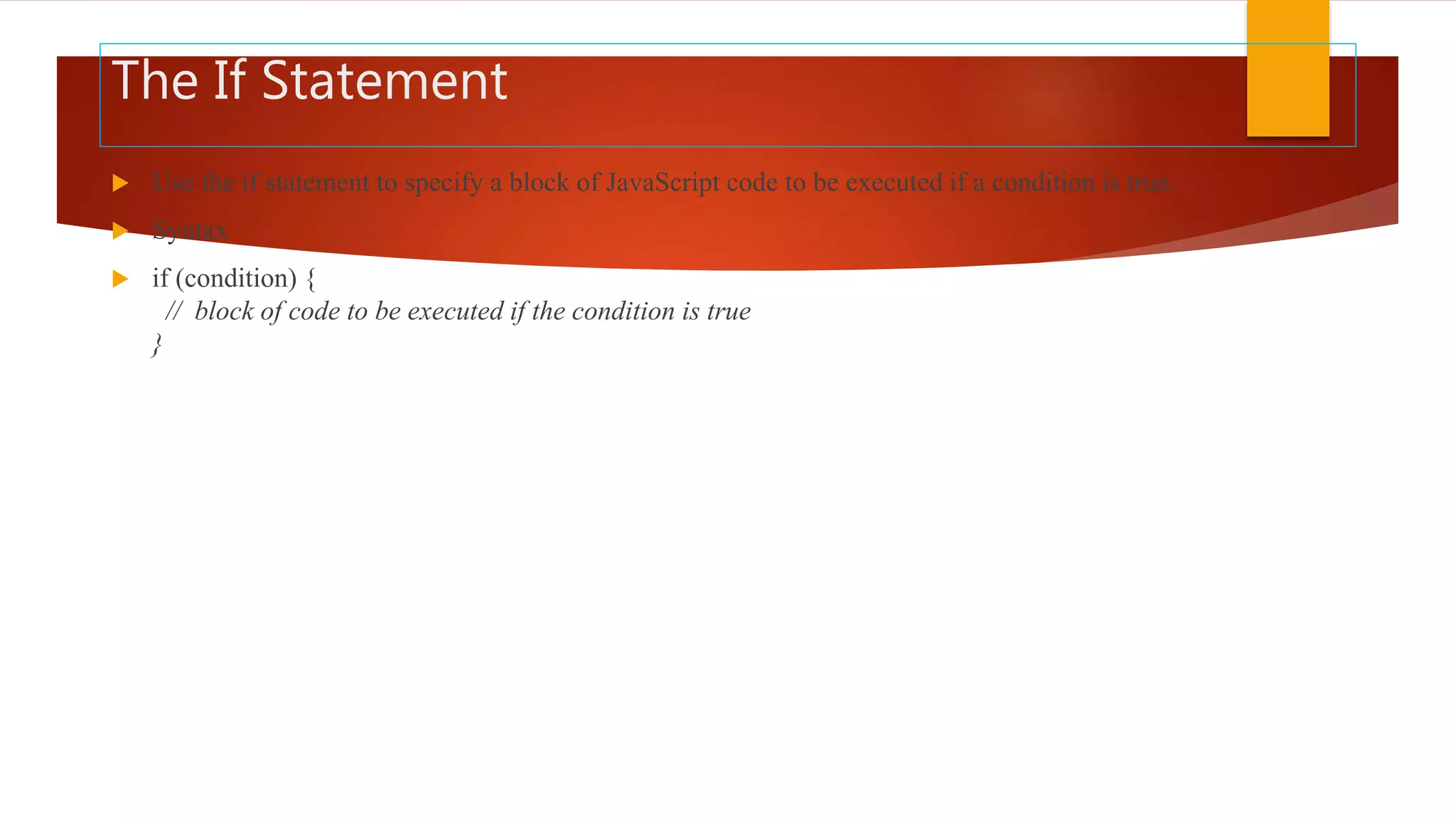
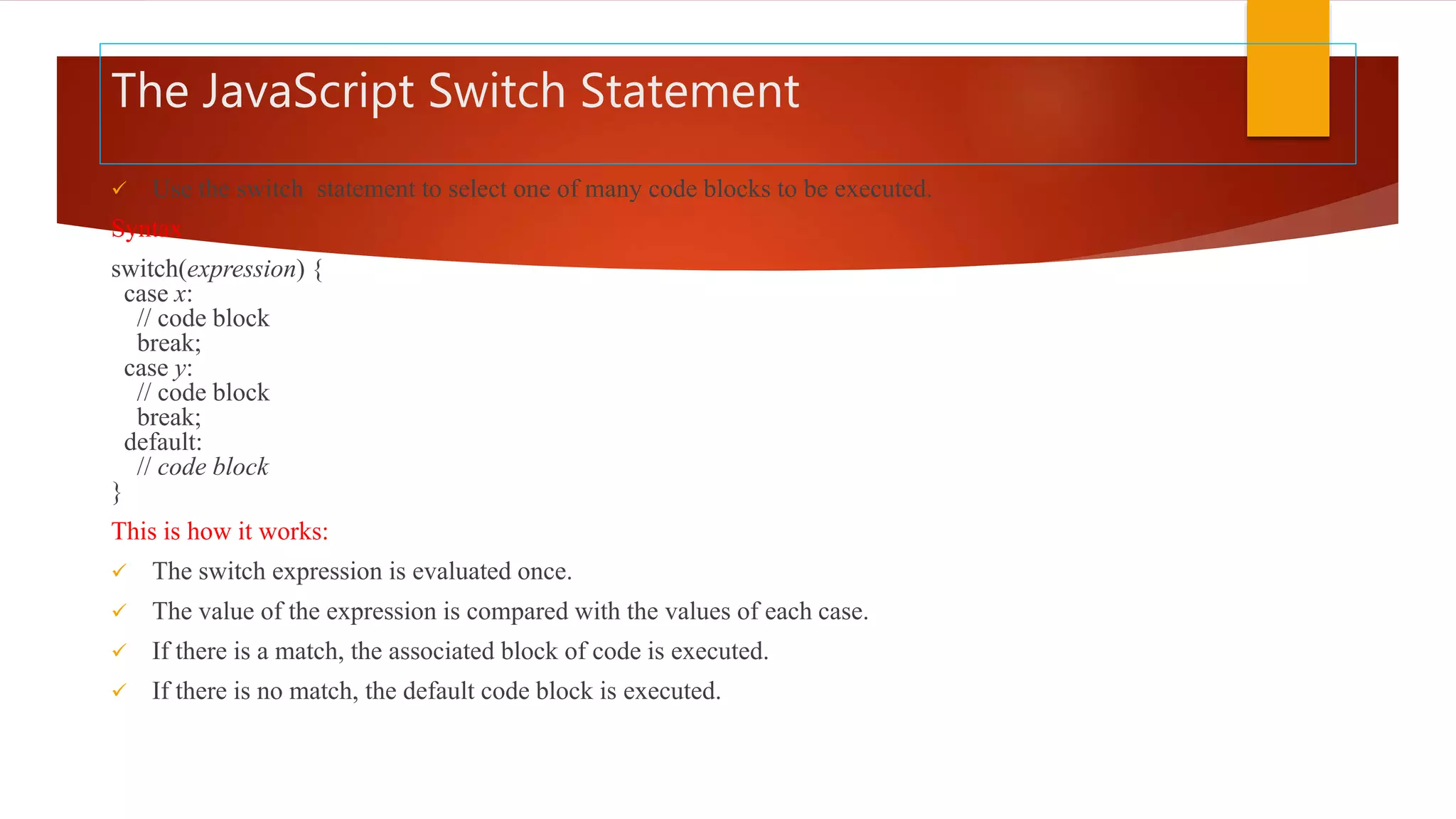
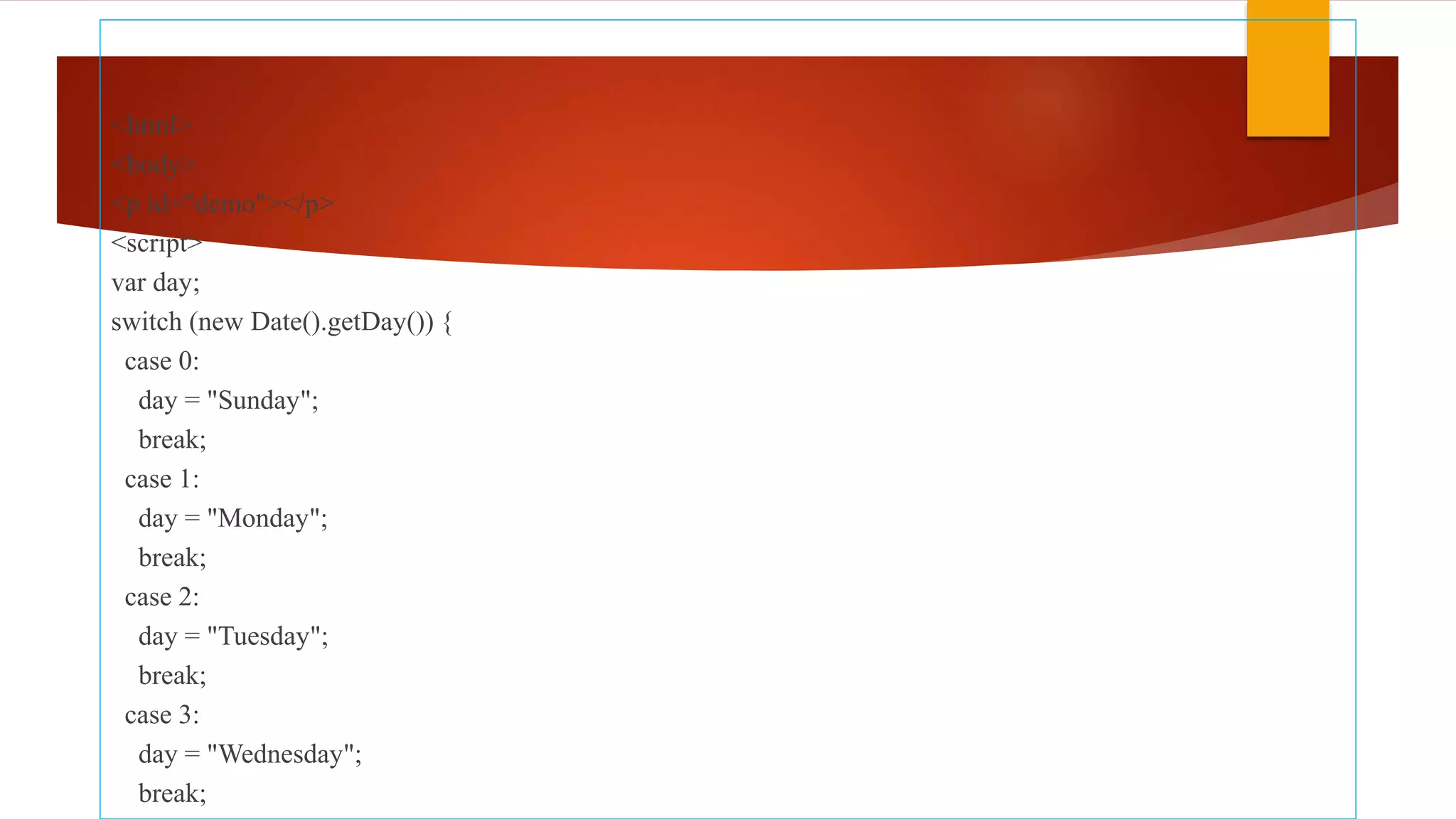
The document discusses various JavaScript operators such as arithmetic, assignment, comparison, logical, and type operators. It provides code examples of using operators to assign values to variables, add and concatenate numbers and strings, compare values, and perform conditional logic. The document also covers JavaScript conditional statements including if/else and switch statements for executing different code blocks based on various conditions.