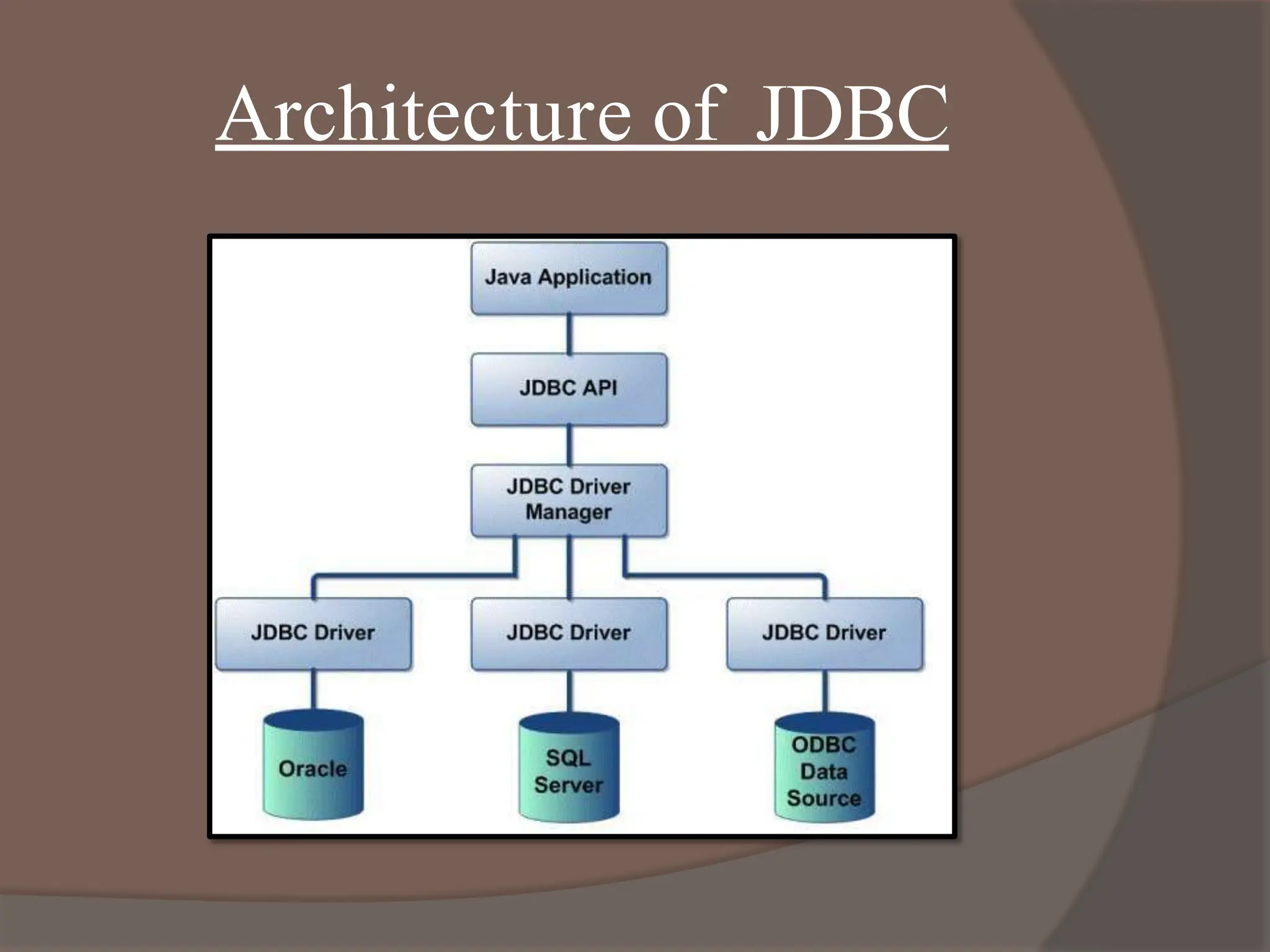
This document discusses Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) and provides details about its architecture and usage. It defines JDBC as an API that allows Java programs to connect to databases and execute SQL statements. The key points covered include:
- The 4 types of JDBC drivers and their differences
- The steps to connect to a database using JDBC, which are defining the connection URL, establishing the connection, creating statements, executing queries, processing results, and closing the connection
- The 3 types of statements in JDBC - Statement, PreparedStatement, and CallableStatement and their usages