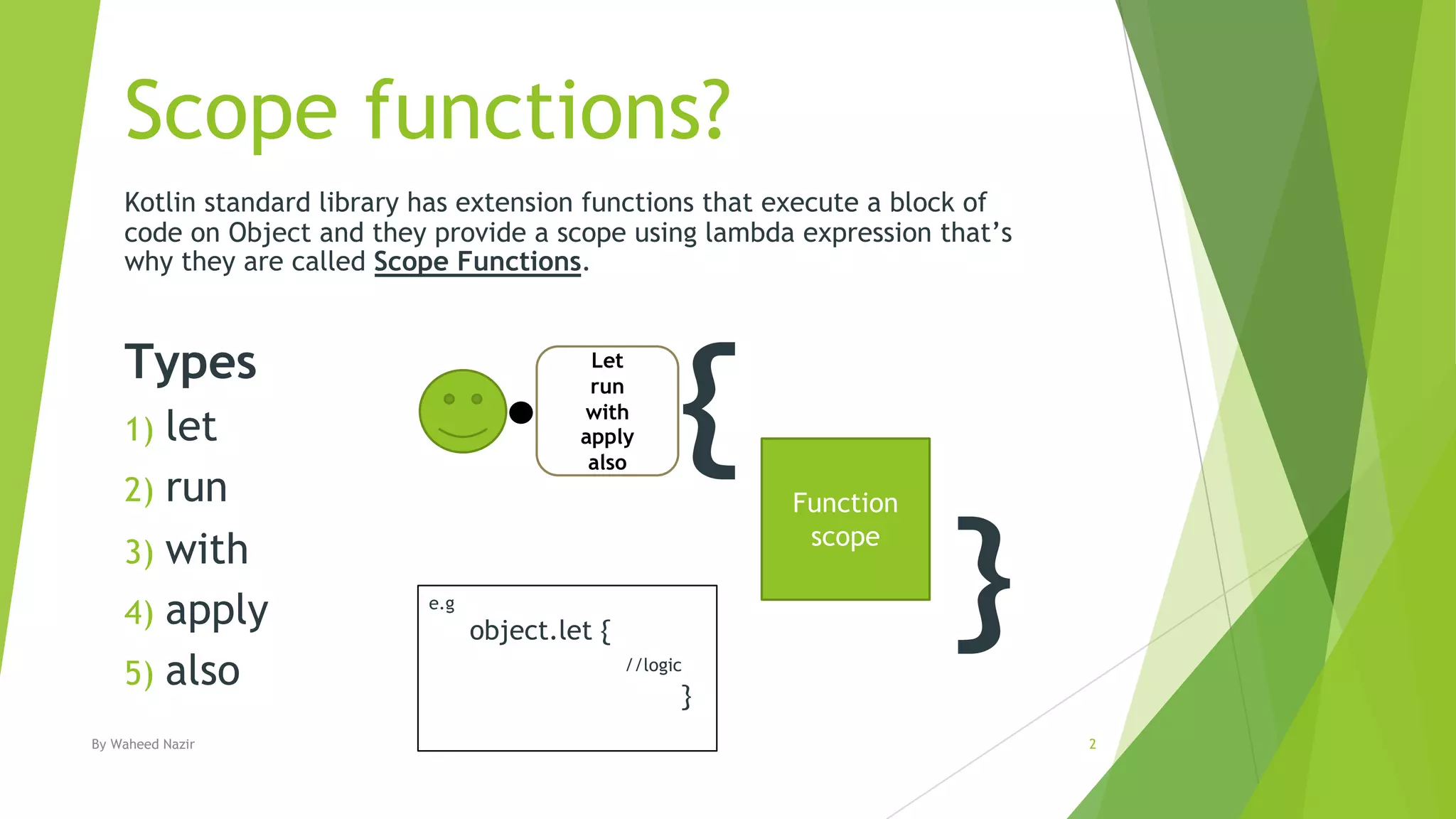
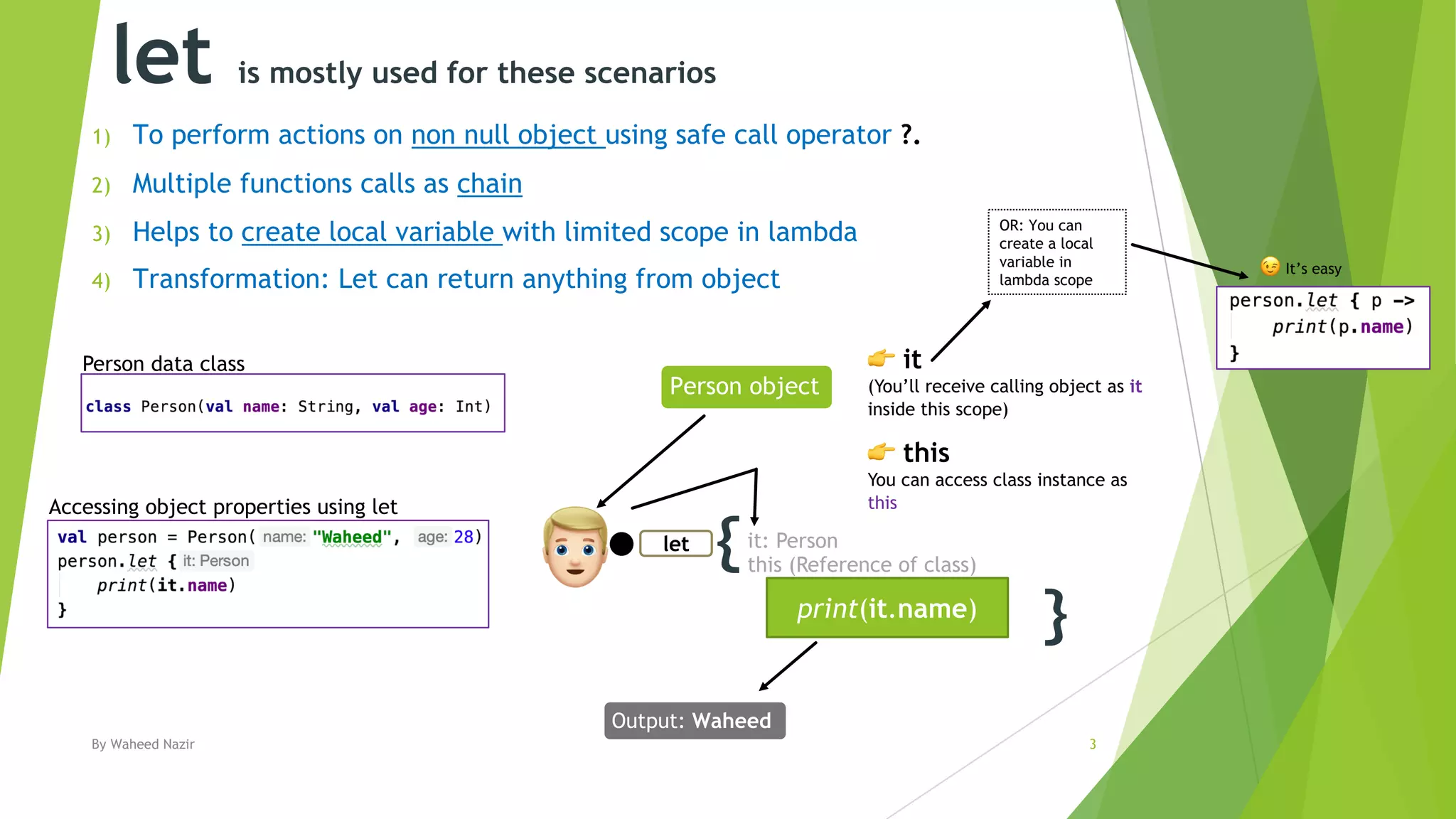
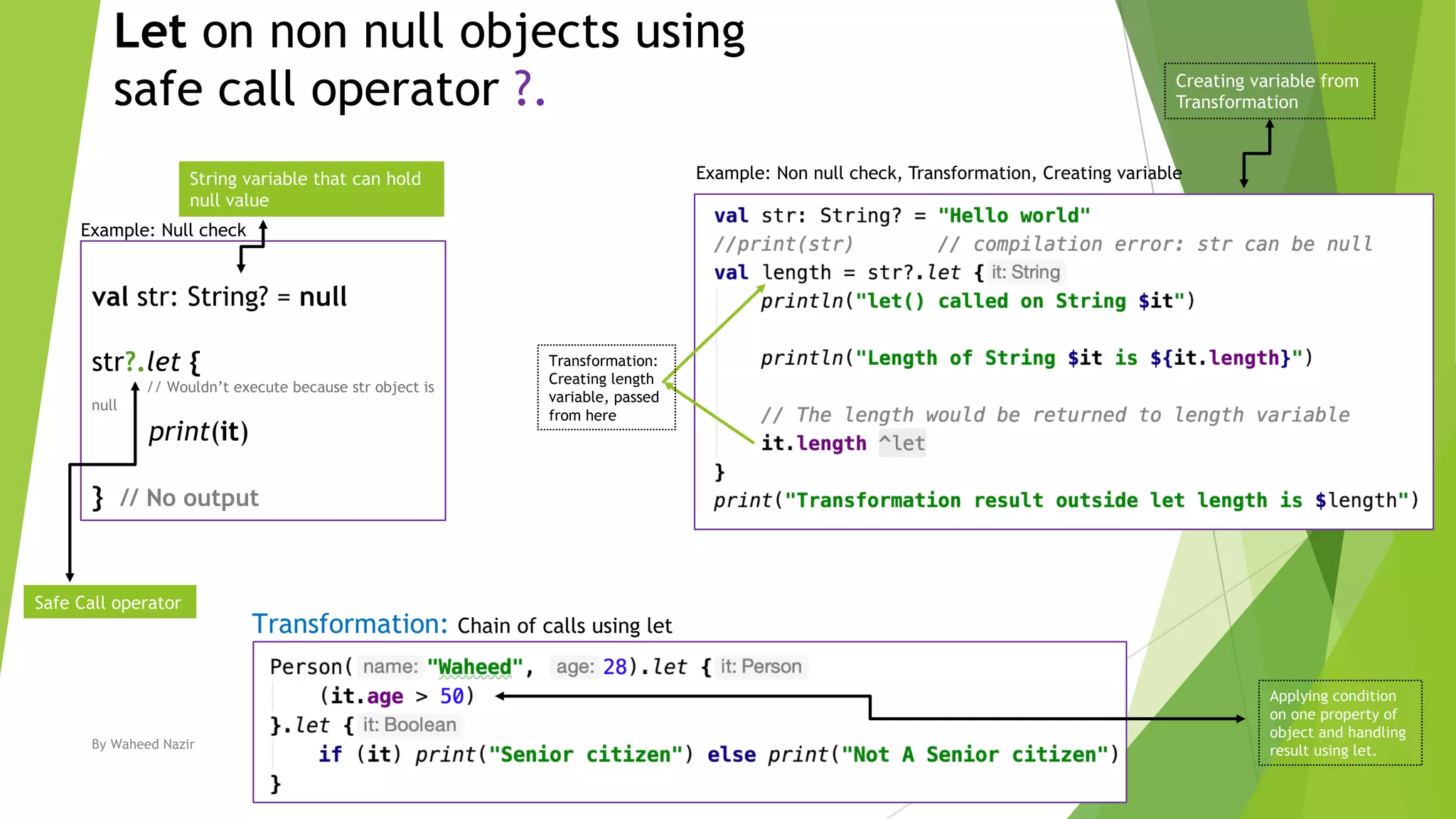
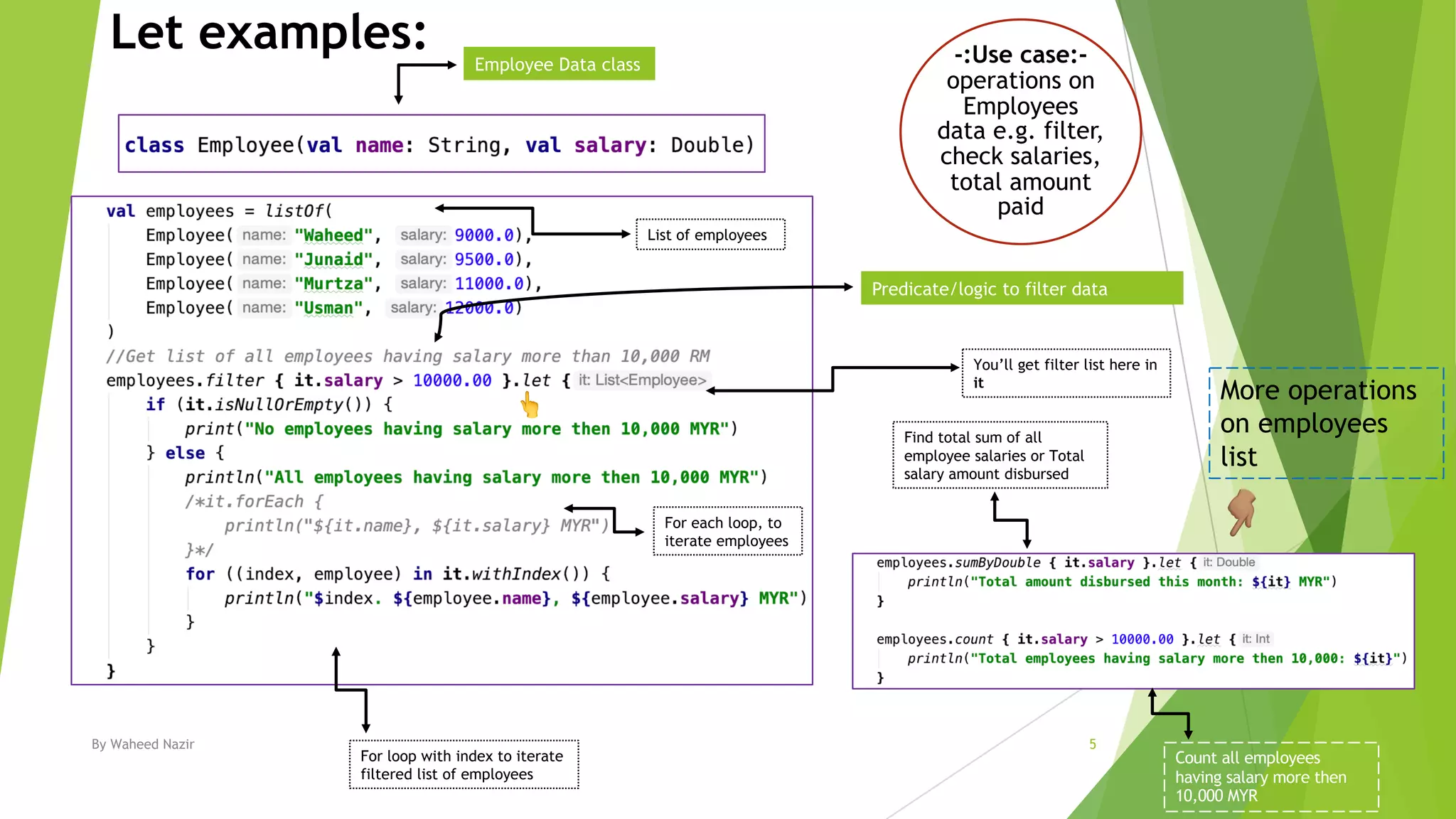
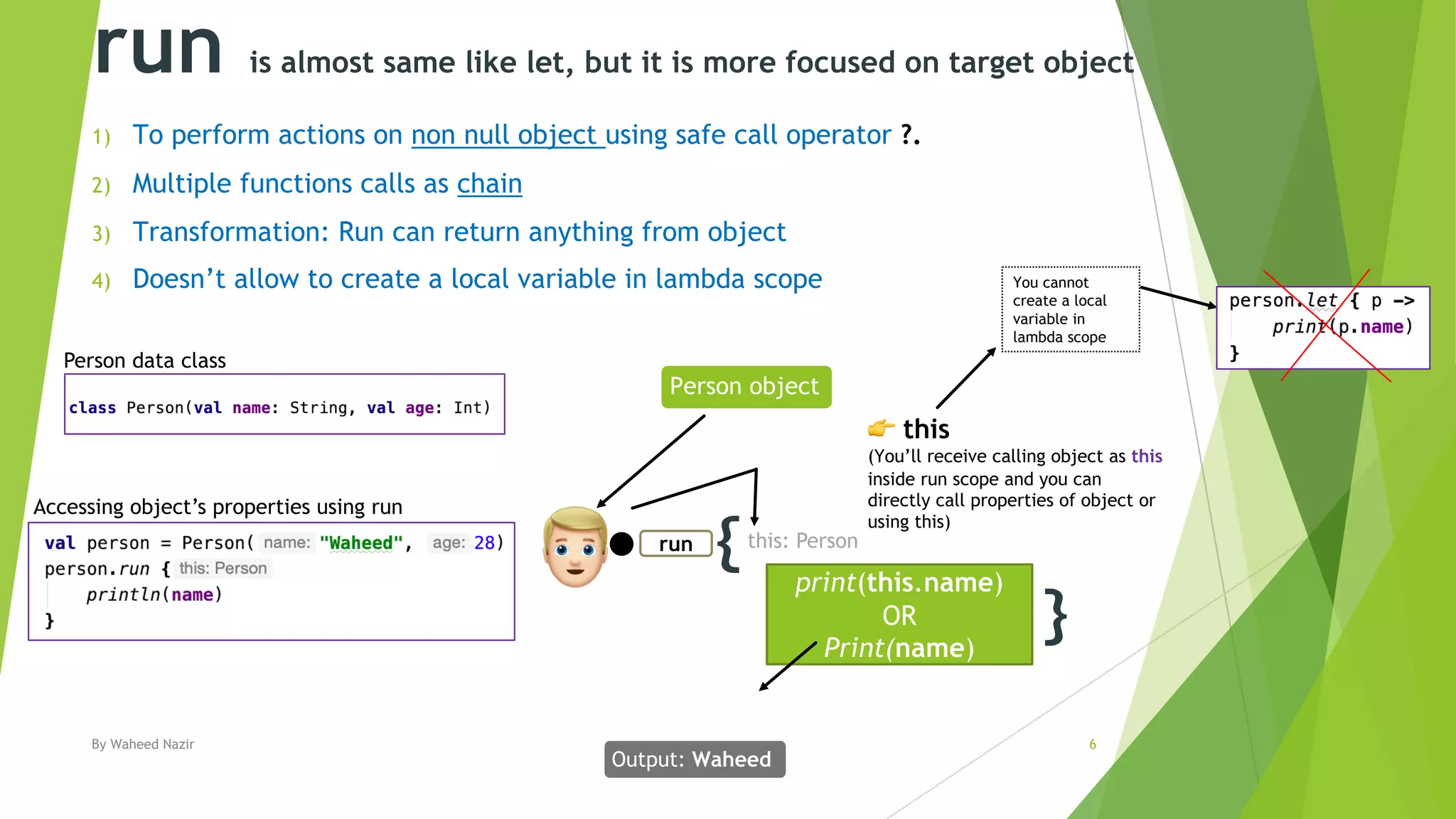
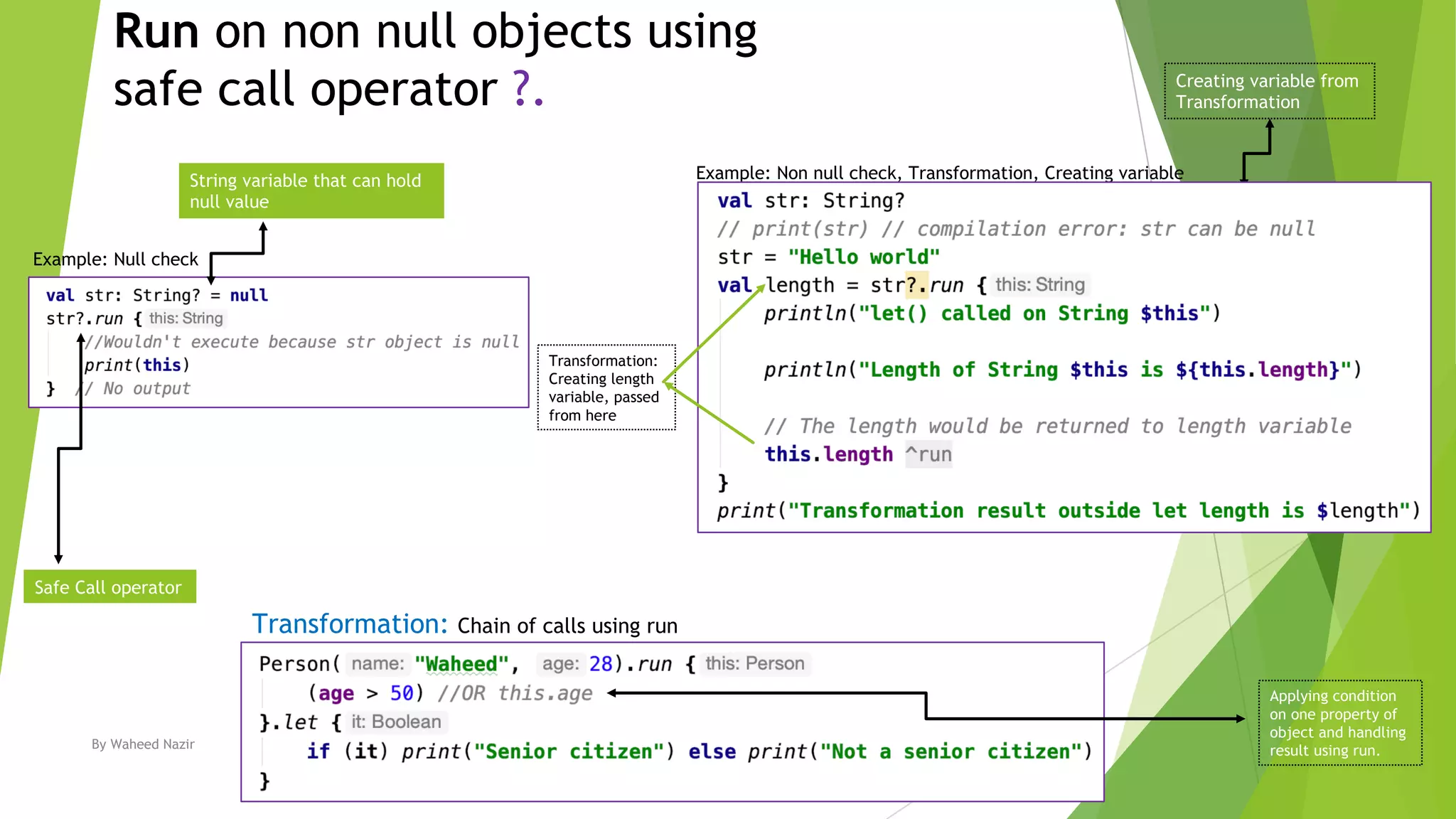
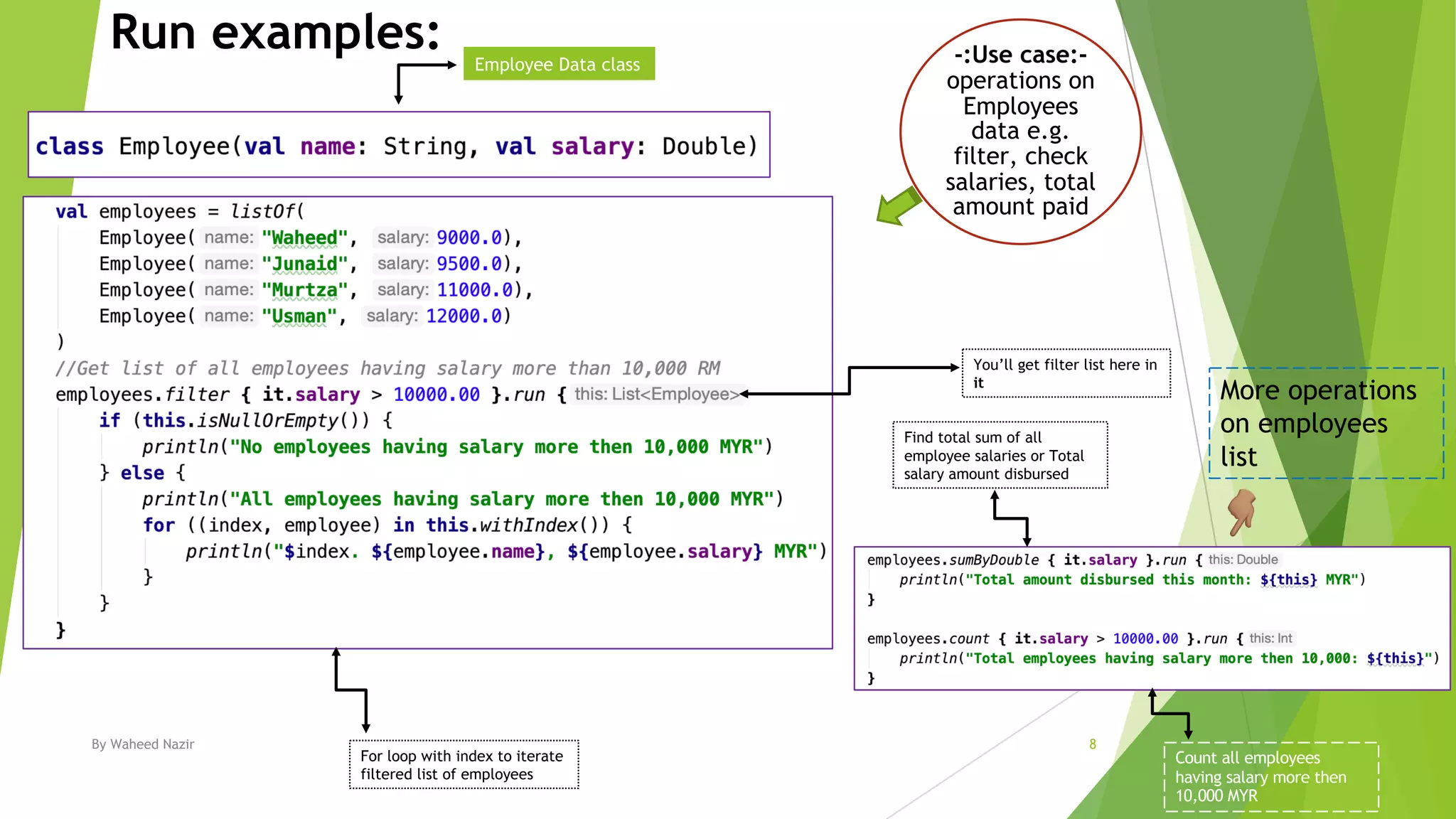
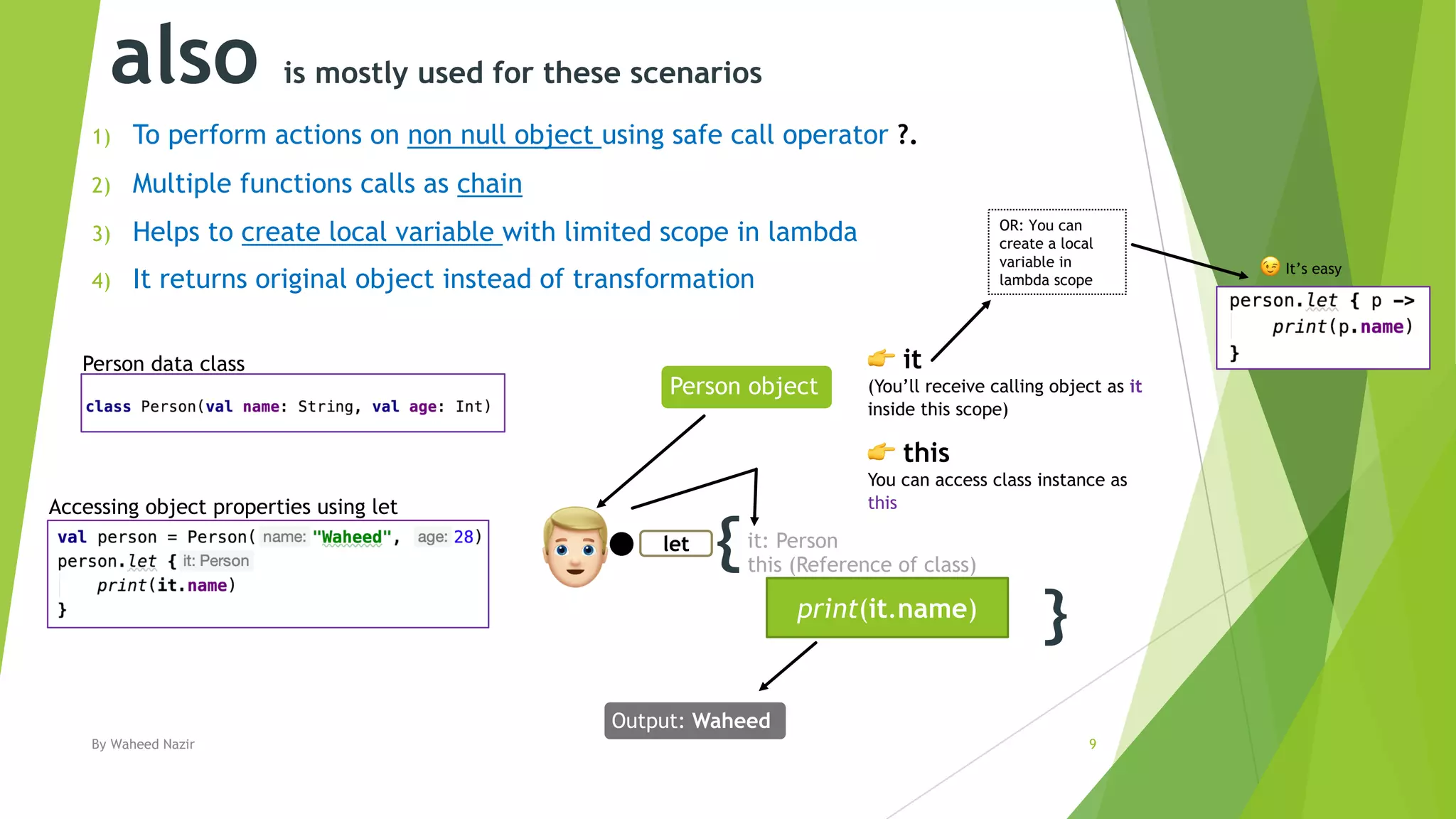
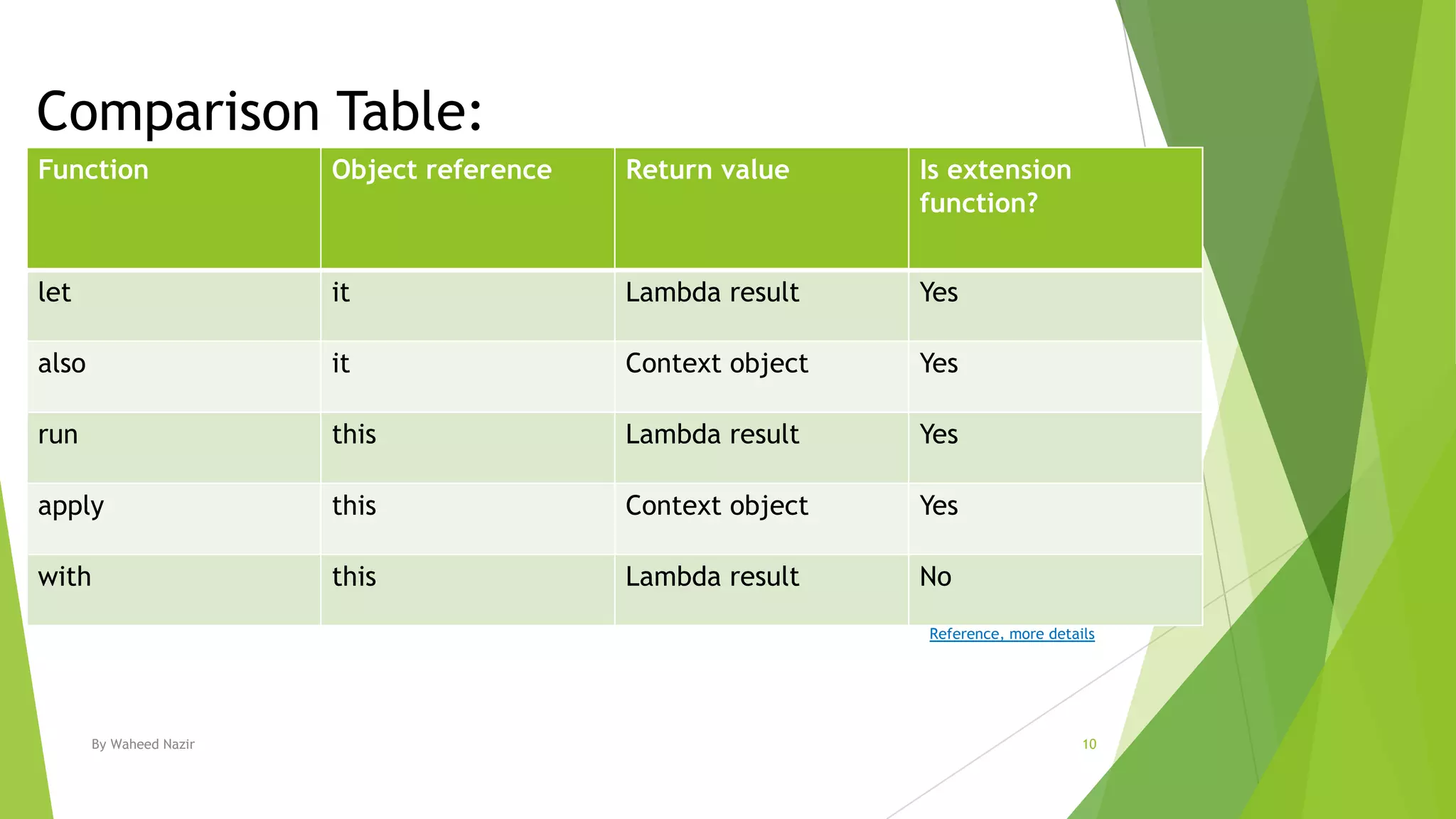
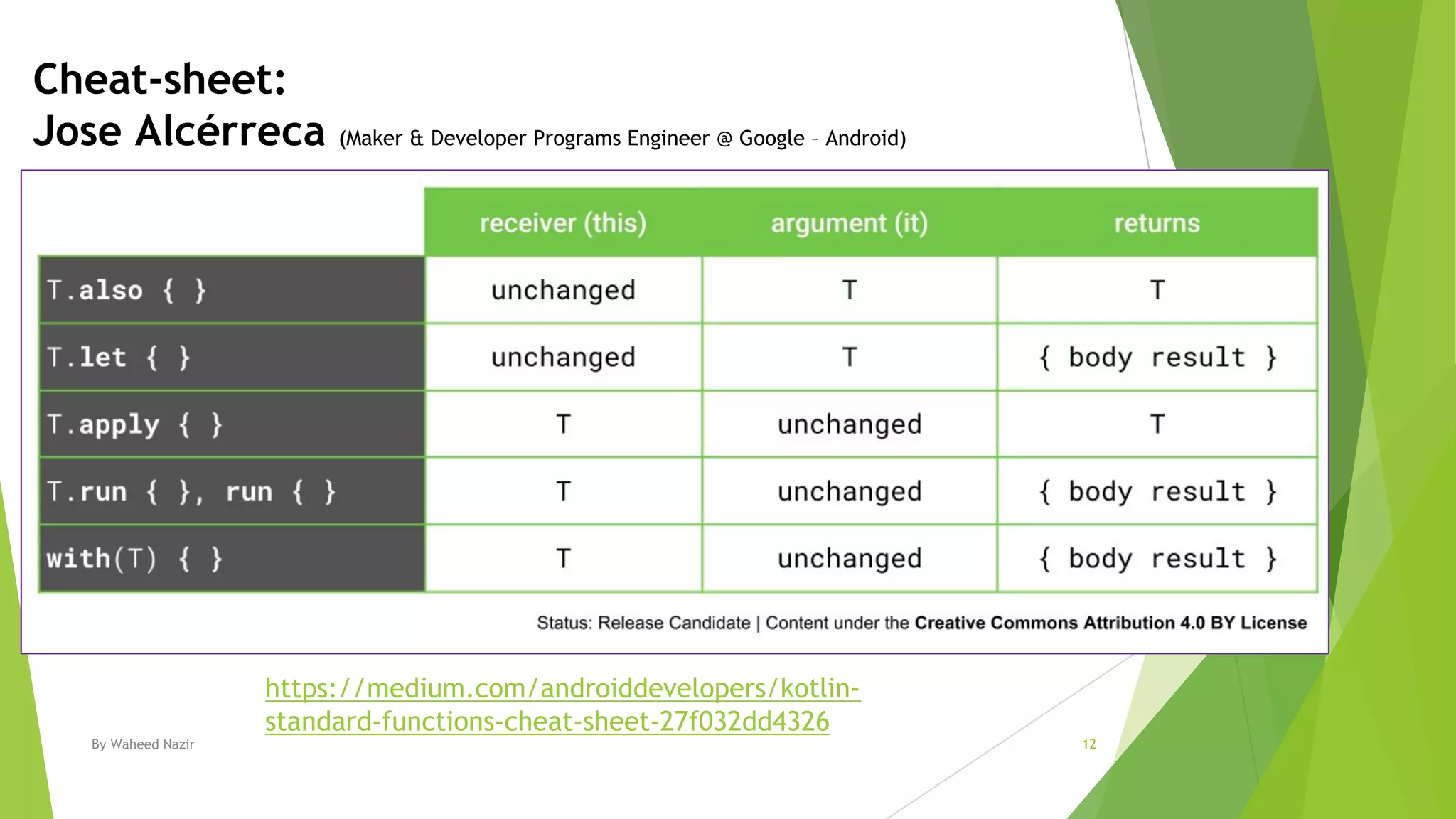
Kotlin has scope functions that execute code on an object and provide a scope via lambda expressions. The main scope functions are let, run, with, apply, and also. Let, run, and also accept the object as a parameter and allow further calls or returning a new object. Apply returns the object but with calls made within. With is similar but does not accept the object as a parameter.