Downloaded 442 times











Lamport's algorithm is a method designed to ensure mutual exclusion for safe usage of shared resources in distributed systems. It maintains a request queue for each site, with messages delivered in a FIFO manner according to timestamps. While it may not fully address contemporary distributed system challenges, it laid the groundwork for modern resource management approaches.
Presentation introduces Lamport’s Algorithm, aimed at enhancing safety in shared resource use via mutual exclusion.
Definitions of mutual exclusion, critical section, logical clocks, and causal message ordering.
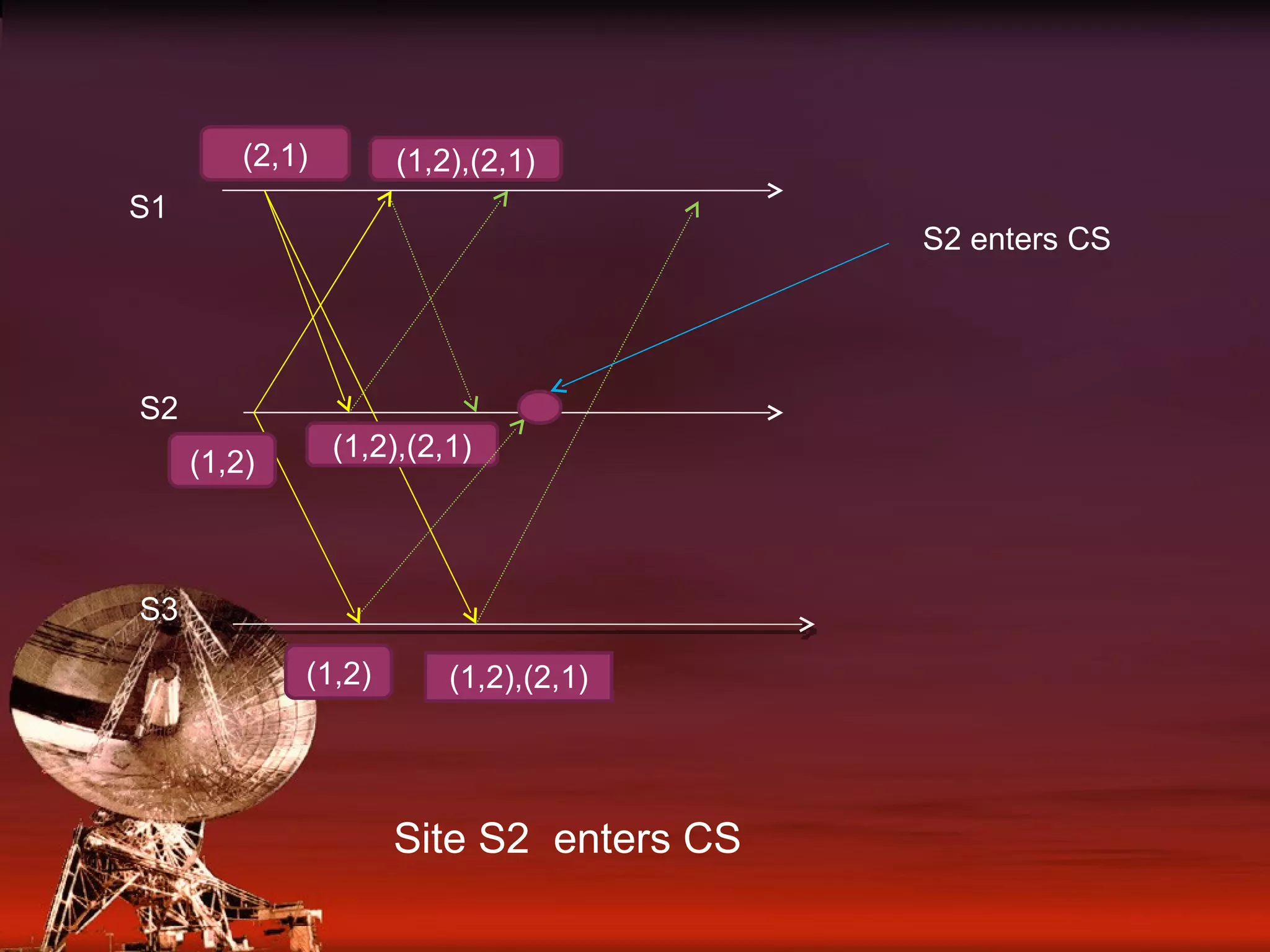
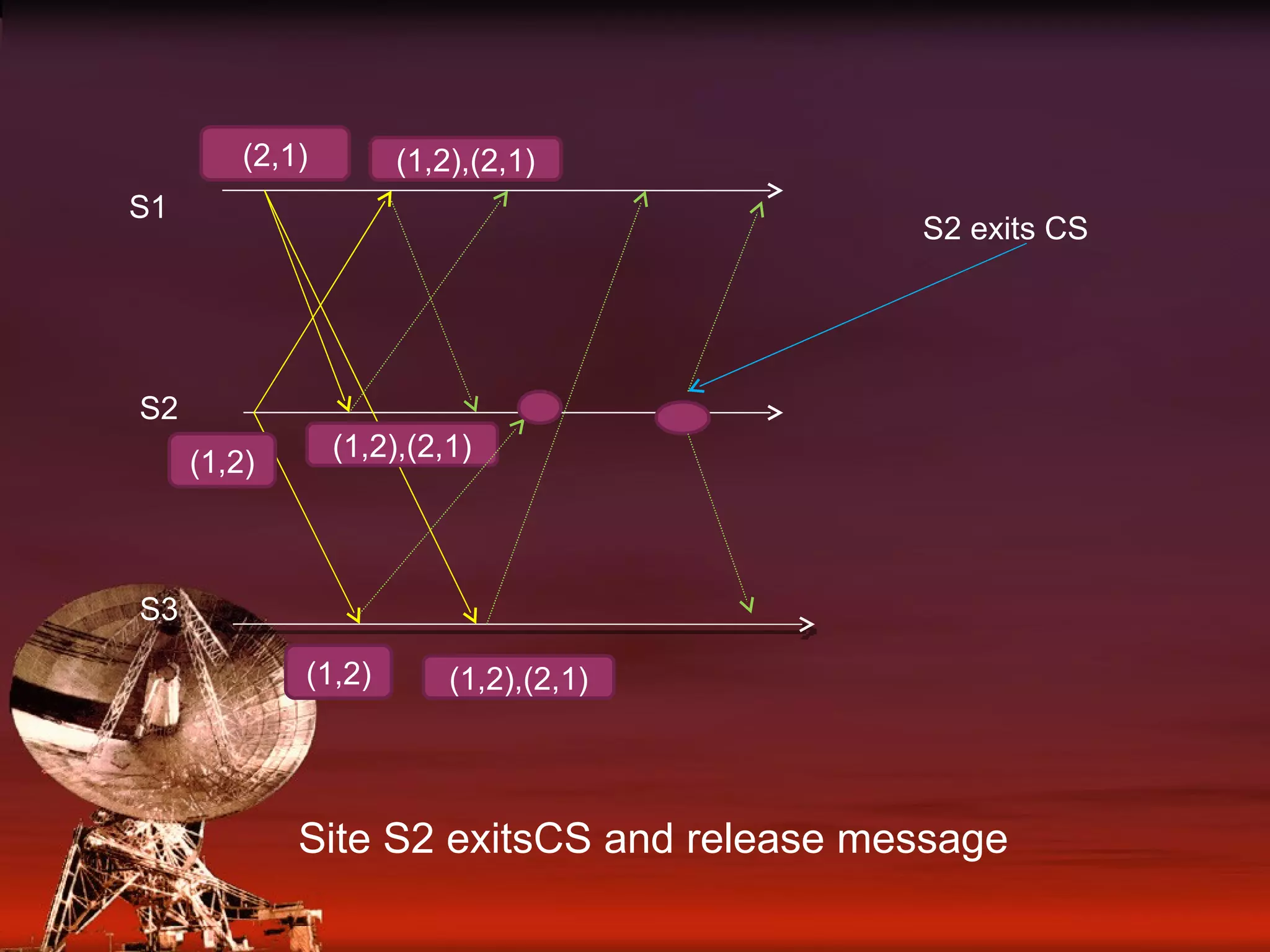
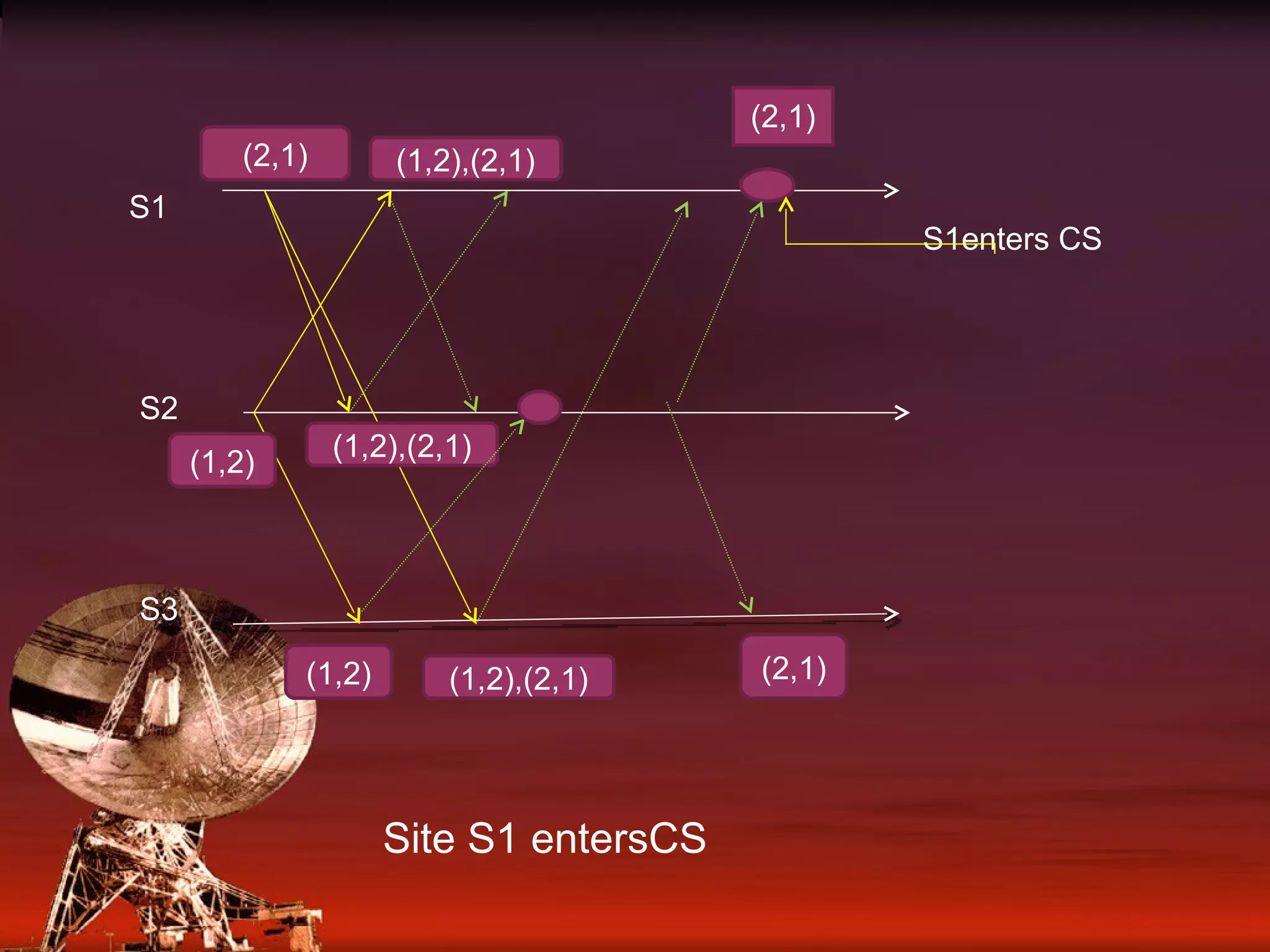
Details on how each site maintains a request queue for mutual exclusion requests with FIFO message delivery.
Examples involving three sites (S1, S2, S3) showing the request and release process for critical sections.
Performance analysis provides formulas for total requests, replies, and releases in the algorithm.
Discussion on the relevance of Lamport's Algorithm in modern distributed systems for handling resources.












