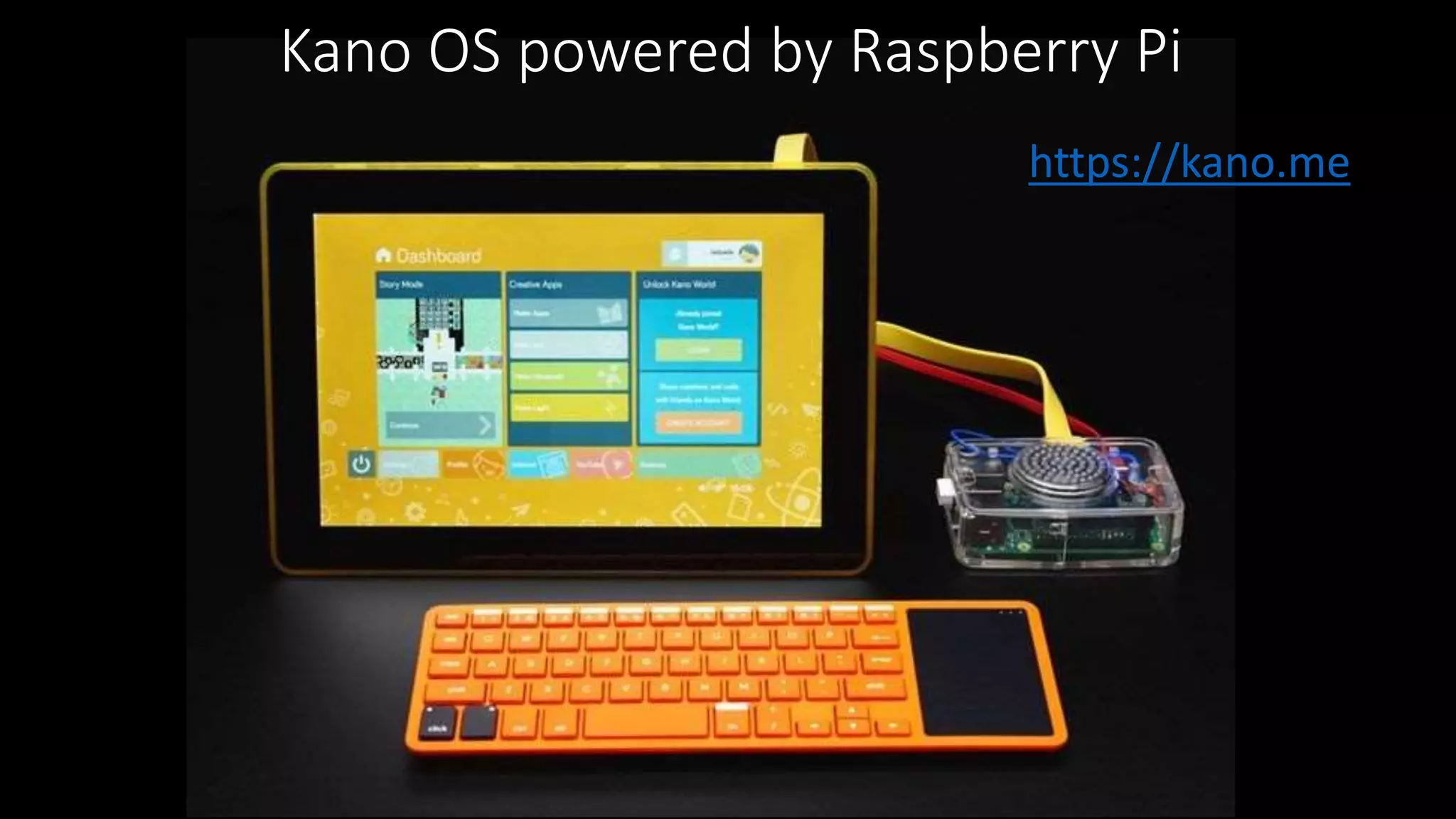
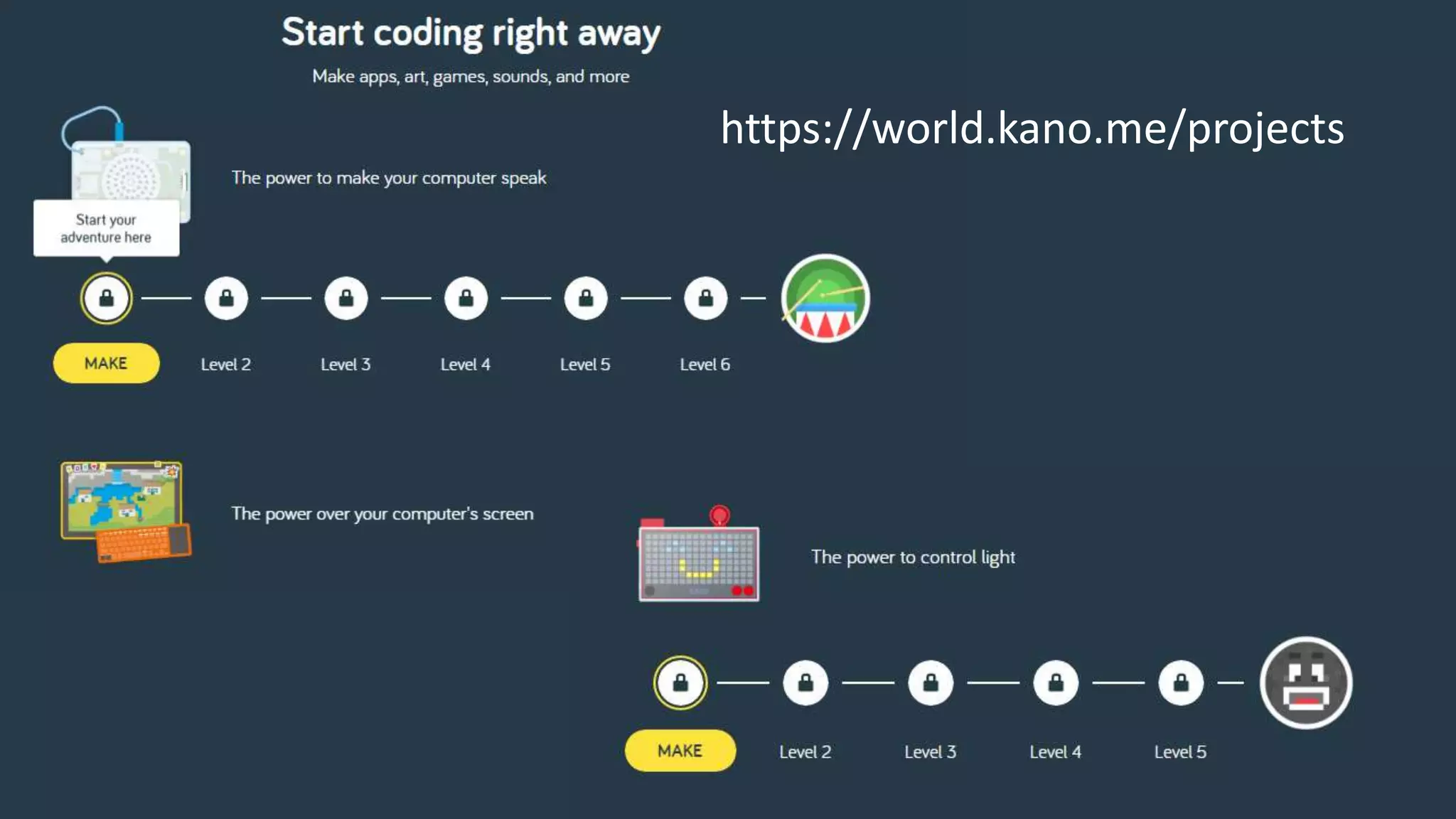
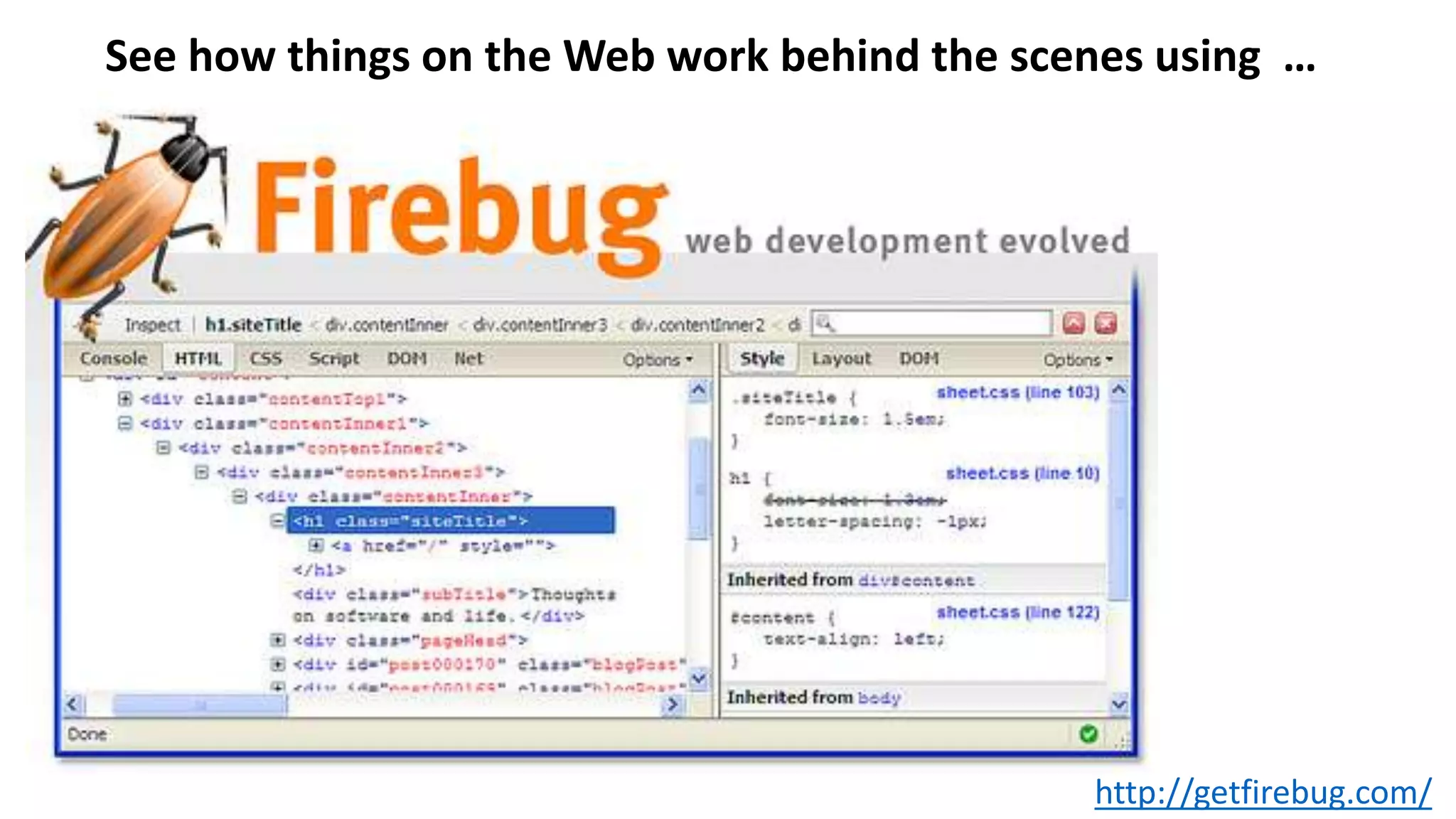
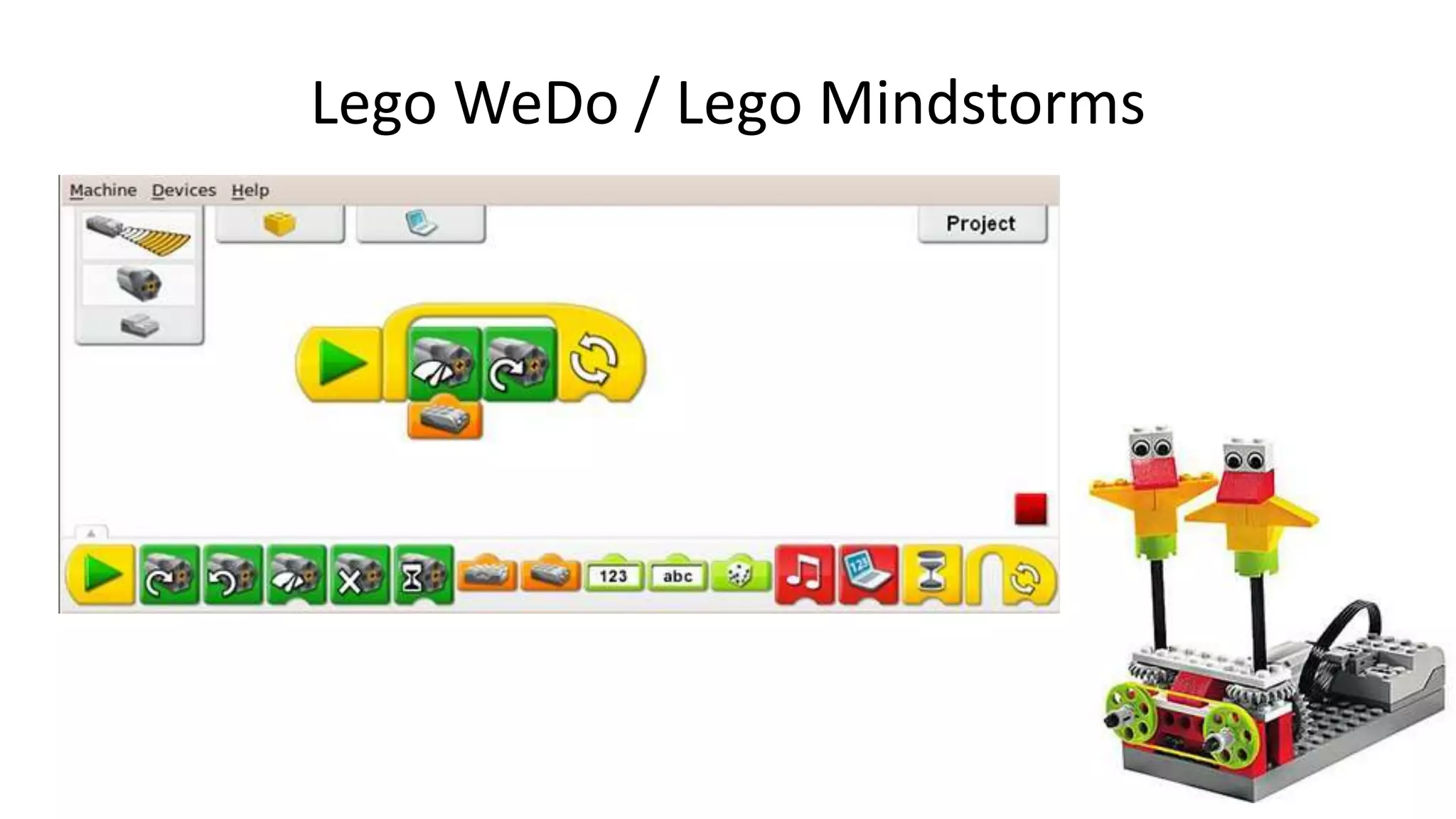
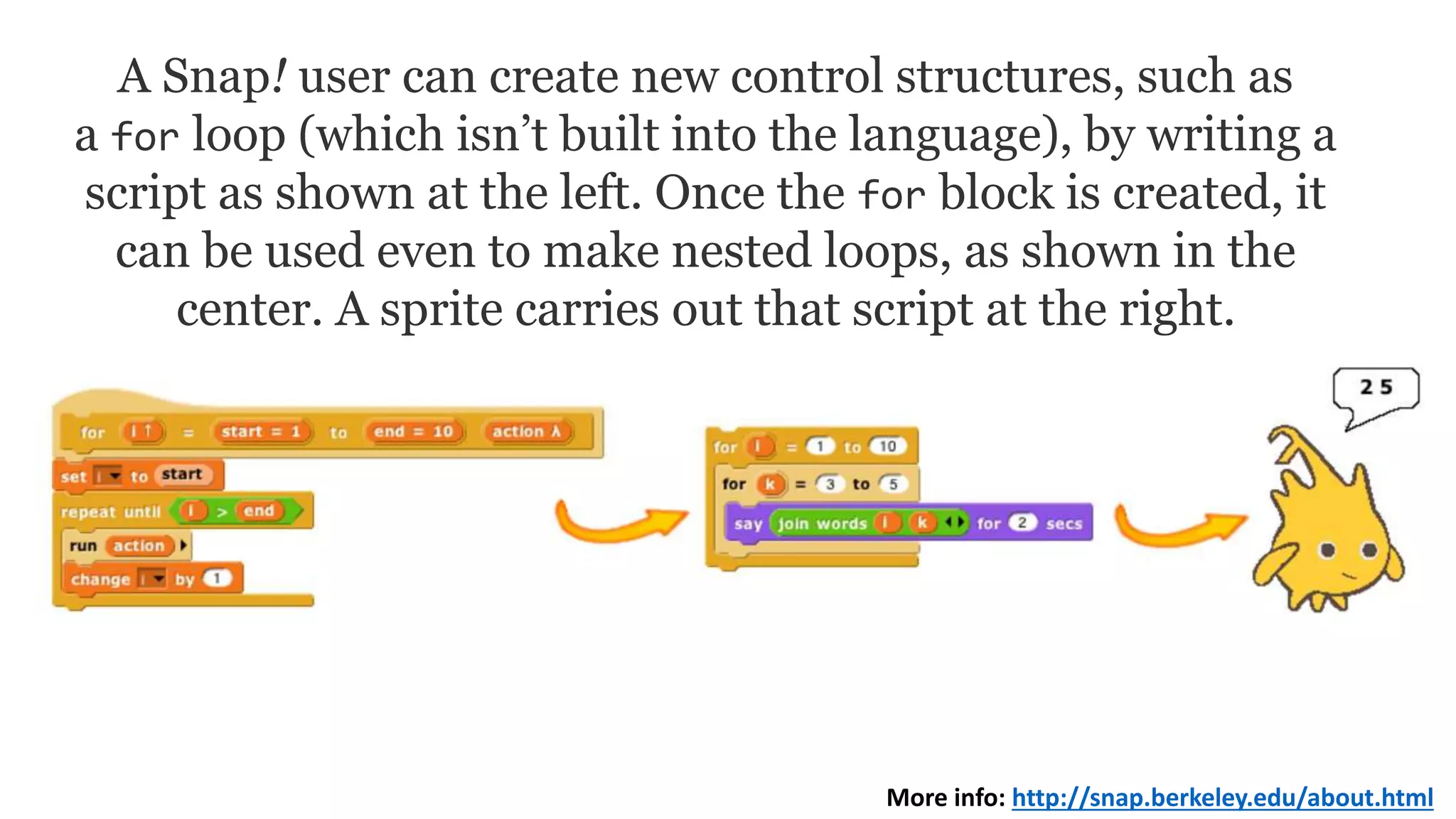
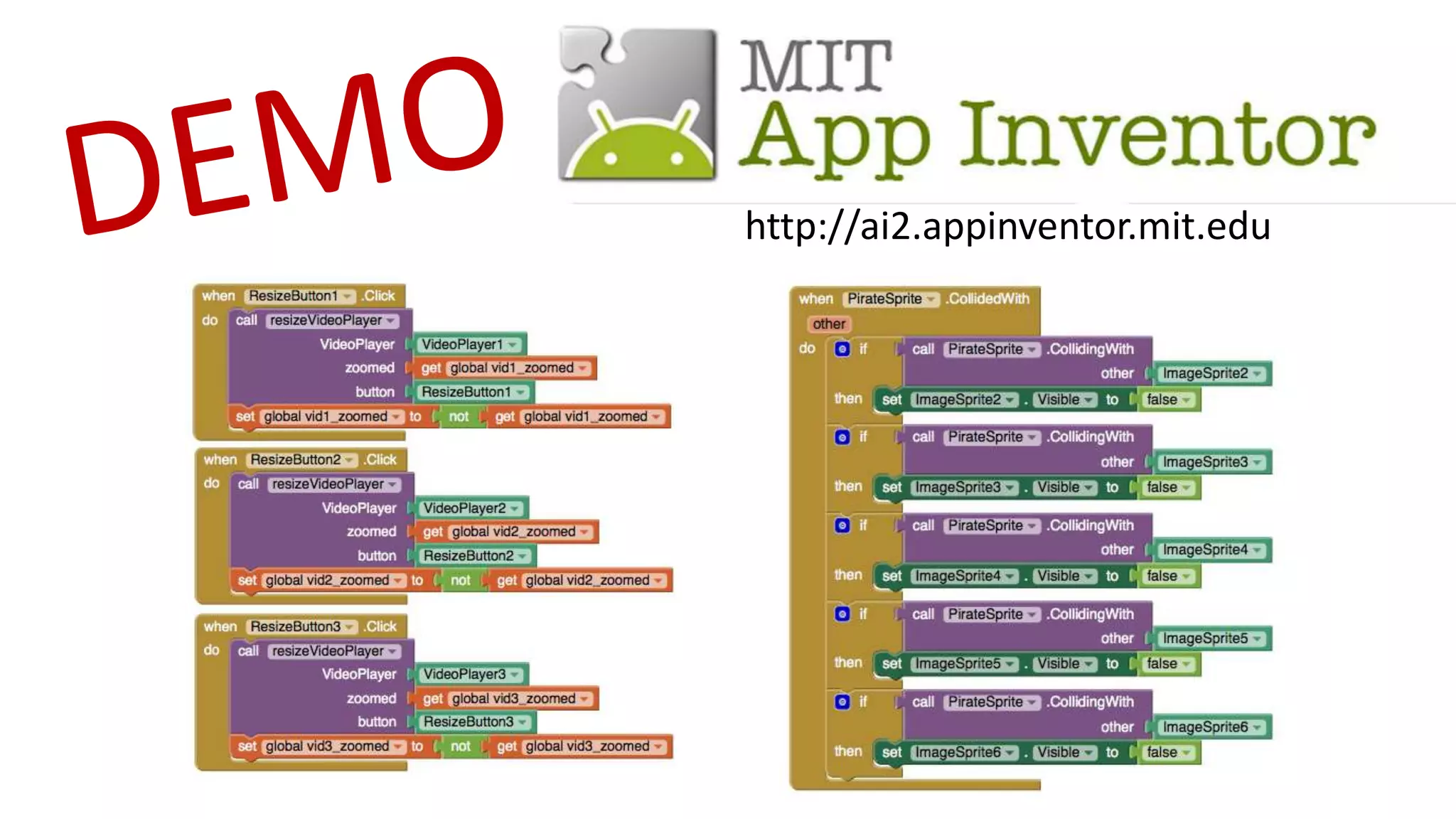
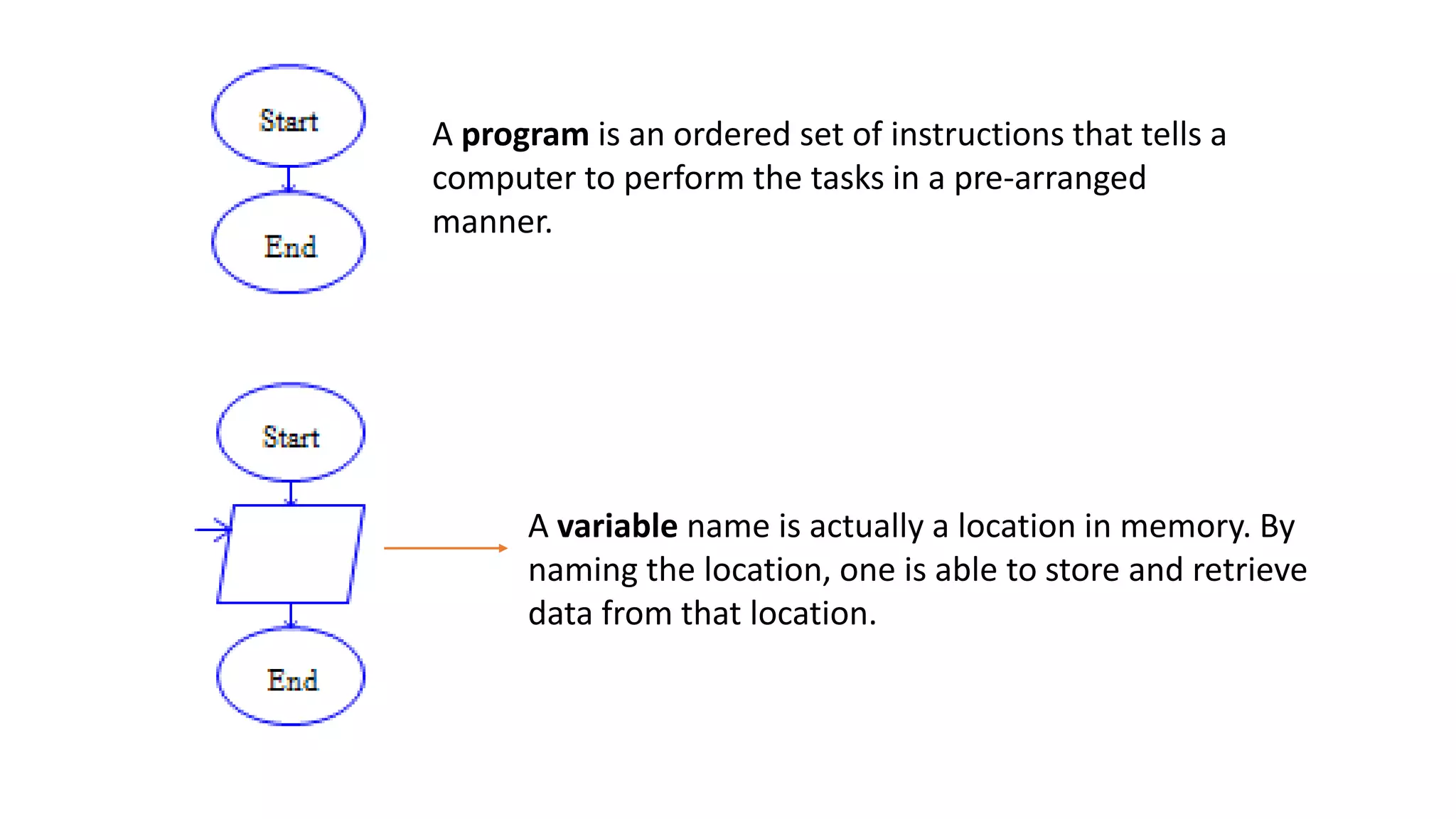
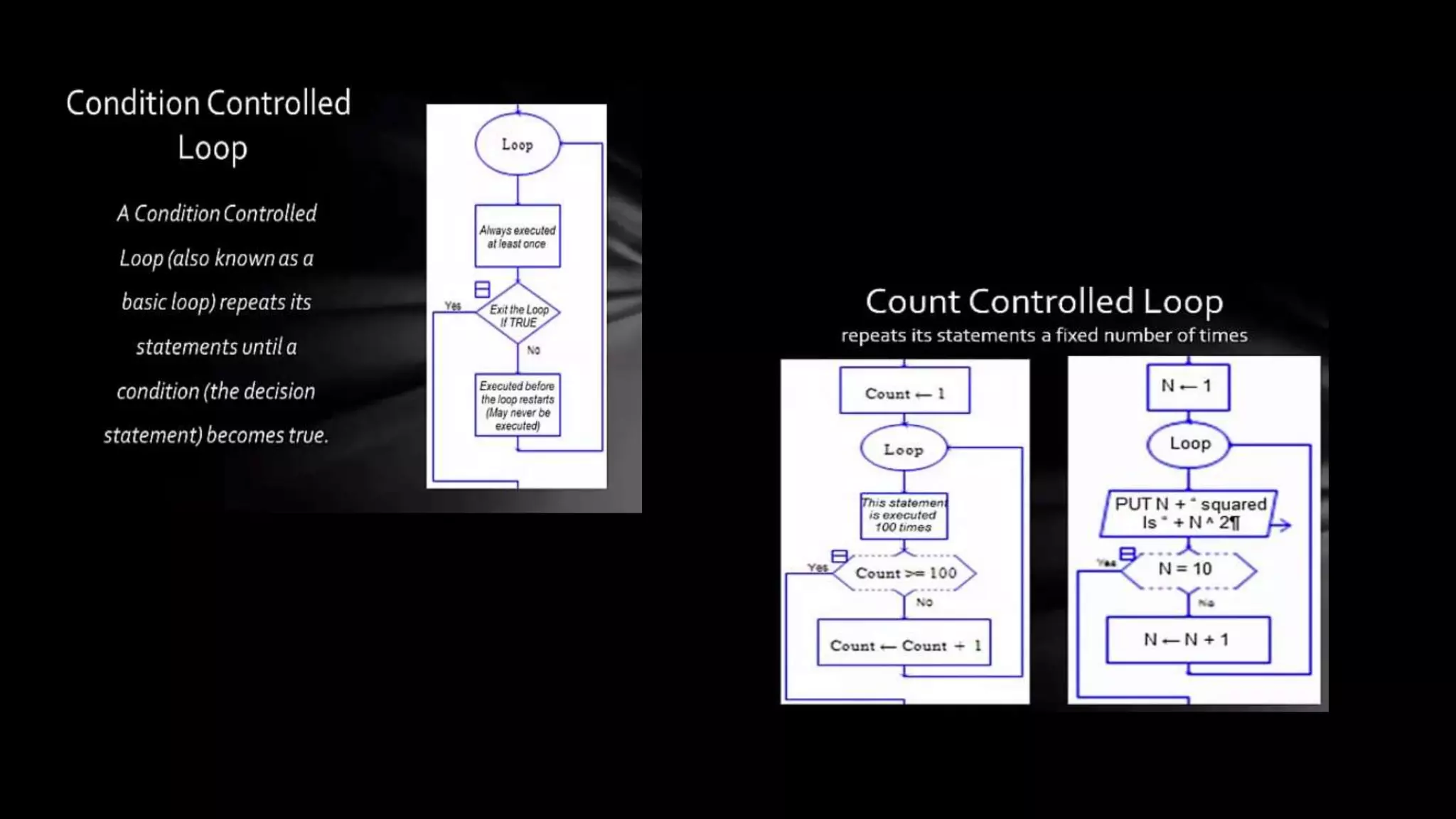
The document outlines an agenda for teaching basic programming concepts using visual programming languages such as Scratch, Hopscotch, and App Inventor. It emphasizes the importance of coding for mathematical, computational, and creative thinking, and discusses various tools and resources available for learning programming in a fun and engaging way. Additionally, it defines key programming components like variables, flow control, and functions, while providing links to educational materials and interactive coding platforms.


















![Variables & Arrays
• An array is a type of variable (or bucket) that holds many pieces of
information.
• Example (language doesn’t matter here; the concept does):
• $FavoriteCities = array(“Orlando”, “Boulder”, “Miami”)
• $FavoriteCities[0] holds “Orlando”
• $FavoriteCities [1] holds “Boulder”
• $States = array(“1” => “Prime”; “FL”=> “Florida”, “CO” => “Colorado”)
• $States[“FL”] holds “Florida”
Slide courtesy of Brian Pichman](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learntocodehavefun-170330184311/75/Learn-to-Code-and-Have-Fun-Doing-It-29-2048.jpg)