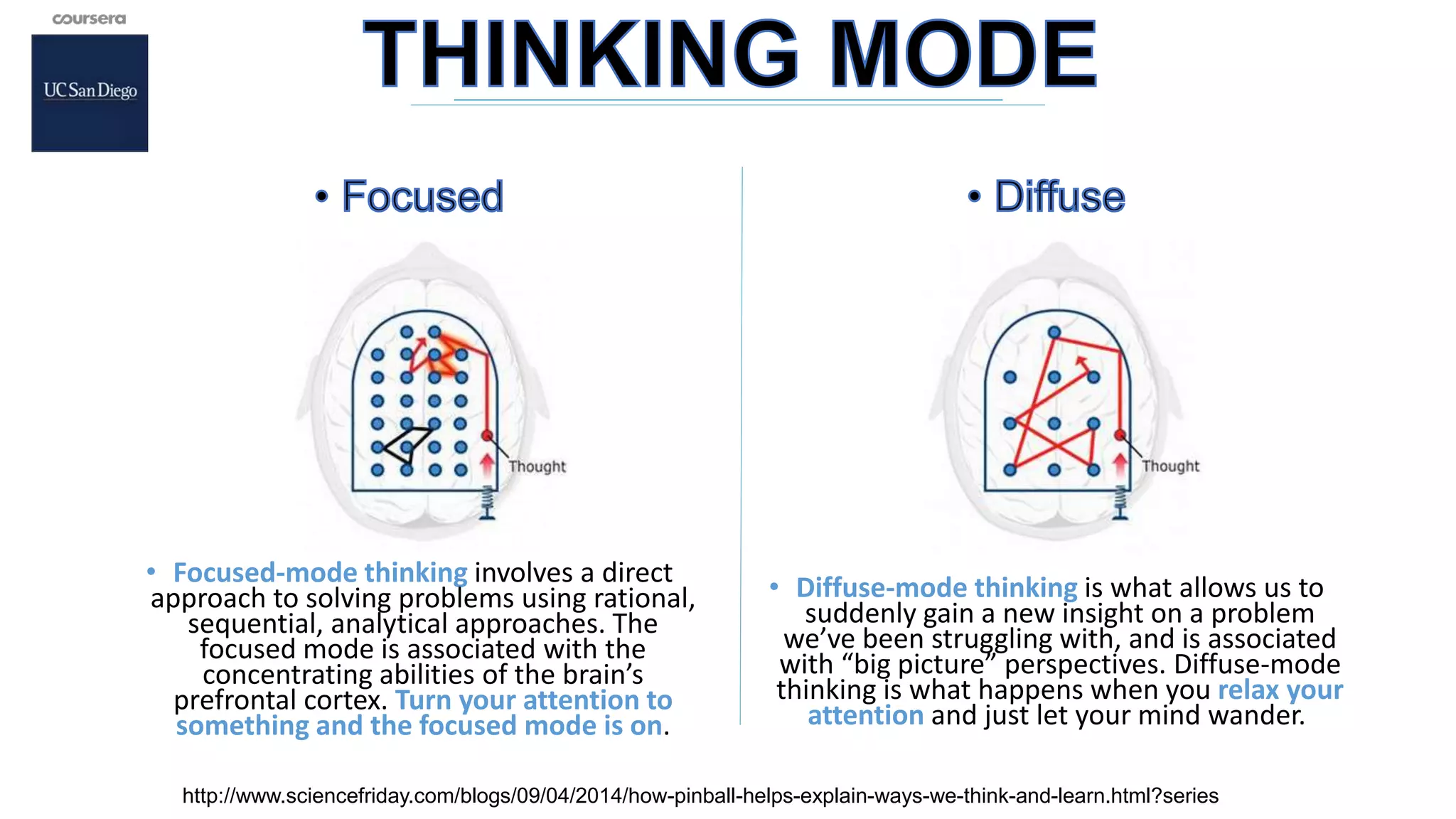
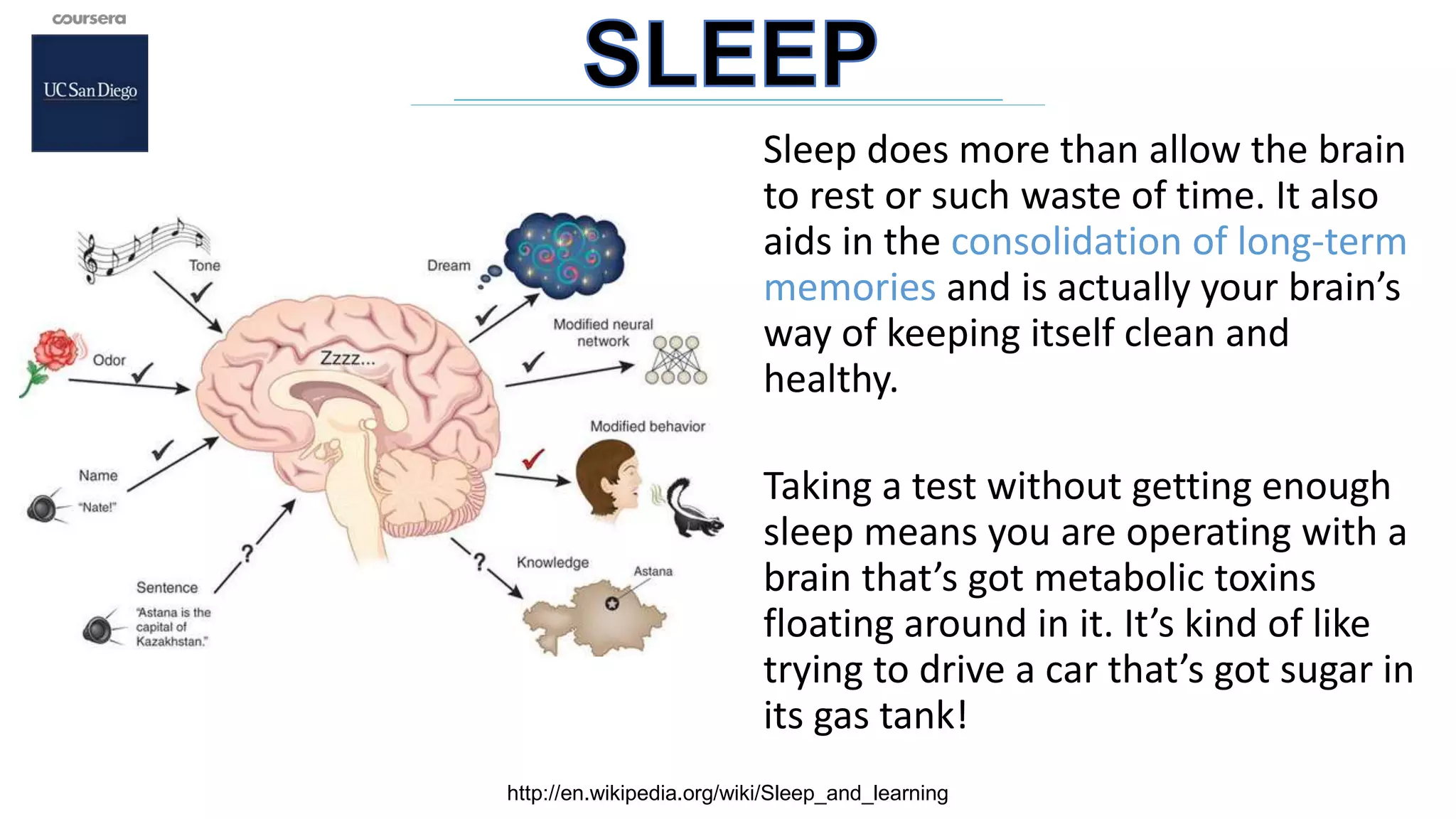
The document outlines strategies for effective learning, highlighting the importance of both focused-mode and diffuse-mode thinking in problem-solving. It emphasizes techniques like the Pomodoro technique, the value of sleep in memory consolidation, and the power of visualization for understanding concepts. Additionally, it discusses how teamwork and a growth mindset can enhance learning experiences, stressing the role of individual context and ongoing motivation in becoming a lifelong learner.