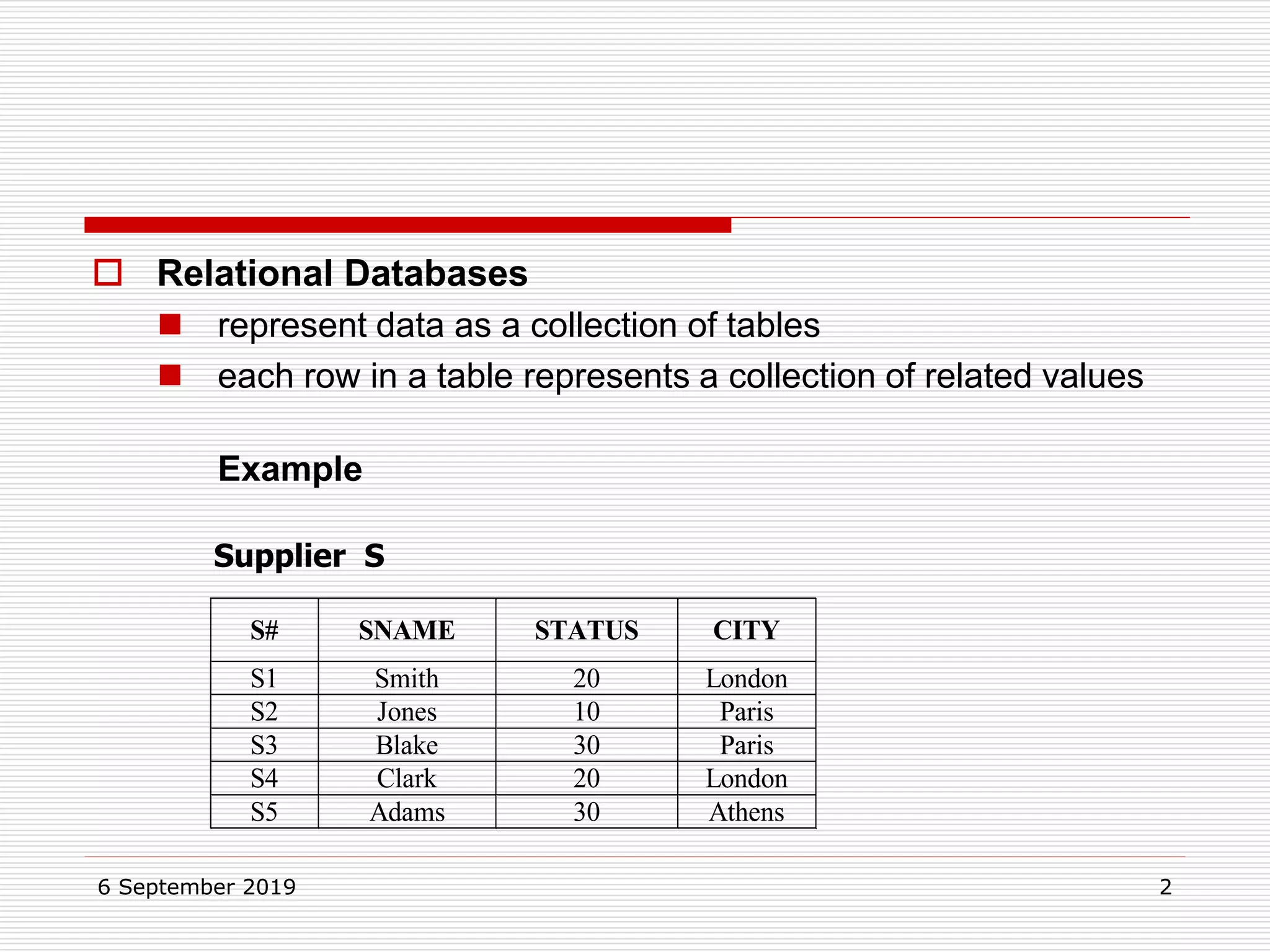
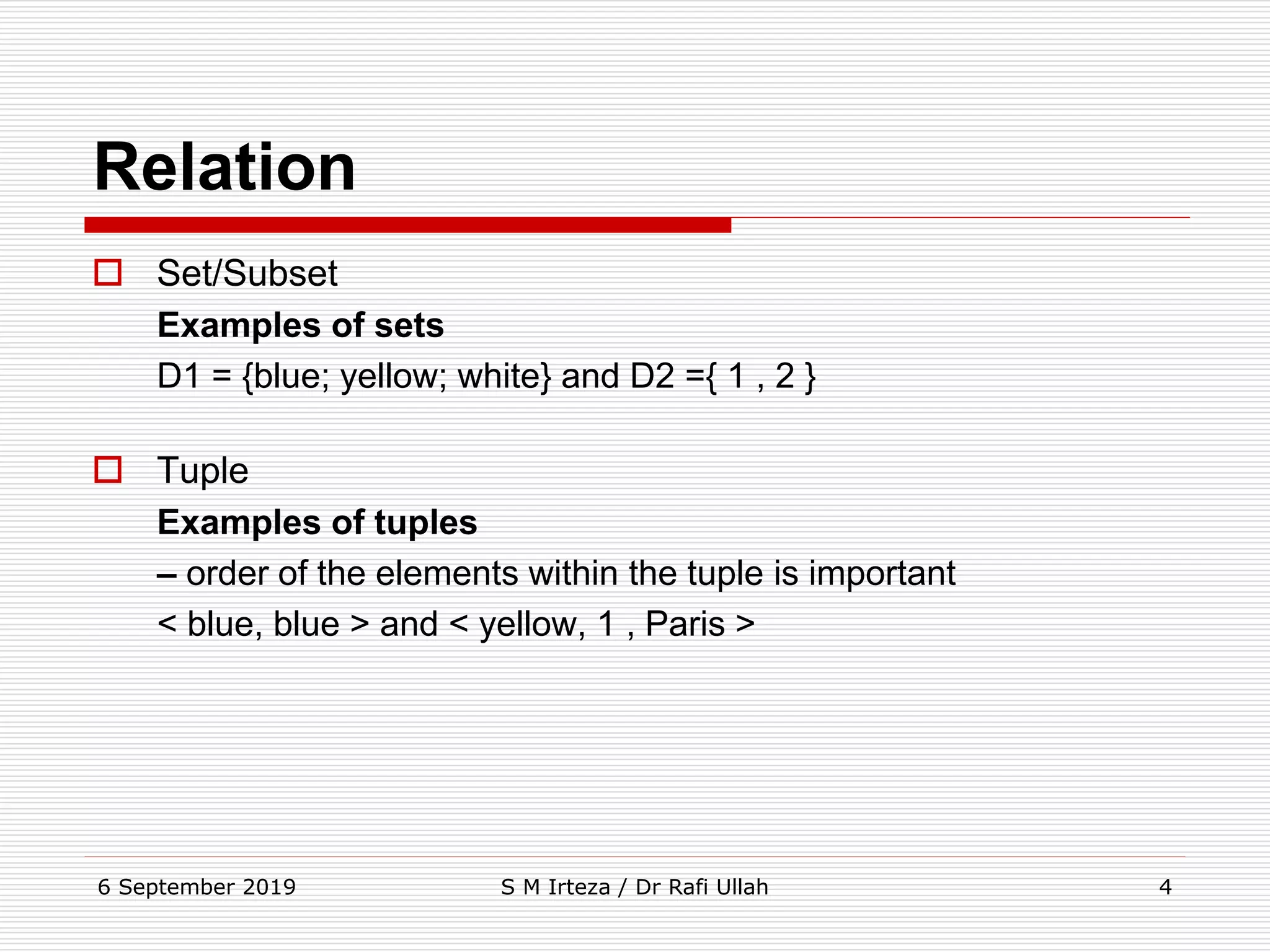
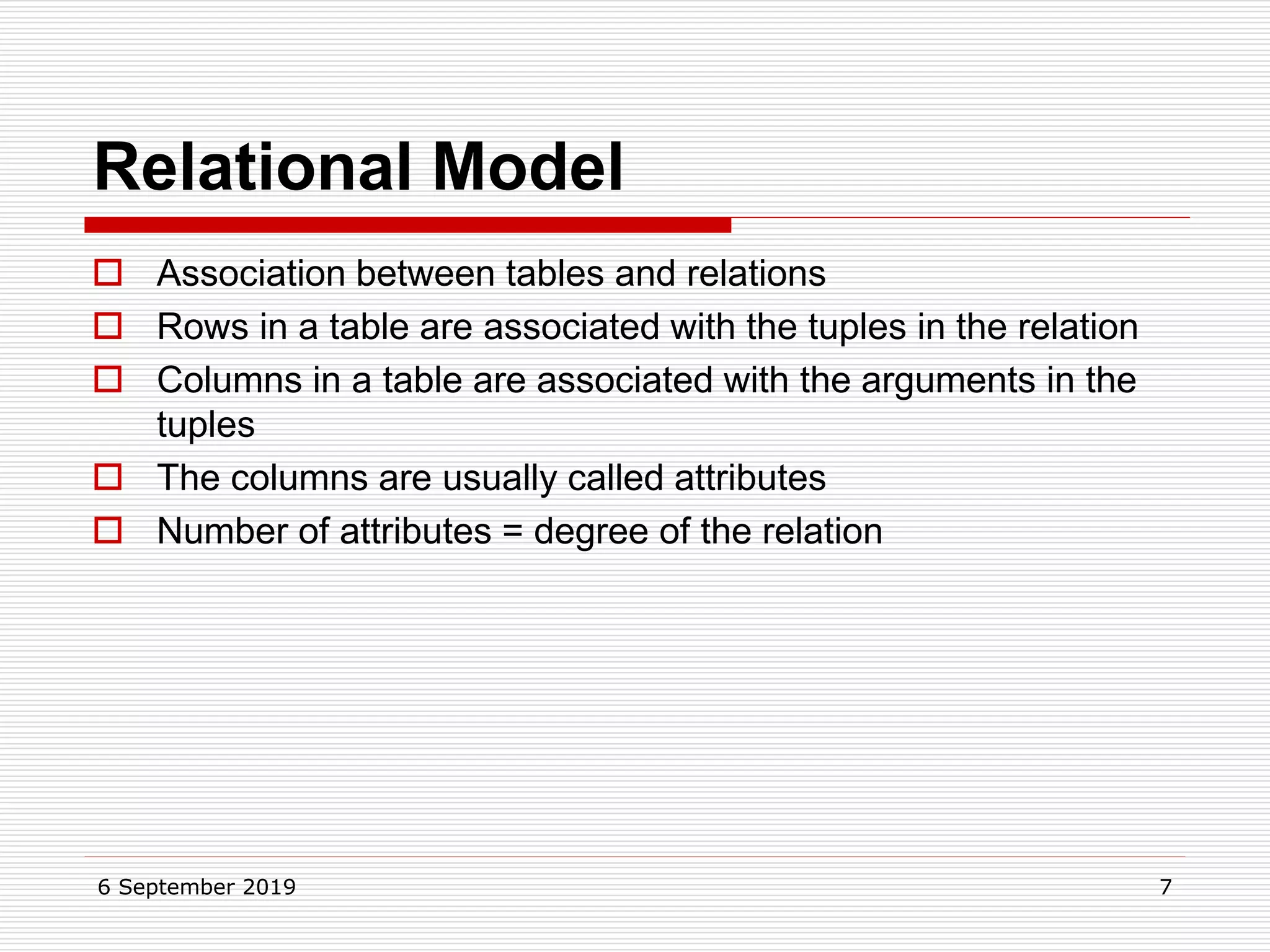
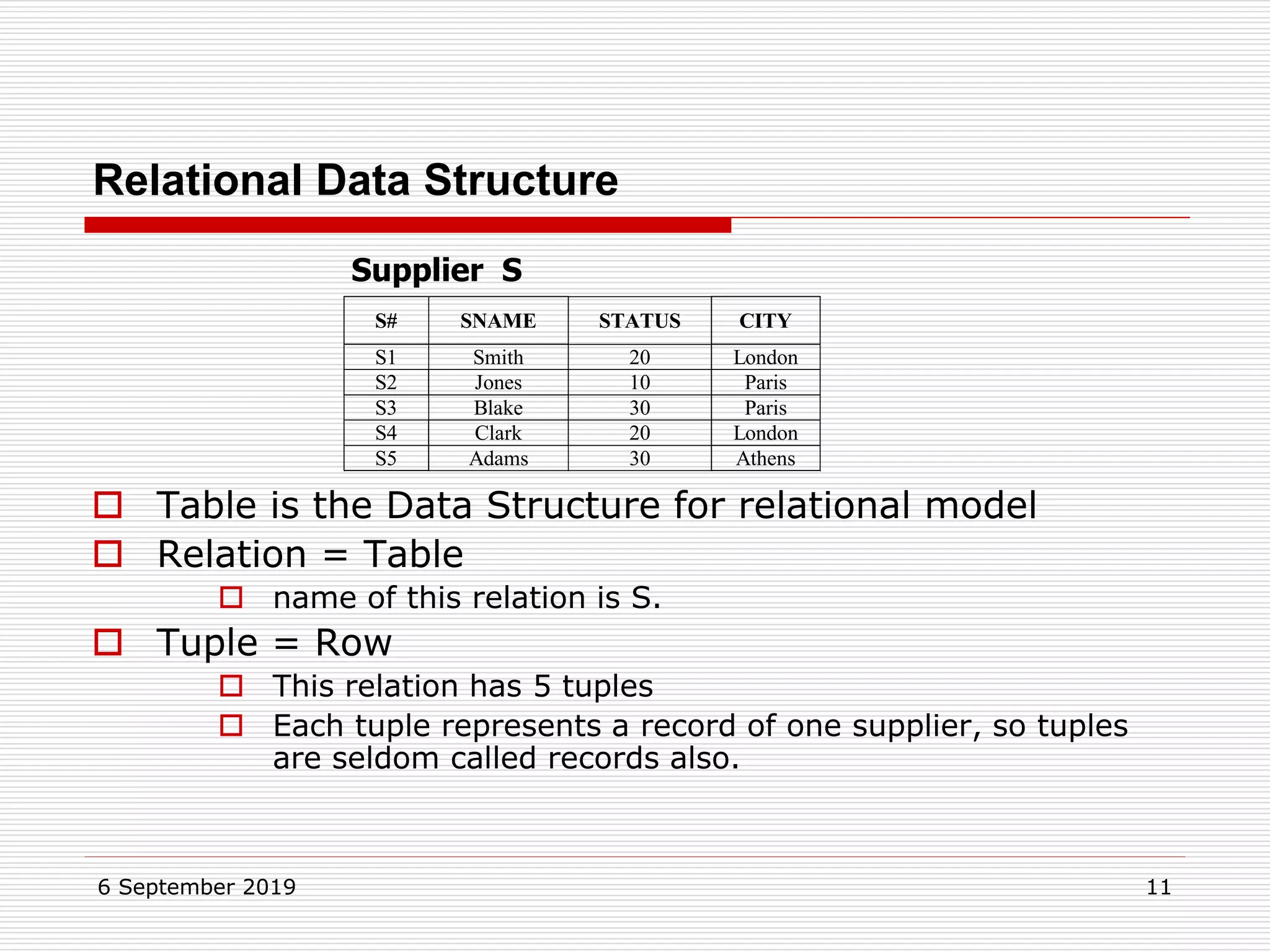
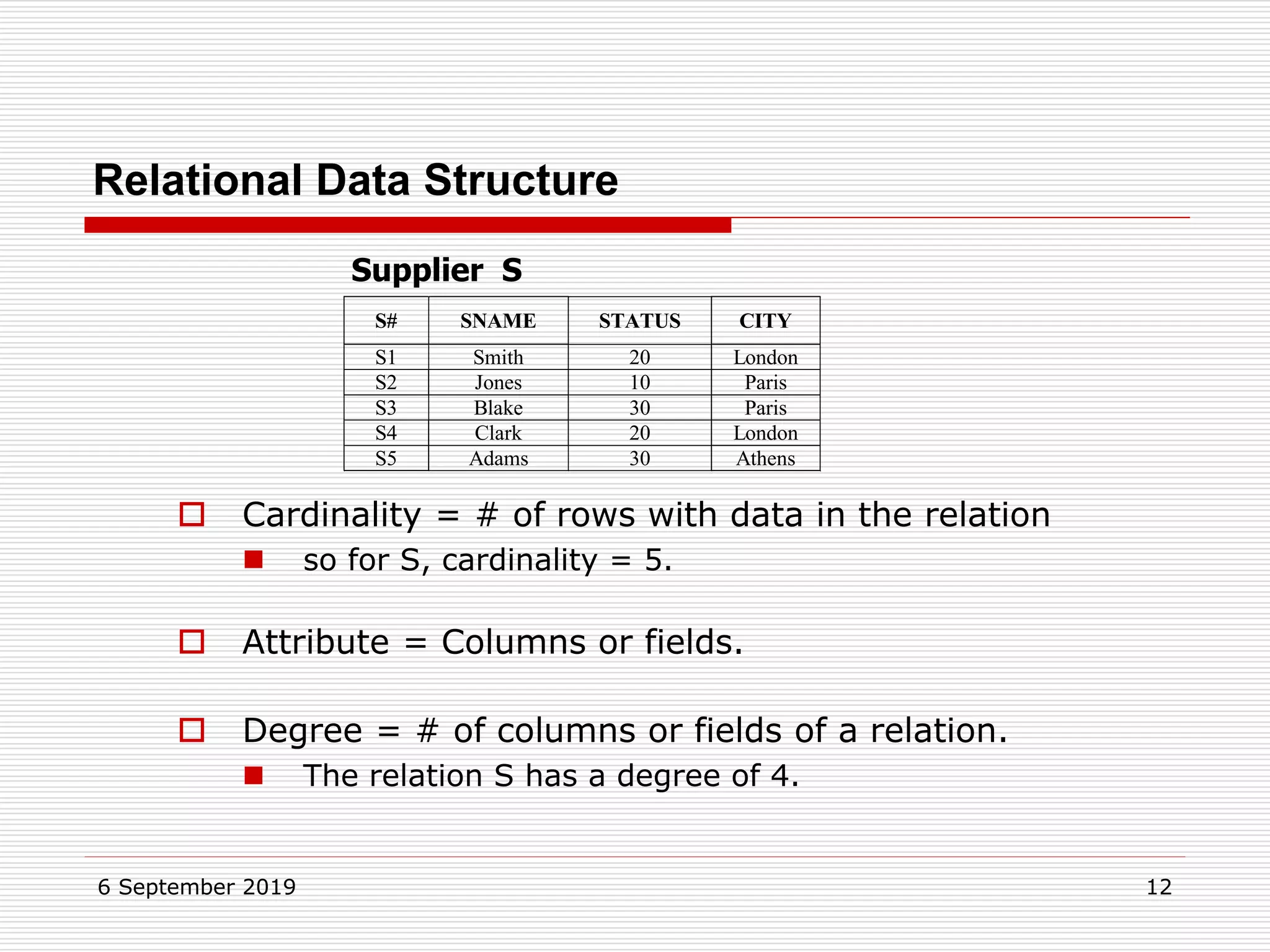
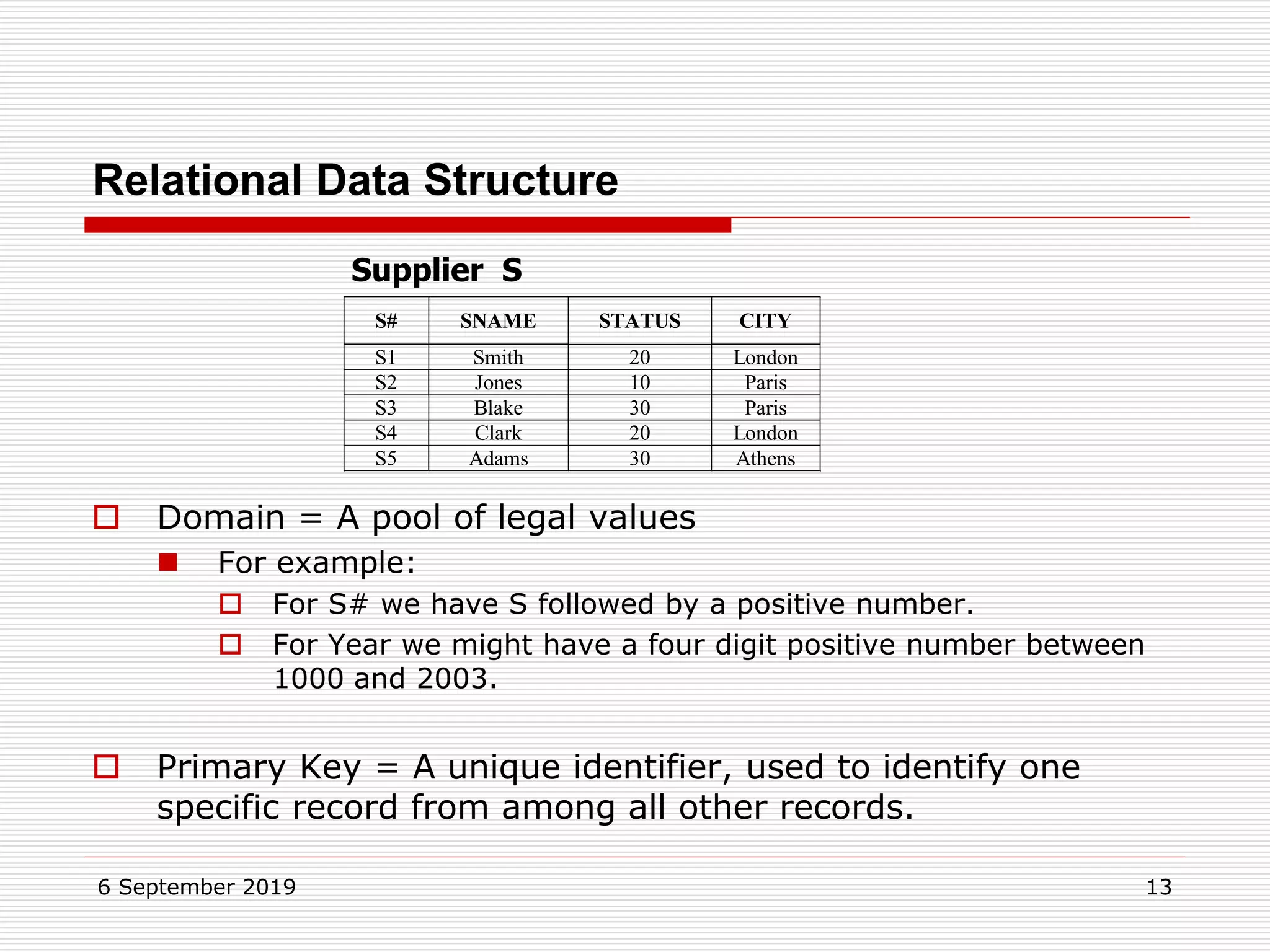
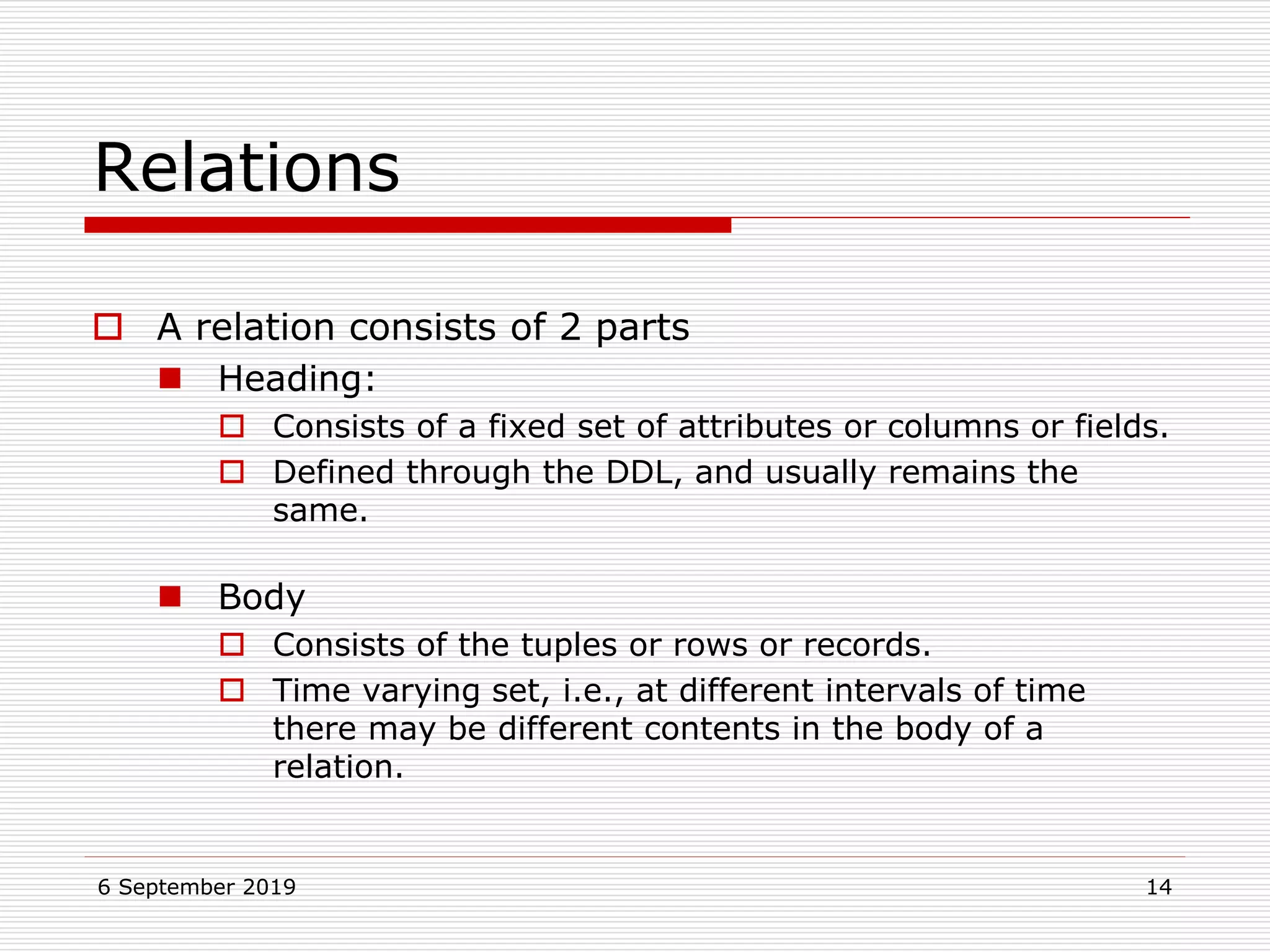
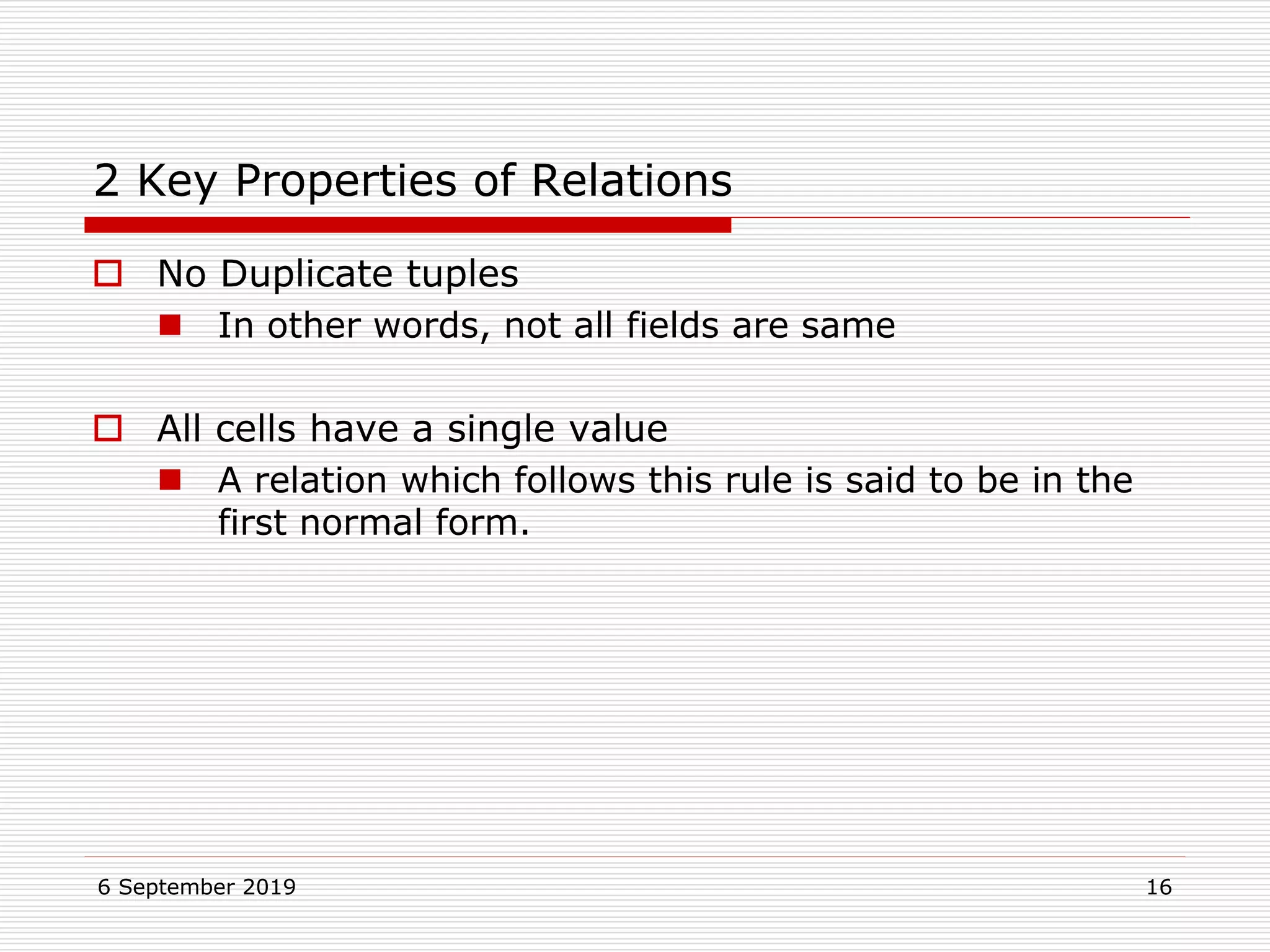
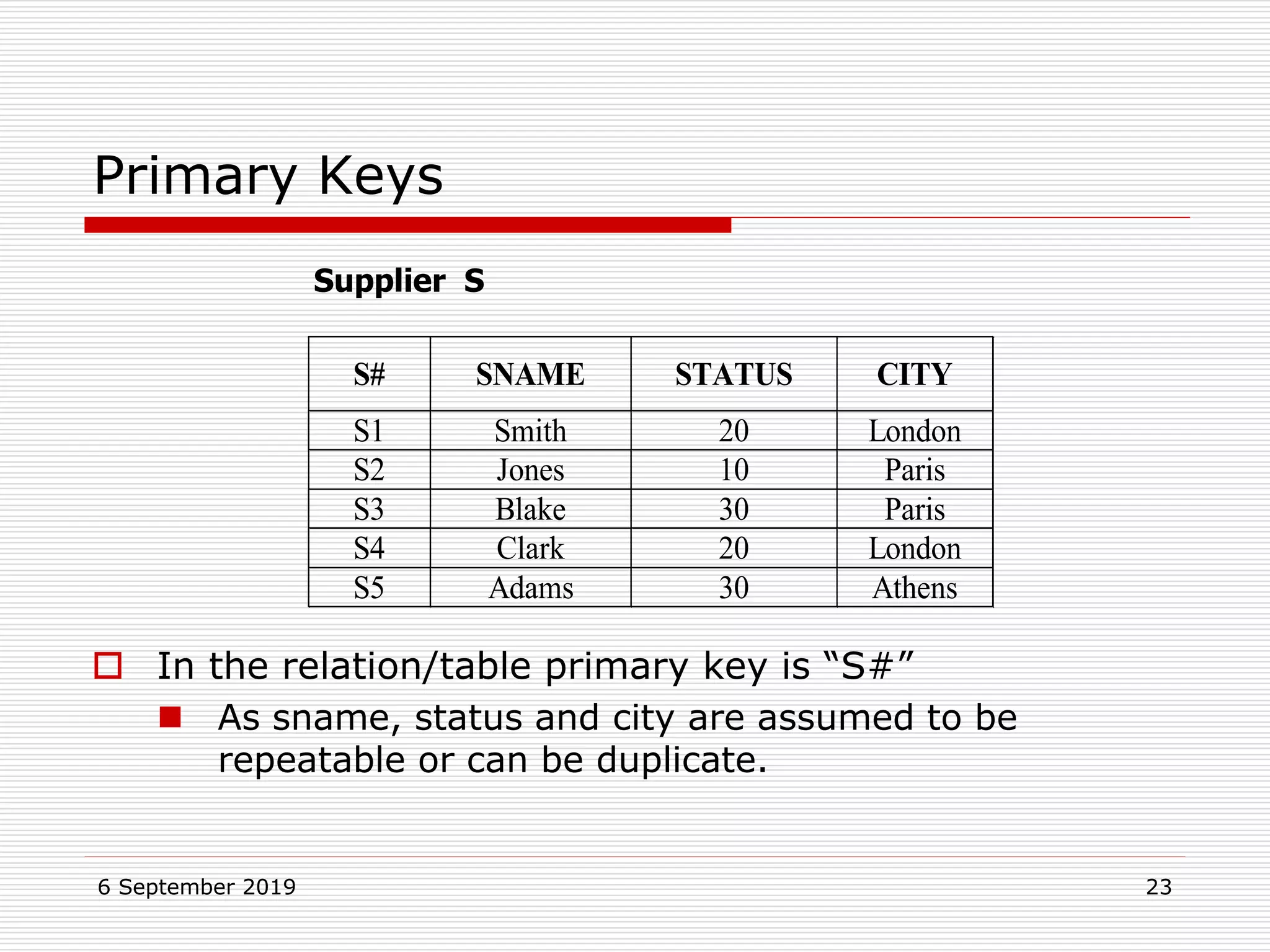
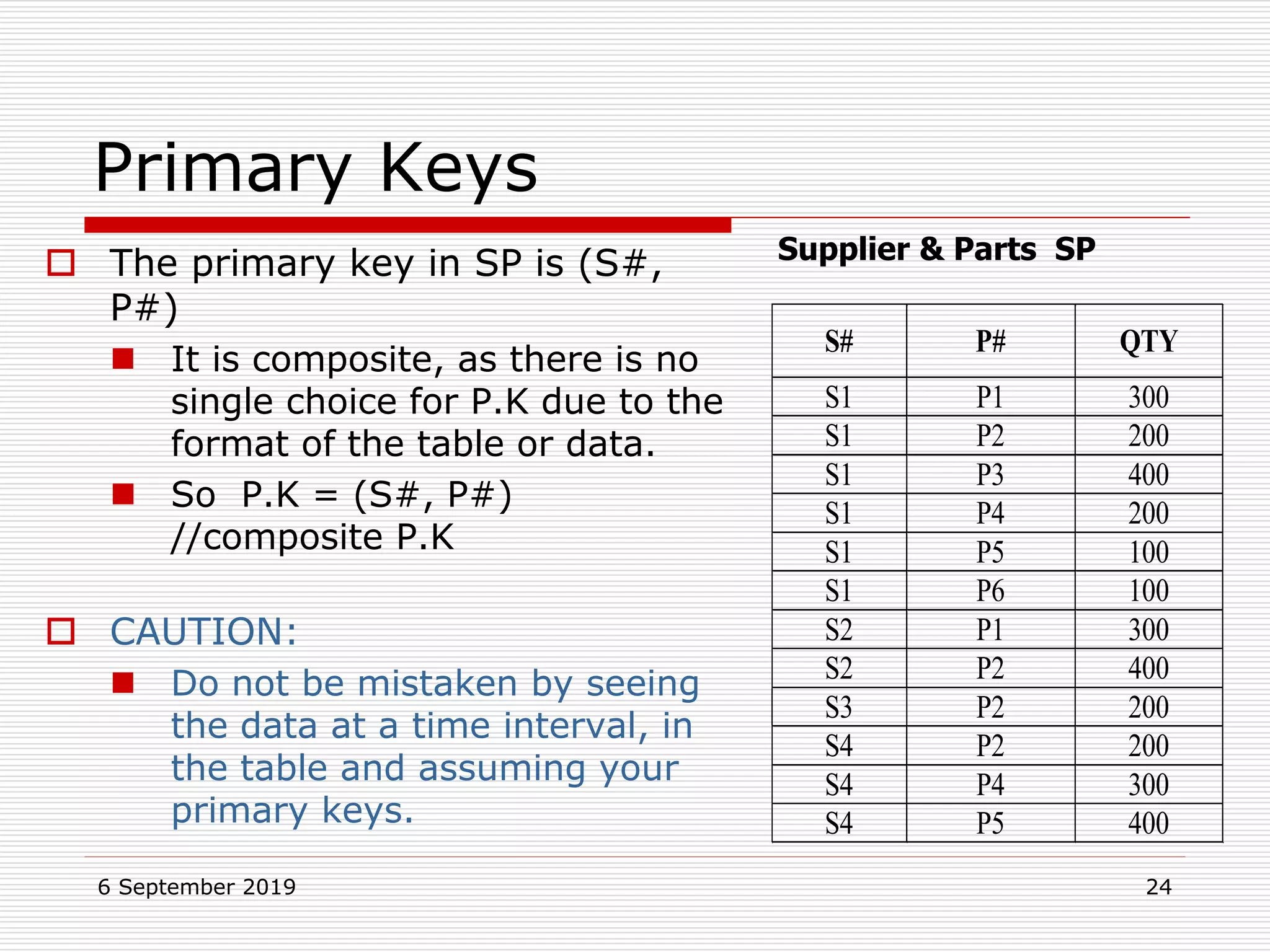
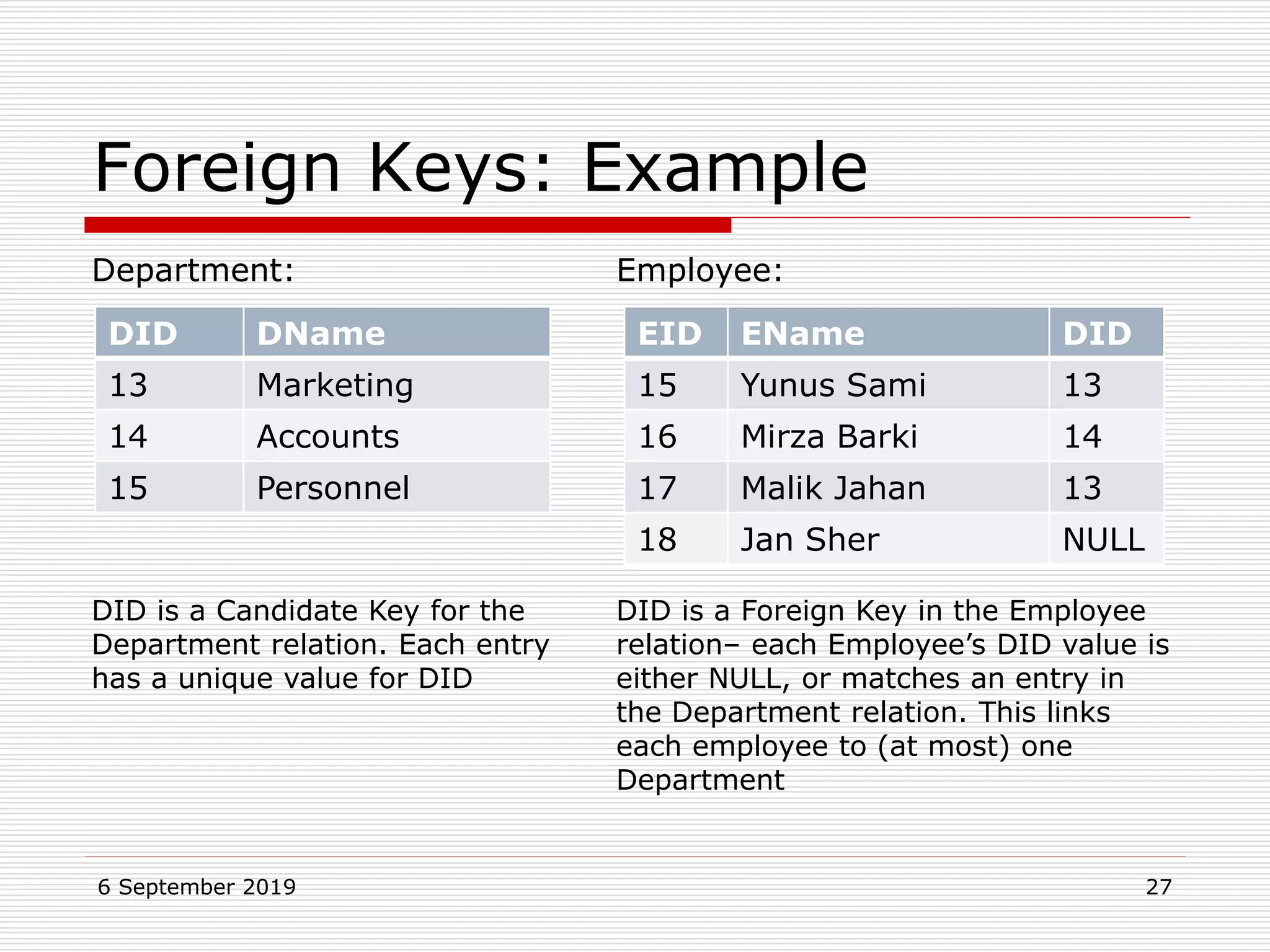
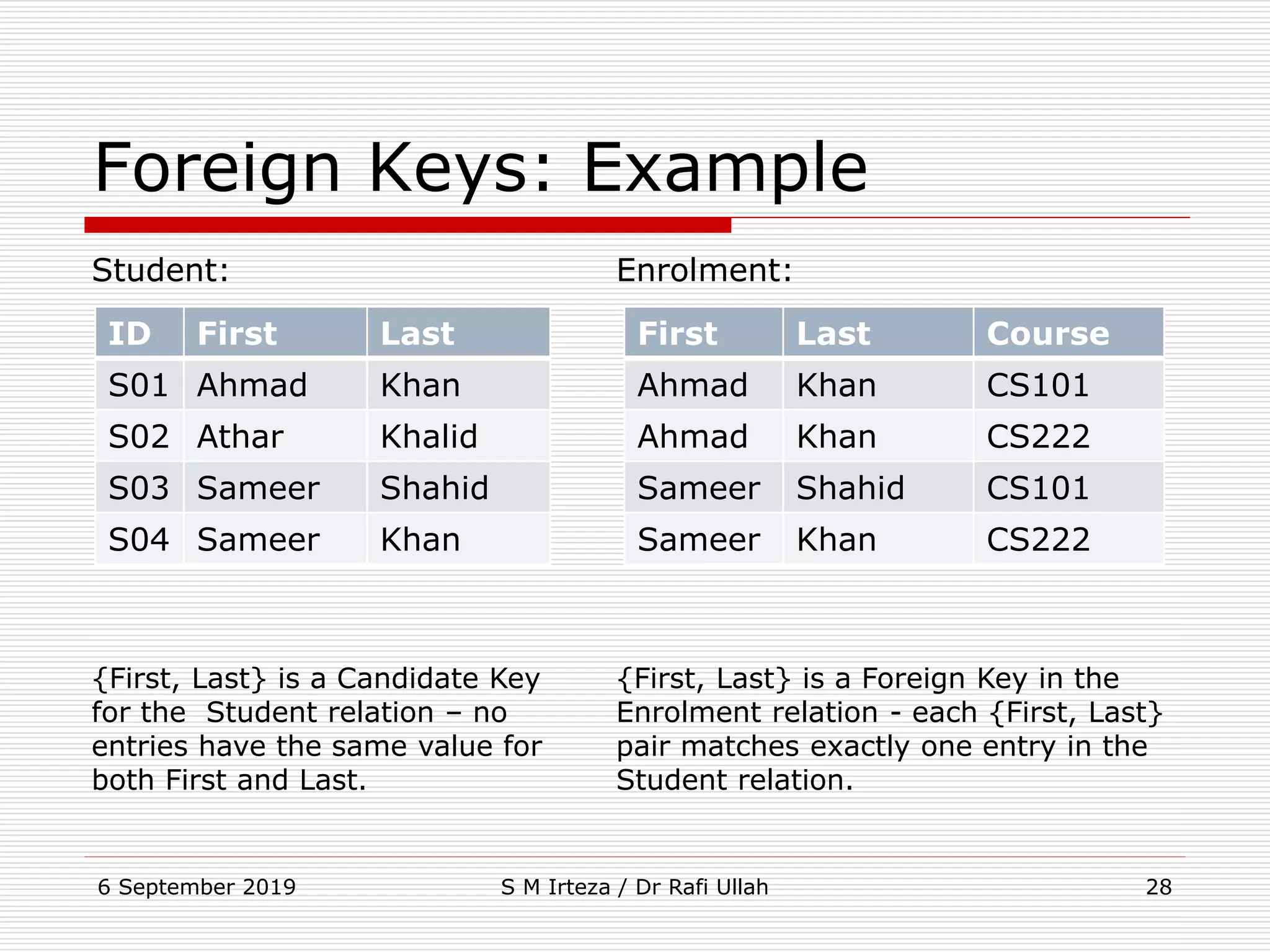
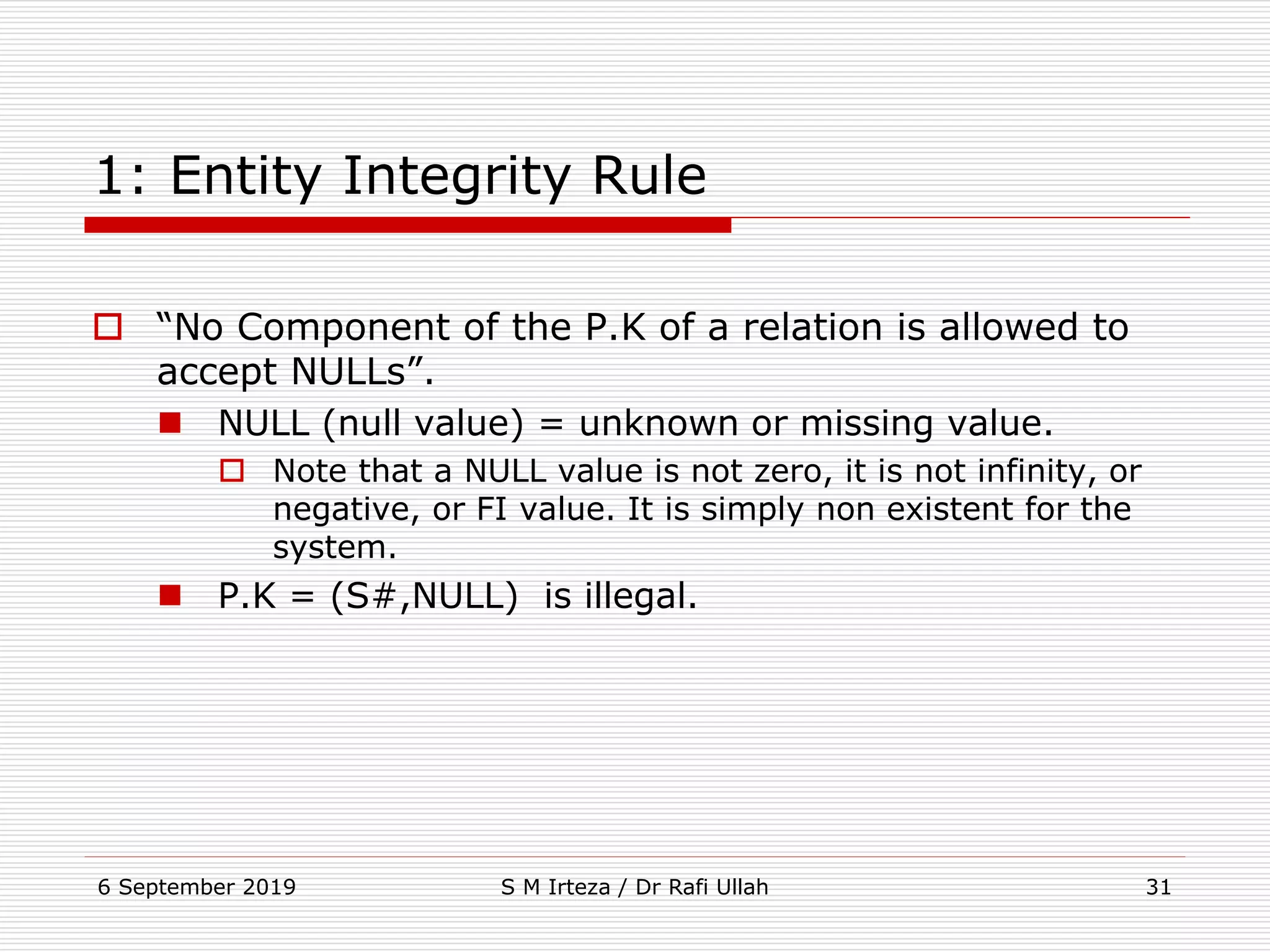
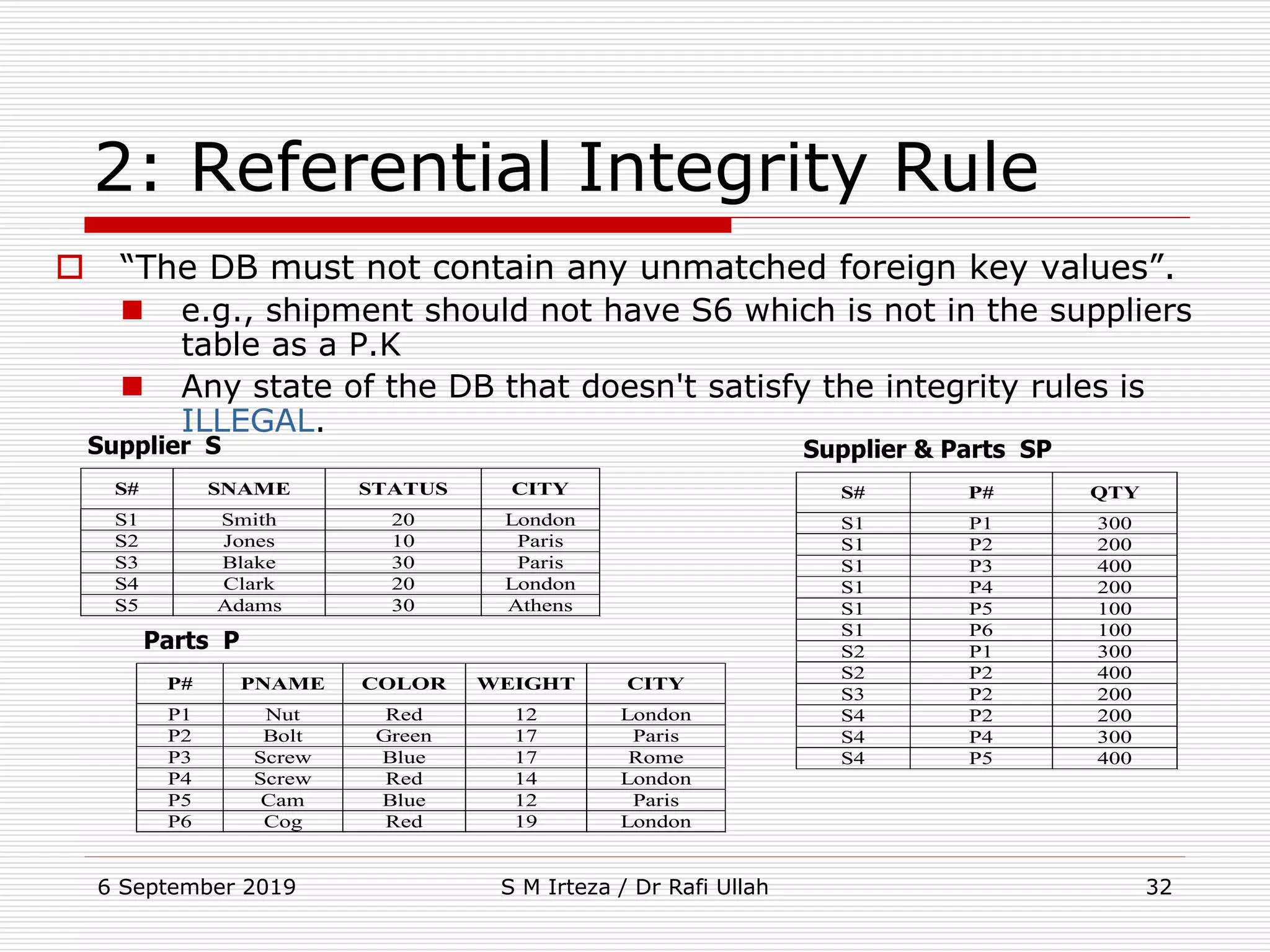
The relational model represents data as a collection of tables, with each row representing related values. A table is similar to a mathematical relation, with attributes corresponding to tuples and rows corresponding to the tuples in the relation. Relations have a heading with attribute names and a body with tuple values. Tuples are unordered and have a single value in each attribute. Relations must satisfy entity integrity, with no null primary key values, and referential integrity, with no unmatched foreign keys. Relations are normalized to eliminate duplication and simplify the structure.