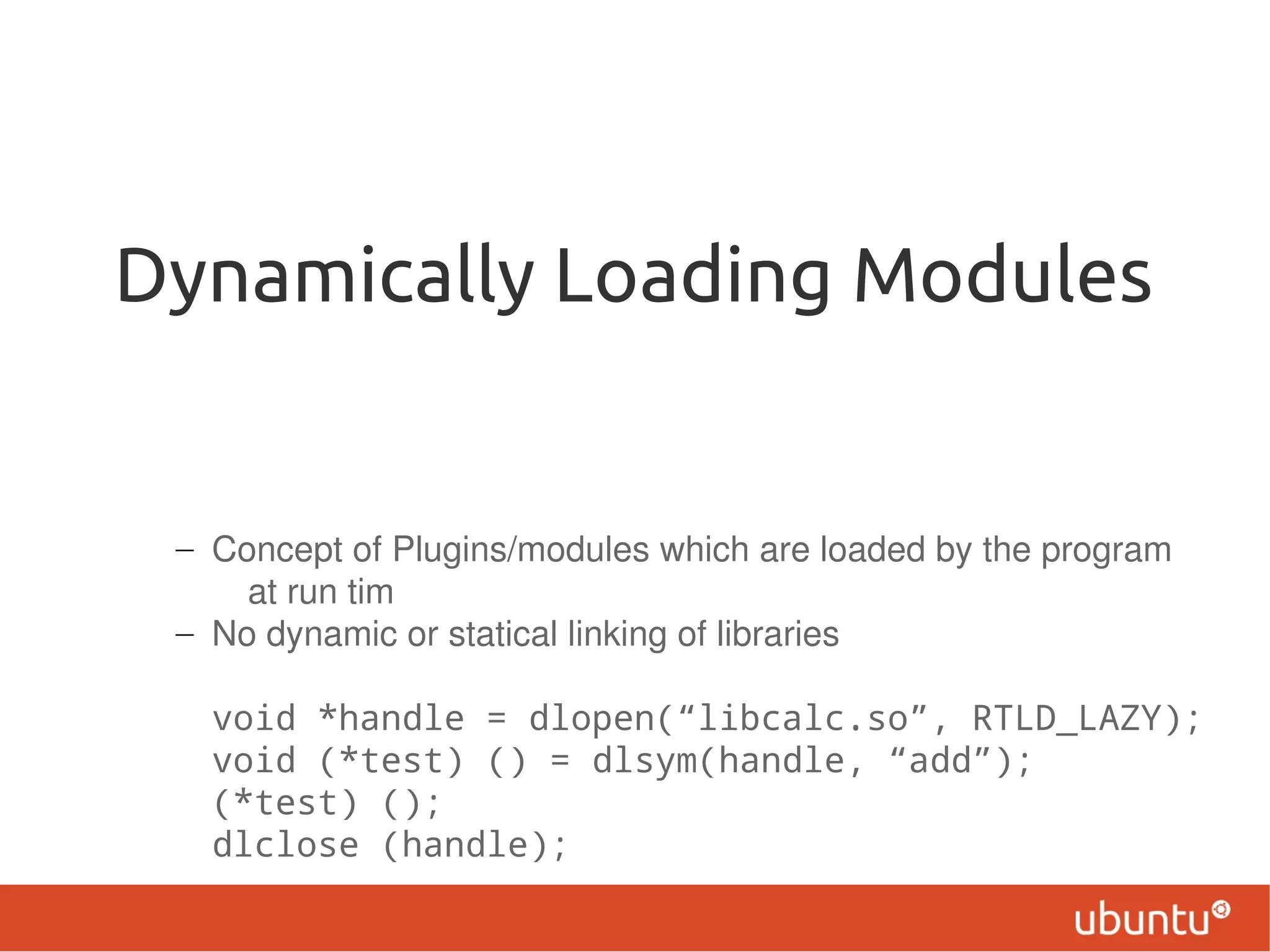
This document provides an overview of programming in the Linux environment. It discusses ISO C and POSIX standards, development tools for Linux like various programming languages, compilers, debuggers, libraries, and dynamic loading of modules. It also covers using GCC for compiling, linking libraries, debugging with GDB, creating and using static and shared libraries, and other productivity tools.