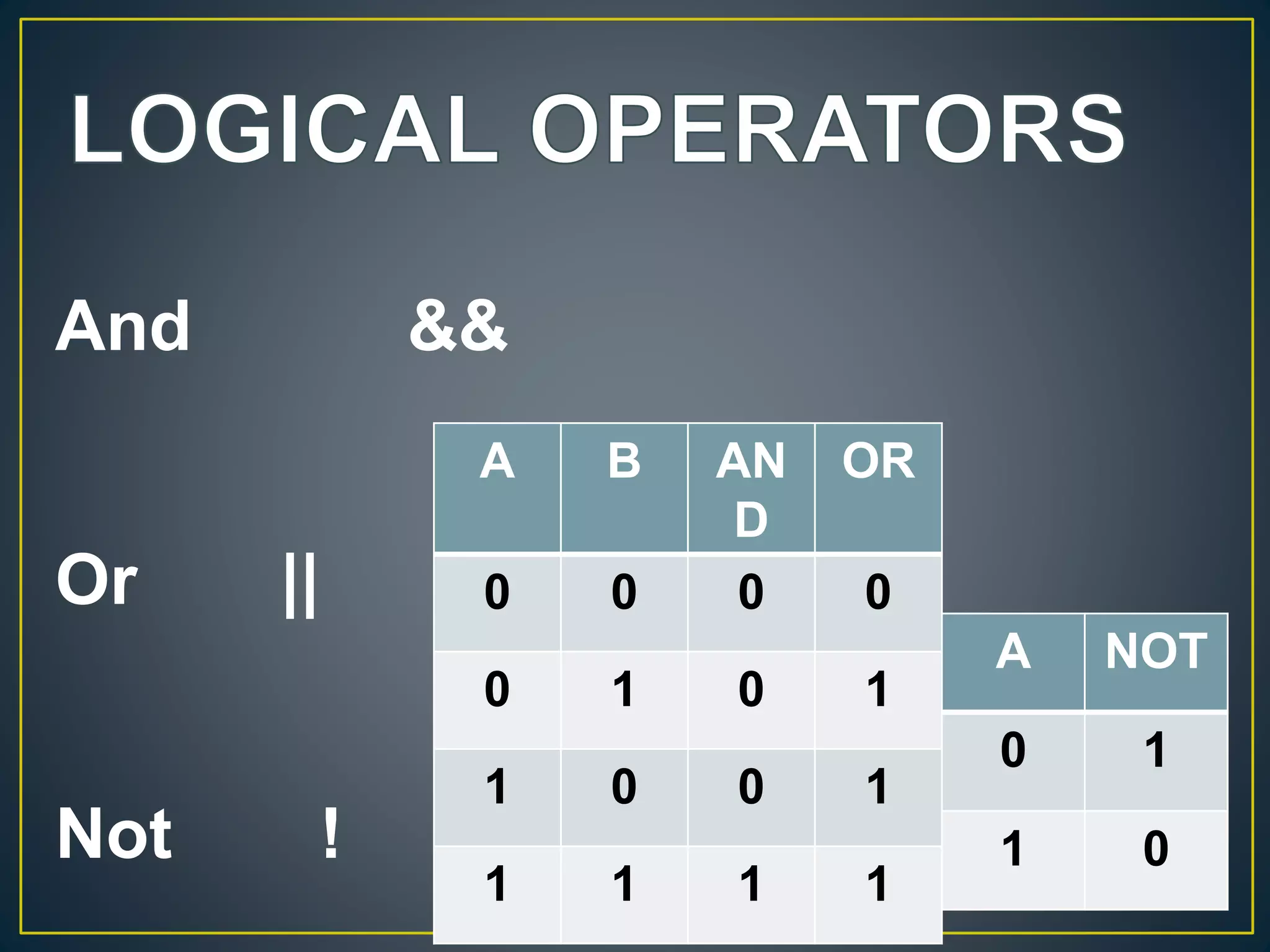
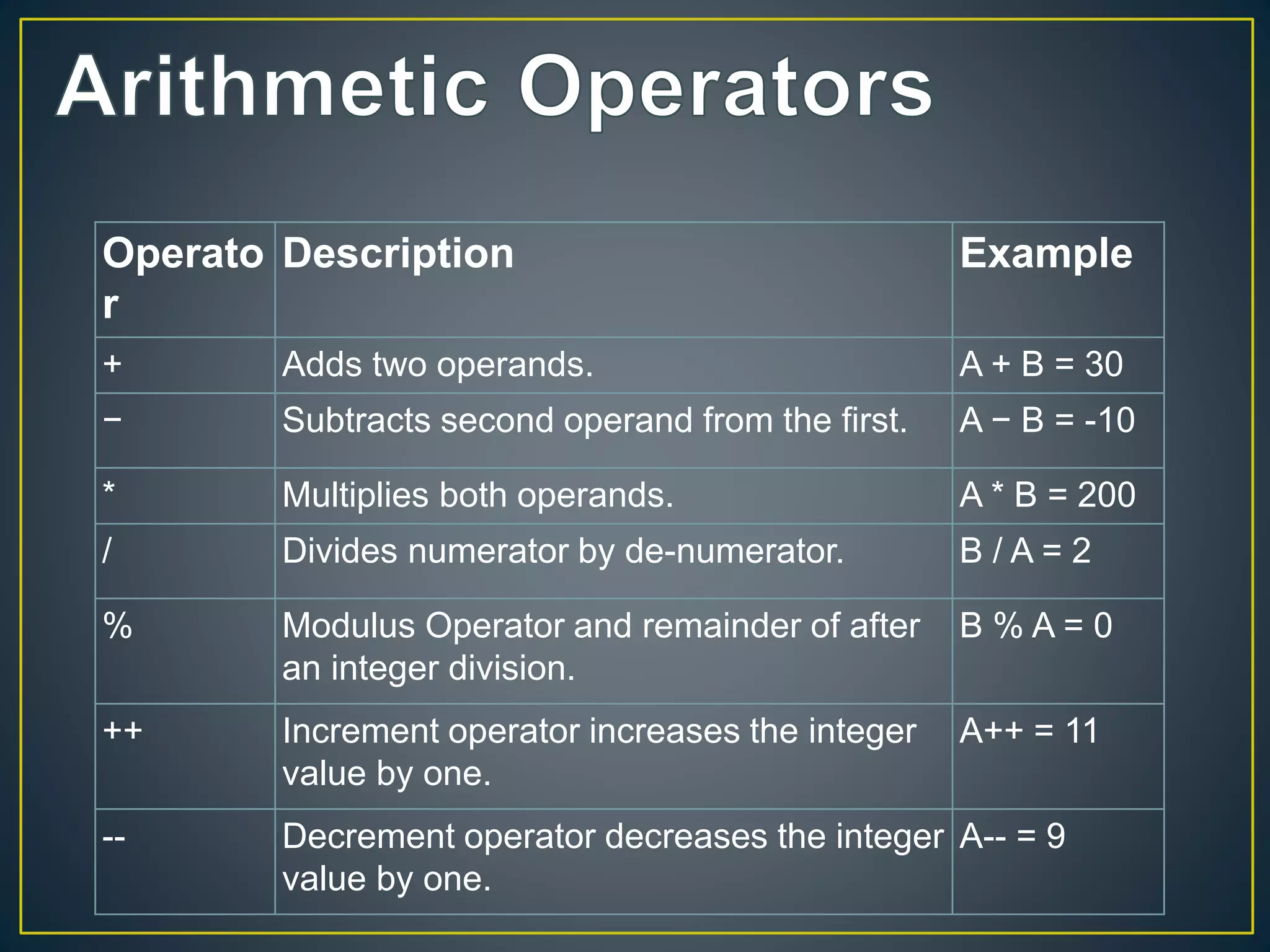
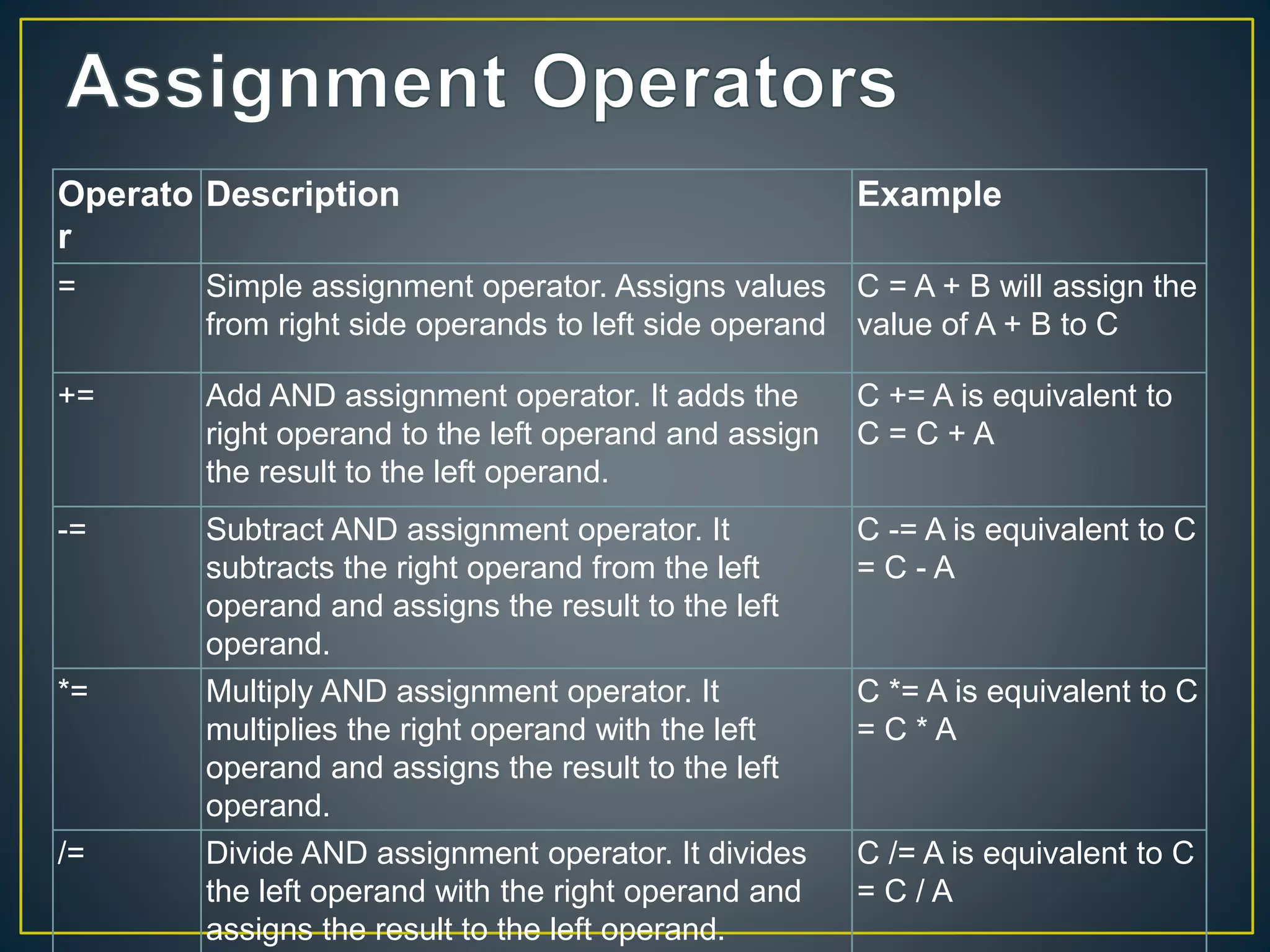
Operators are symbols that tell the compiler to perform mathematical or logical functions. There are different types of operators including arithmetic, relational, logical, assignment, increment/decrement, ternary, and bitwise. Operators have precedence rules where those in parentheses are evaluated first, then multiplication/division, followed by addition/subtraction from left to right. Common operators include arithmetic operators like addition and subtraction, relational operators like equal and not equal, logical operators like AND and OR, and assignment operators like addition assignment and subtraction assignment.