The document provides an overview of various operators in Java, including arithmetic, unary, relational, logical, bitwise, and assignment operators. Each operator type is described with its functionality and includes code examples that illustrate how these operators work in practice. Additionally, it offers short practice questions related to the use of these operators.

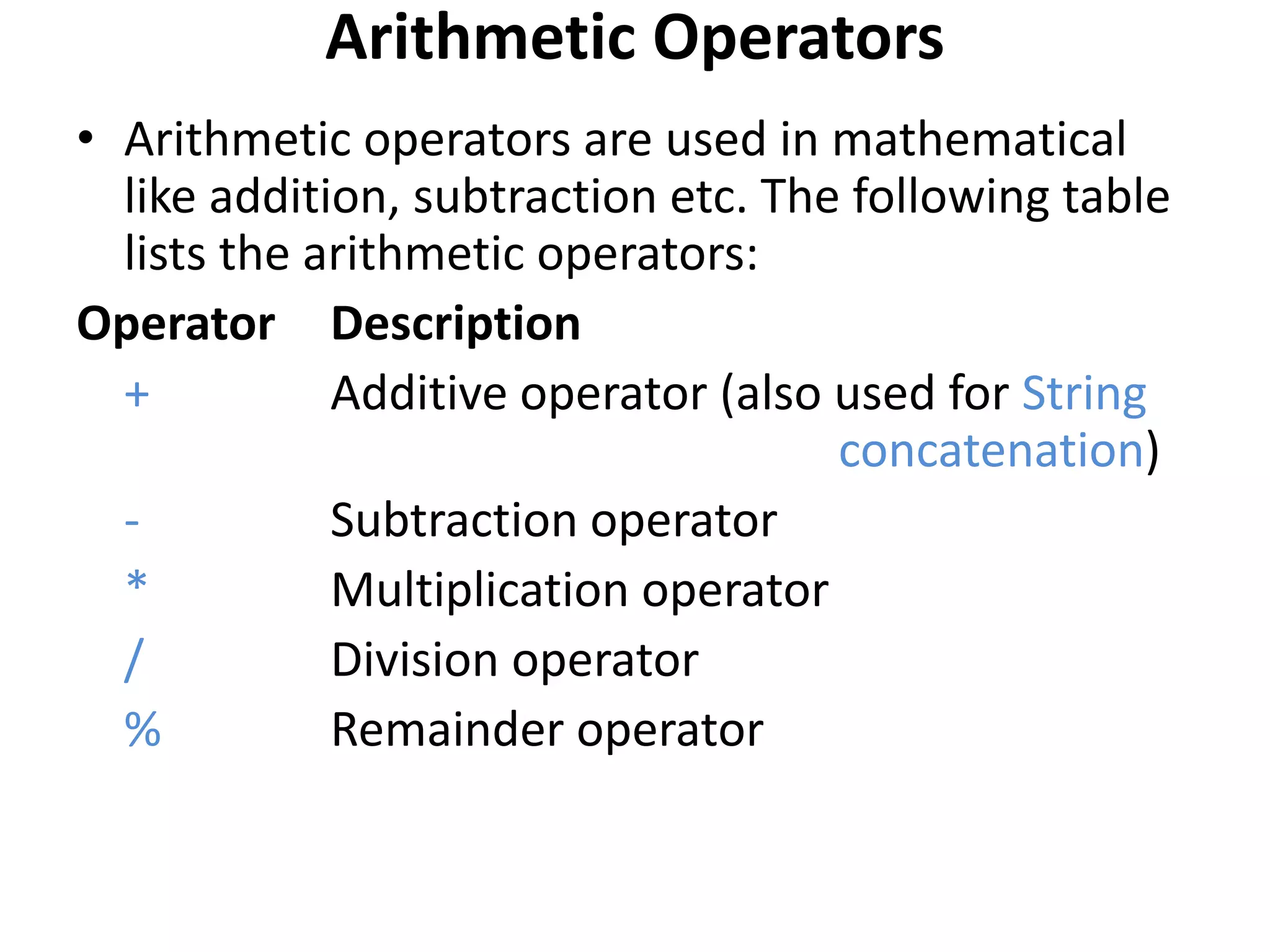
![public static void main(String[] a)
{
System.out.println("Arithmetic operator");
System.out.println("the + operator value for 1 + 3 "+(1+3));
System.out.println("the - operator value for 1 + 3 "+(1-3));
System.out.println("the * operator value for 1 + 3 "+(1*3));
System.out.println("the / operator value for 1 + 3 "+(1/3));
System.out.println("the % operator value for 1 + 3 "+(1%3));
}
Do and See the output
Goto<<slide1>>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operatorsinjava-160526072136/75/Operators-in-java-3-2048.jpg)

![public static void main(String[] a)
{
int post_increment=1;
int post_decrement=2;
int pre_increment=3;
int pre_decrement=4;
post_increment++; post_decrement--; ++pre_increment; --pre_decrement;
boolean boolean_variable=true;
System.out.println("Unary operator");
System.out.println("the + operator value for +1::"+(+1));
System.out.println("the - operator value for -1::"+(-1));
System.out.println("the ++ operator value for 1++::"+
(post_increment));
System.out.println("the -- operator value for 2--::"+
(post_decrement));
System.out.println("the ++ operator value for ++3::"+
(pre_increment));
System.out.println("the -- operator value for --4::"+
(pre_decrement));
System.out.println("the ! operator value for !true::"+(!
boolean_variable));
}
Do and See the output
GoTo<<SLide1>>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operatorsinjava-160526072136/75/Operators-in-java-5-2048.jpg)
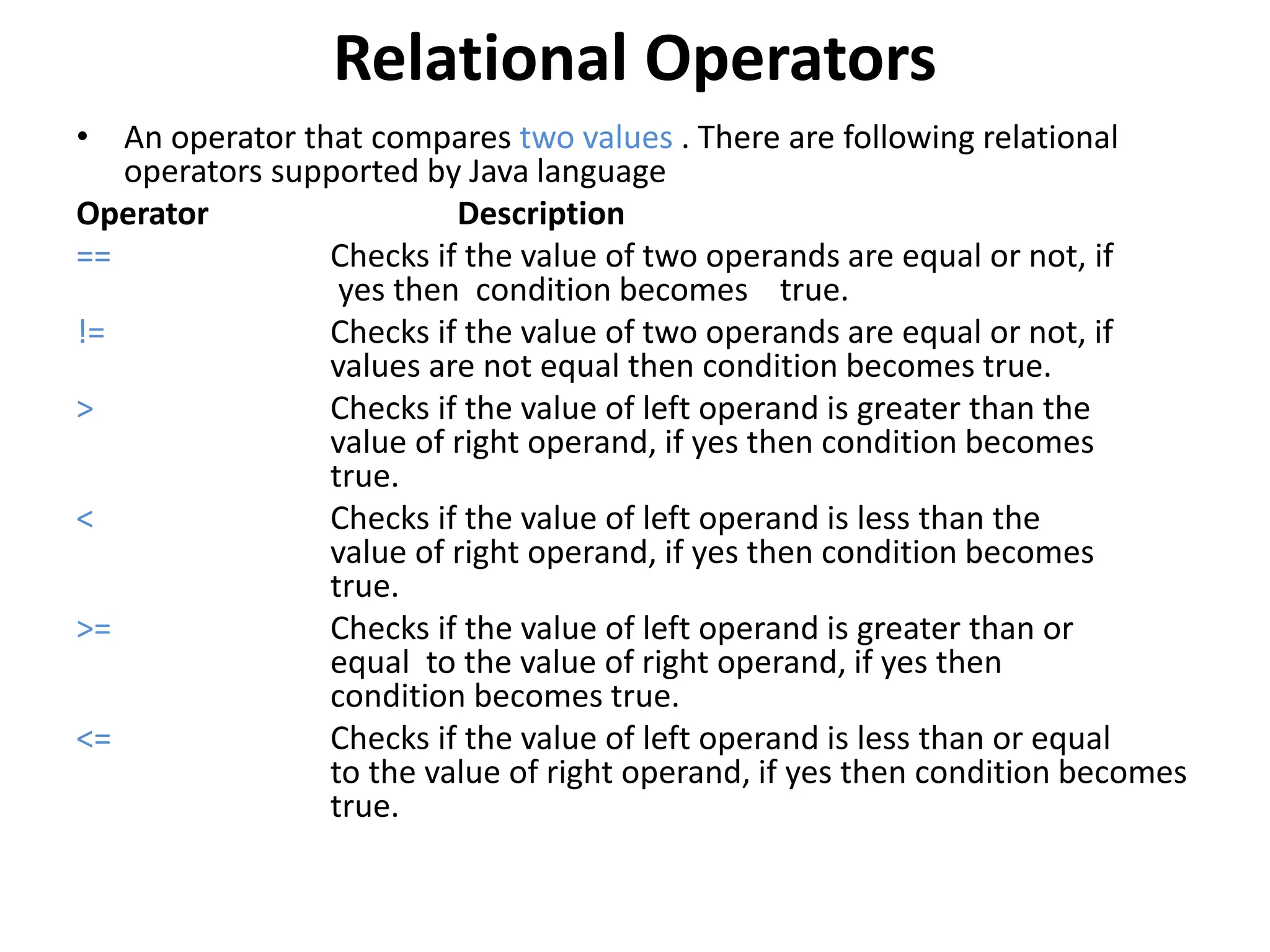
![public static void main(String[] y)
{
System.out.println("Relational operators");
System.out.println("the == operator is 1==1::"+(1==1));
System.out.println("the != operator is 1!=1::"+(1!=1));
System.out.println("the > operator is 1>2::"+(1>2));
System.out.println("the < operator is 1<2::"+(1<2));
System.out.println("the <= operator is 1<=2::"+(1<=2));
System.out.println("the >= operator is 1>=2::"+(1>=2));
}
Do and See the output
GoTo<<Slide1>>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operatorsinjava-160526072136/75/Operators-in-java-7-2048.jpg)

![public static void main(String[] y)
{
int x=10, Y=20;
boolean a=false;
if(x<20&&Y>10)
{
System.out.println(" the && if condition true"); }
else
{ System.out.println(" the && if condition false"); }
if(x<=10||x!=10)
{
System.out.println(" the || if condition true"); }
else
{ System.out.println(" the || if condition false");}
if(!a)
{ System.out.println(" the ! if condition true"); }
else
{ System.out.println(" the !if condition false"); }
}
Do and See the output
GoTo<<Slide1>>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operatorsinjava-160526072136/75/Operators-in-java-9-2048.jpg)

![public static void main(String[] y)
{
int a1=12;
int a2=2;
int a3=0;
int a4=16;
/*8421
* 12=1100
* 1=0001
* & both bits are then it is 1 else it is 0
*/
System.out.println("& operator is "+(a1& a2));
System.out.println("| operator is "+(a1| a2));
System.out.println("~ operator is "+(~a1));
System.out.println("<< operator is "+(a1<<1));
System.out.println(">> operator is "+(a1>>1));
}
• Do and See the output
• GoTo<<Slide1>>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operatorsinjava-160526072136/75/Operators-in-java-11-2048.jpg)

![public static void main(String[] y)
{
System.out.println("assignment operator");
int a5=3;
System.out.println("the value a5 += is"+(a5+=1));
System.out.println("the value a5 -= is"+(a5-=1));
System.out.println("the value a5 -= is"+(a5<<=2));
}
• Do and See the output
• GoTo<<Slide1>>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operatorsinjava-160526072136/75/Operators-in-java-13-2048.jpg)
