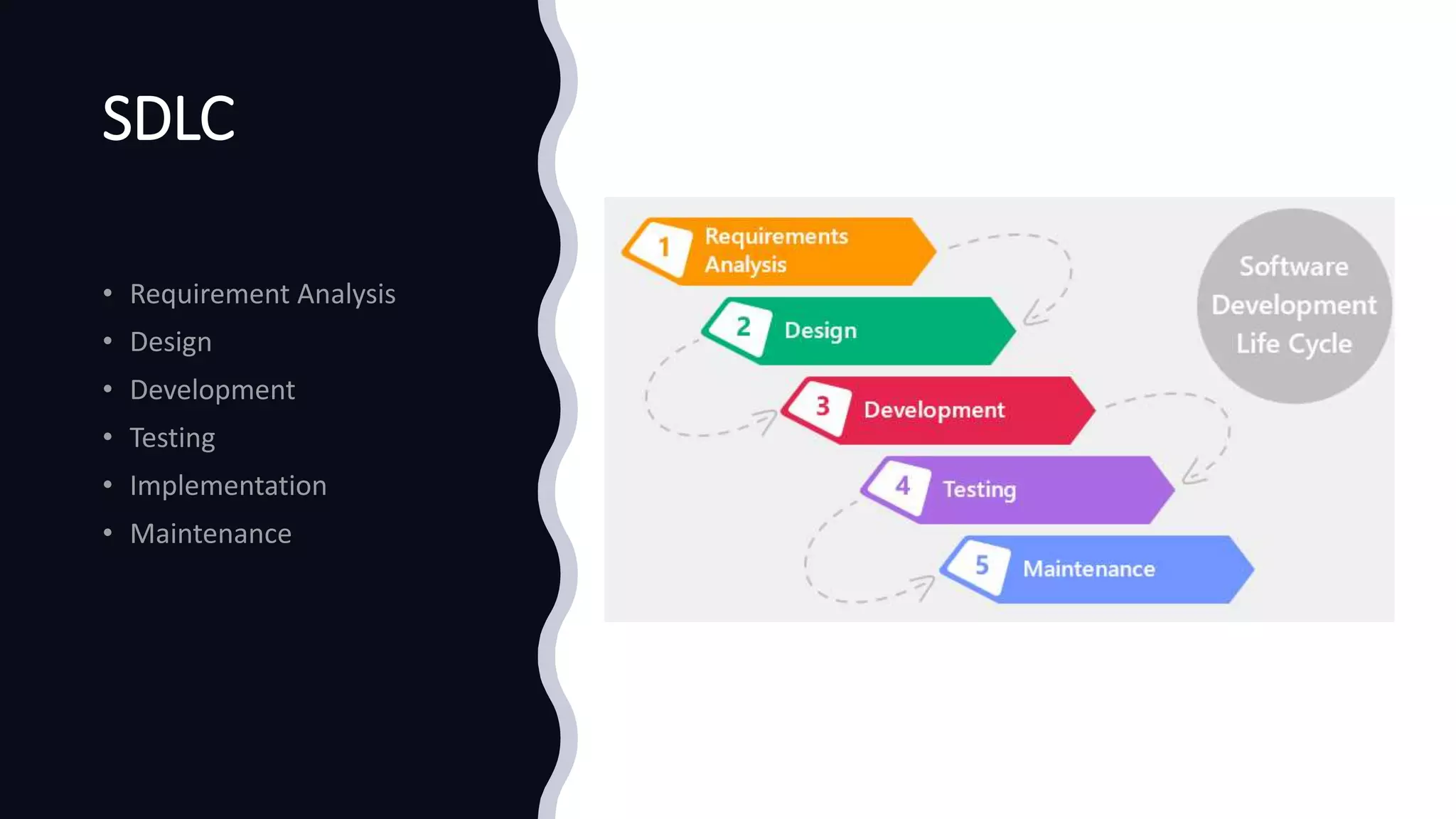
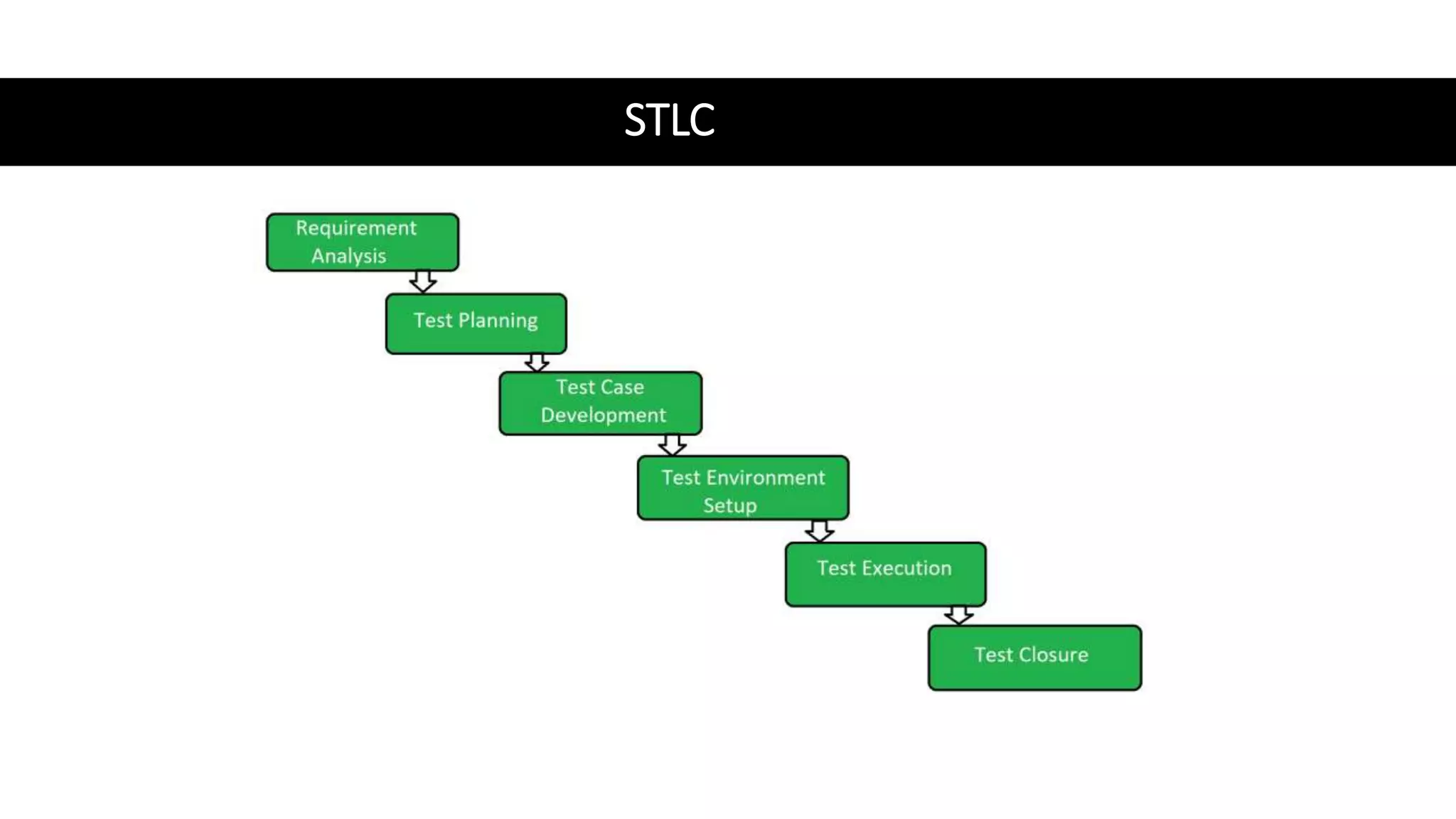
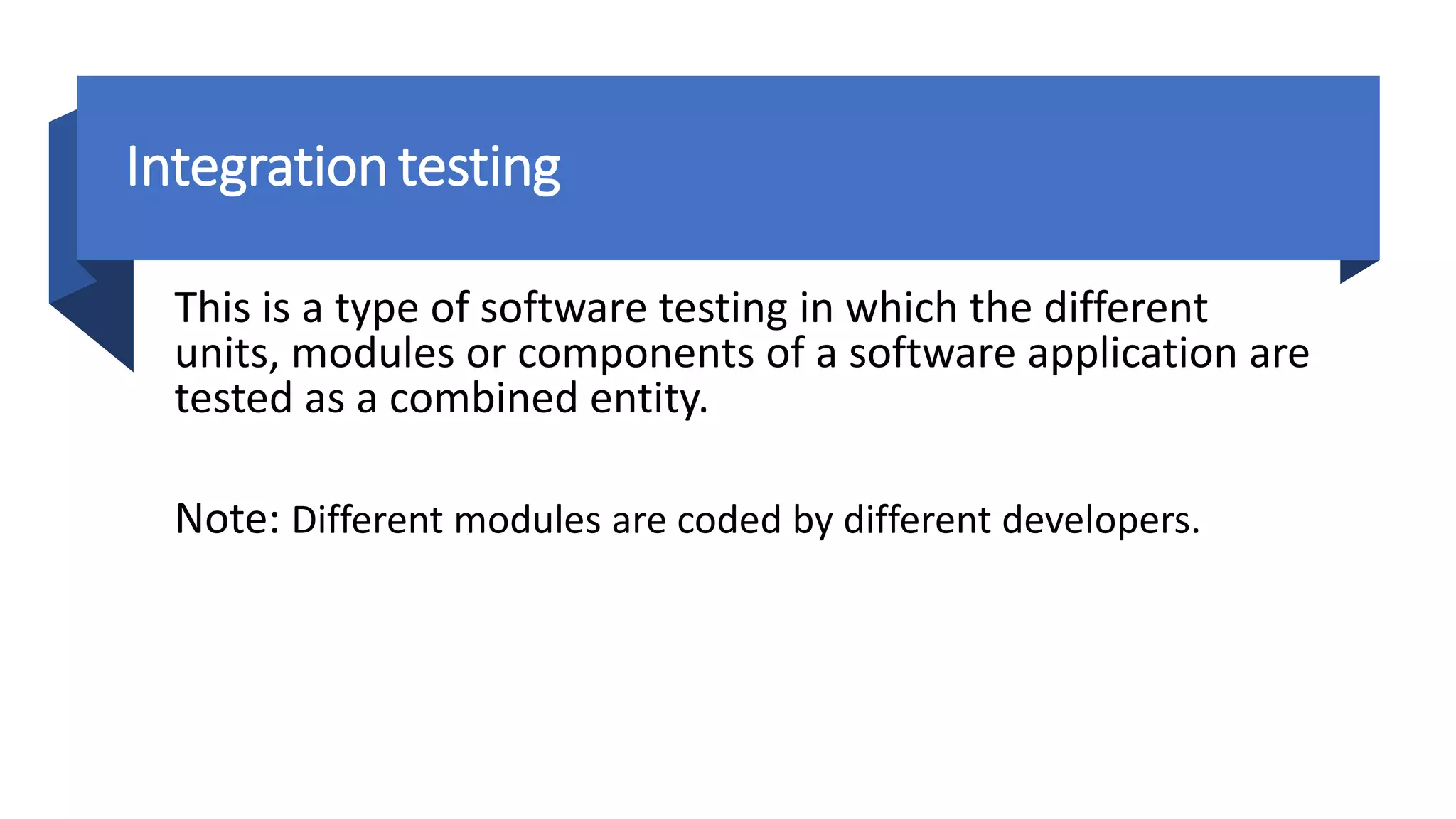
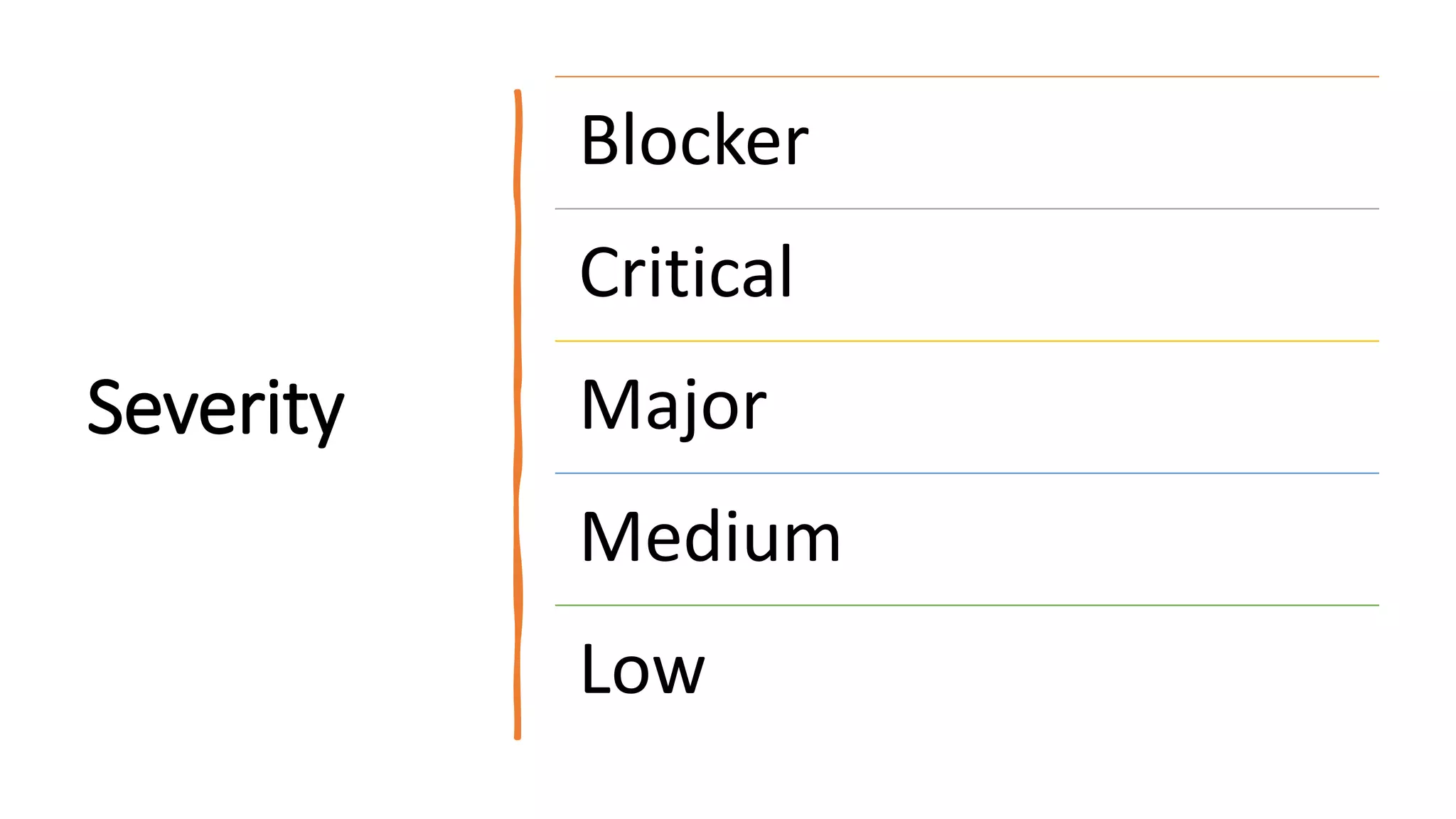
The document outlines various software testing methodologies, including functional and non-functional testing types such as unit, integration, and performance testing. It also discusses agile project management and scrum frameworks, along with specific testing techniques for mobile applications. Additionally, it addresses concepts like the pesticide paradox and root cause analysis, which are essential in understanding software quality assurance.