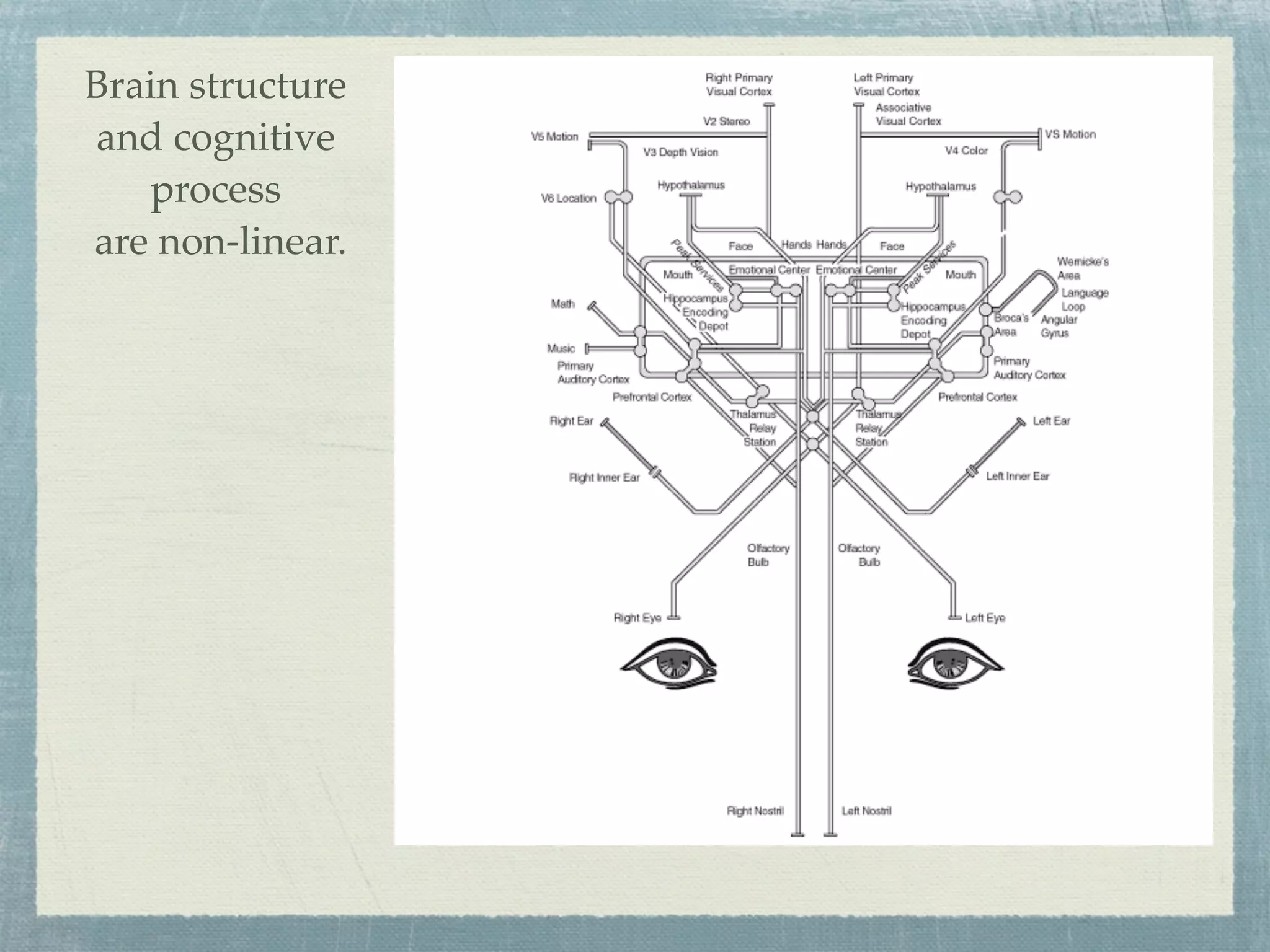
This document provides an overview of mind mapping techniques. It discusses what mind maps are, how they are structured, and how they can be used. Some key points:
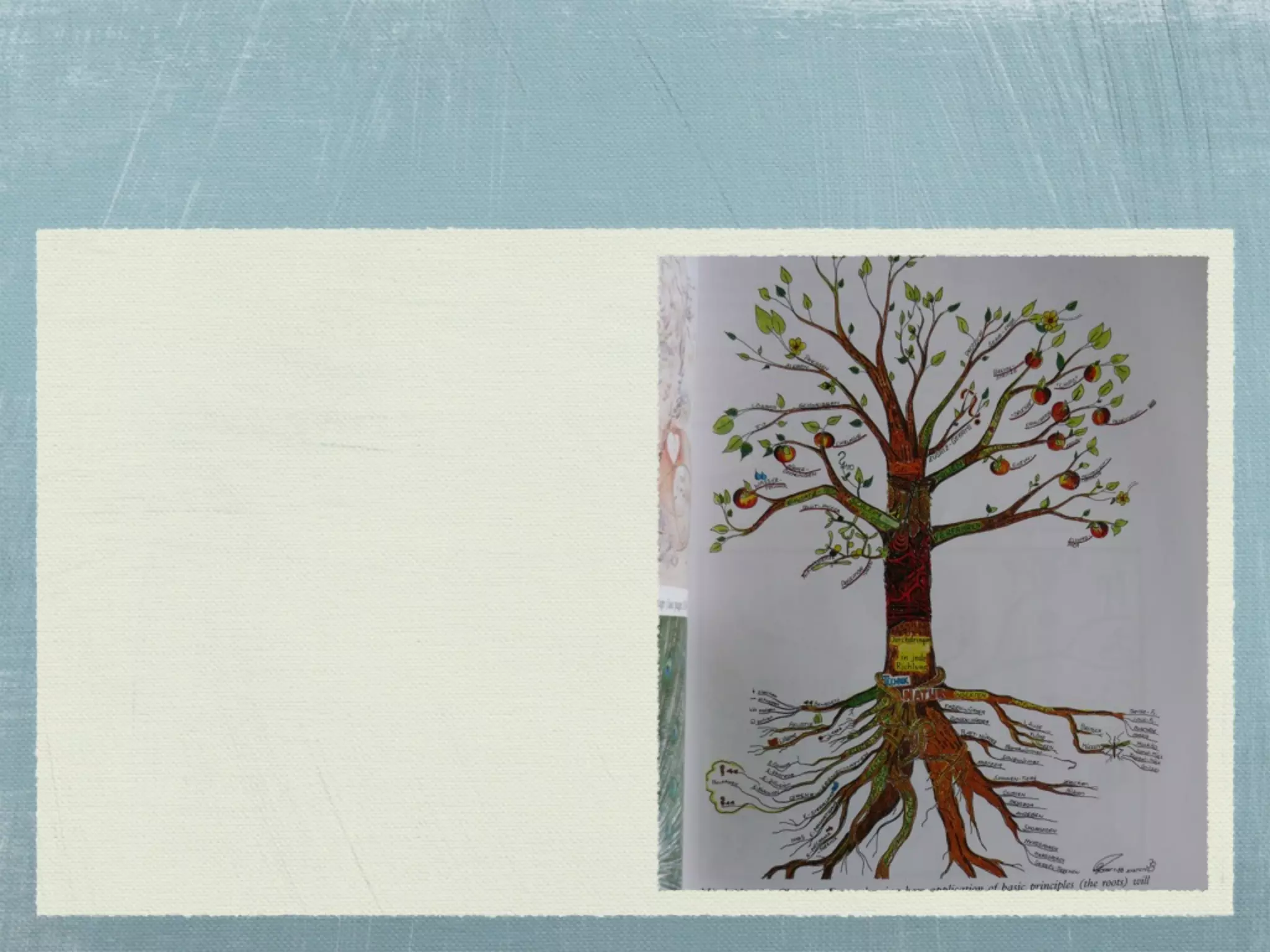
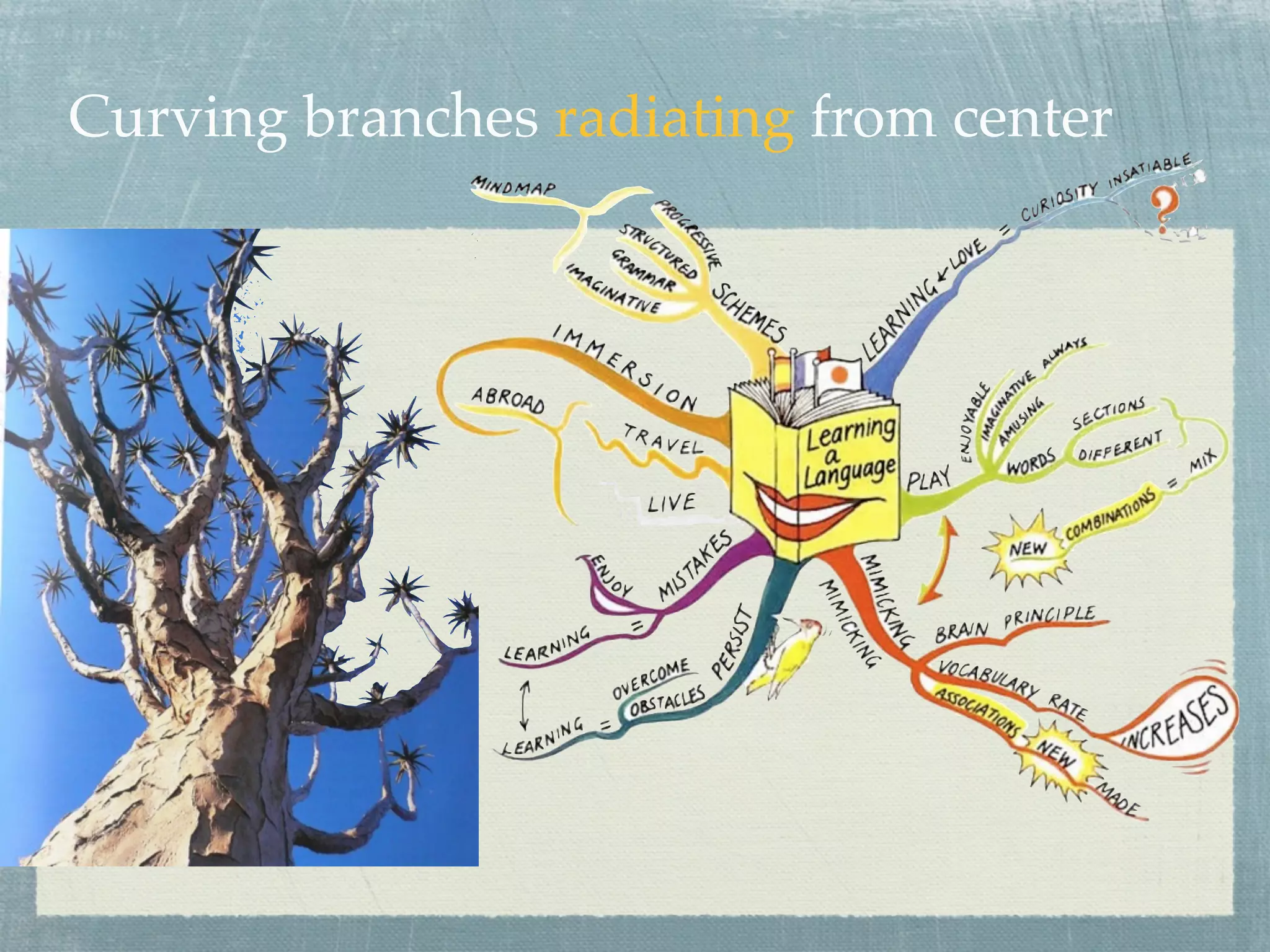
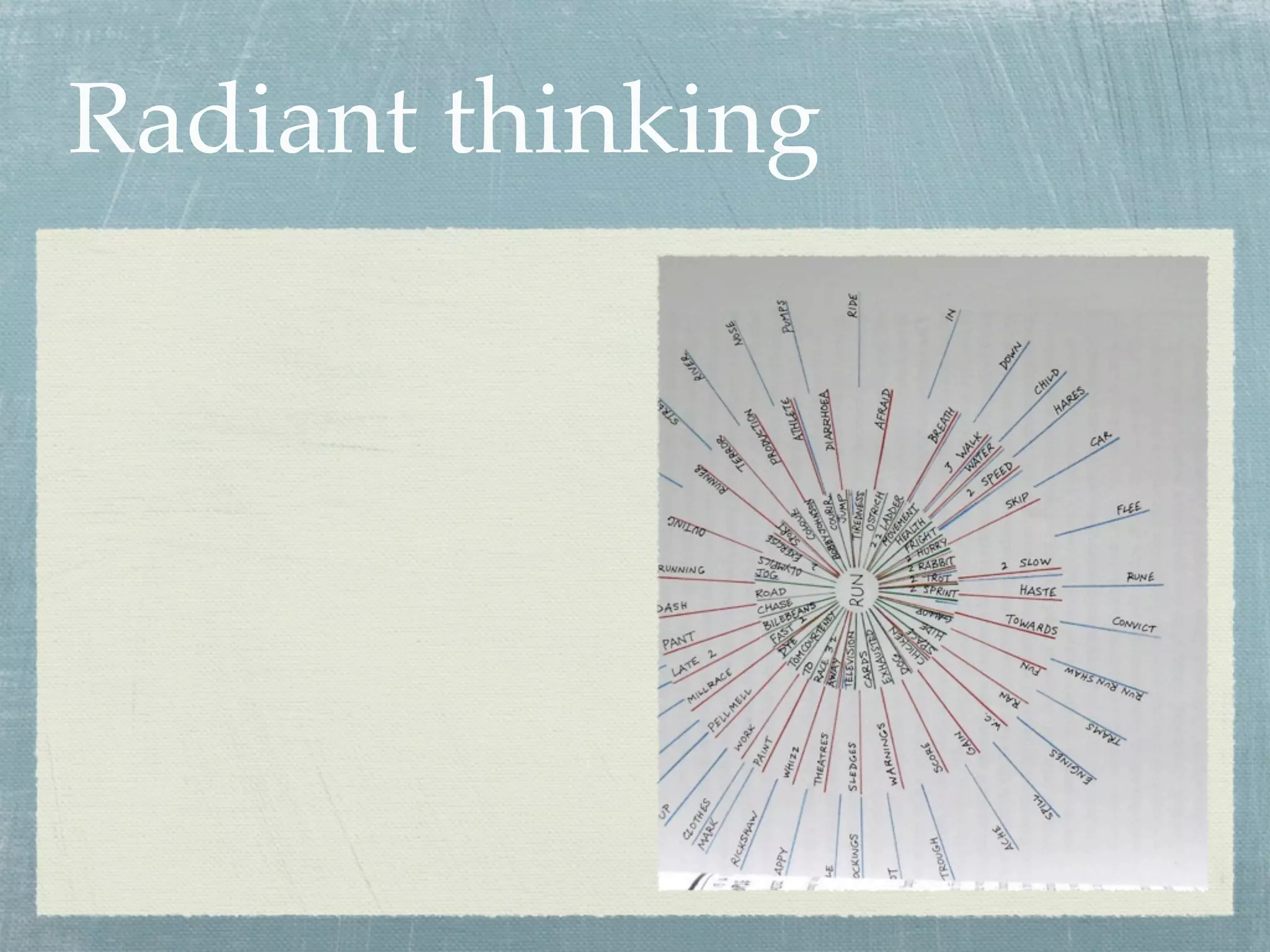
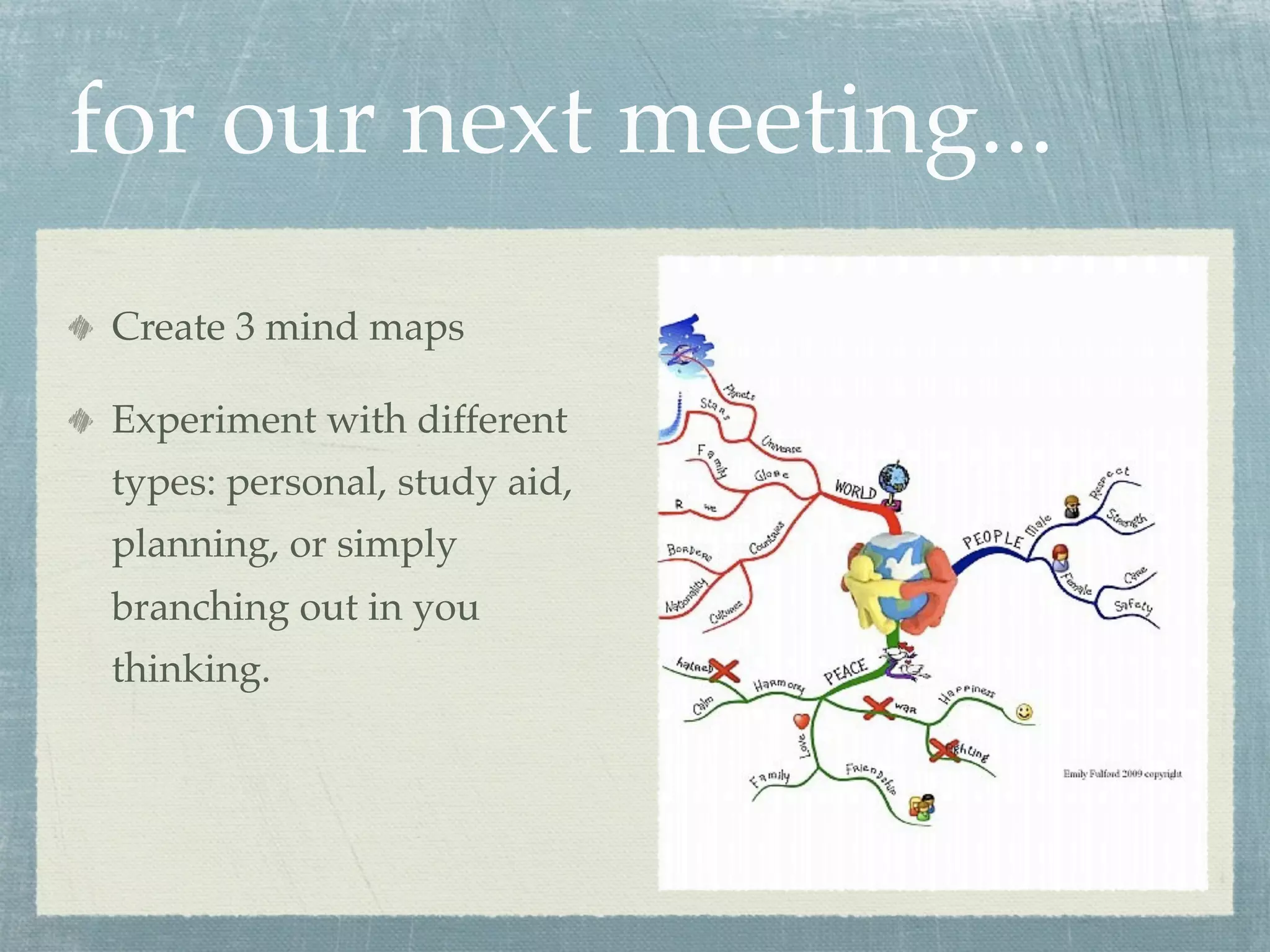
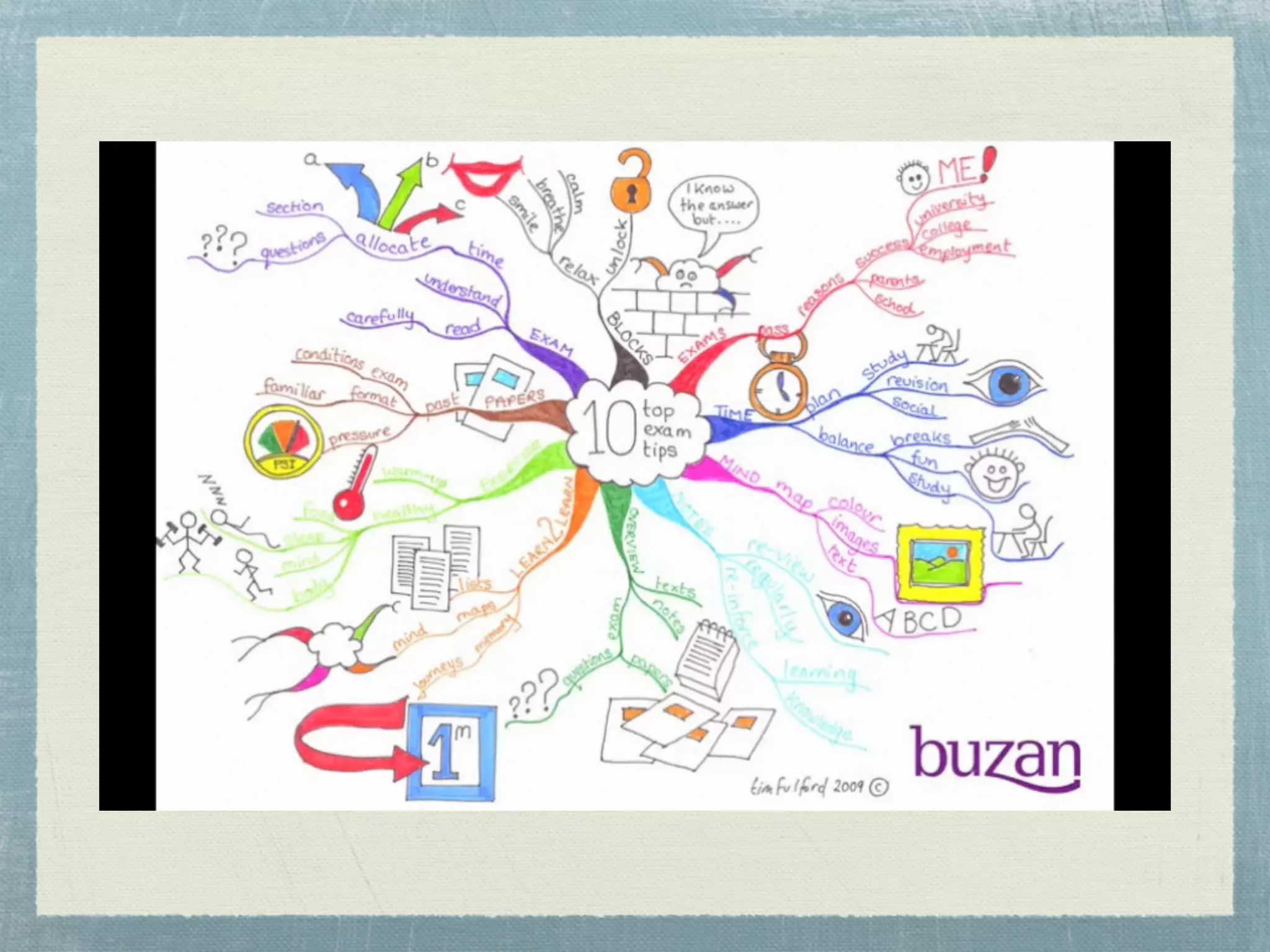
- Mind maps are visual tools that use images, words, and colors to depict relationships between concepts in a nonlinear, tree-like structure radiating from a central concept.
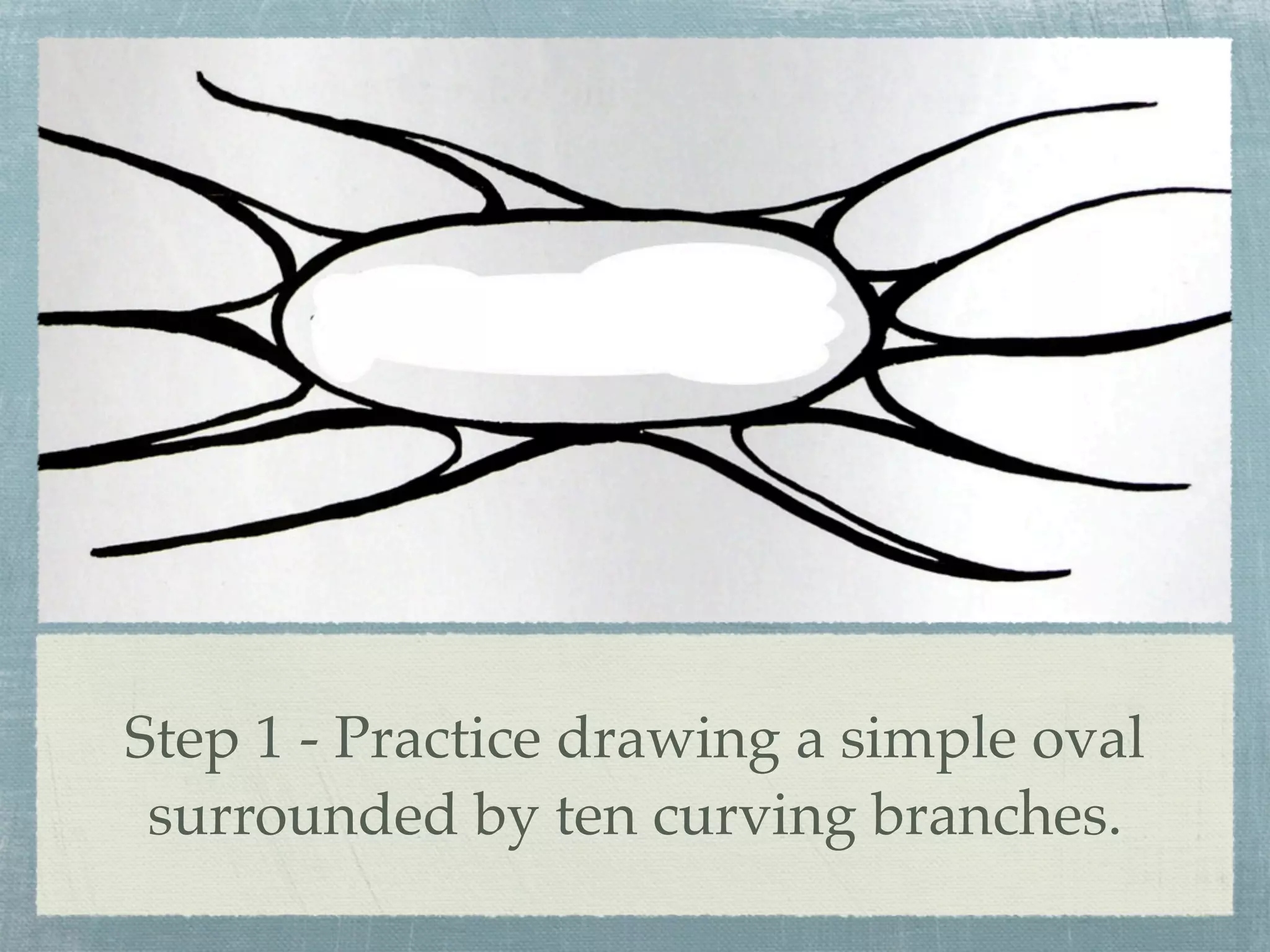
- Effective mind maps follow basic rules - using plain paper in landscape orientation, placing a central image, and adding keywords along curved branches.
- Mind maps can be used for brainstorming, note-taking, decision-making, planning, and more. They allow for richer associations between concepts compared to linear lists.
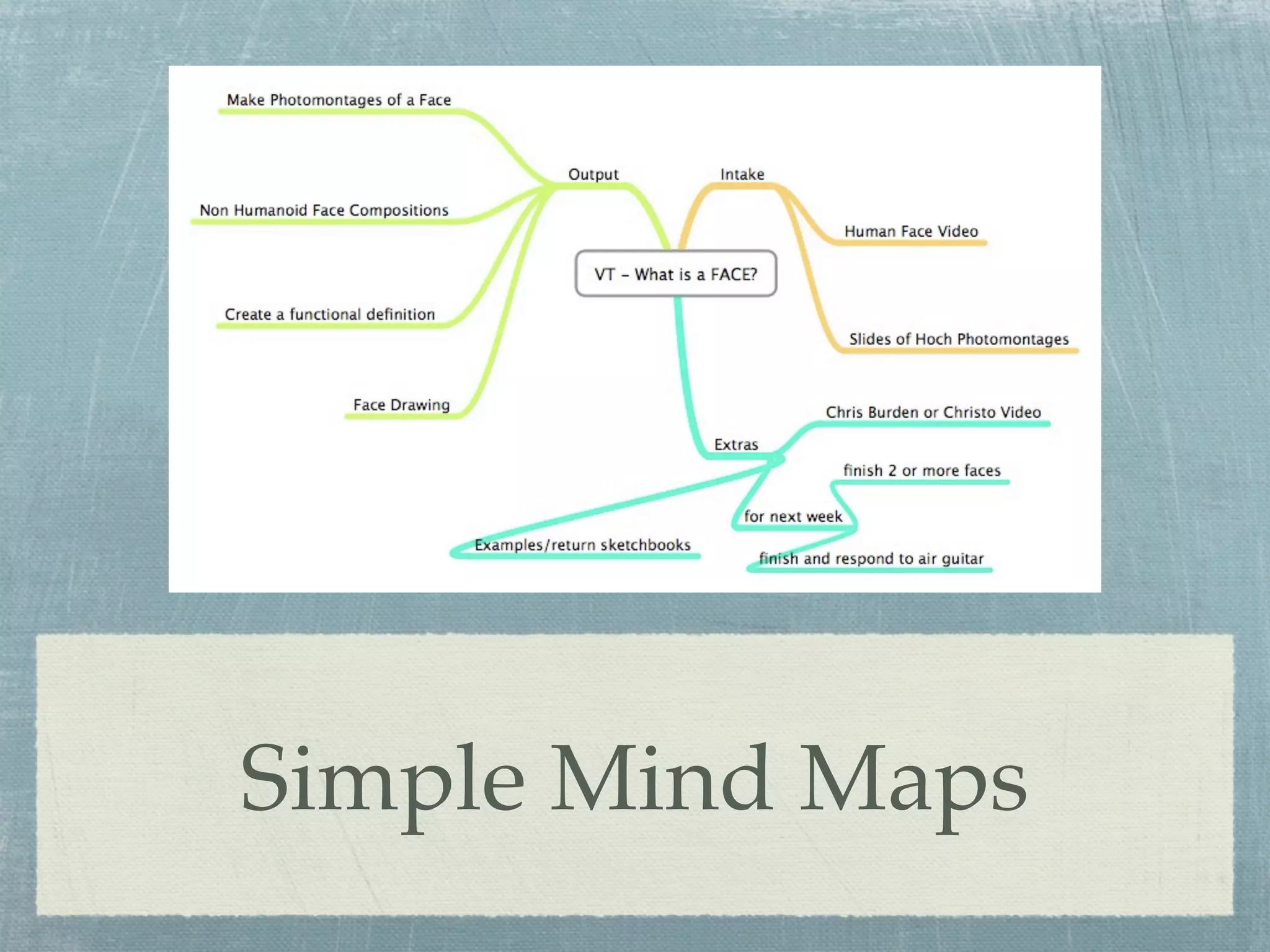
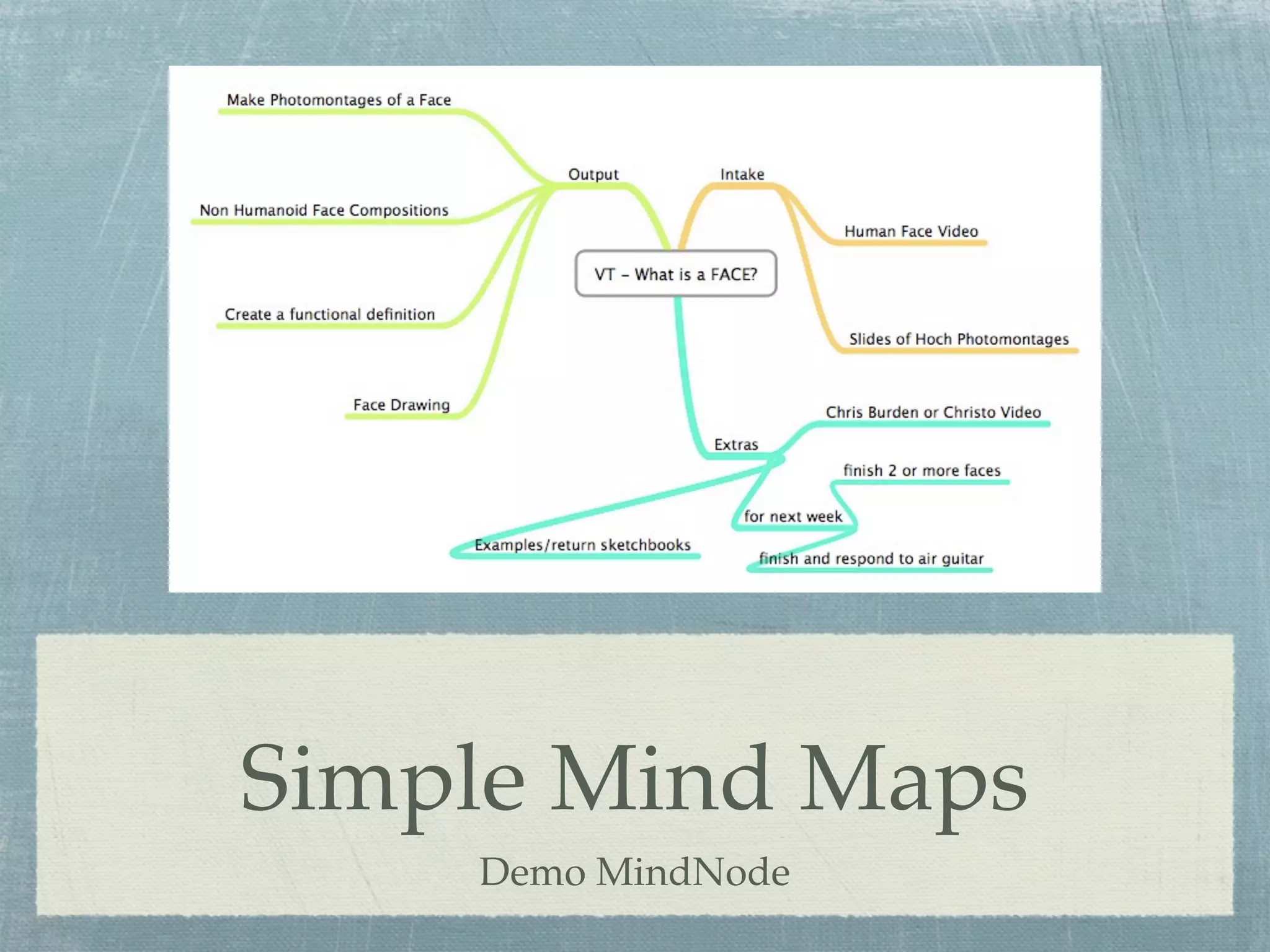
- Examples are provided of simple mind maps