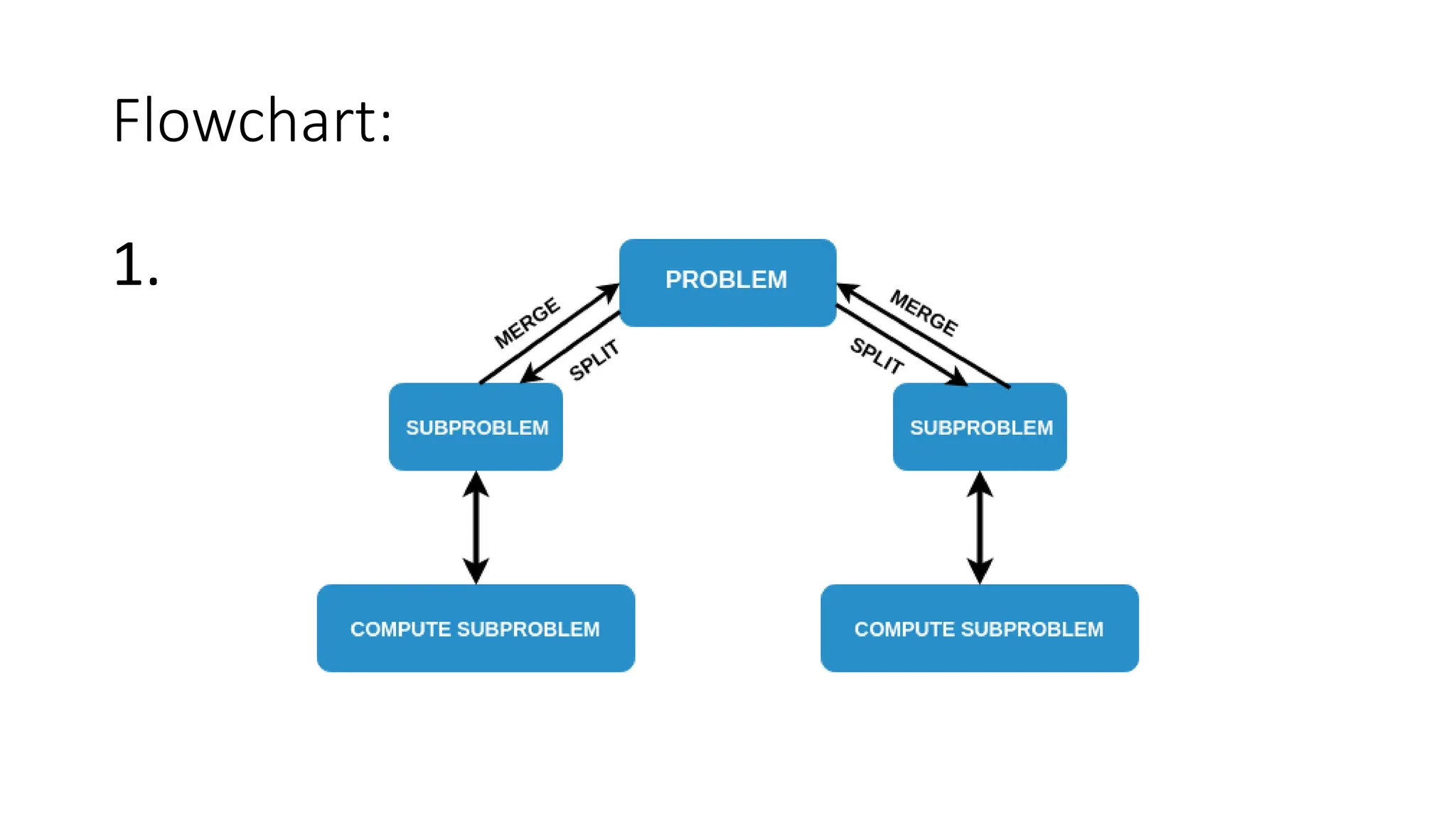
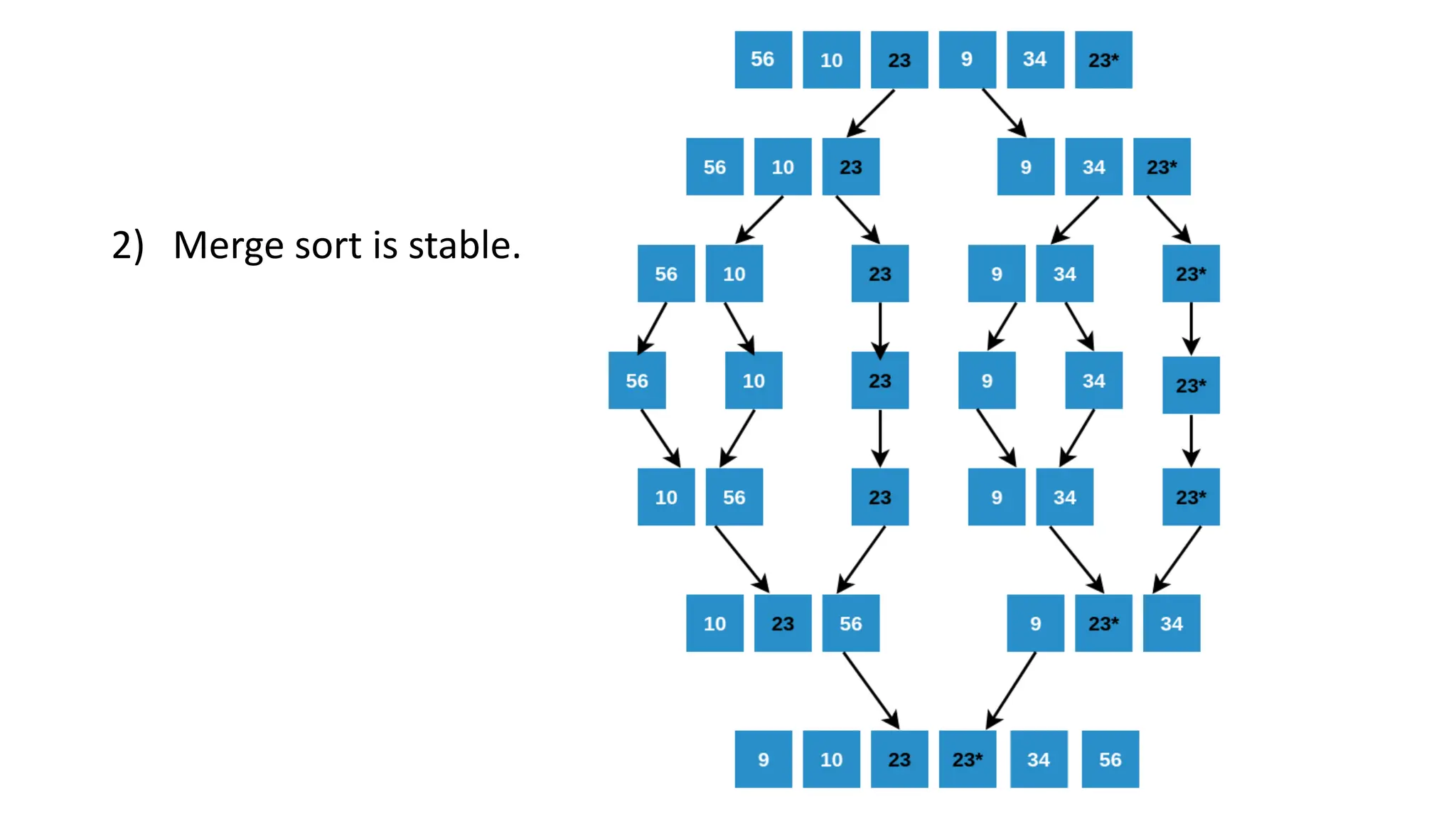
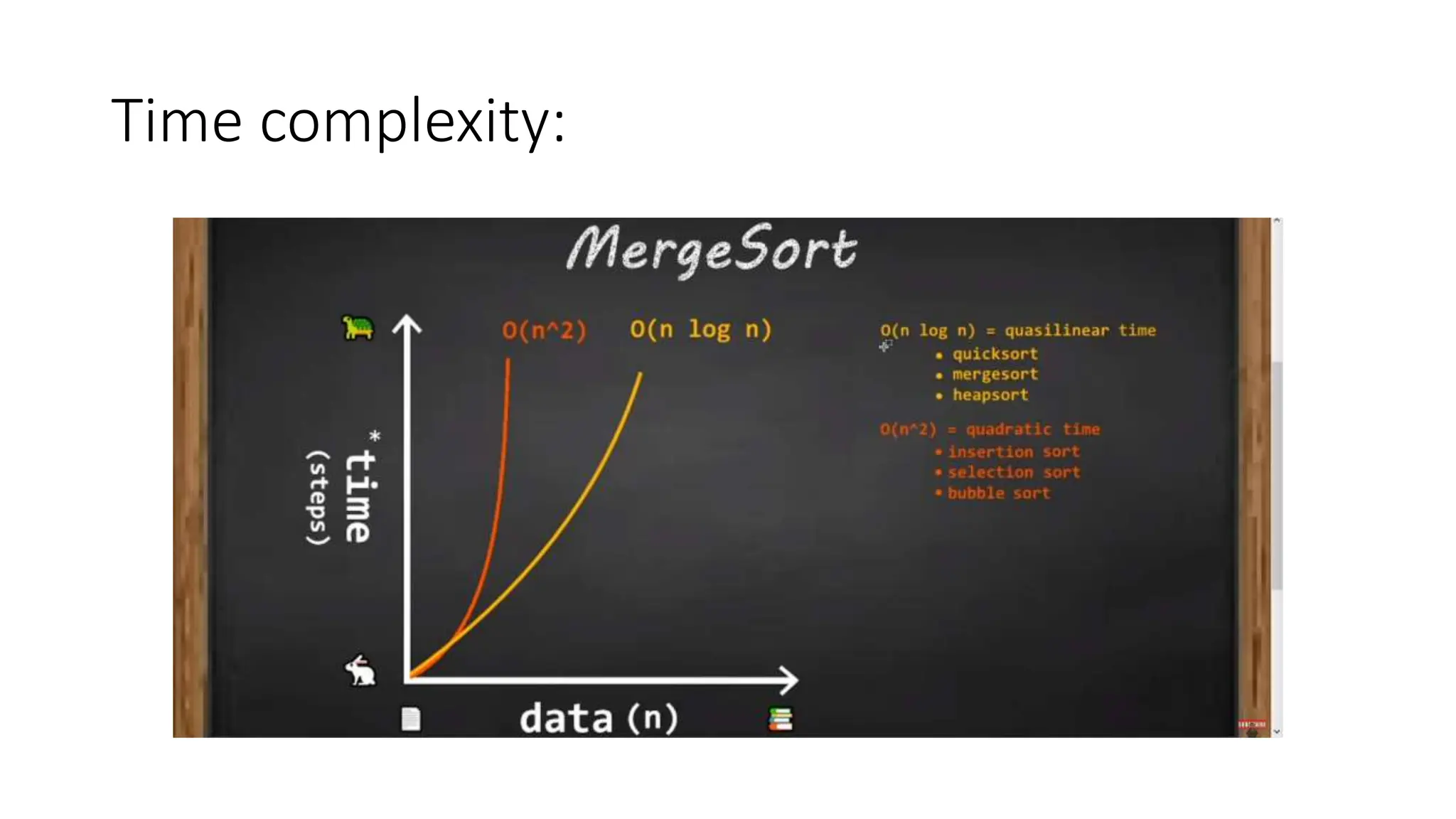
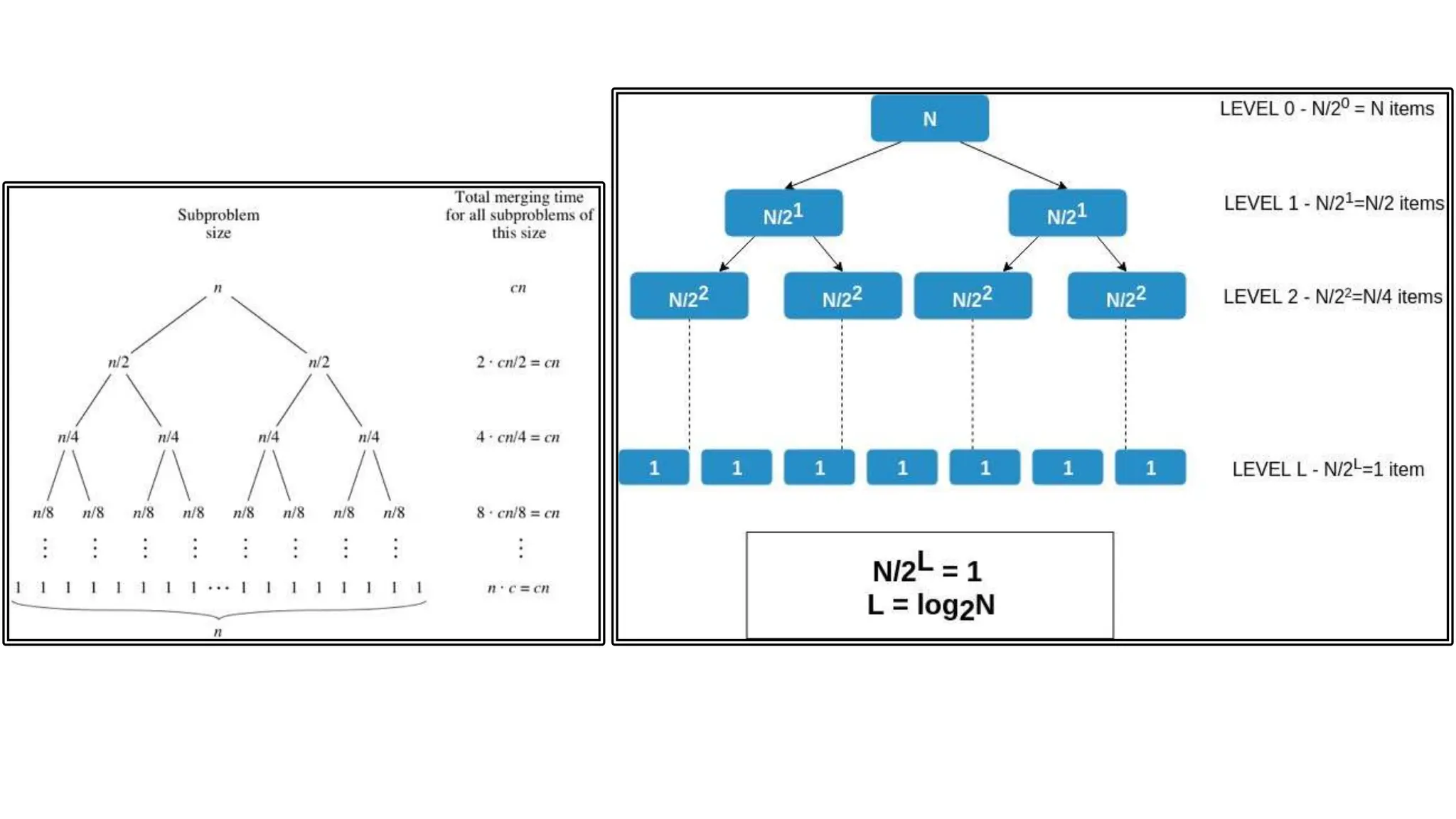
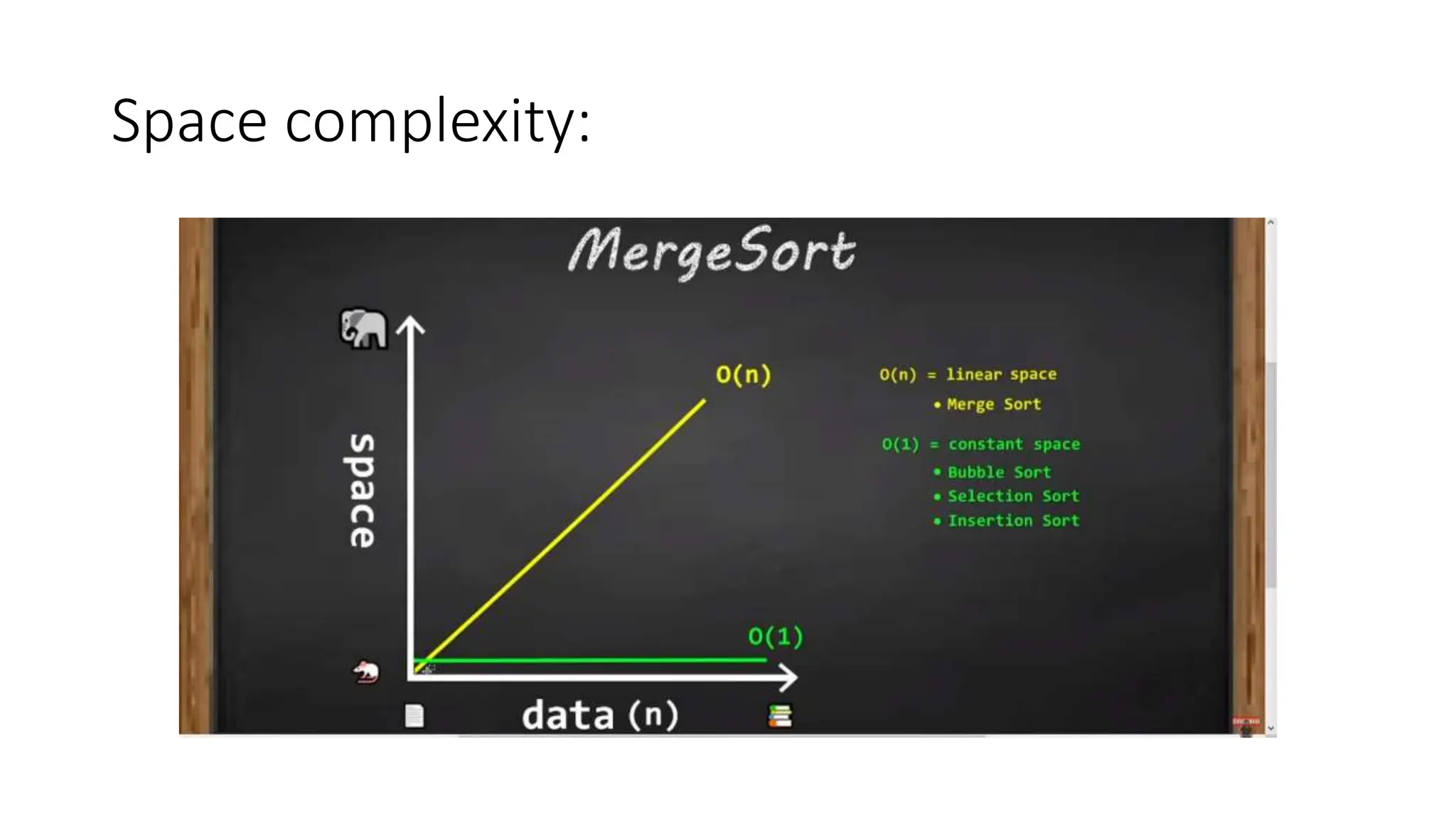
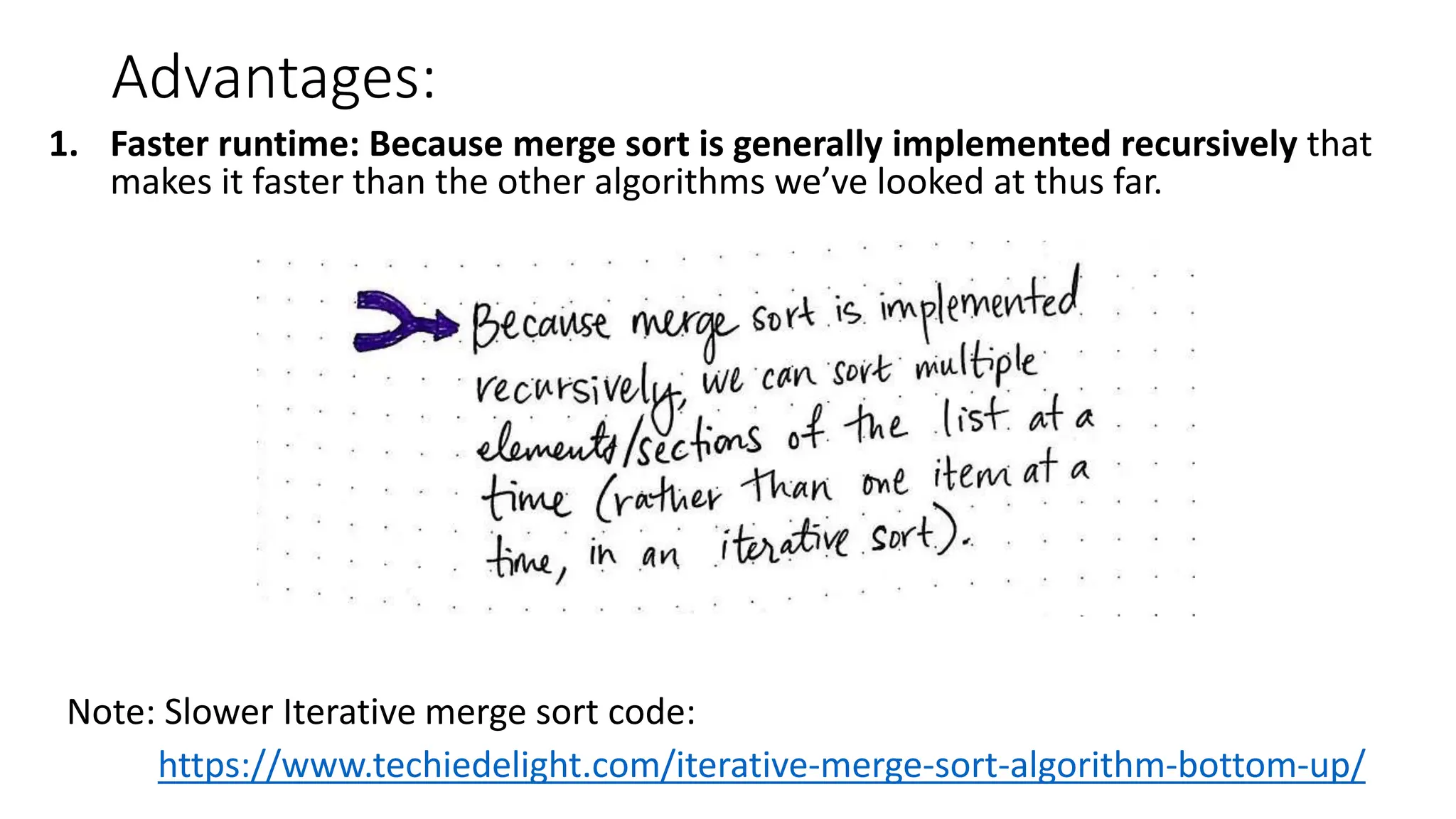
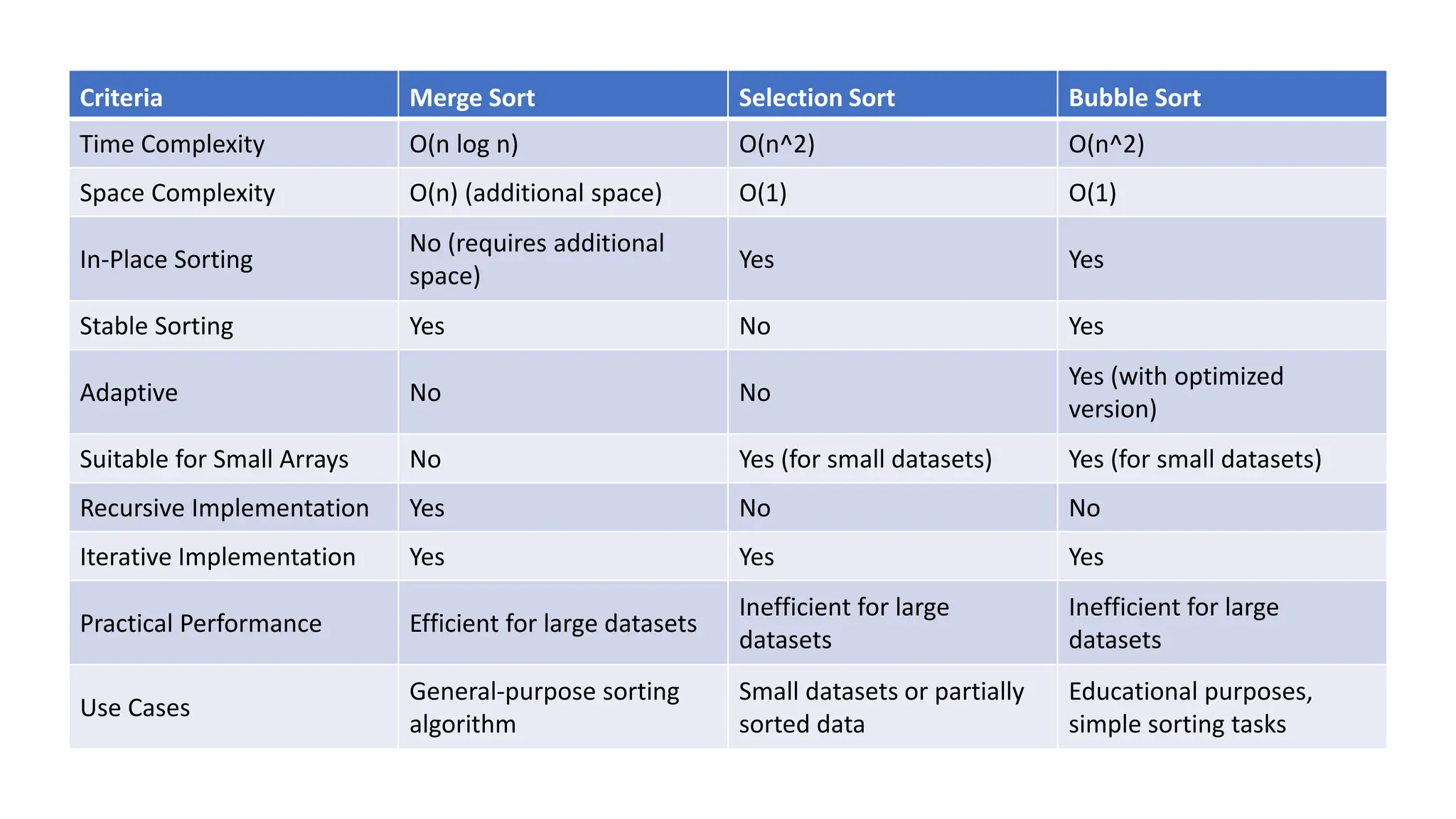
Merge sort is a sorting algorithm that divides an array into halves, recursively sorts them, and then merges the sorted halves into a single sorted array. It has several advantages, including a time complexity of O(n log n) in all cases, efficiency for linked lists and external sorting, and producing a stable sort. However, it requires additional space and is not an in-place algorithm.