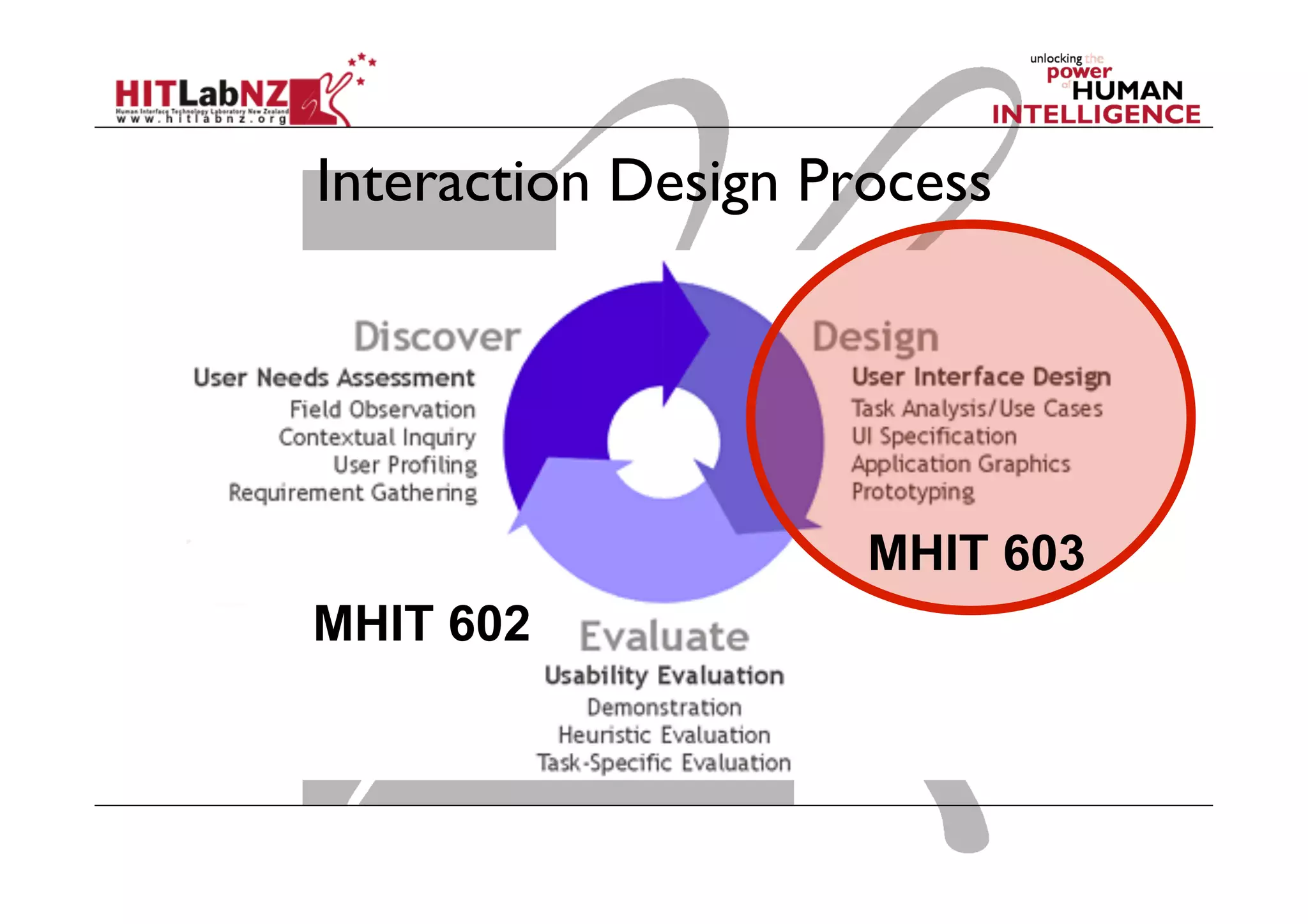
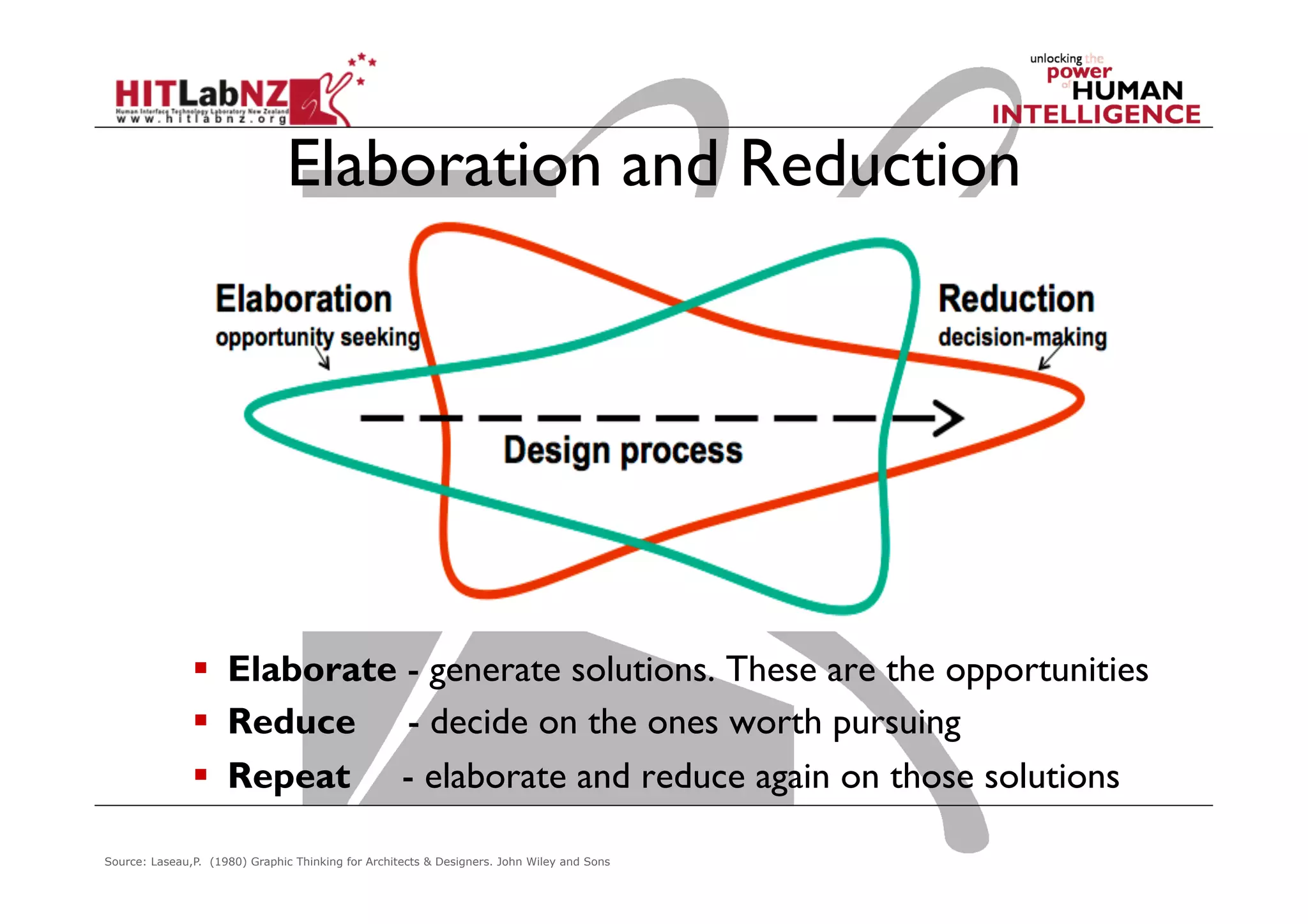
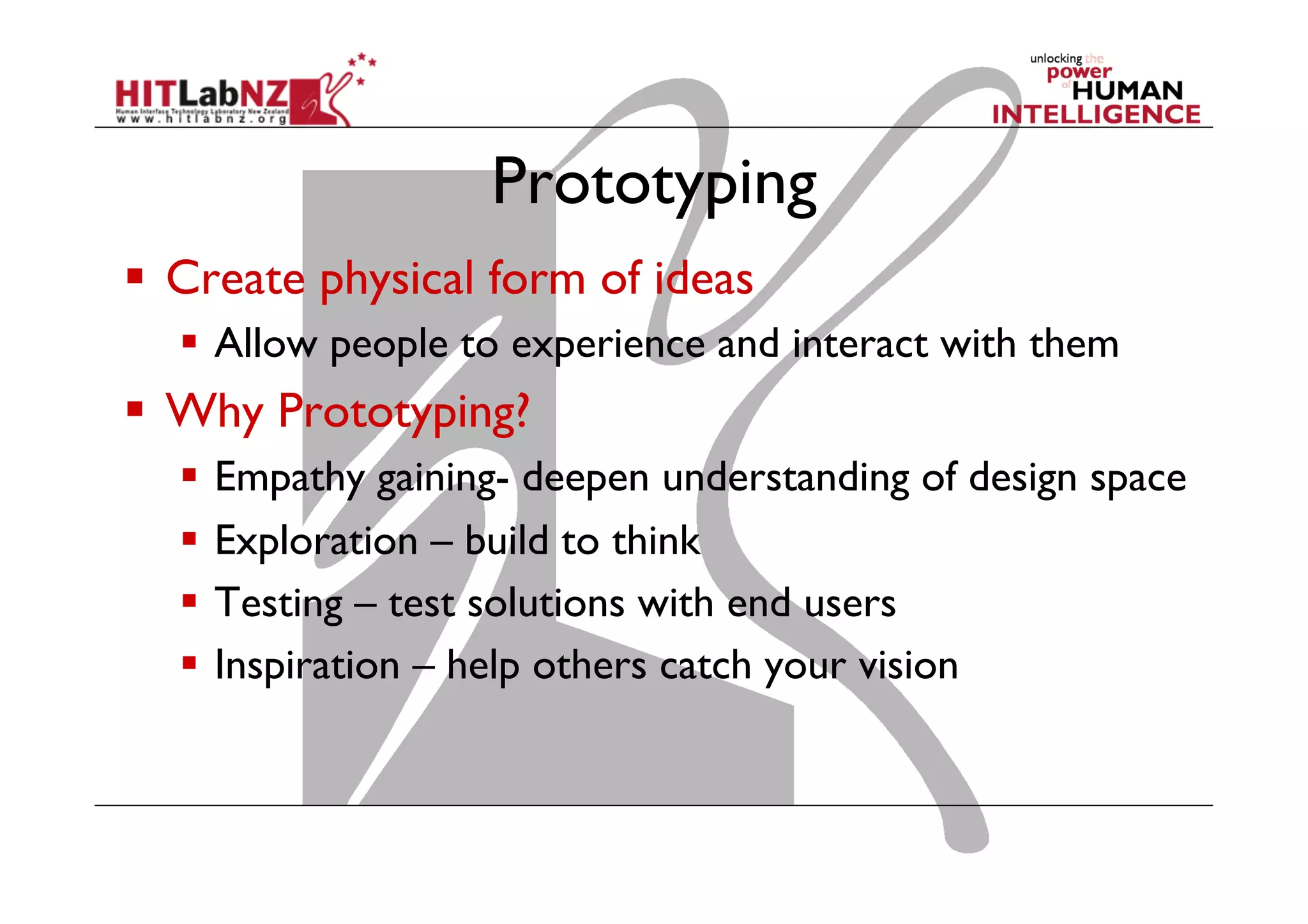
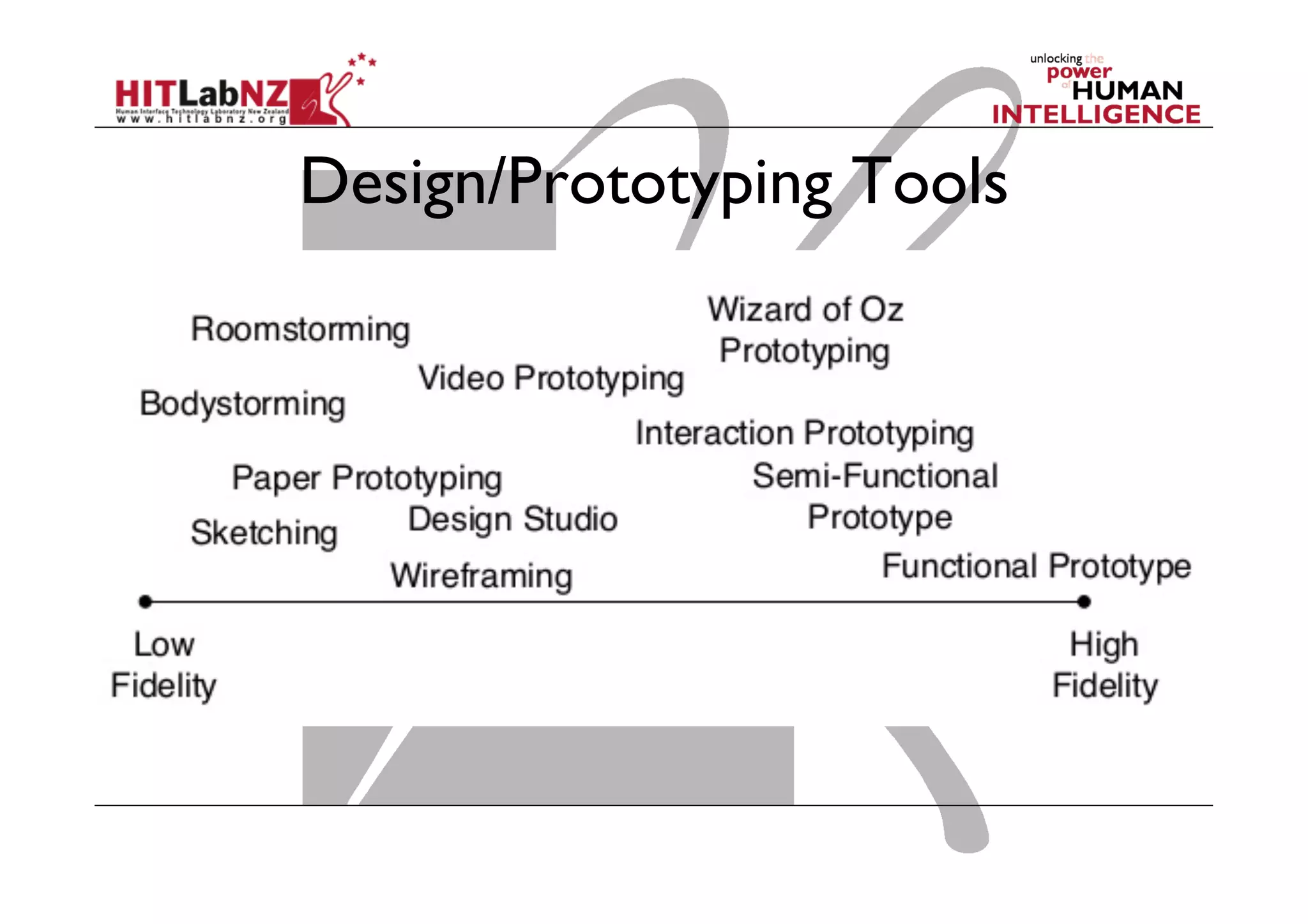
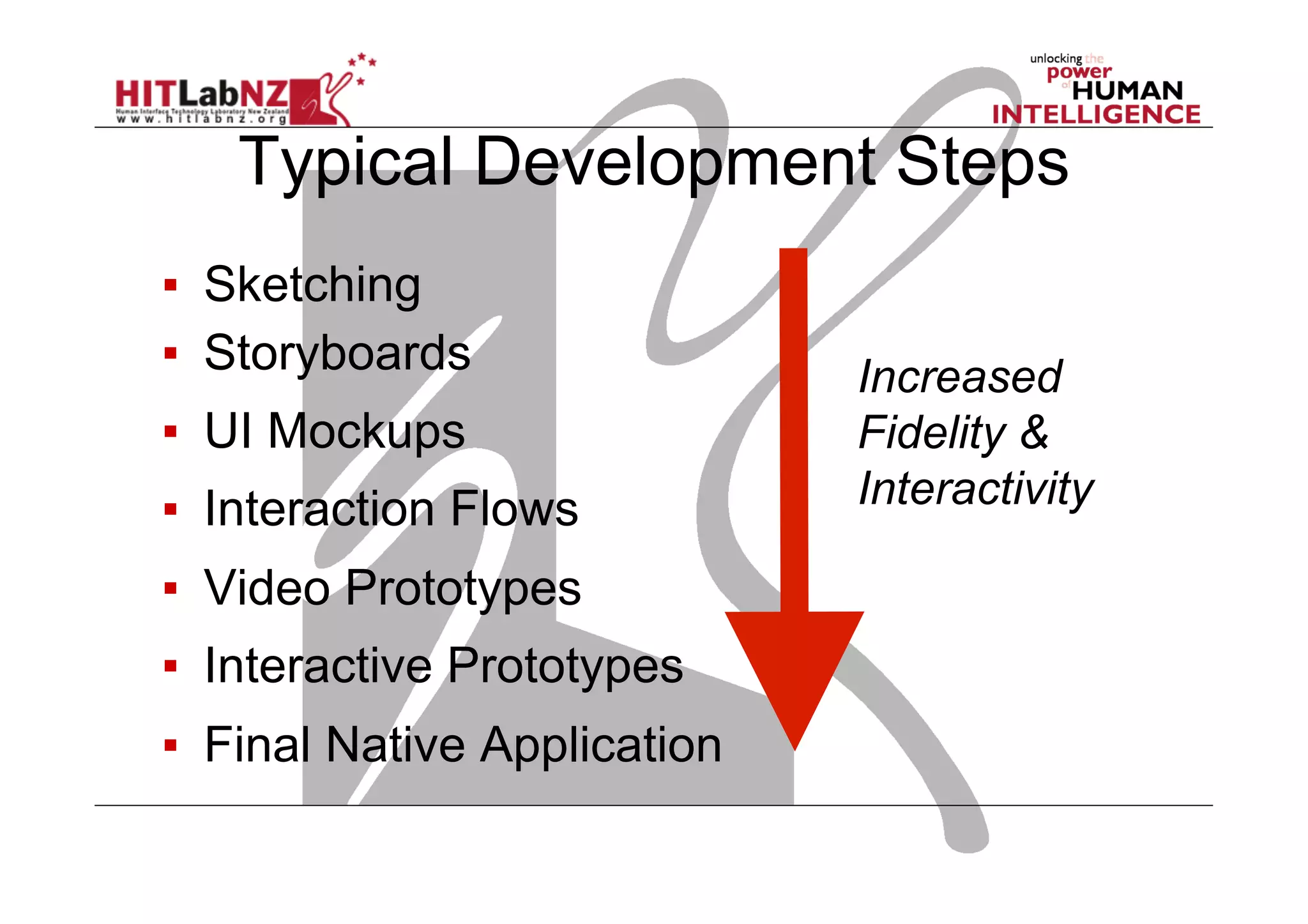
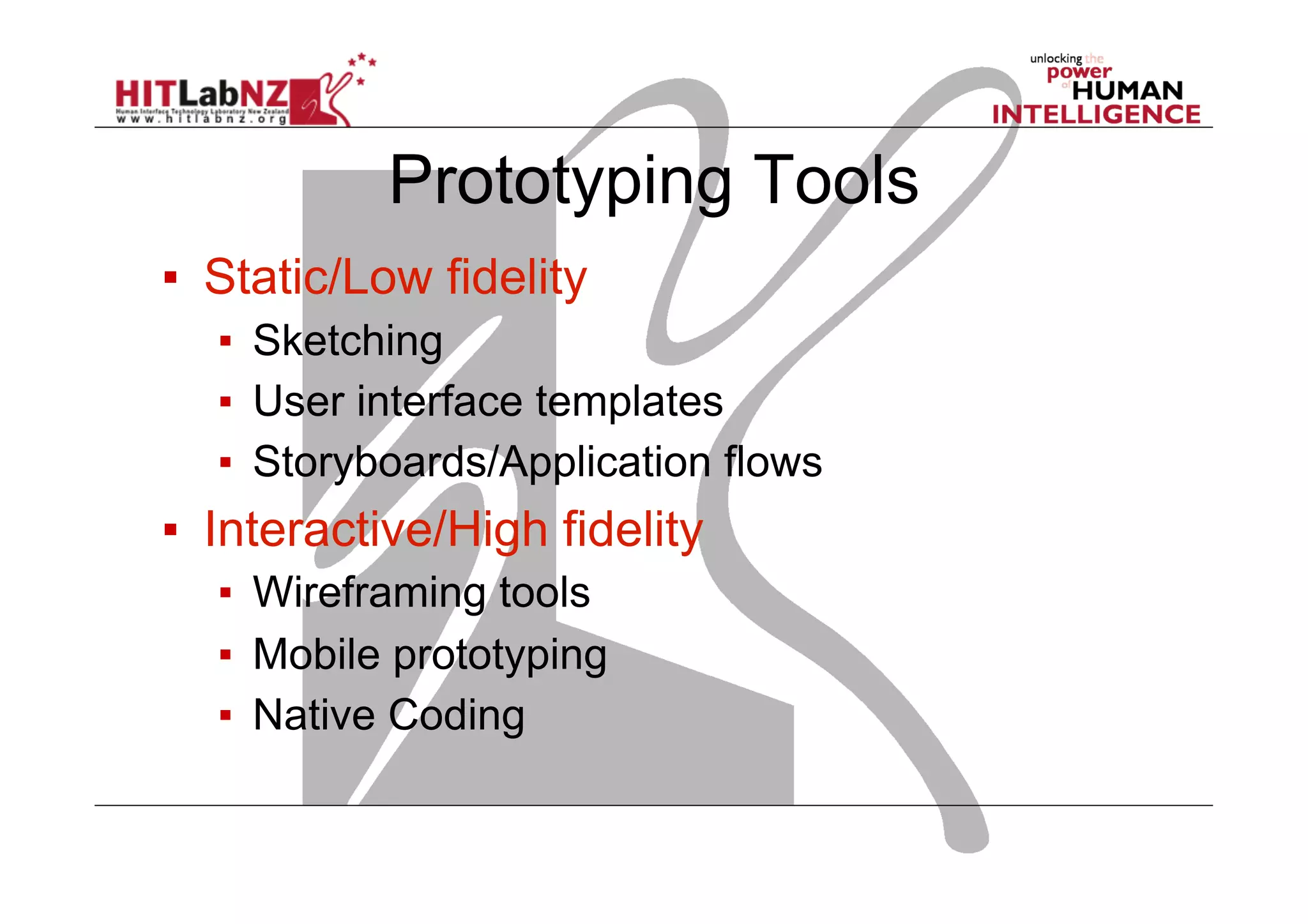
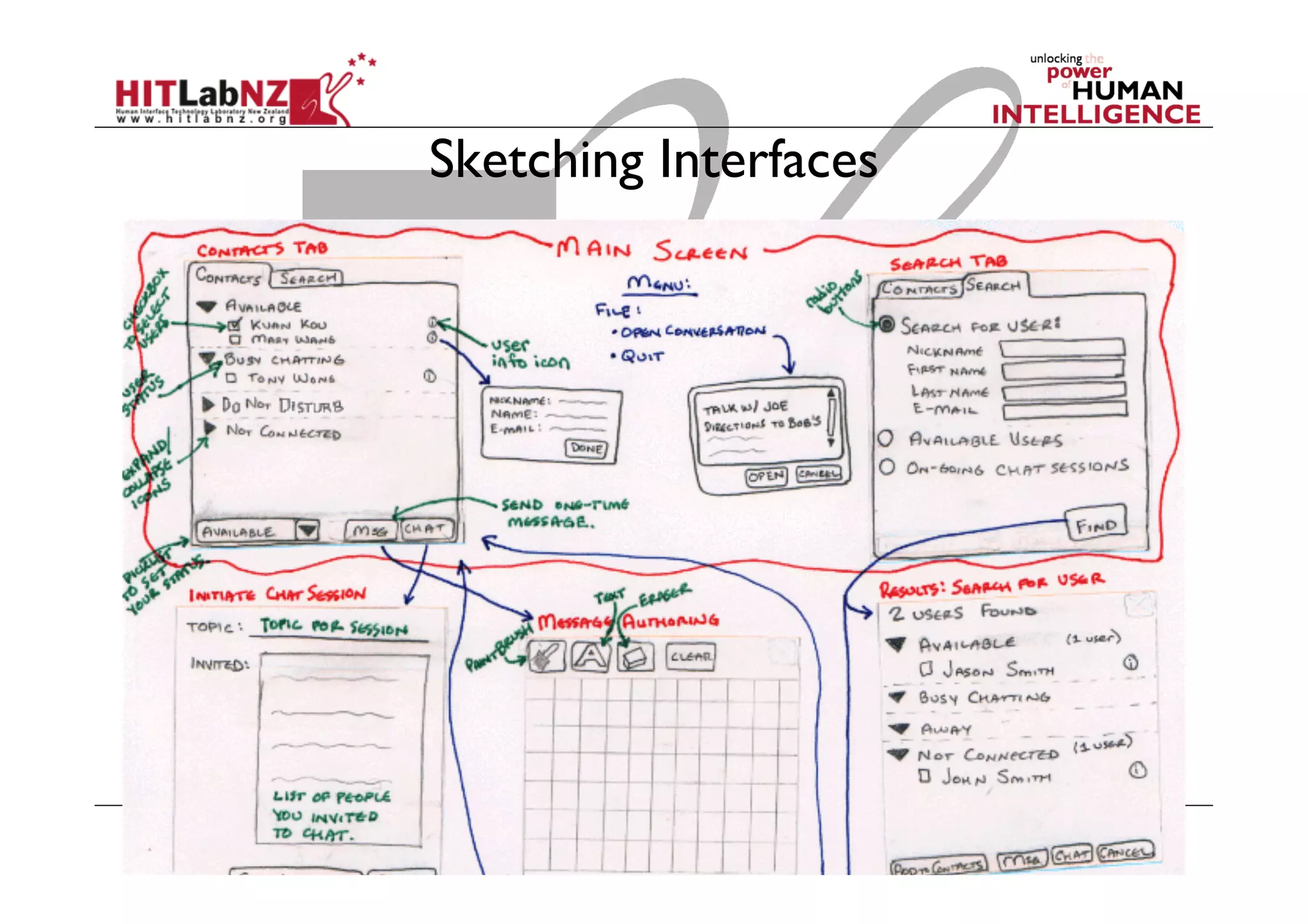
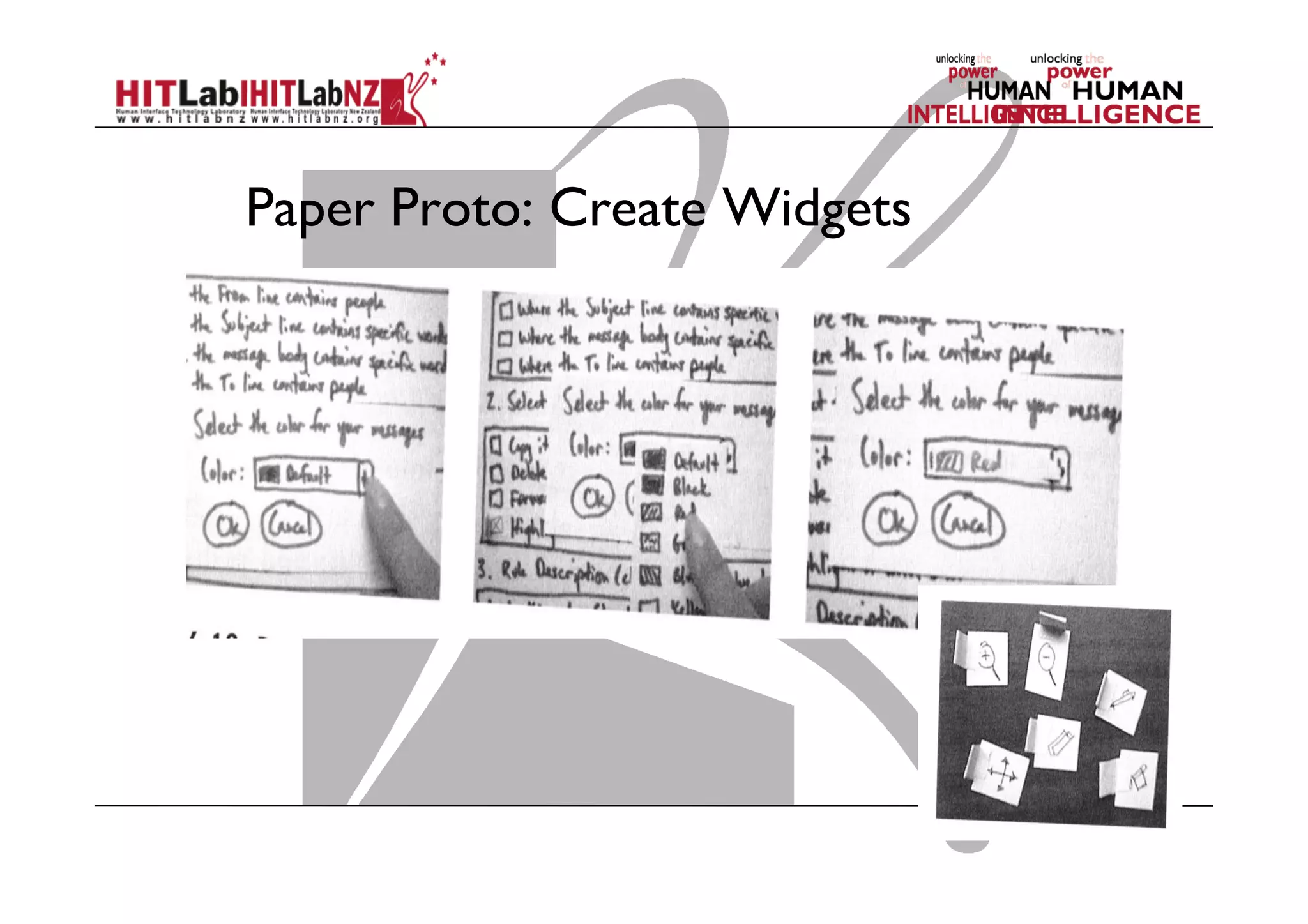
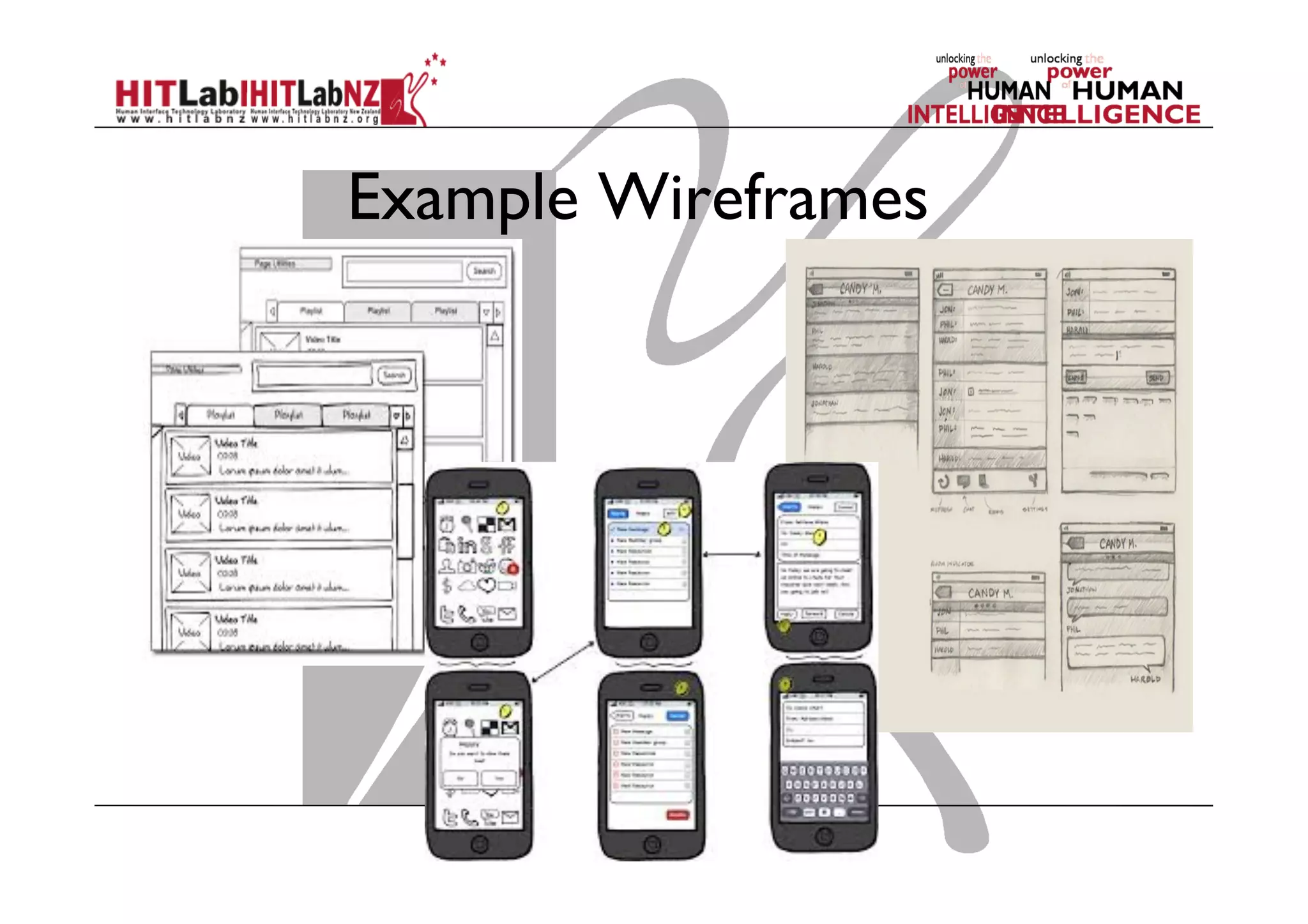
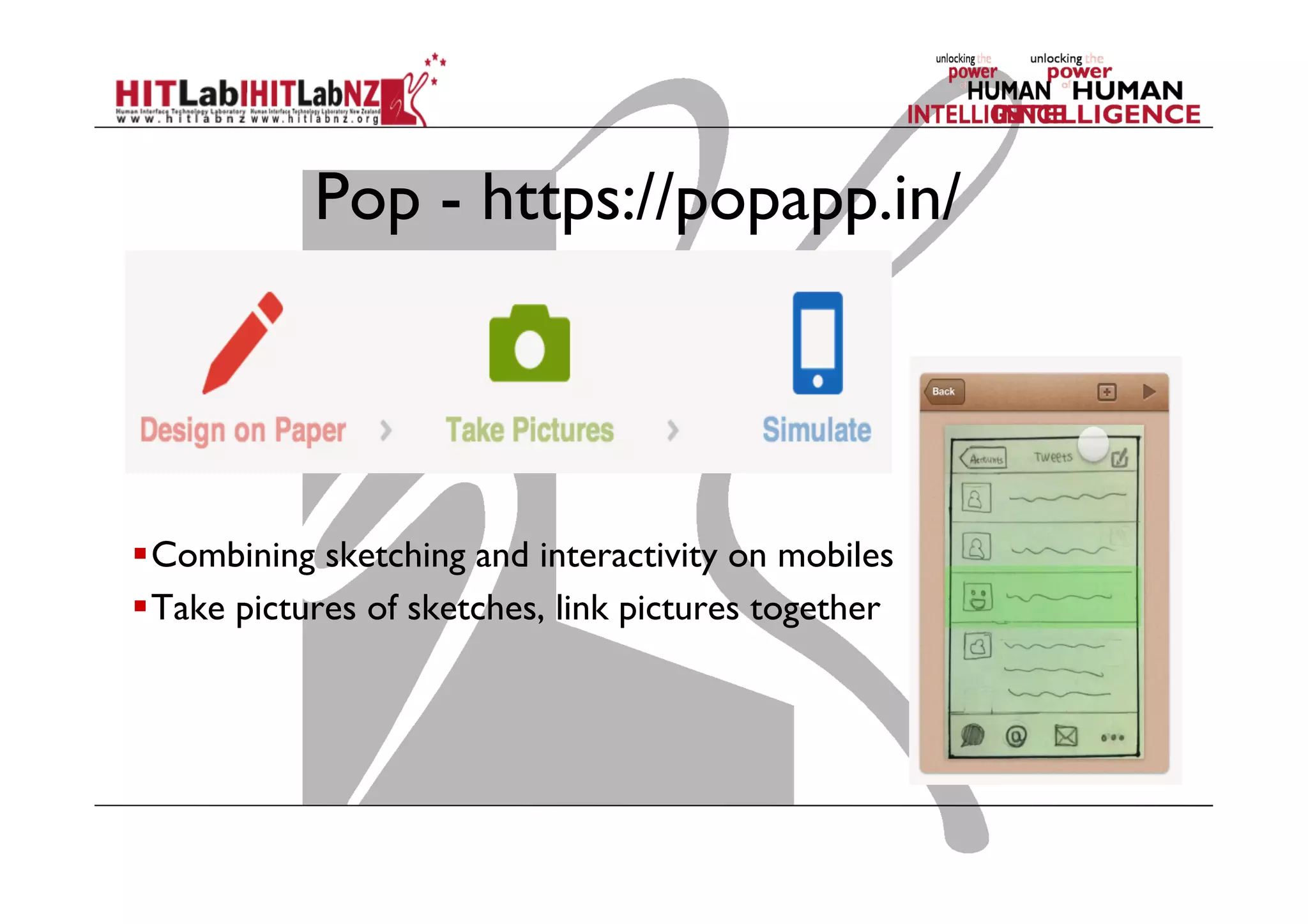
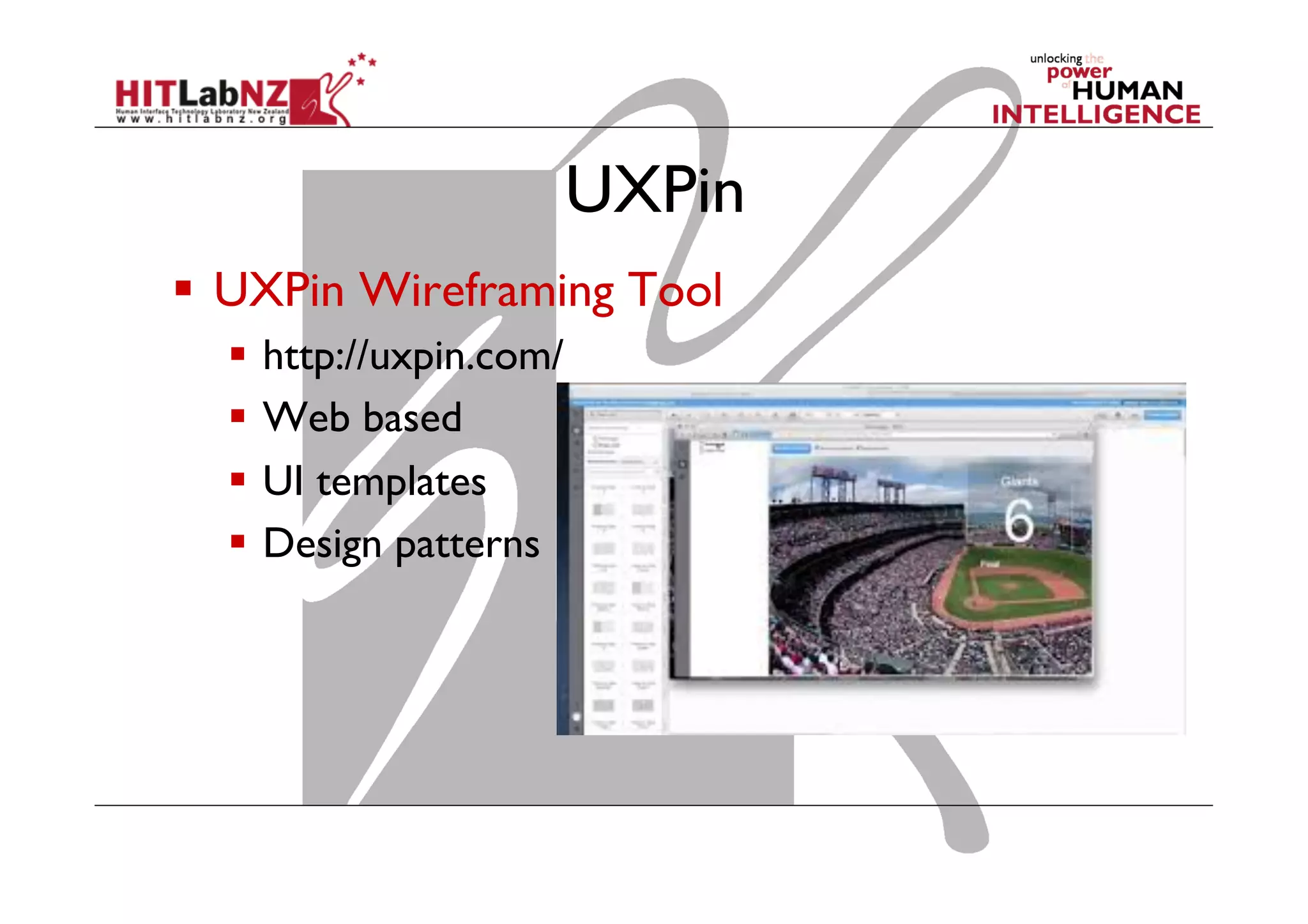
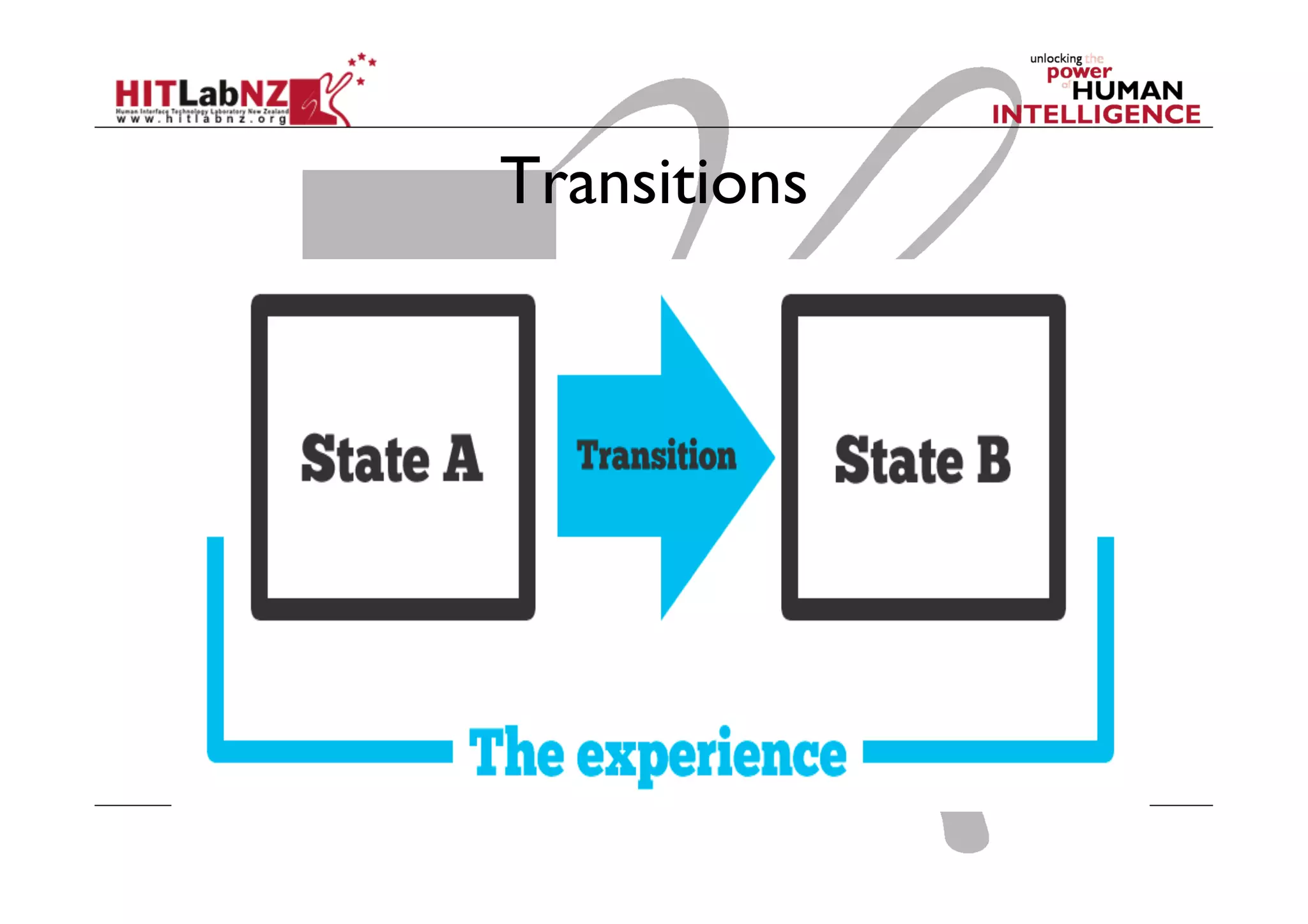
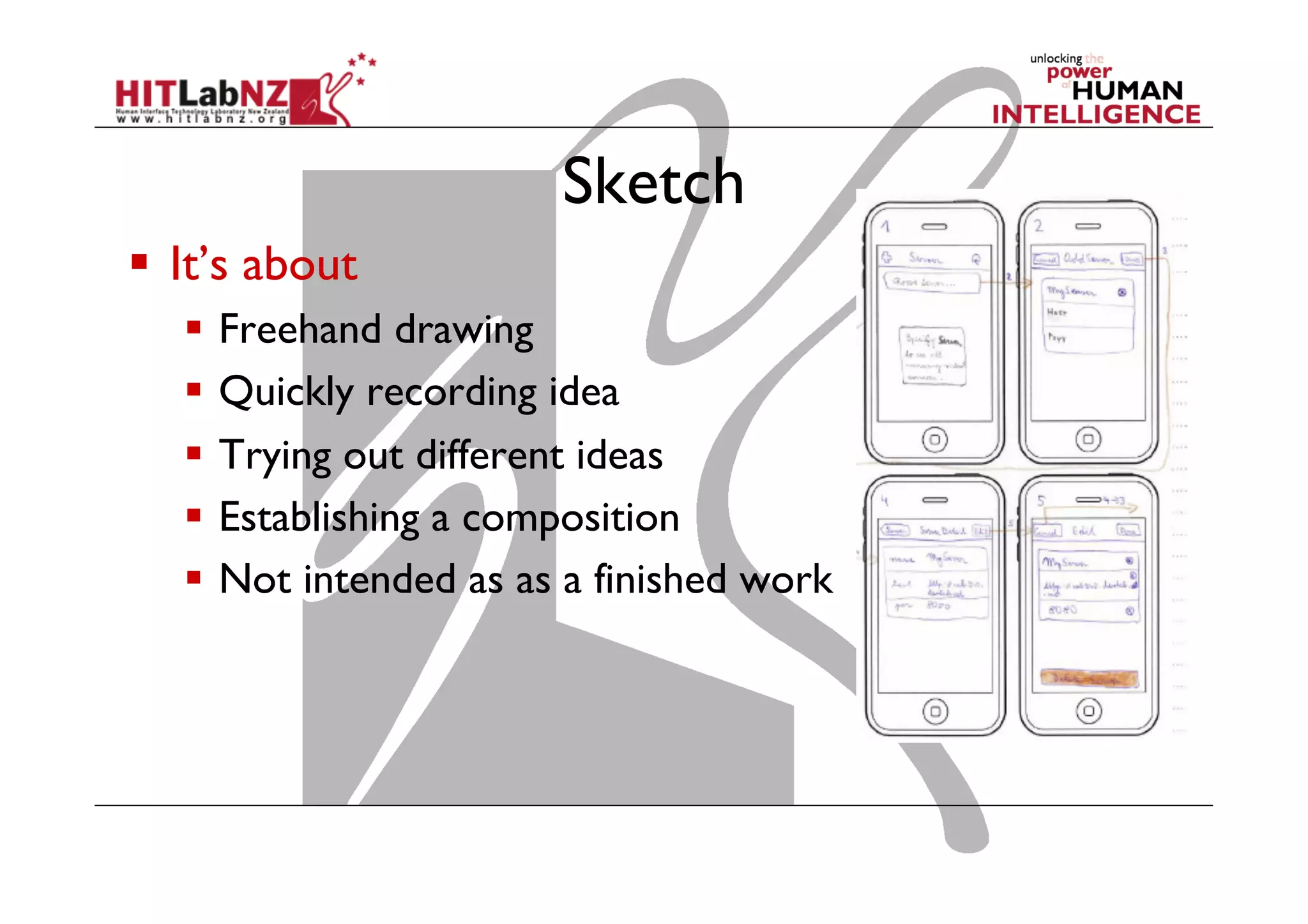
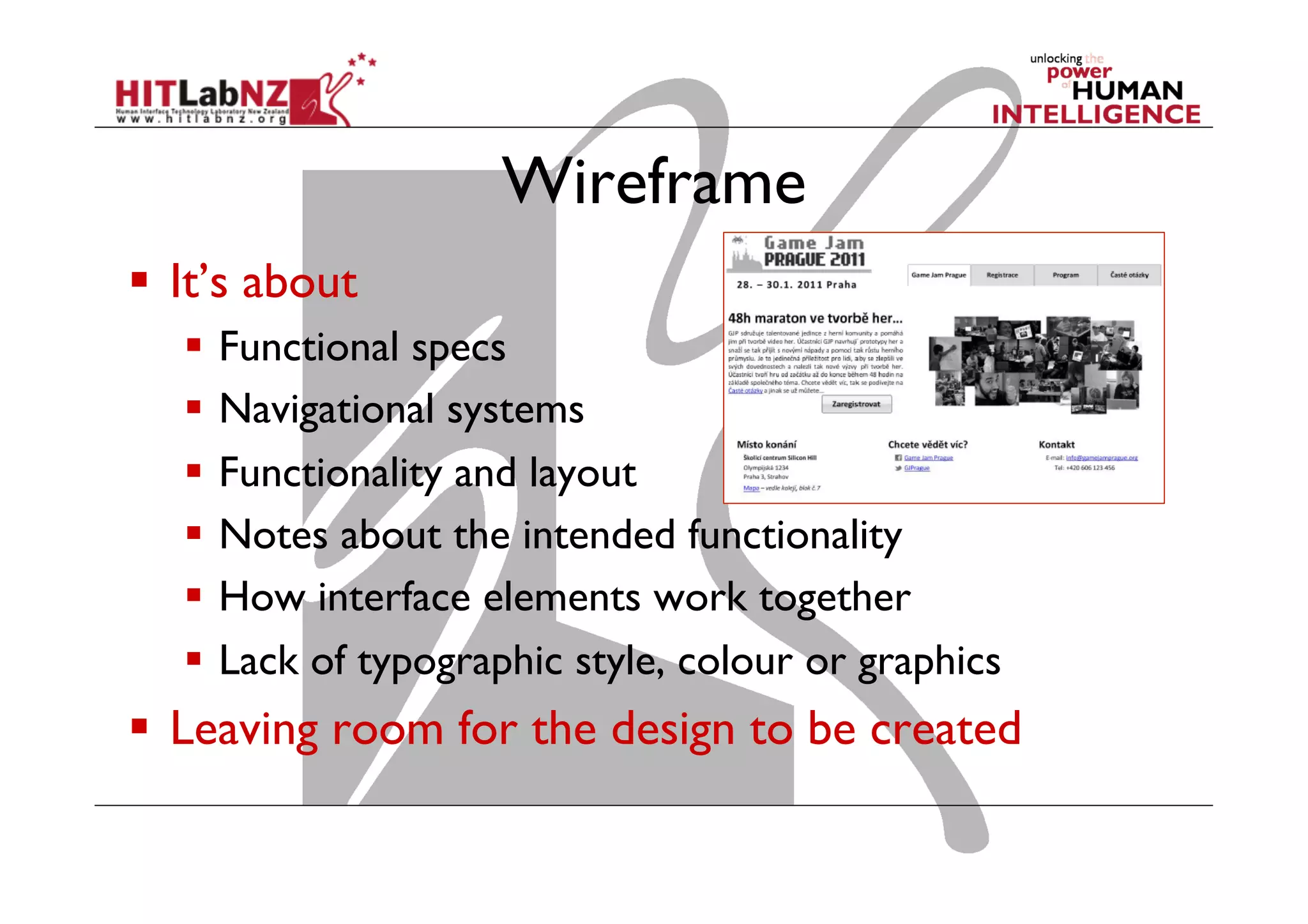
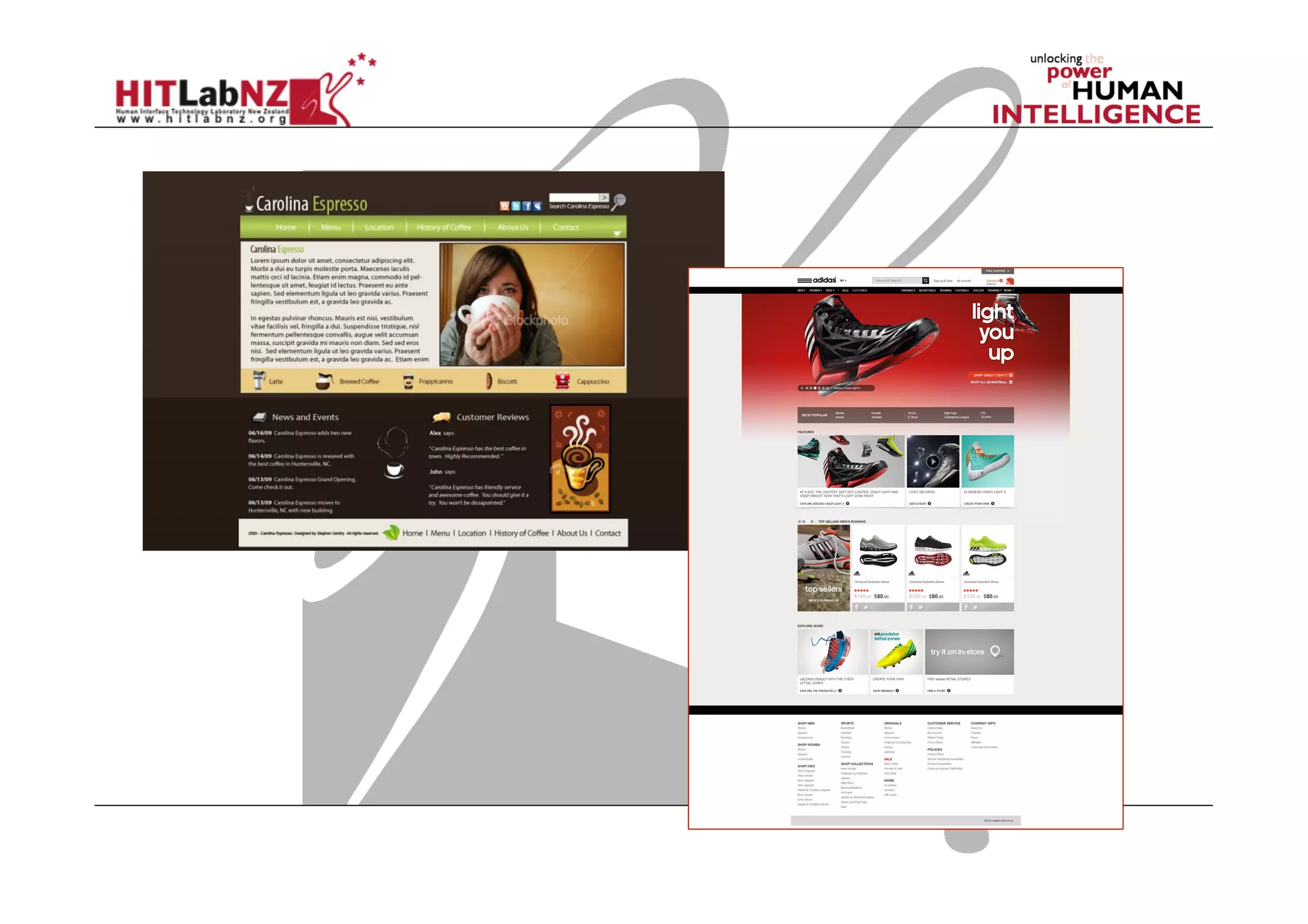
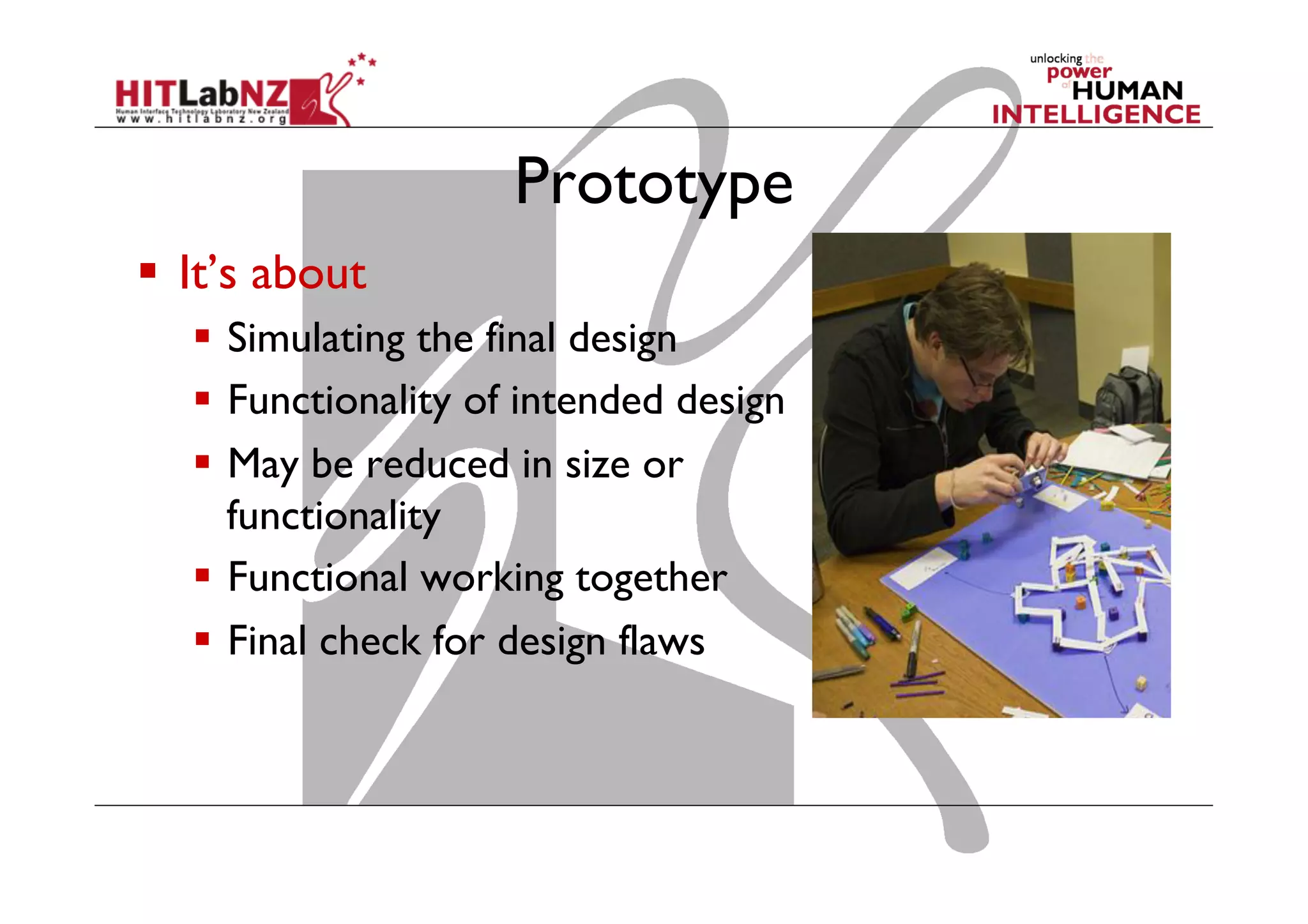
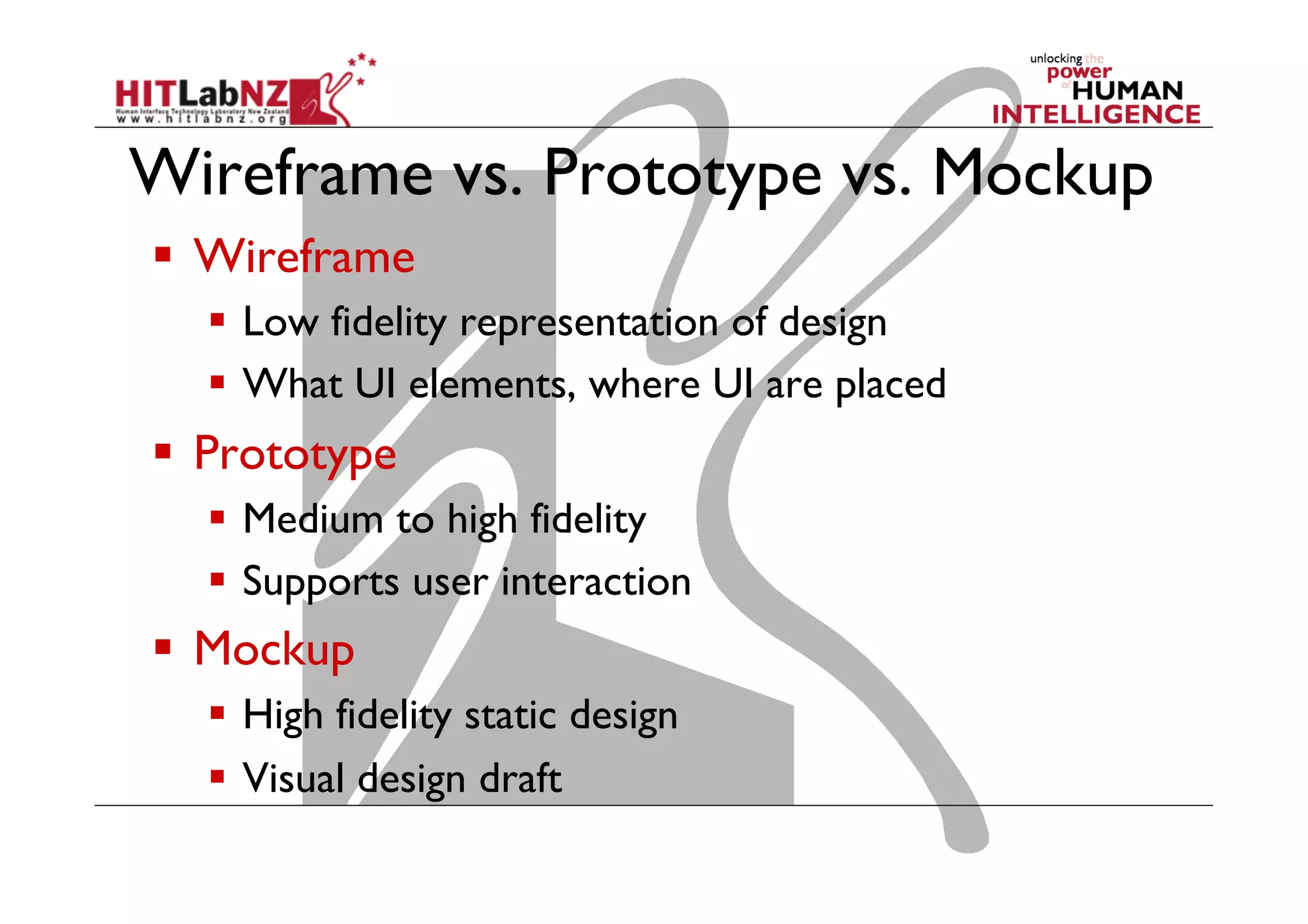
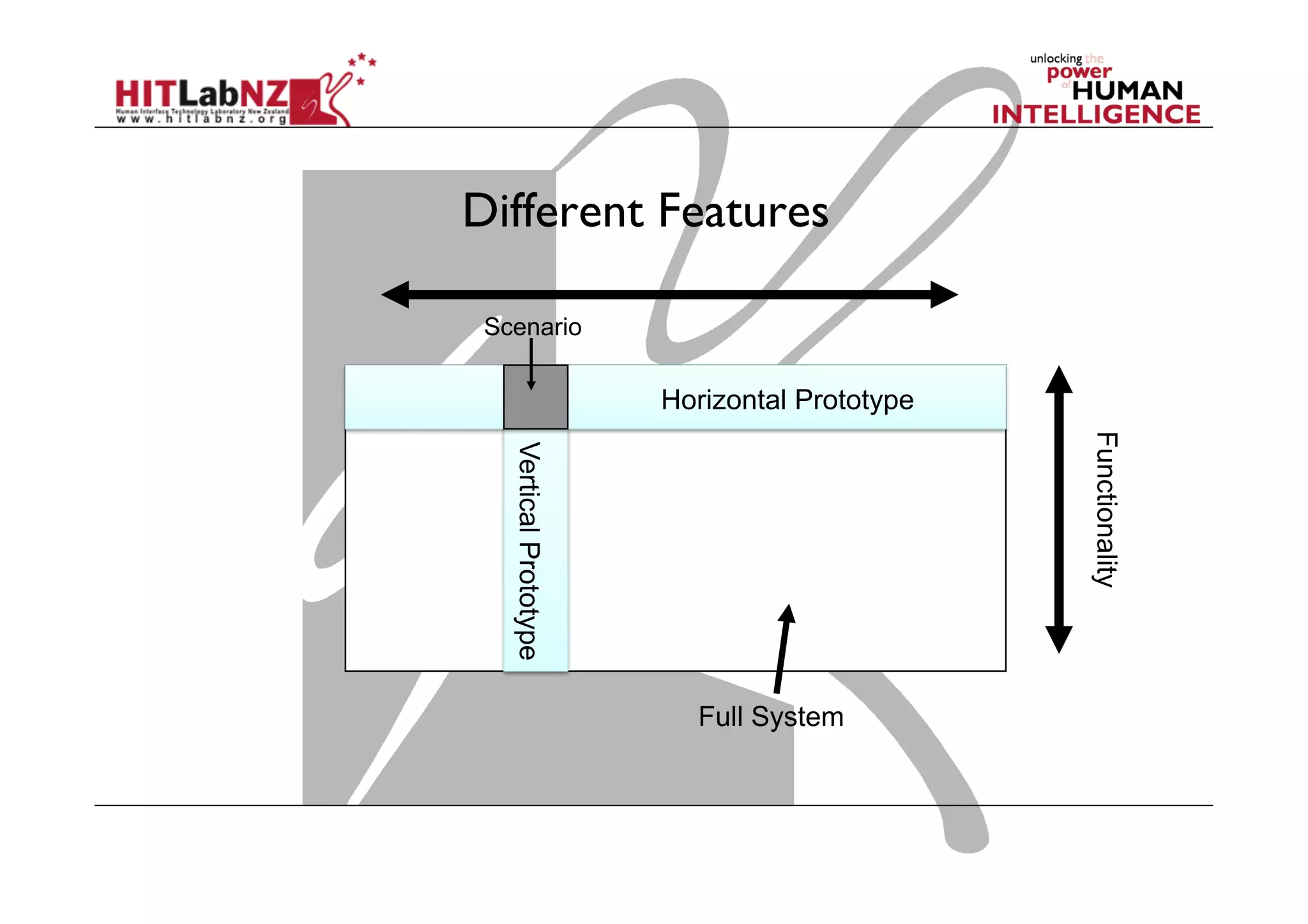
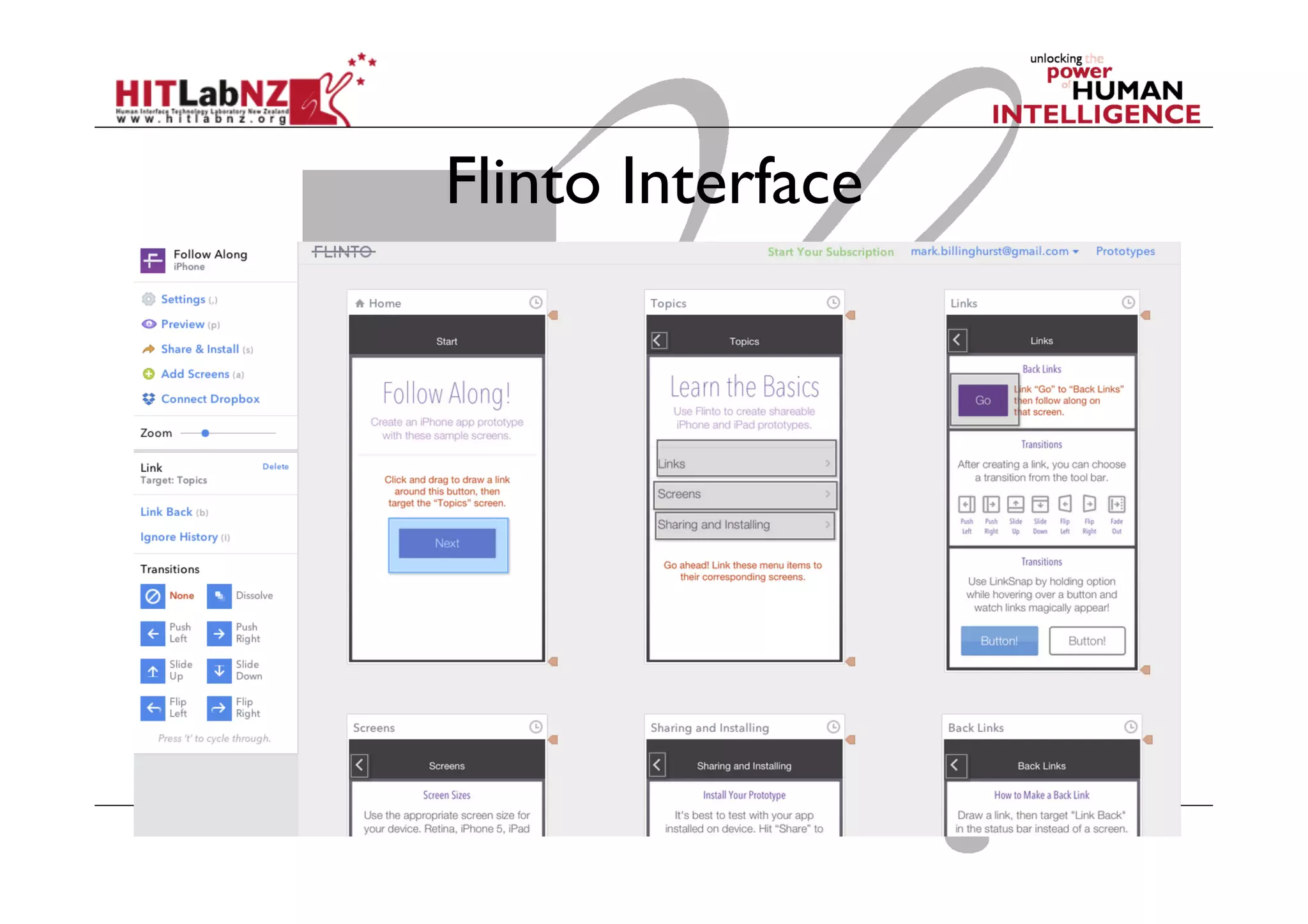
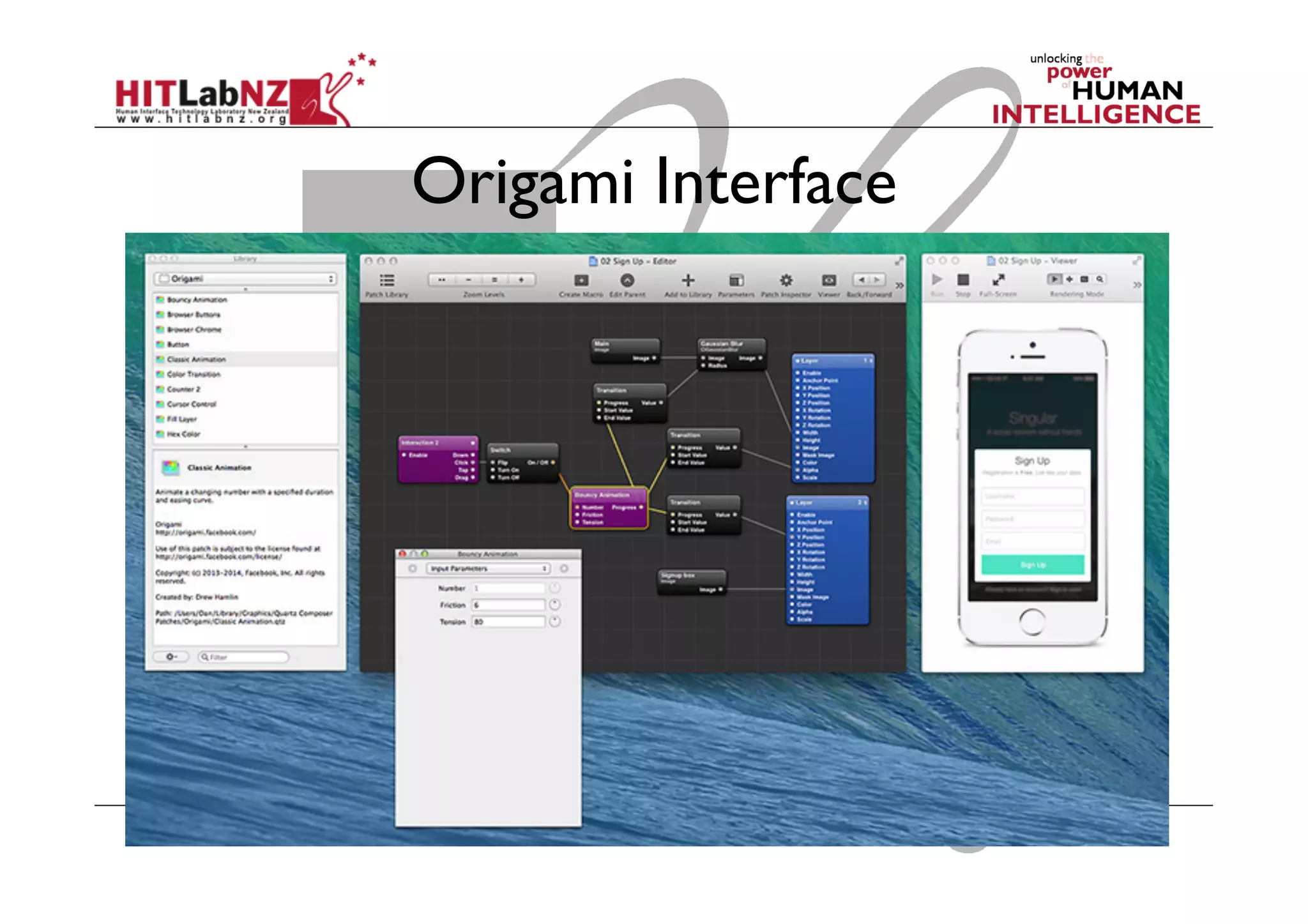
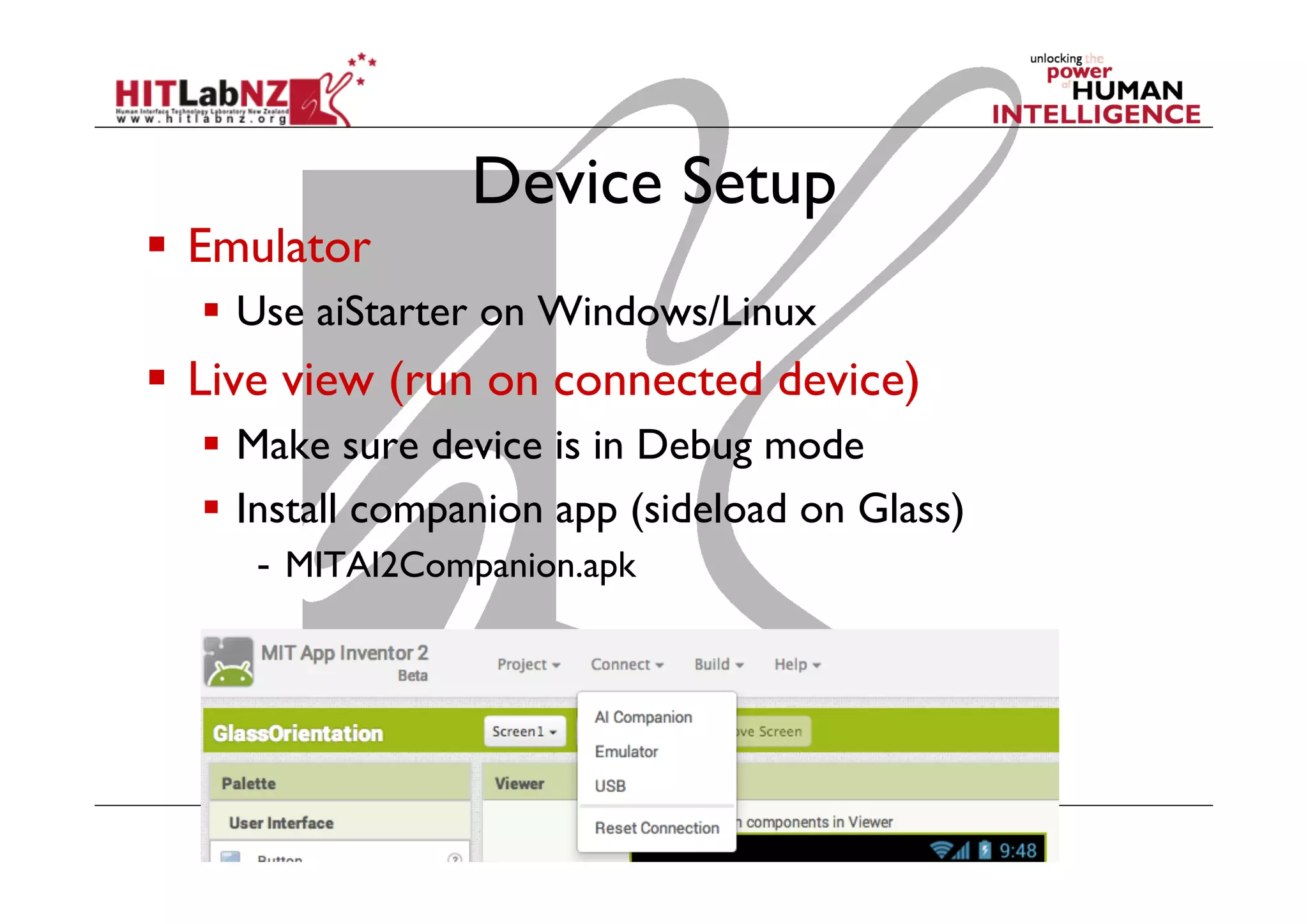
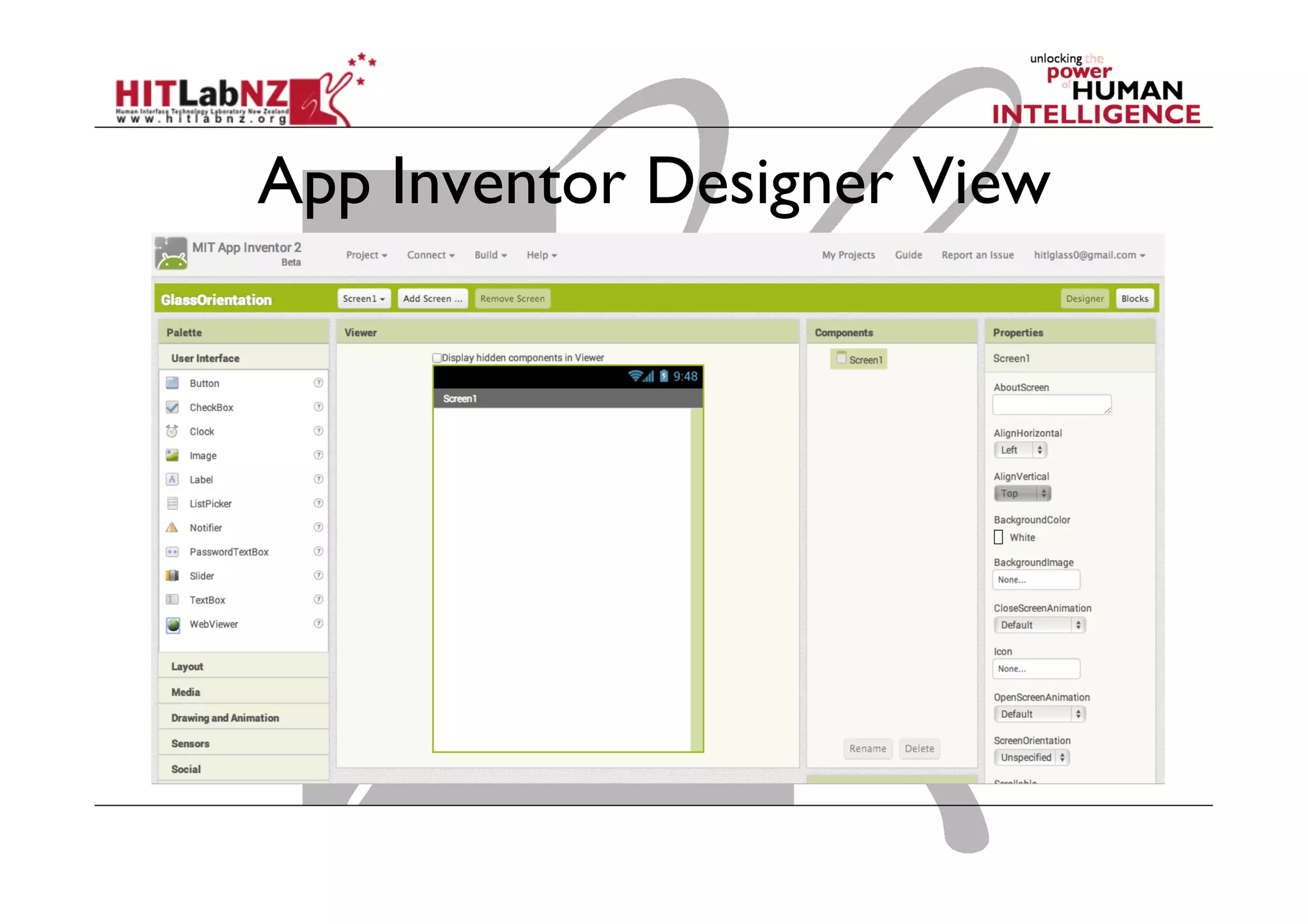
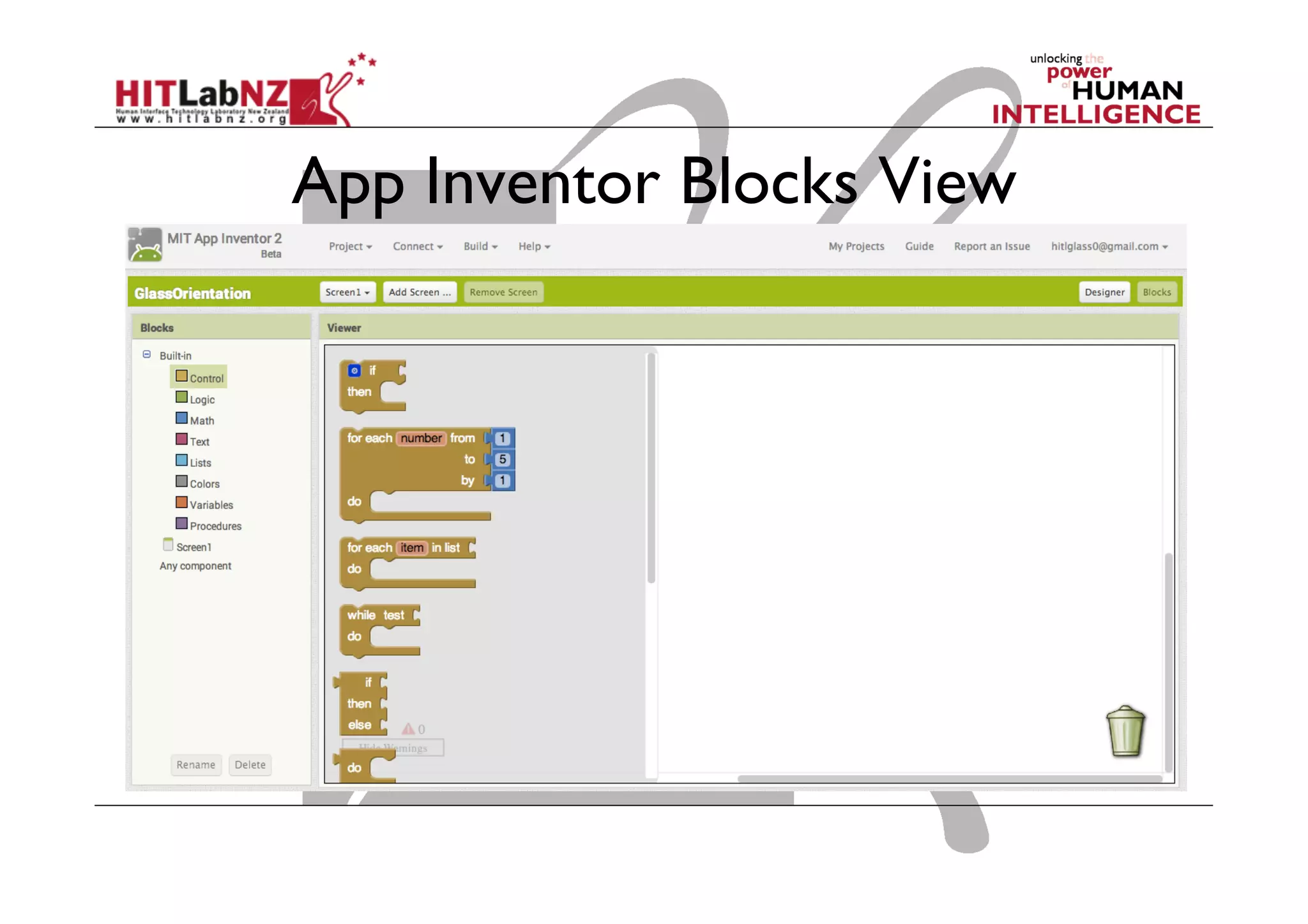
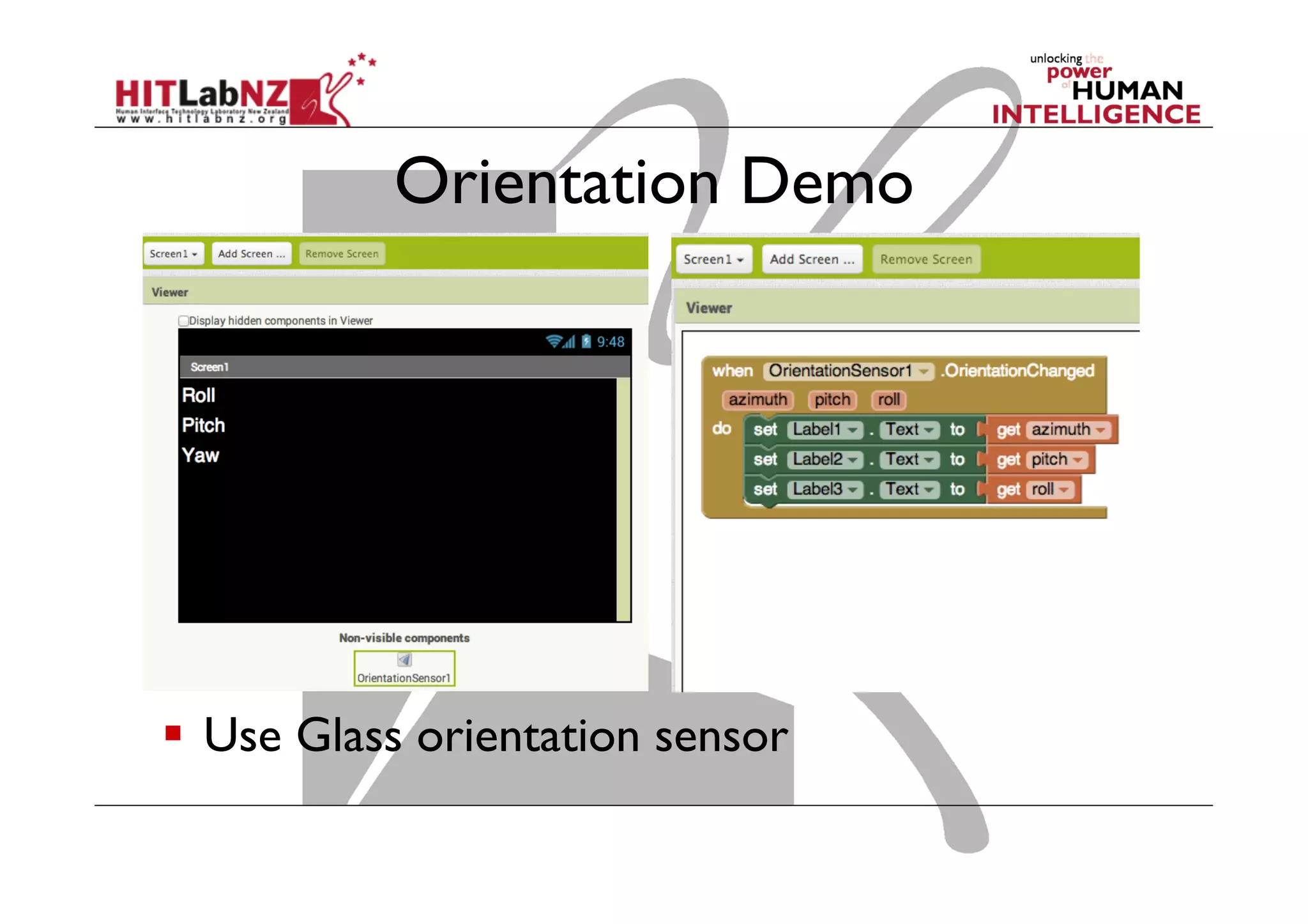
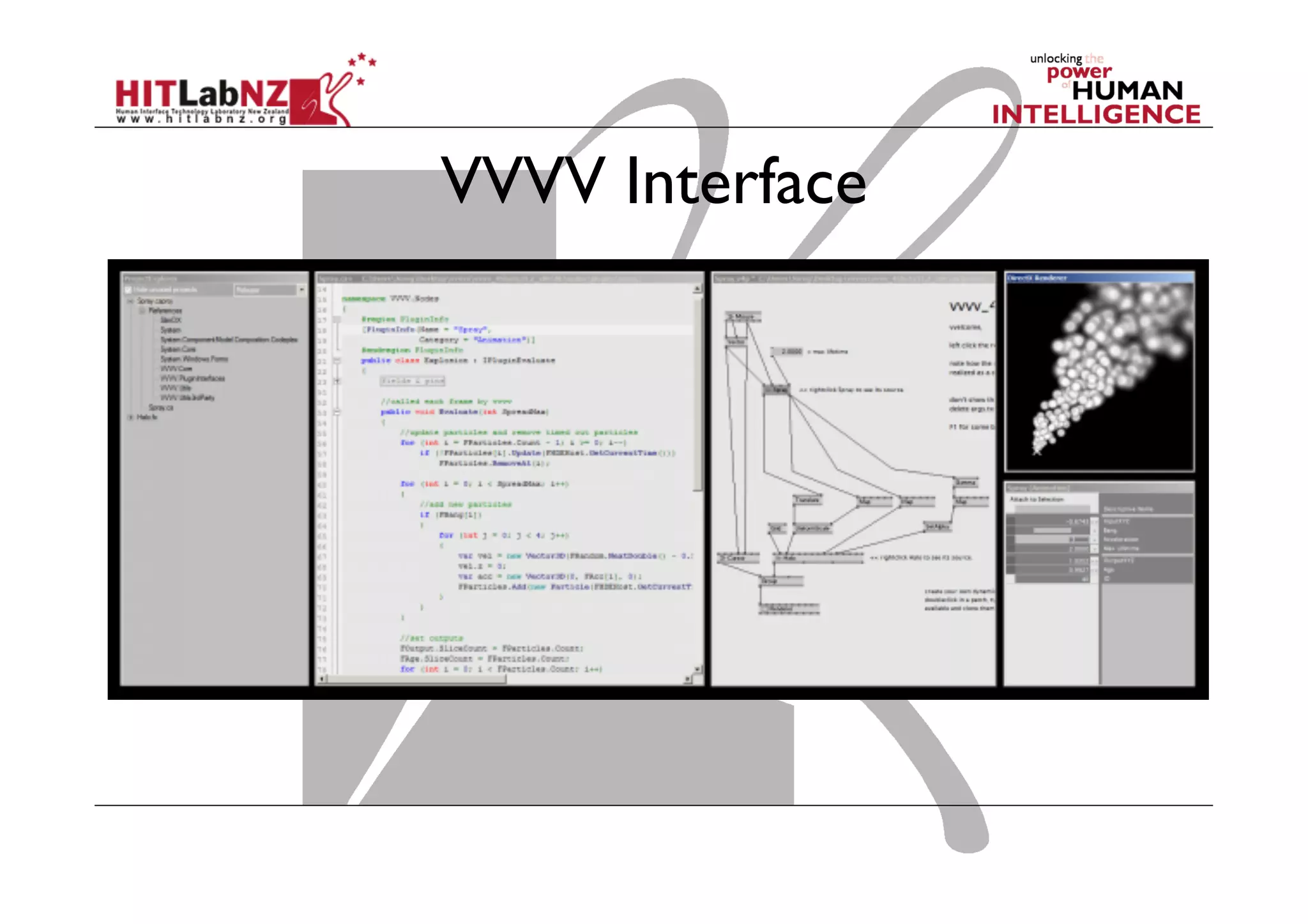
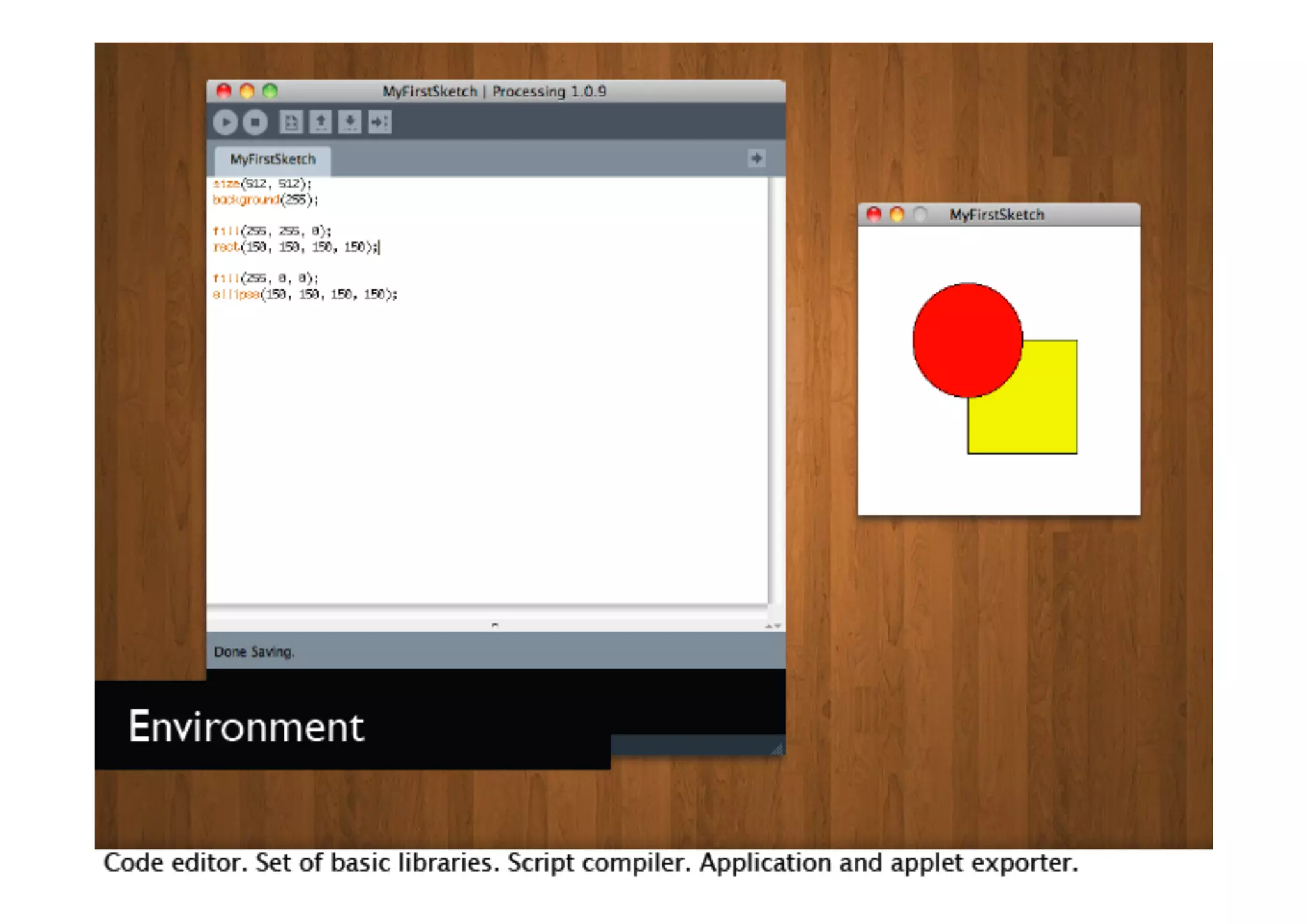
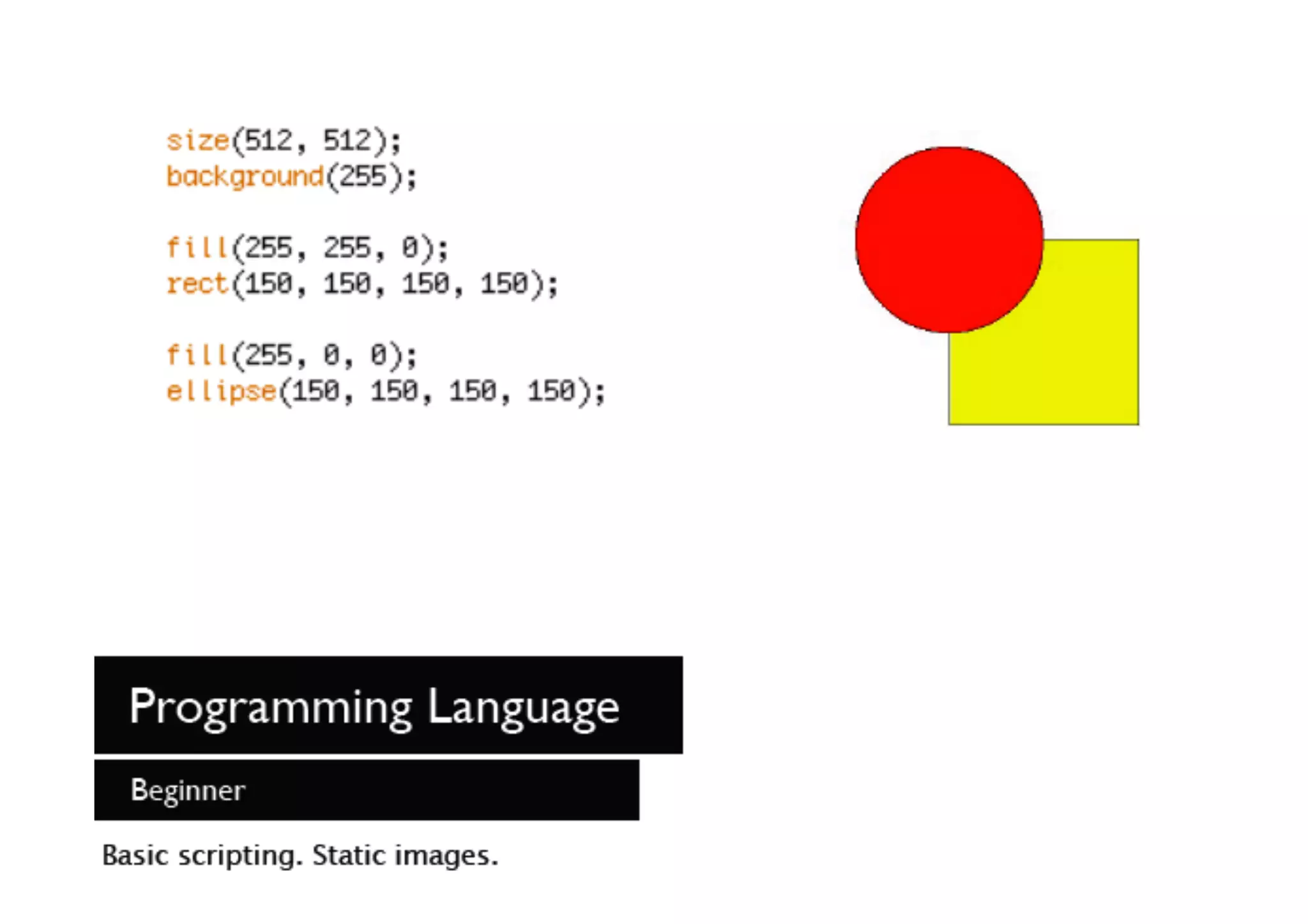
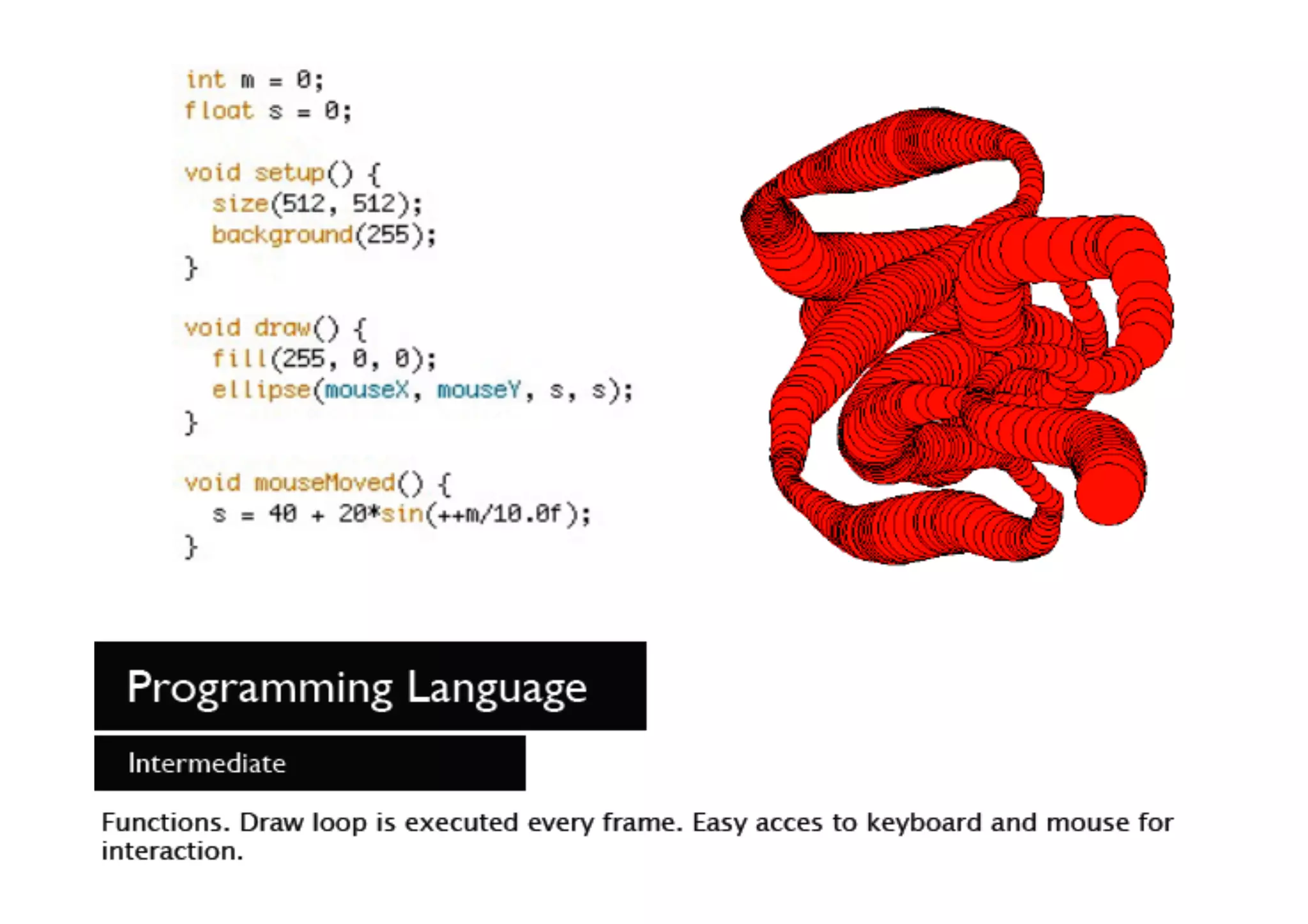
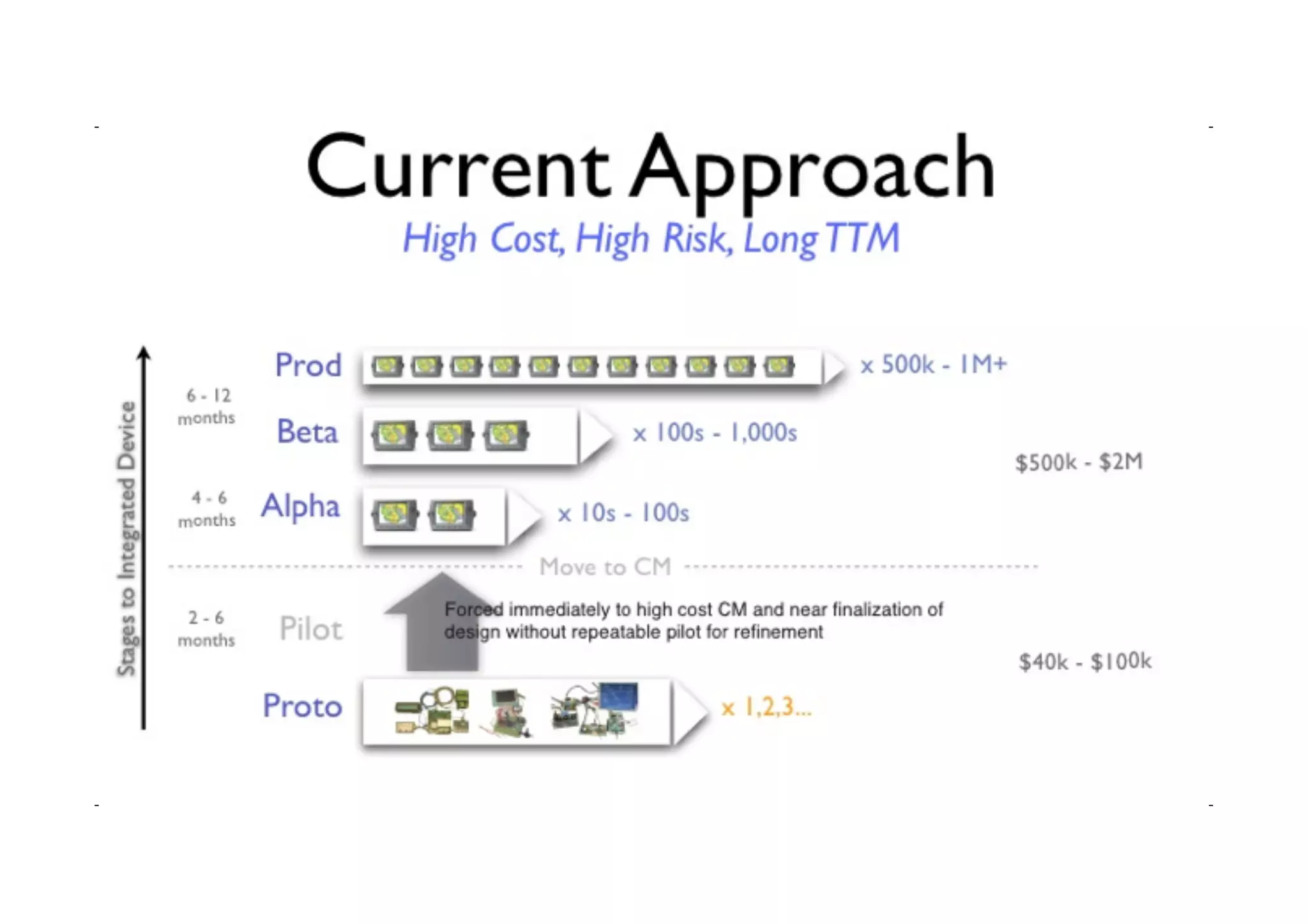
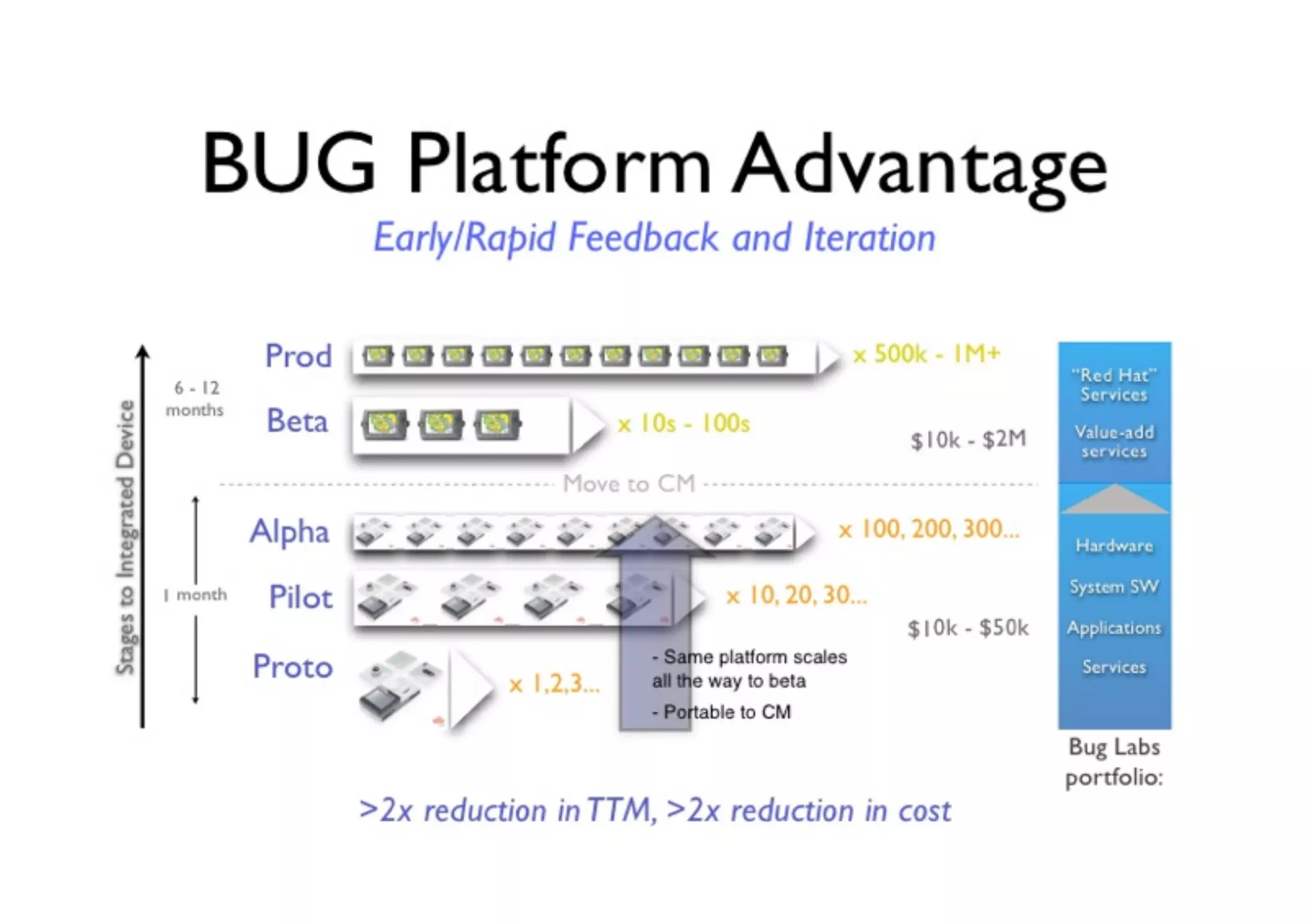
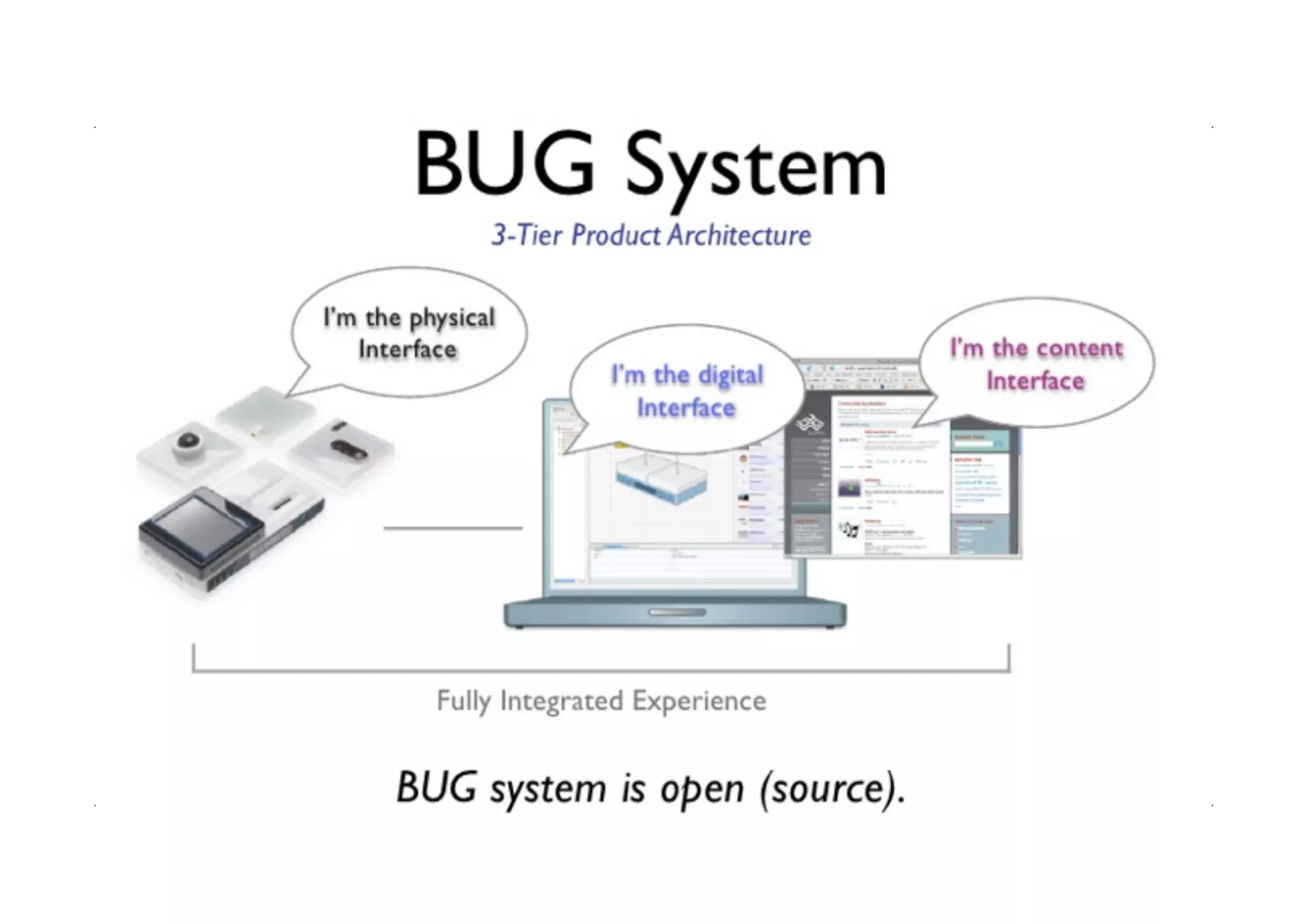
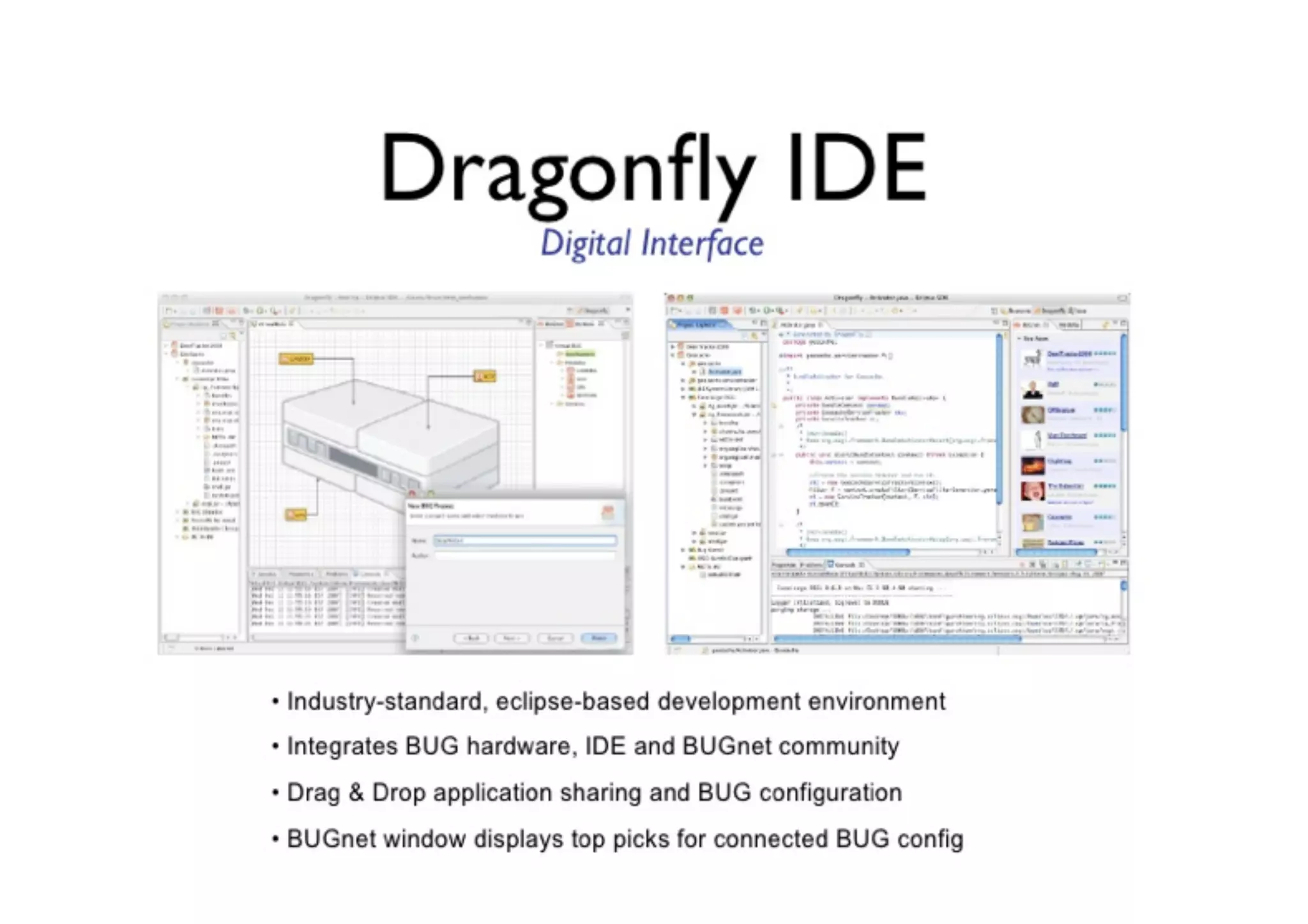
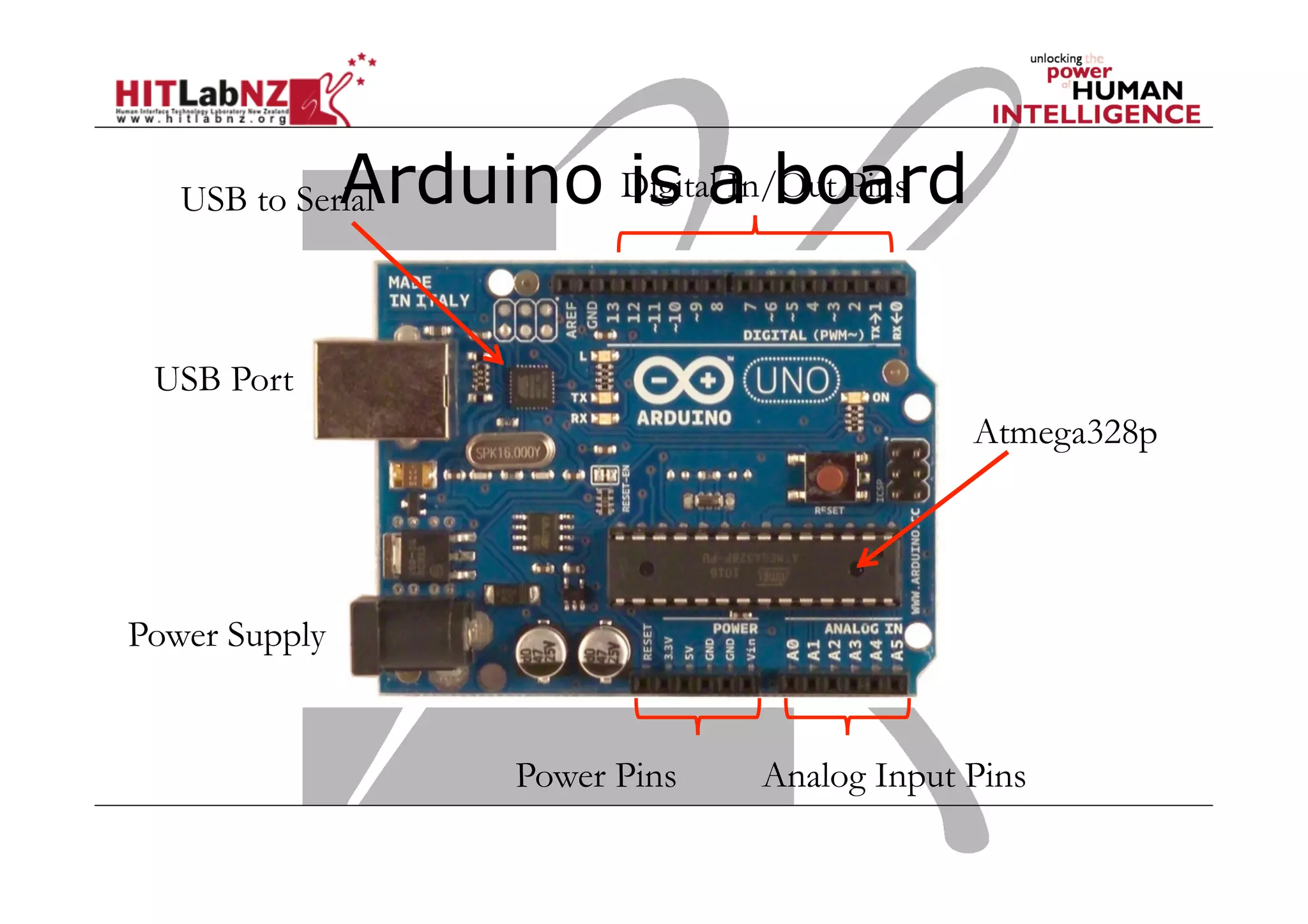
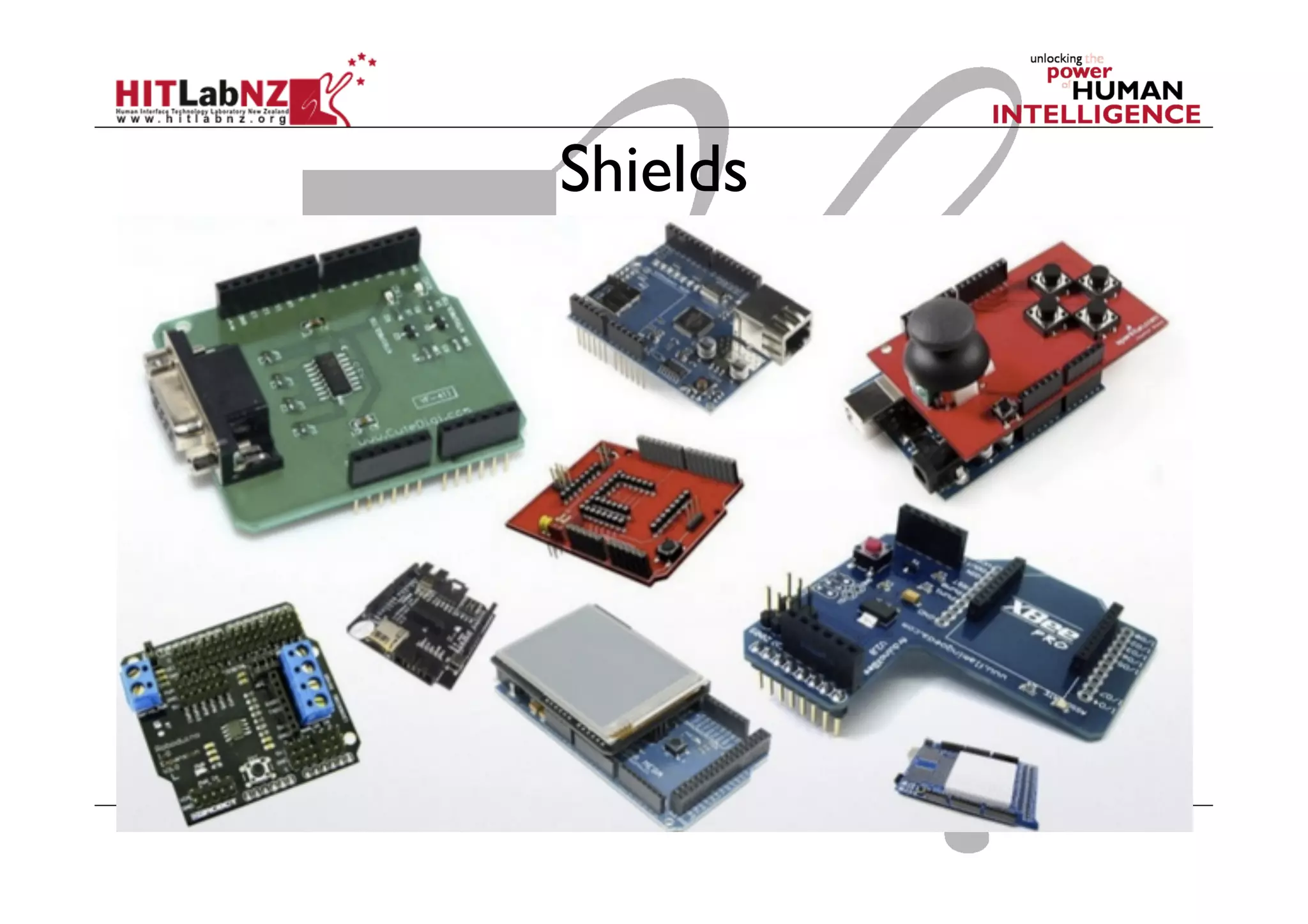
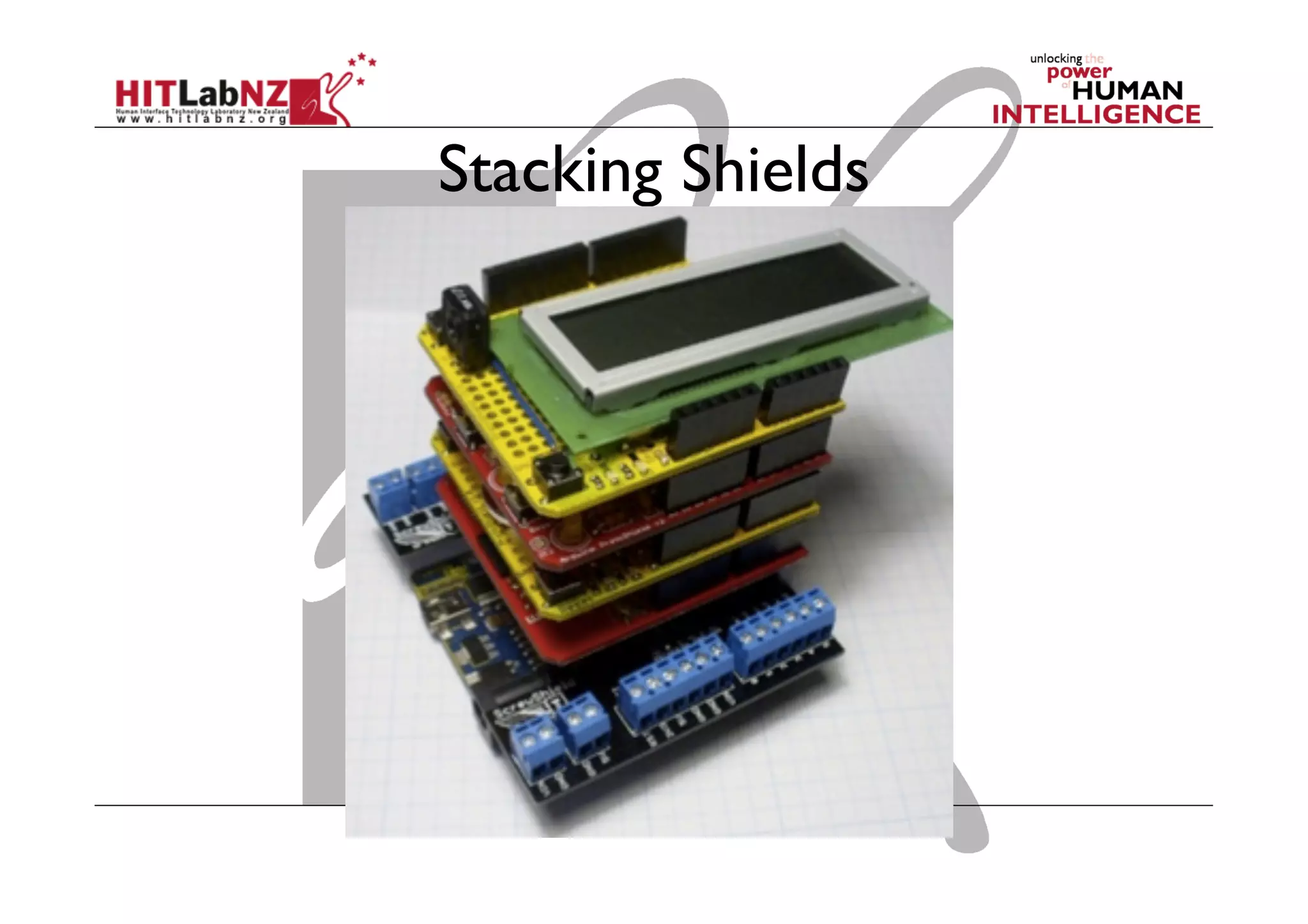
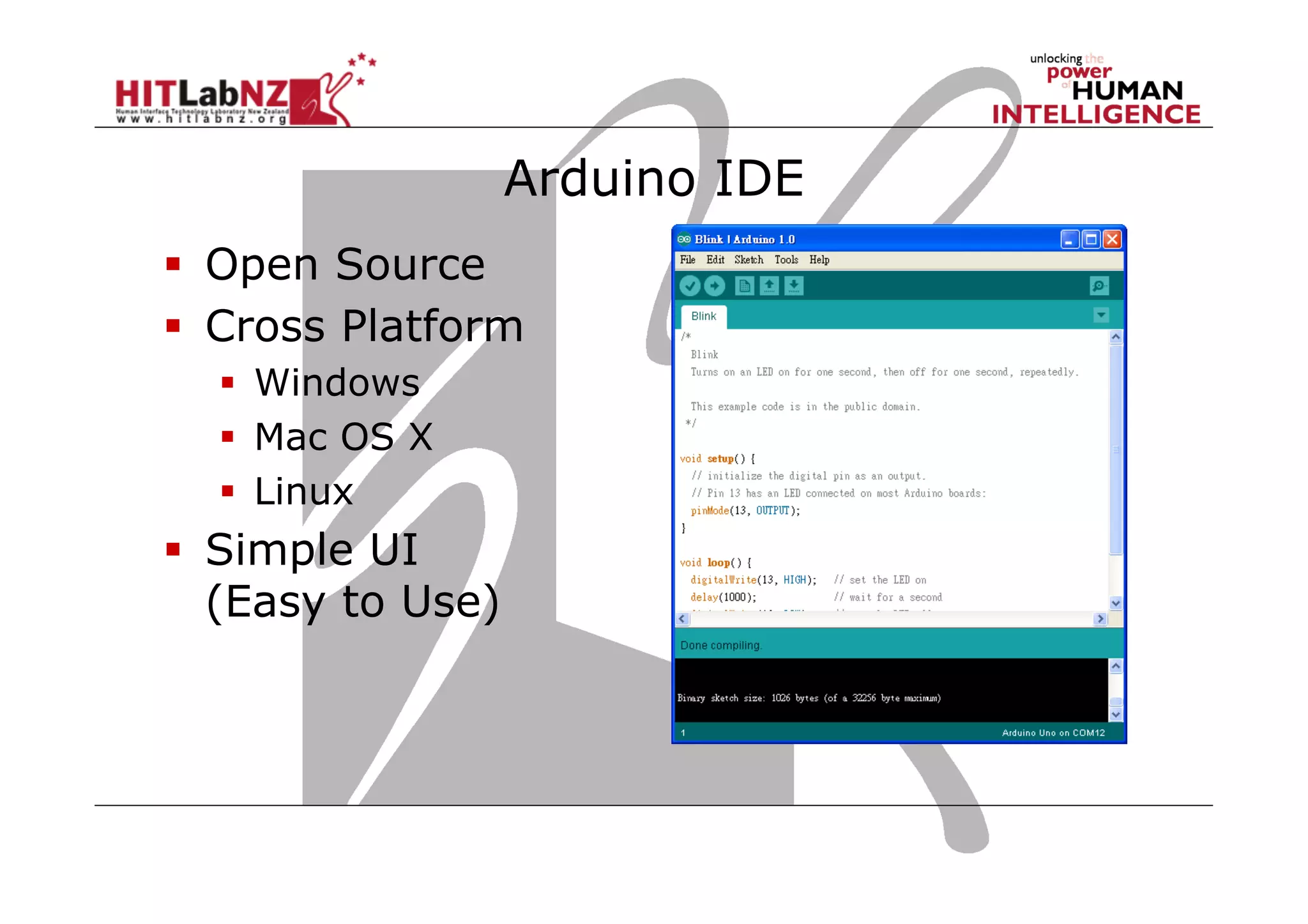
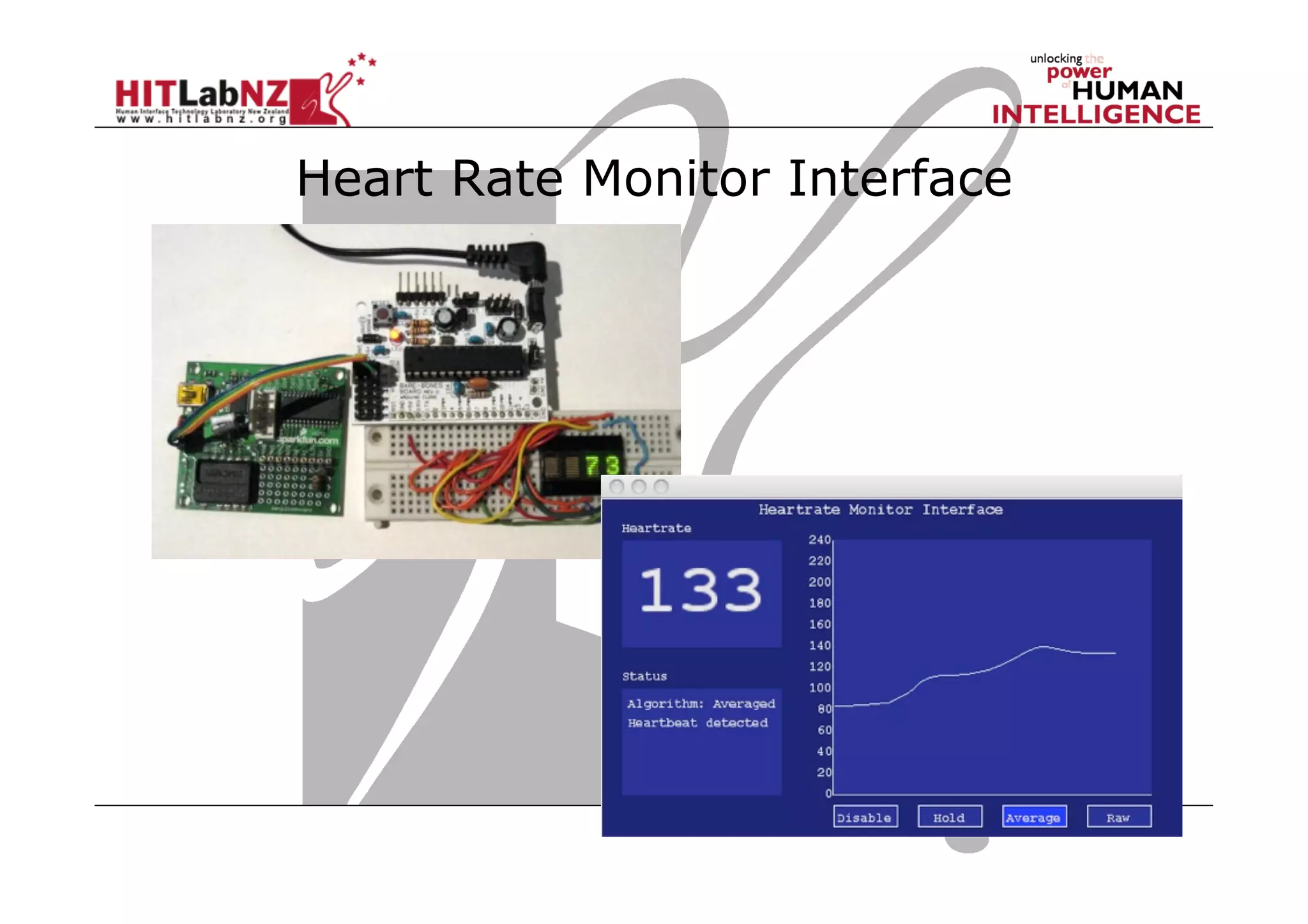
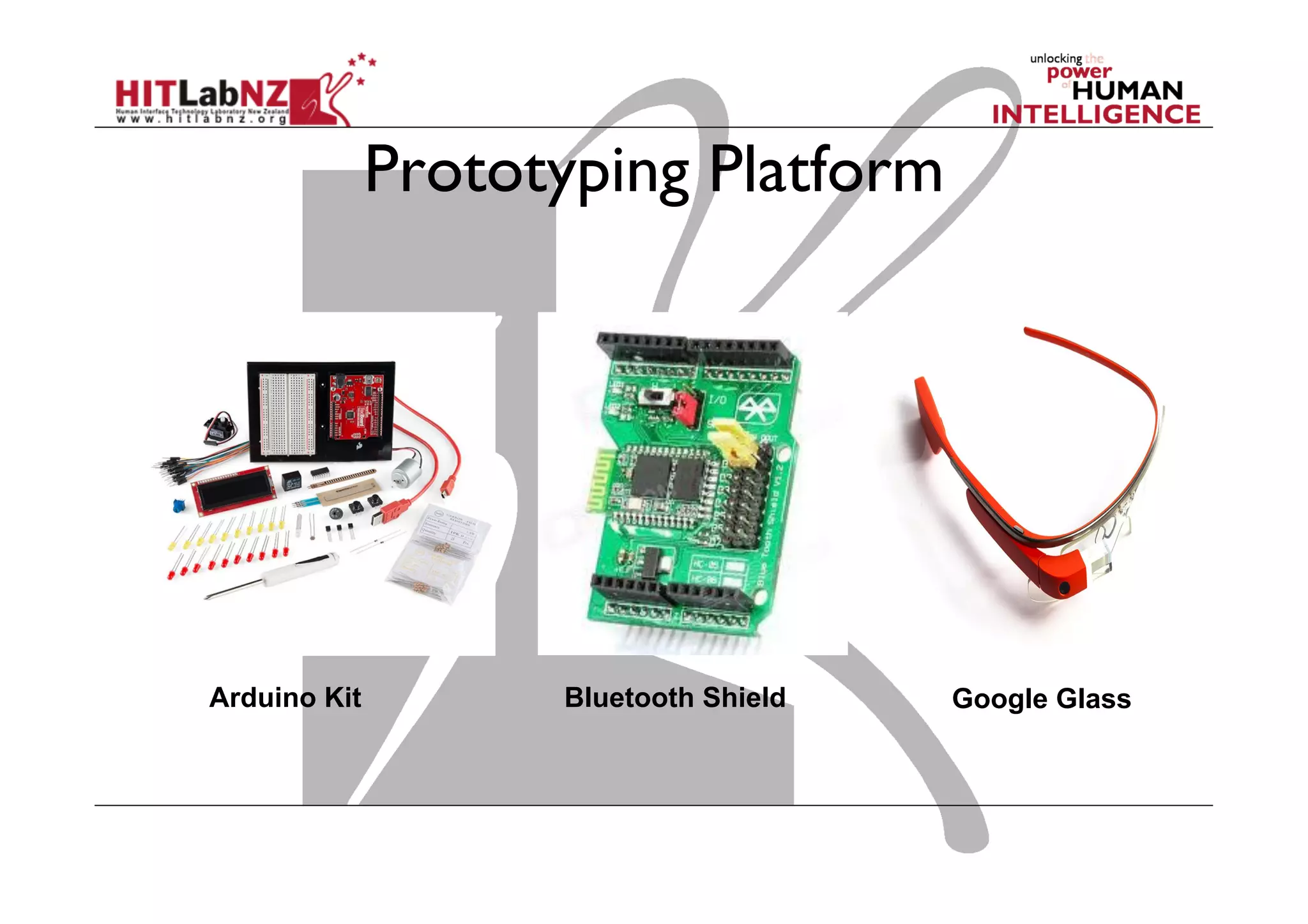
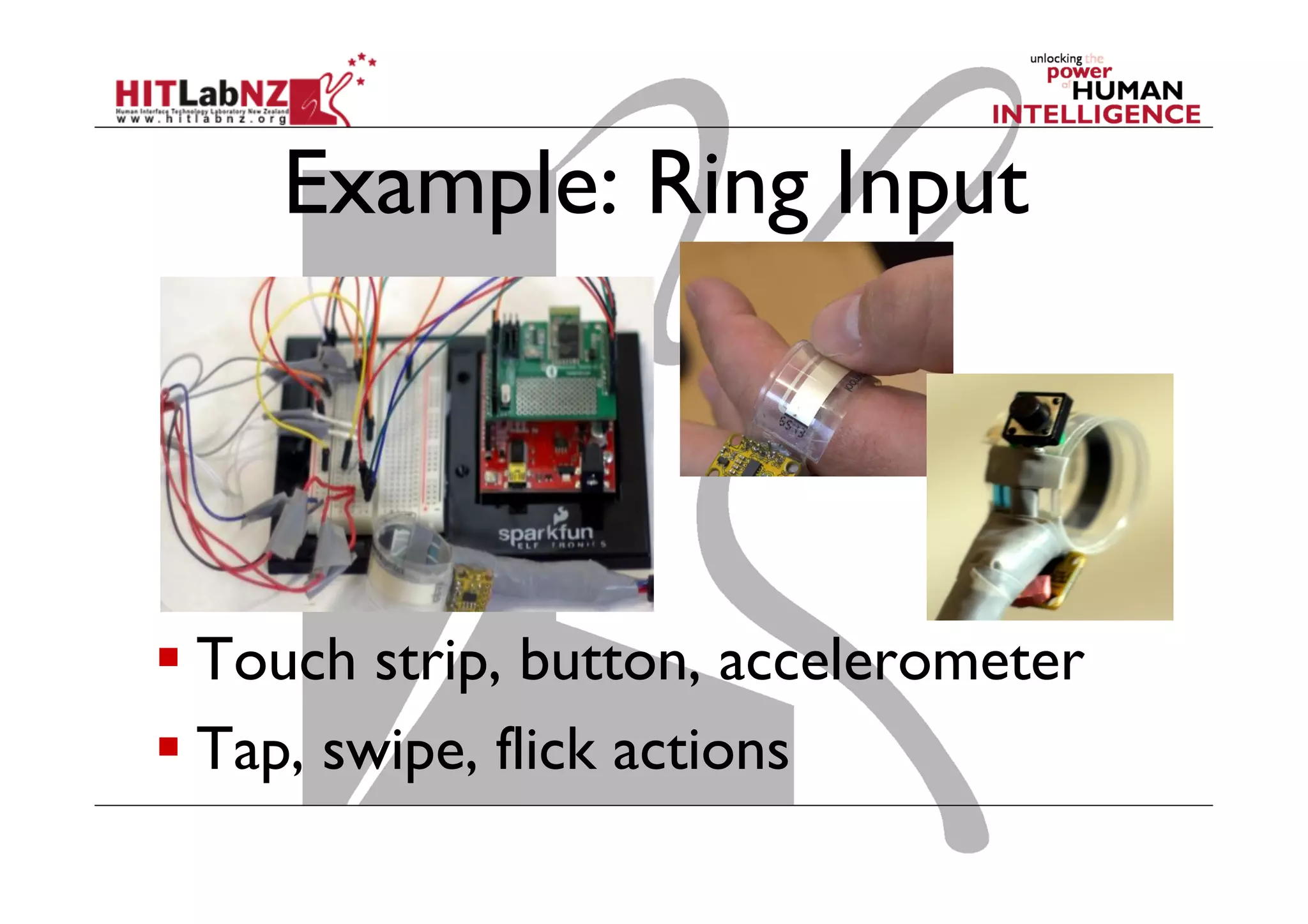
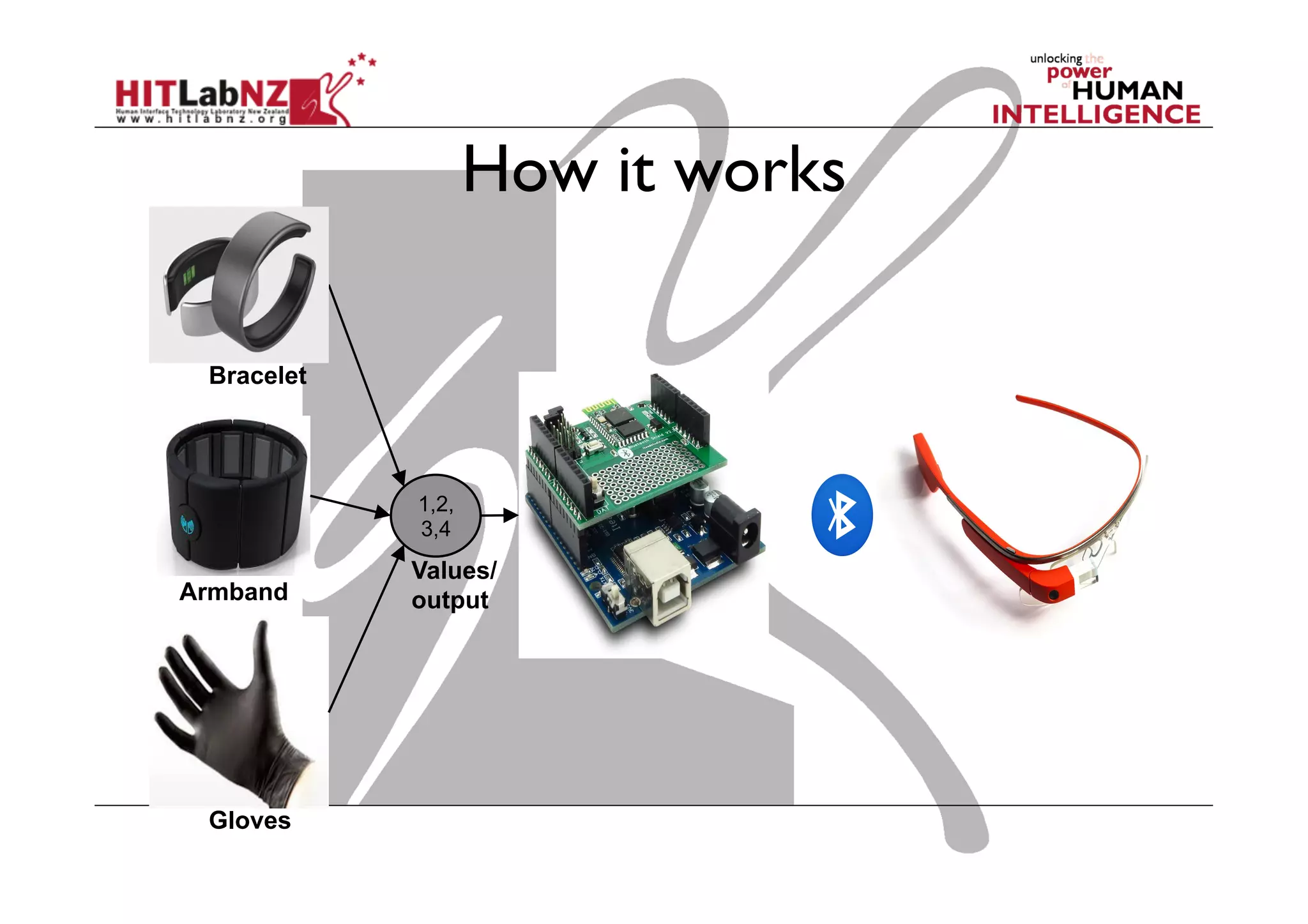
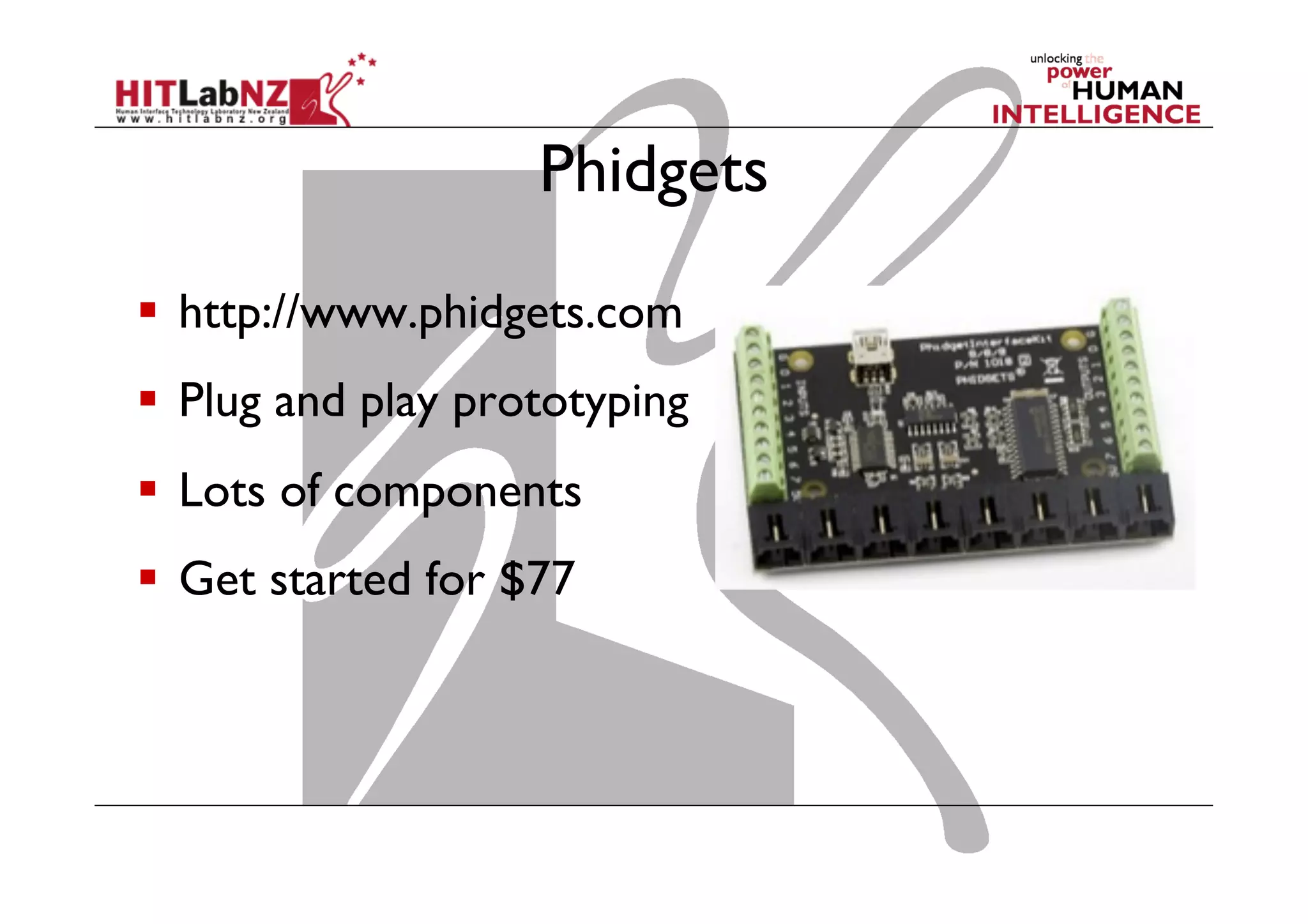
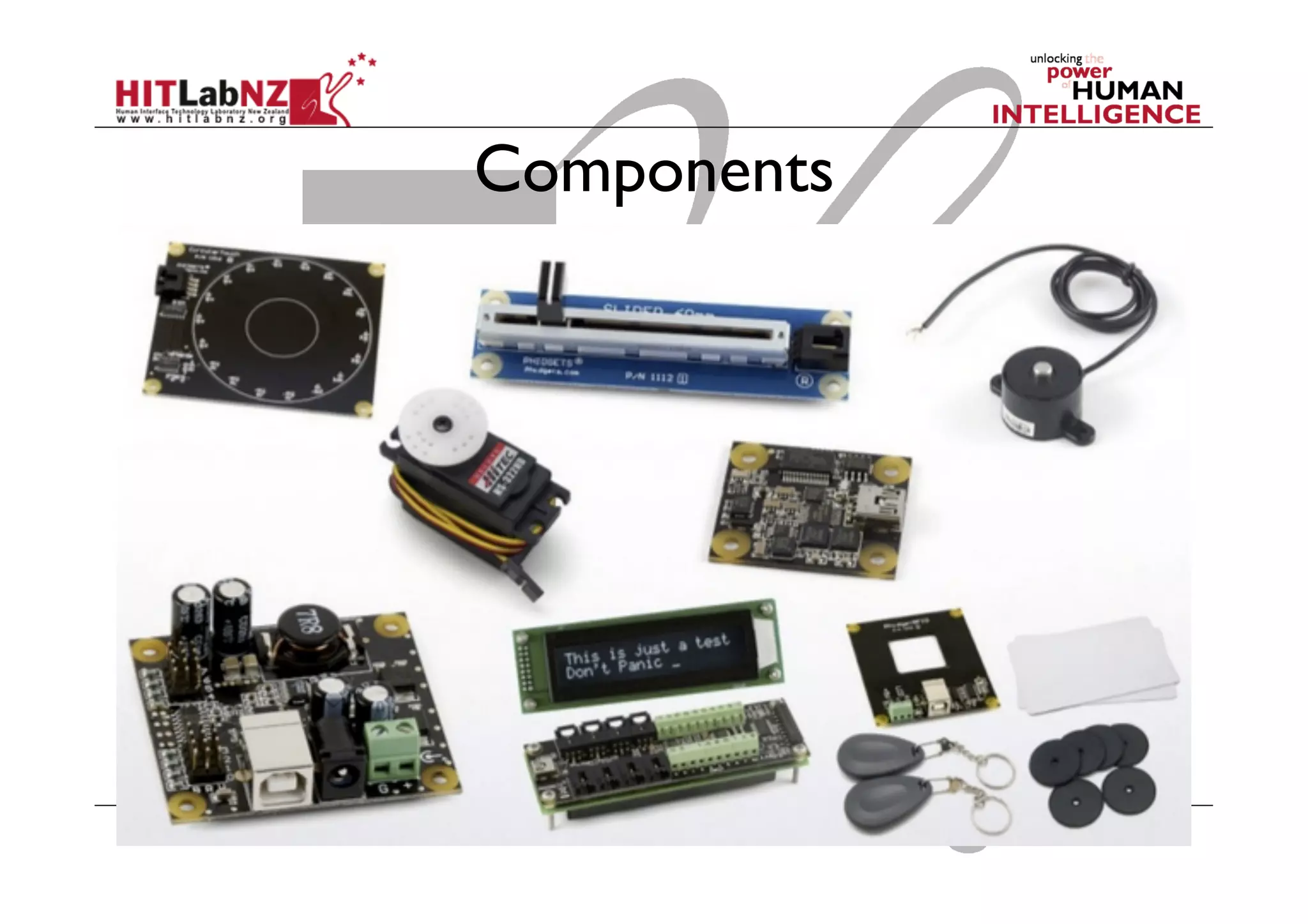
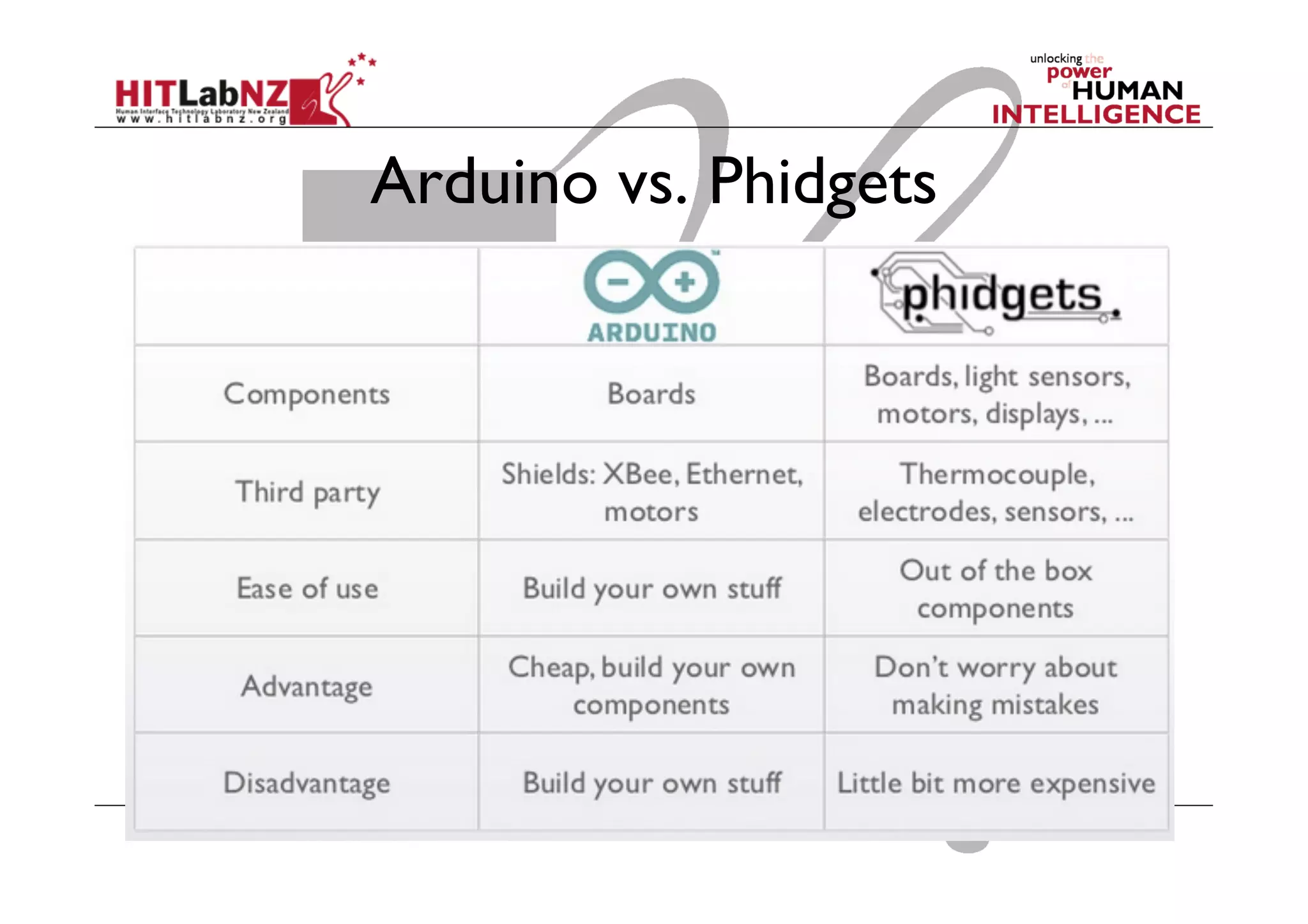
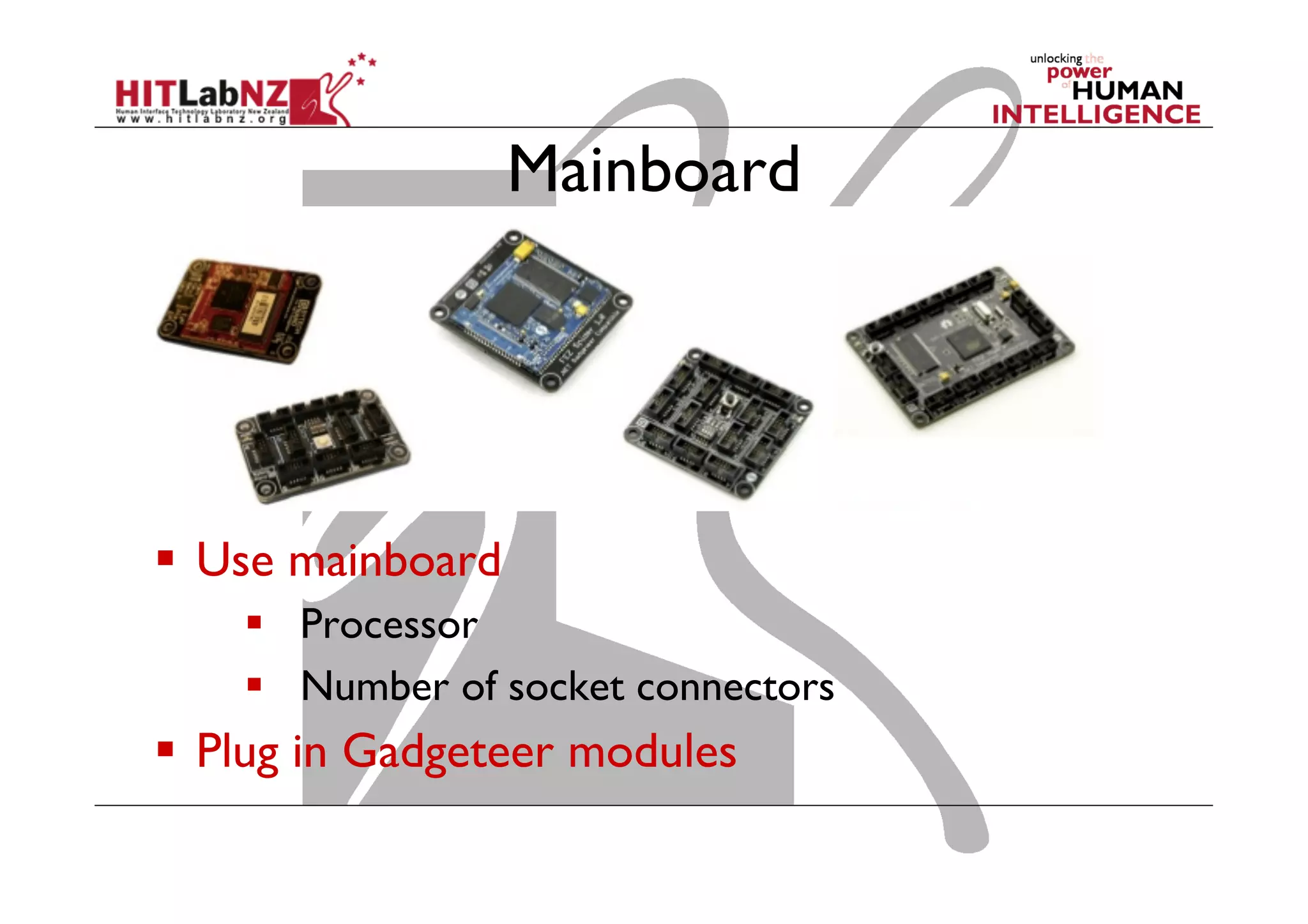
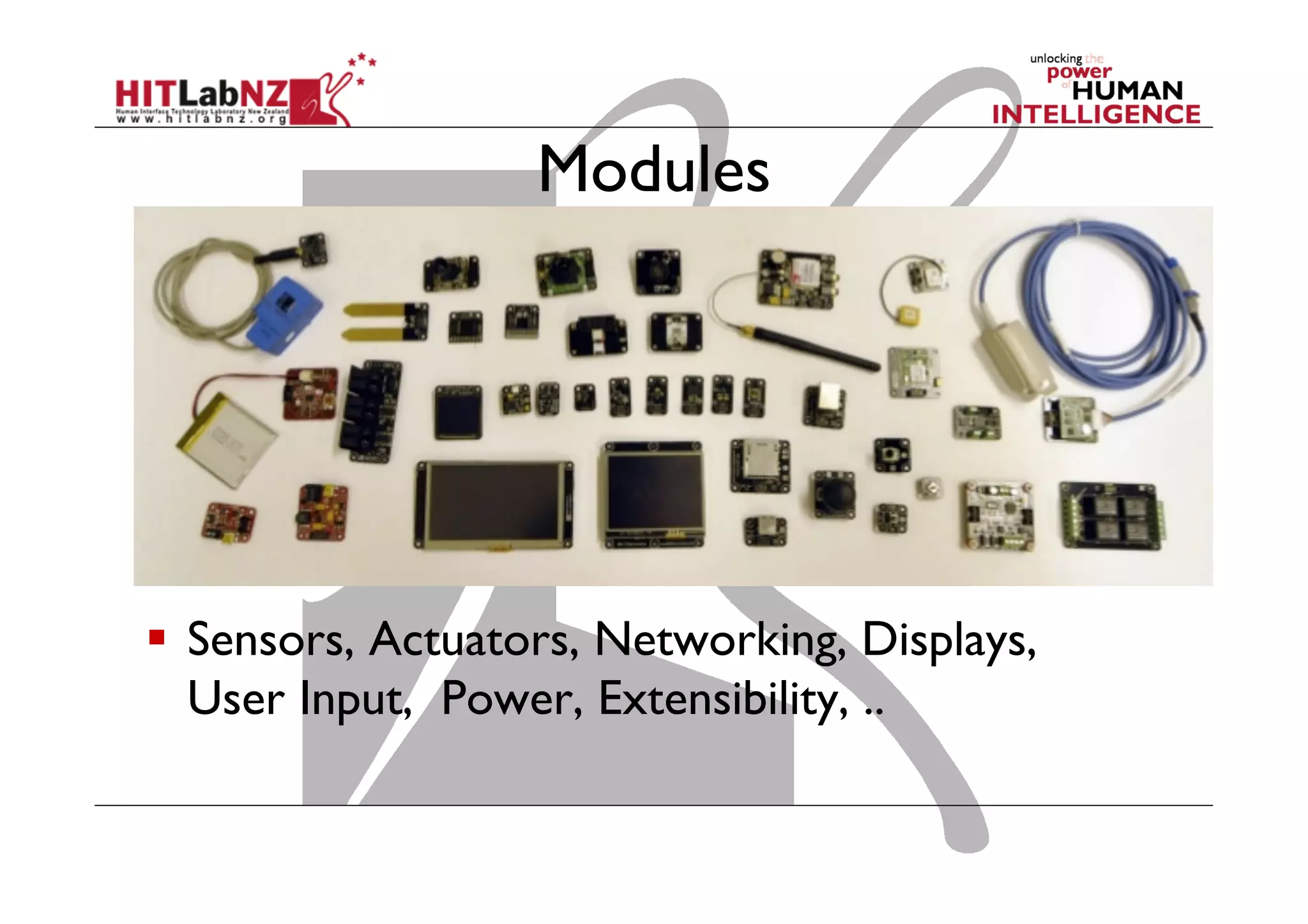
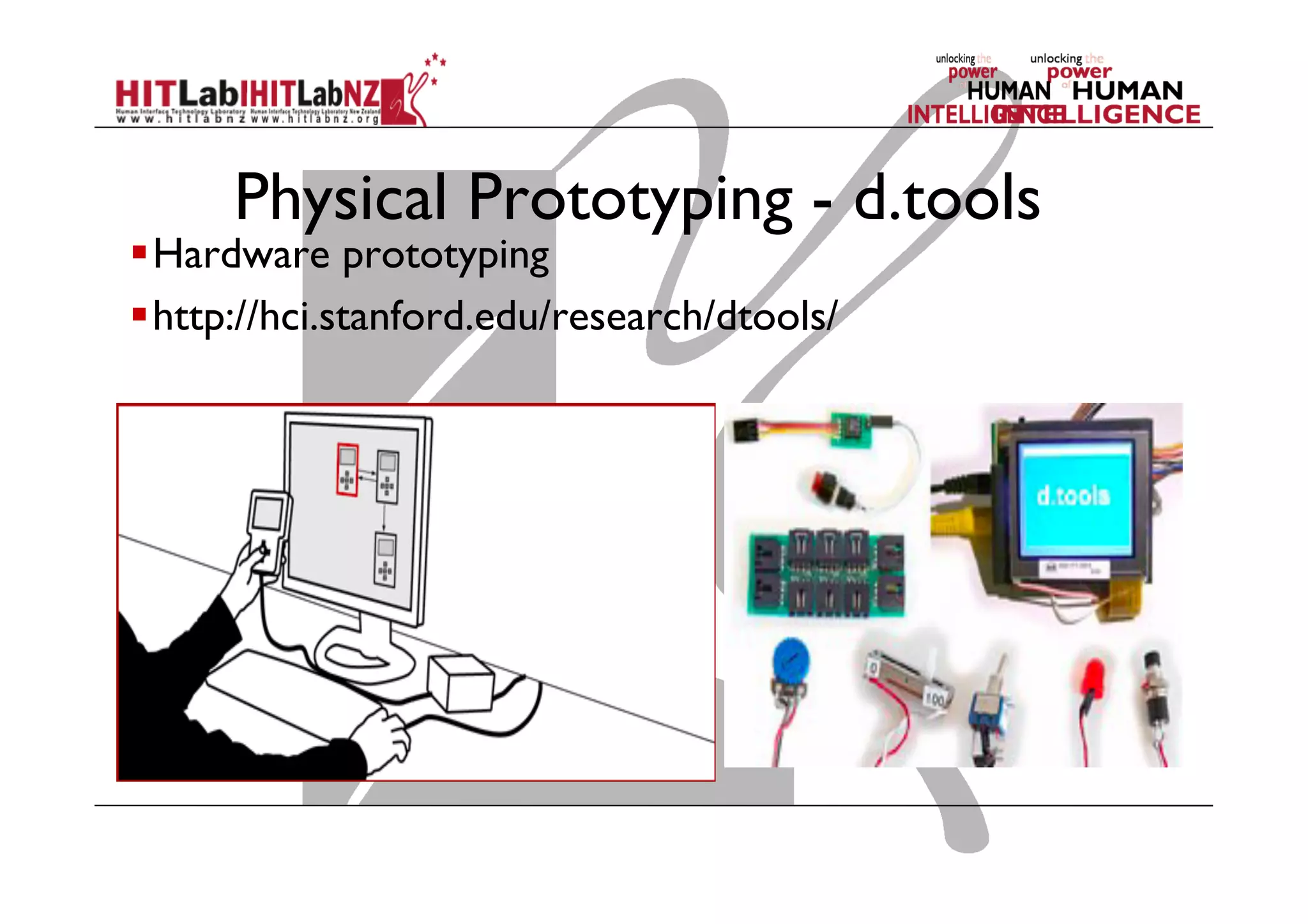
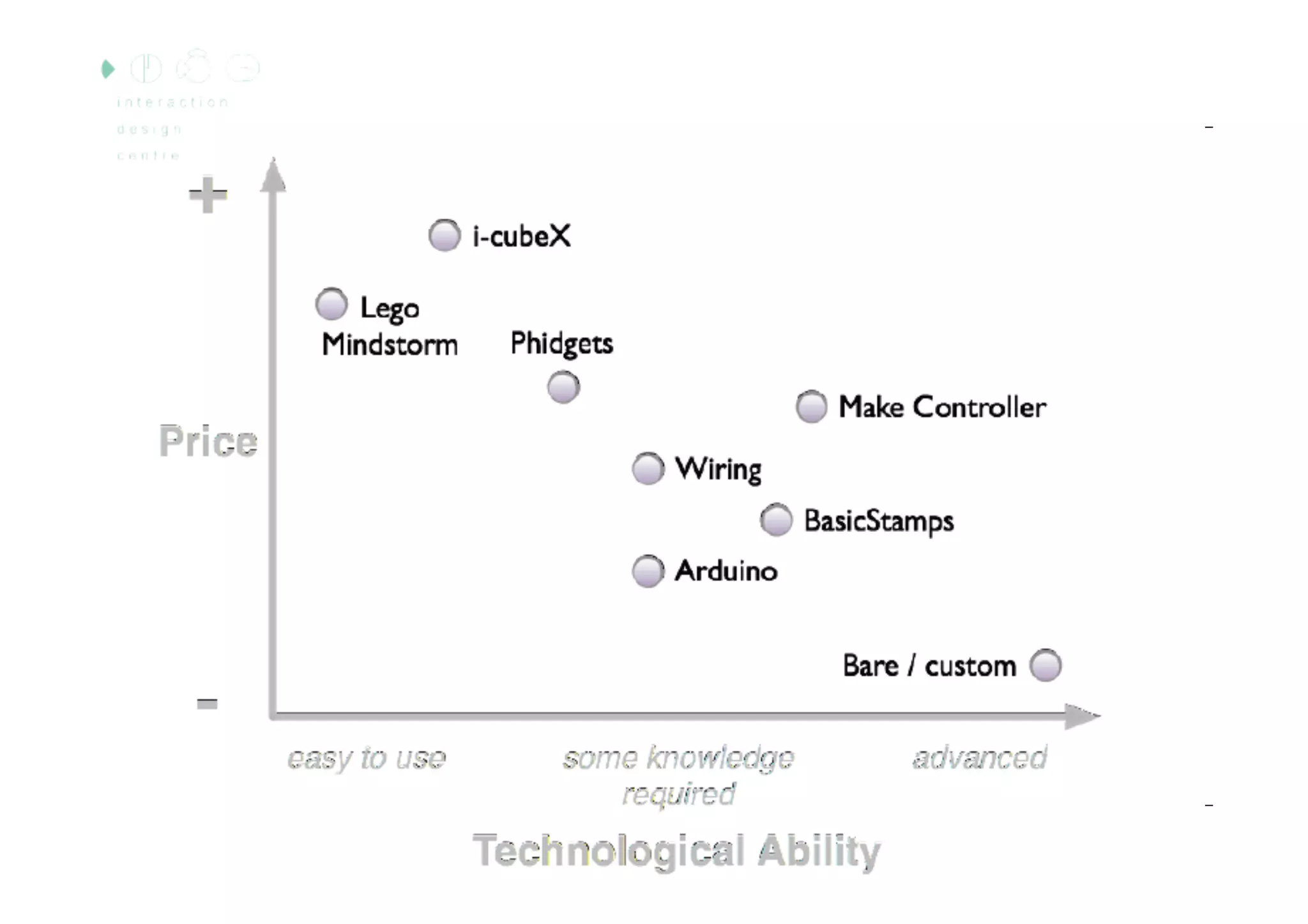
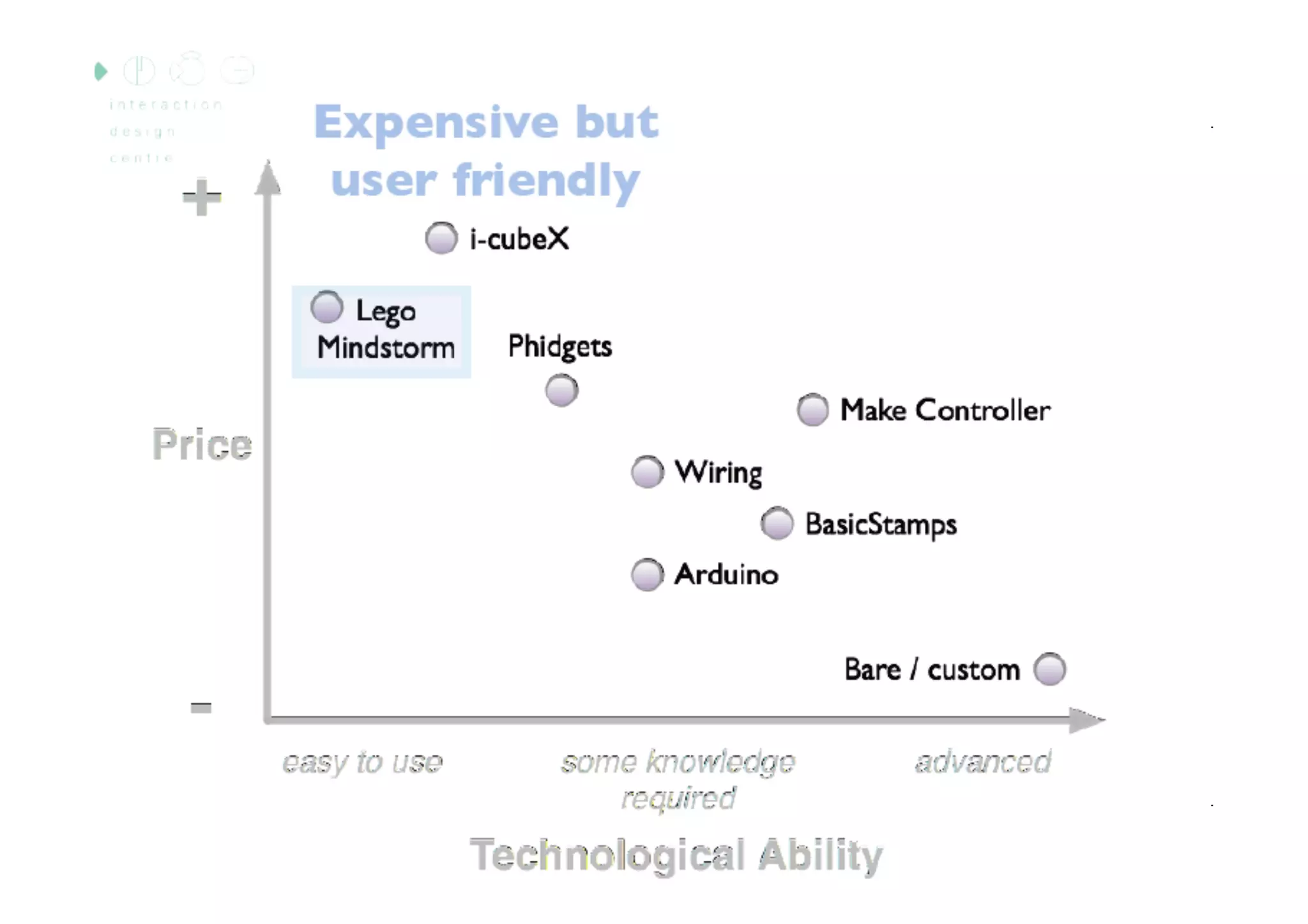
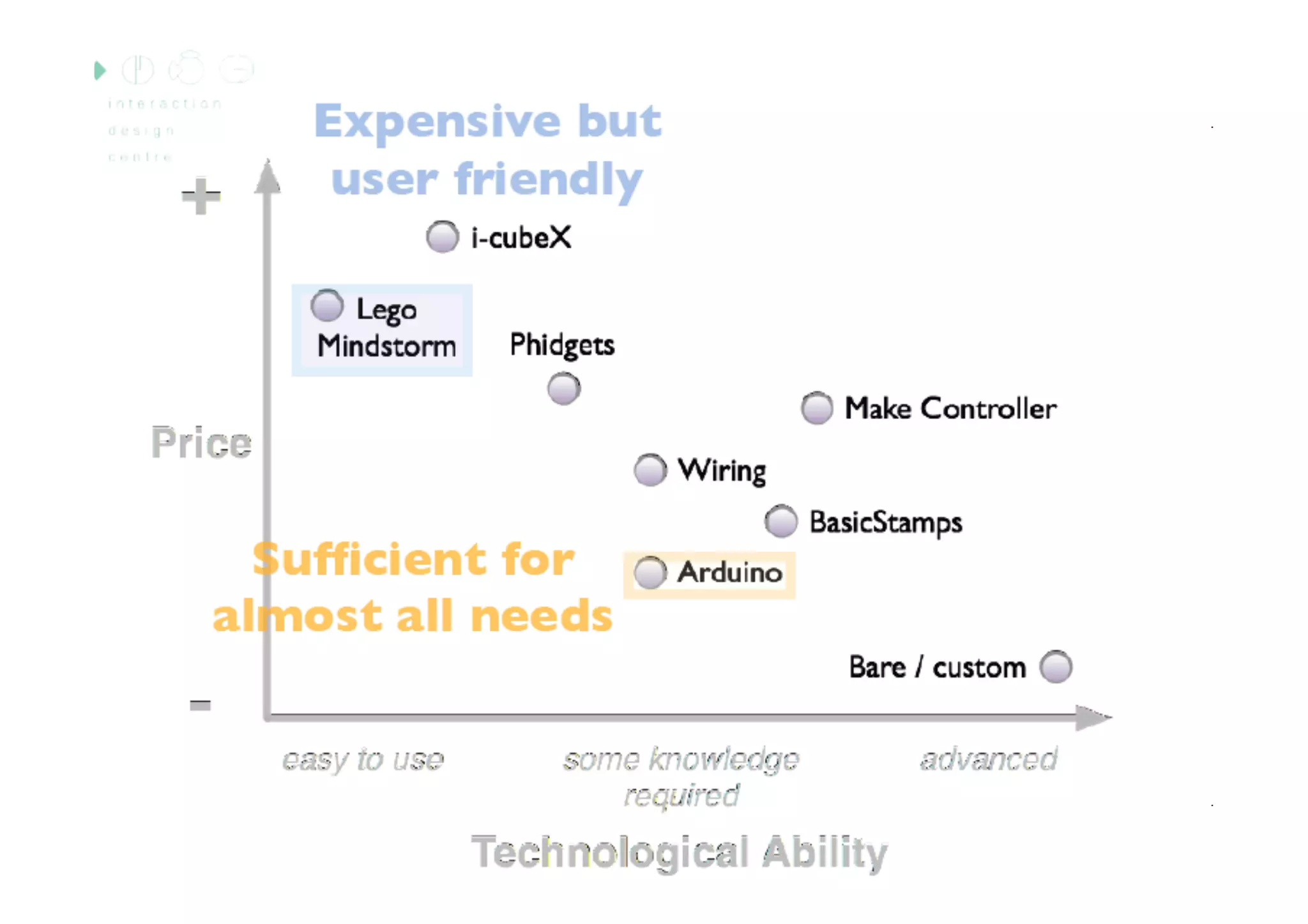
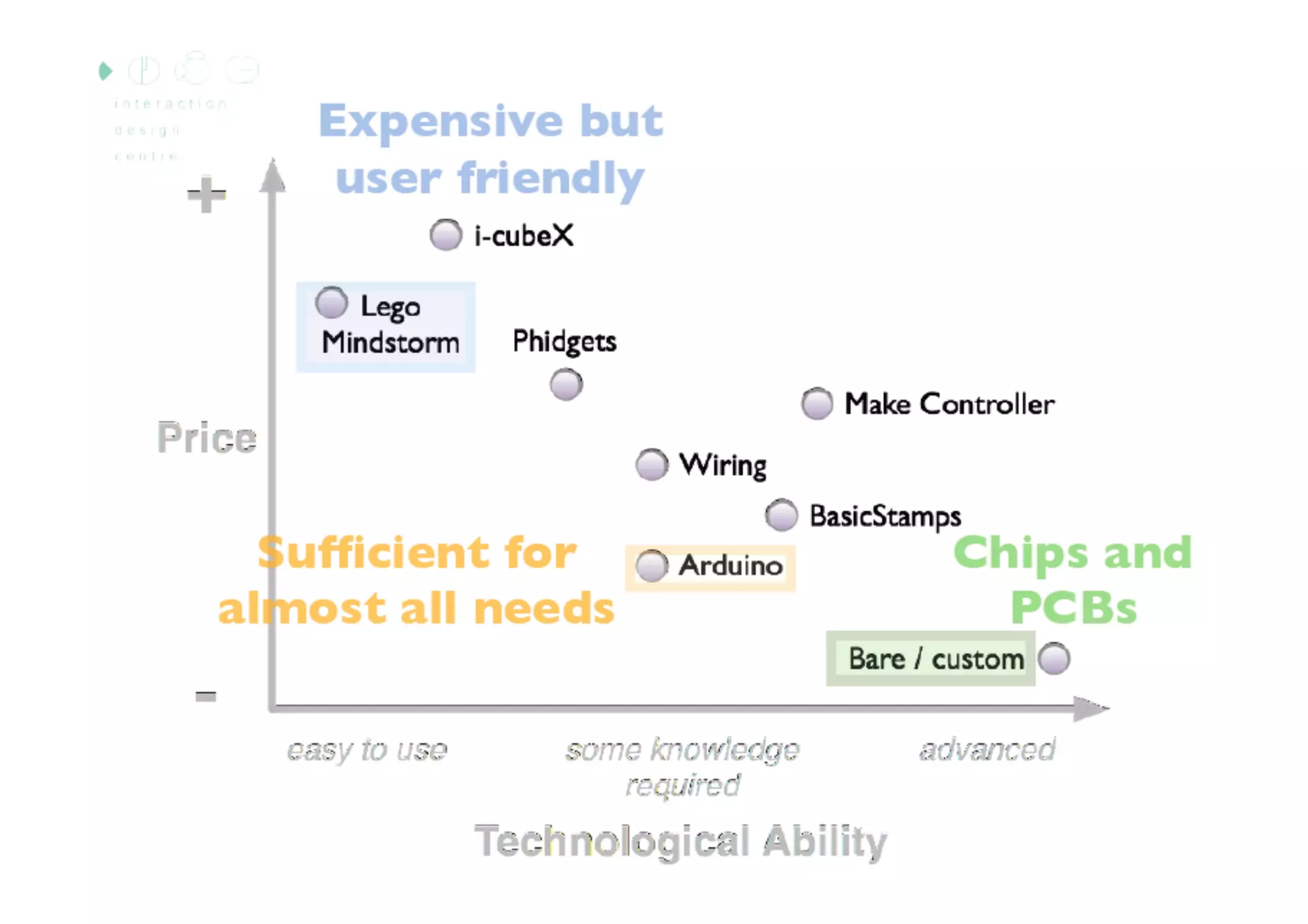
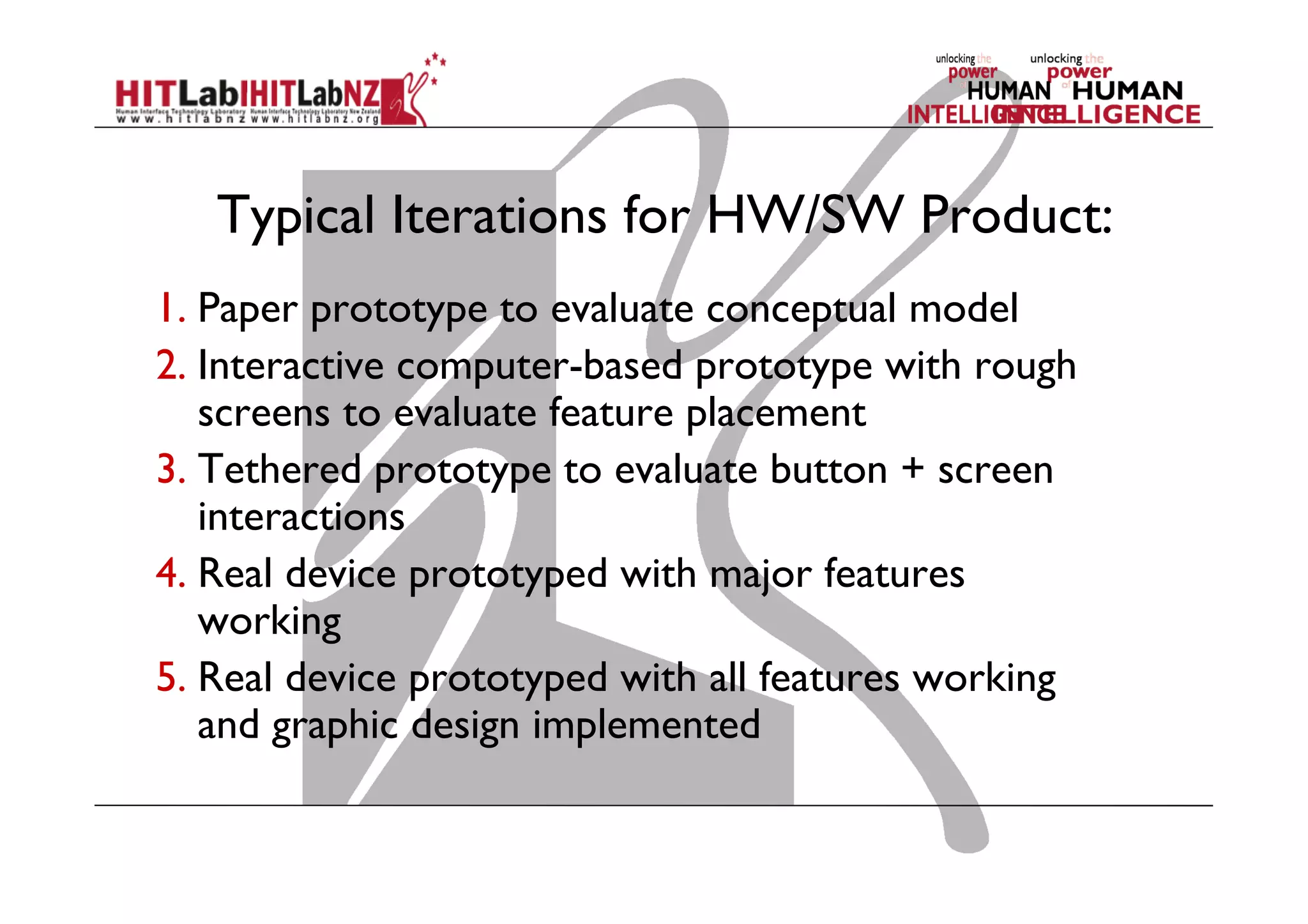
The document discusses prototyping tools for interaction design. It describes the purposes of prototyping as creating early versions of ideas to gain empathy, explore designs, and test with users. A variety of prototyping tools are presented, ranging from low-fidelity sketching and paper prototypes to high-fidelity interactive digital prototypes. Key tools mentioned include UXPin, Axure, Balsamiq, Origami, App Inventor, and Arduino. The document emphasizes that prototypes allow for elaboration and refinement of ideas through repeated testing and user feedback.