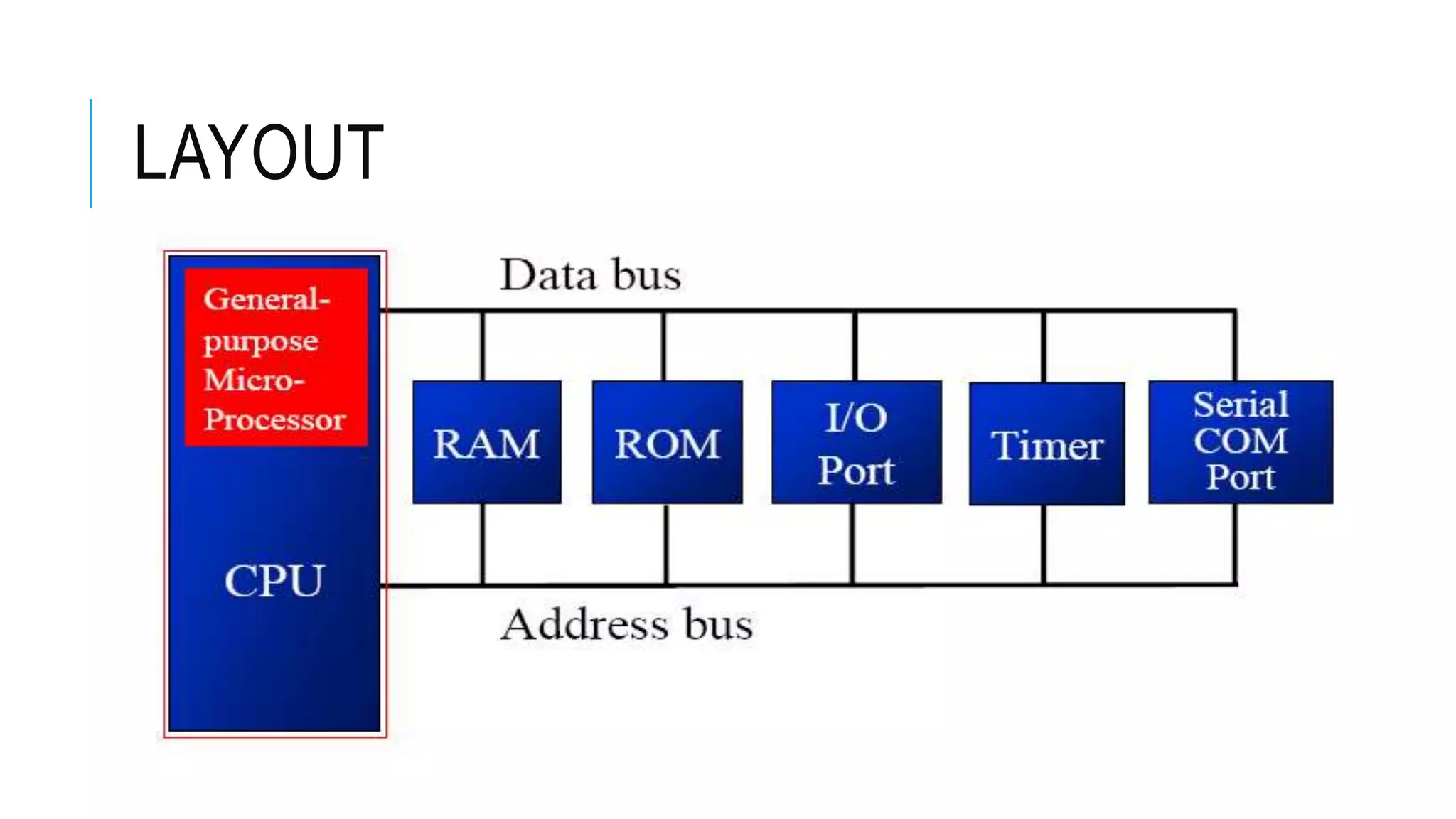
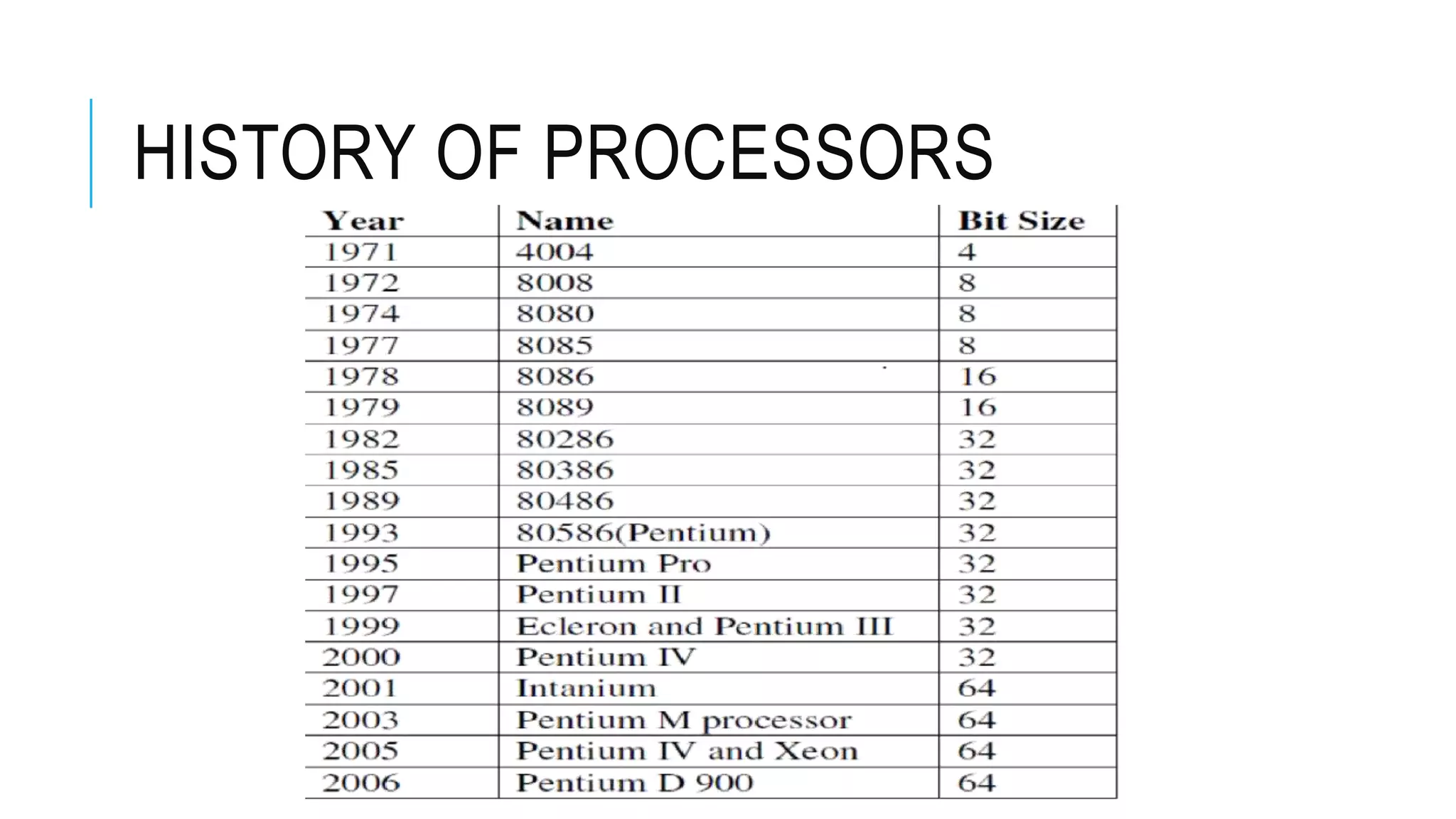
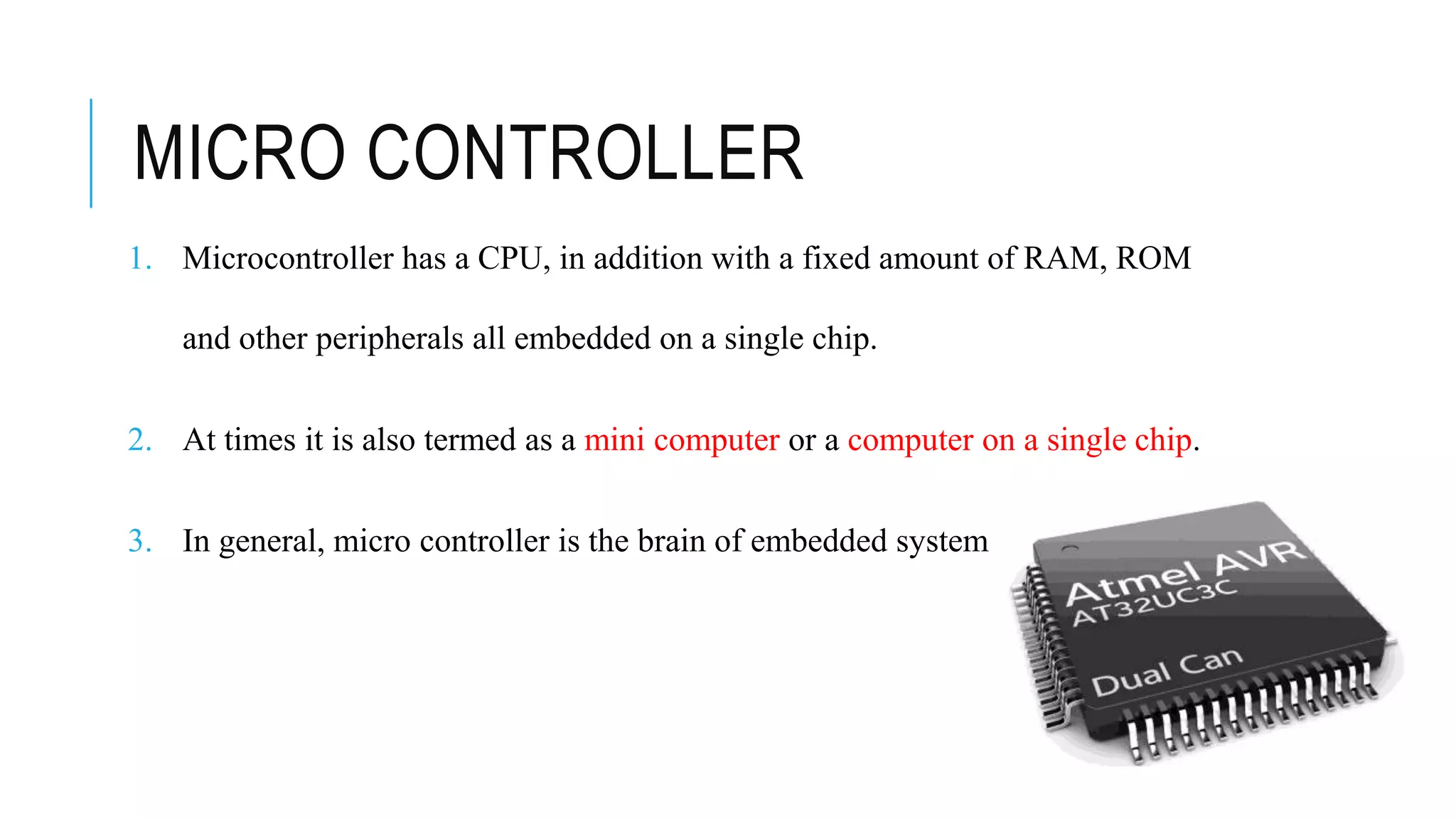
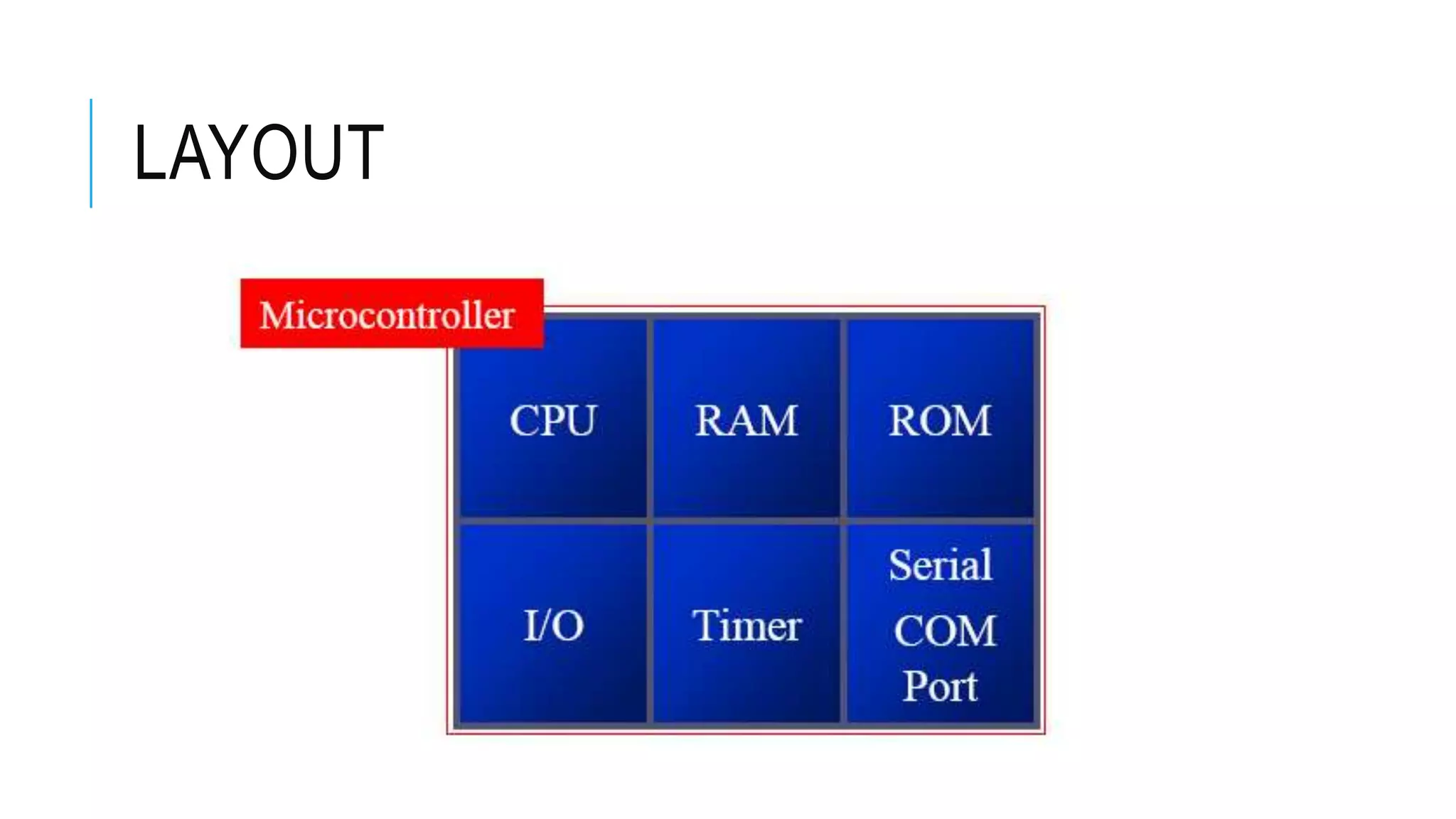
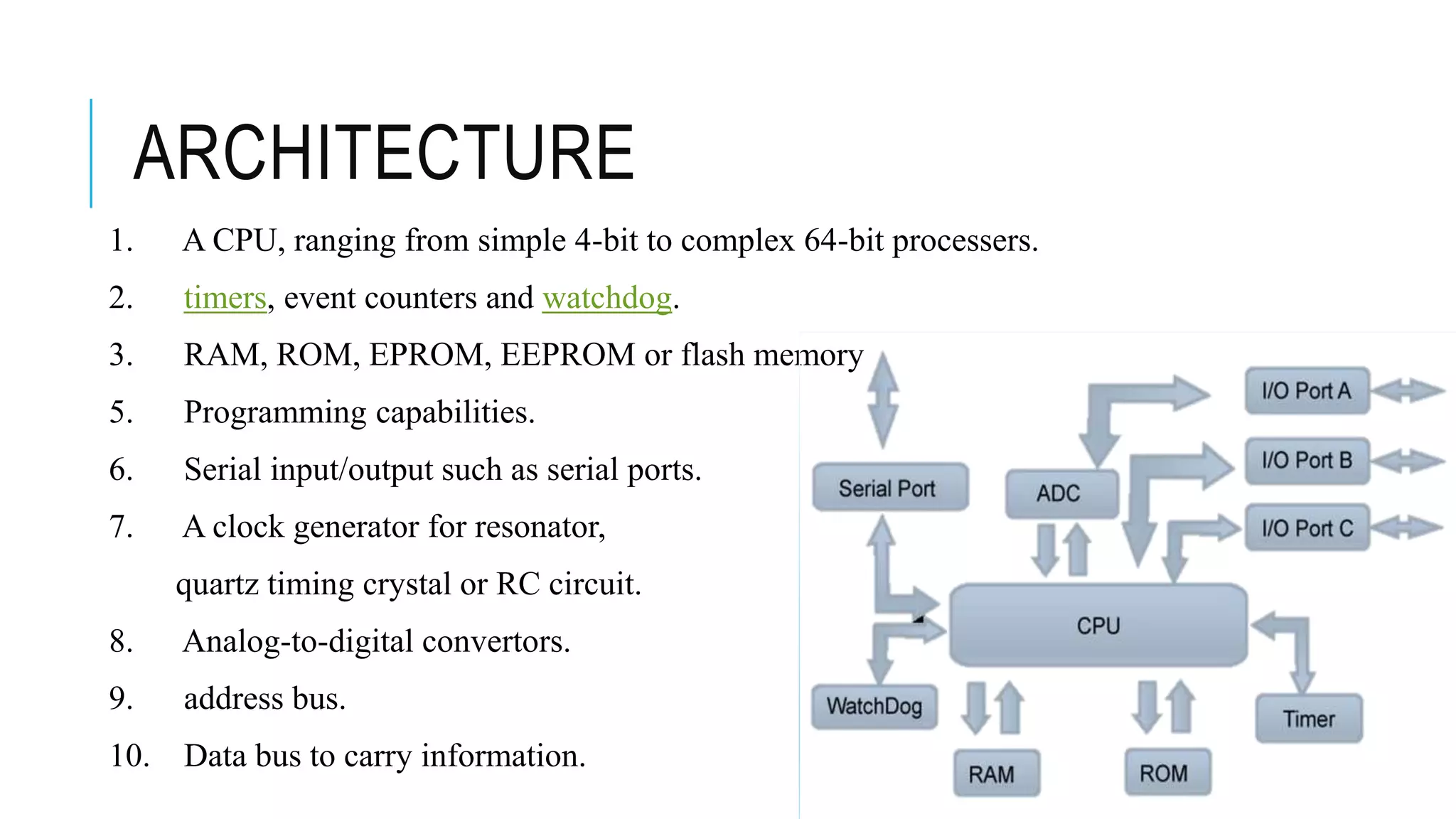
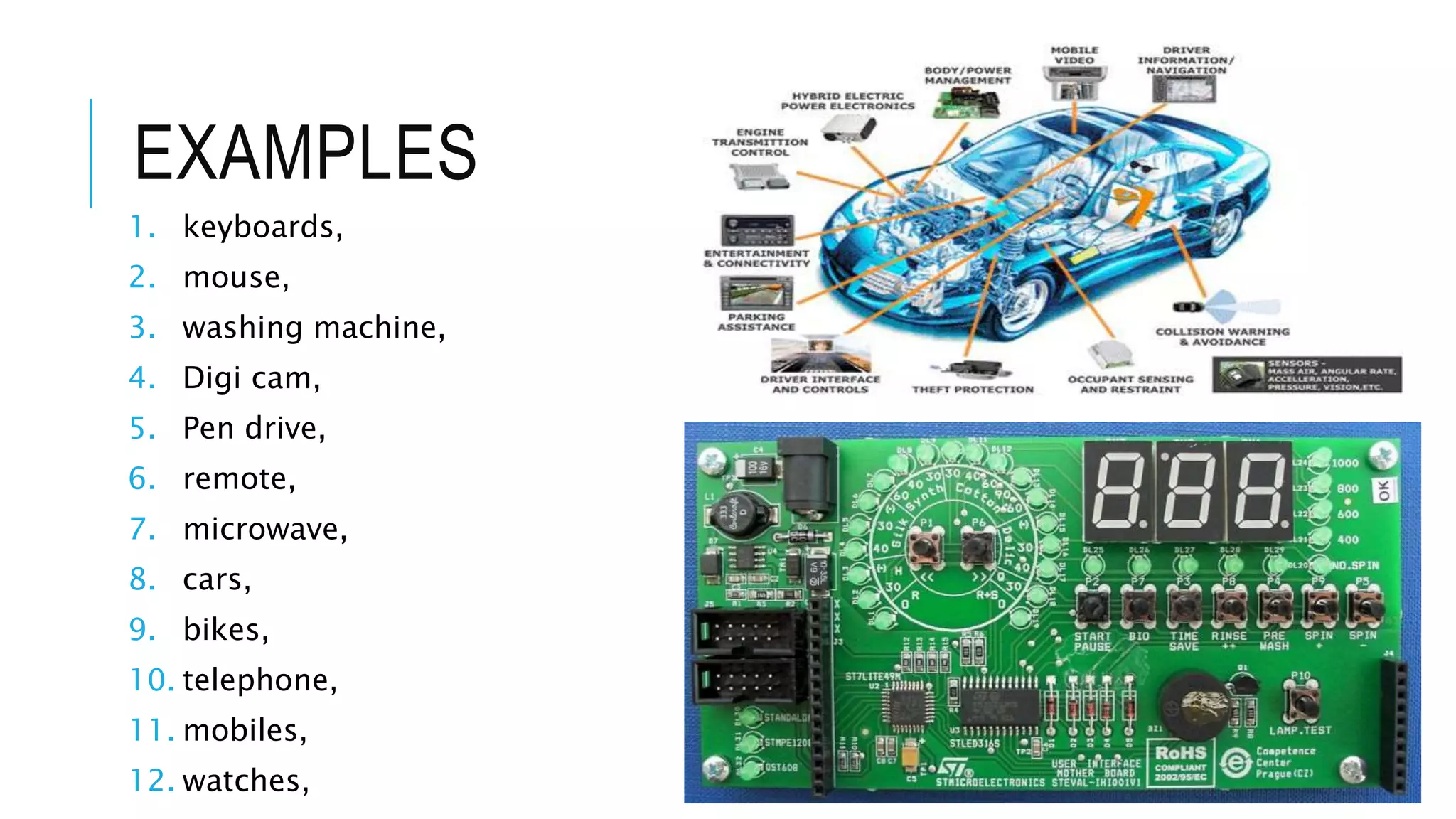
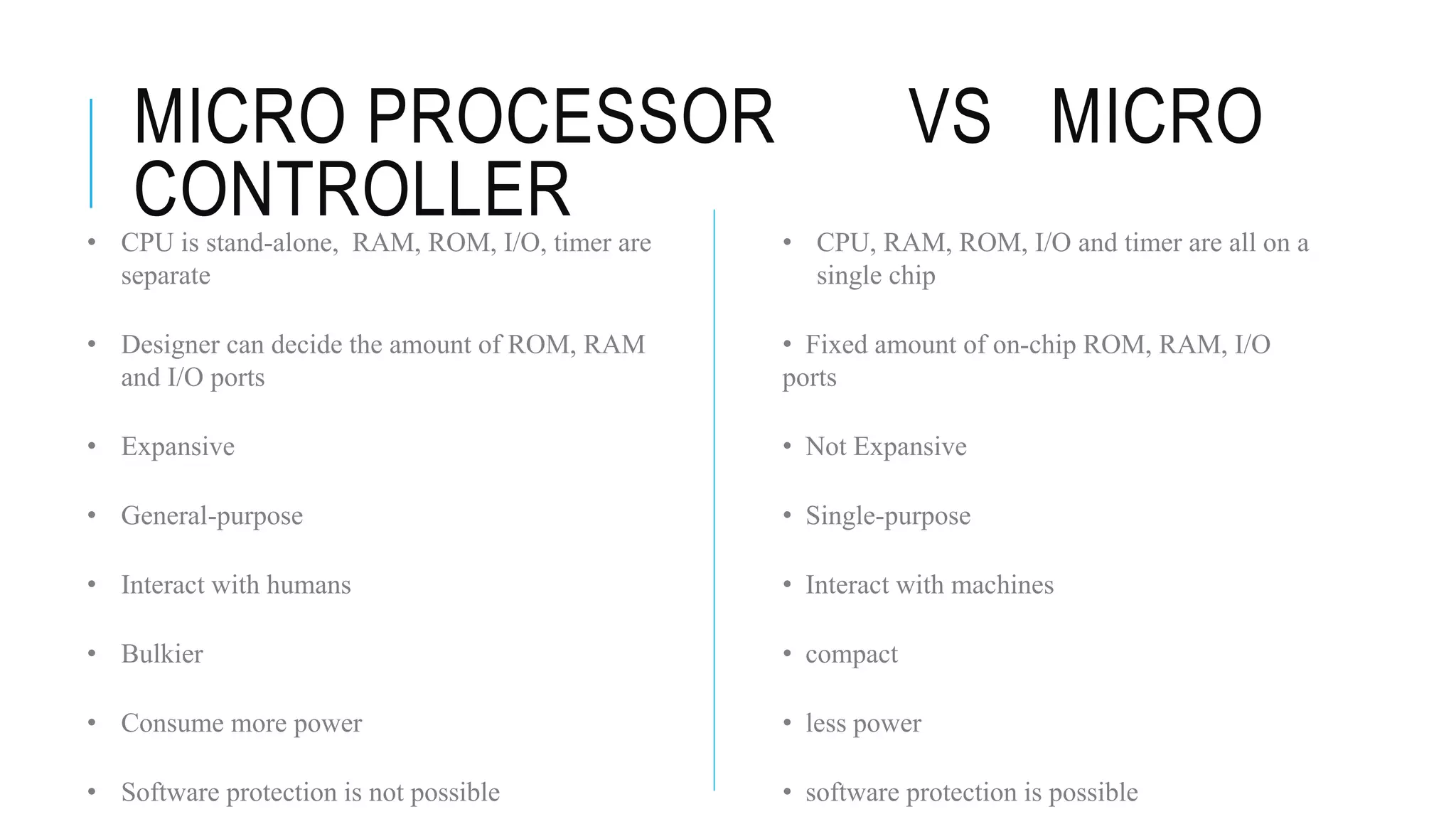
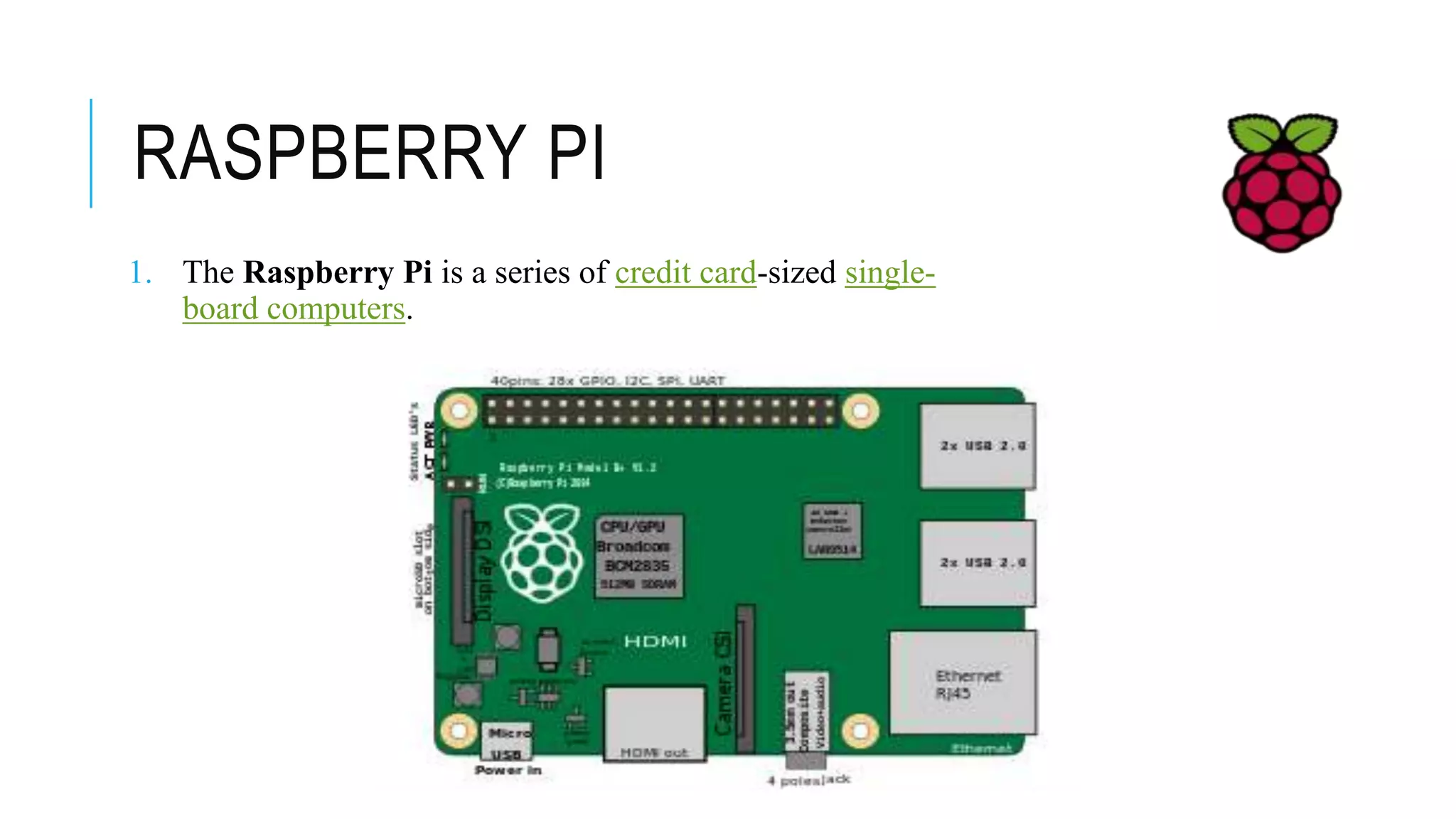
The document provides an overview of the evolution of microprocessors and microcontrollers, detailing their advancements through five generations from serial processing to multi-million transistor designs. It distinguishes between microprocessors, which lack integrated RAM and ROM, and microcontrollers, which are complete systems on a chip with various peripherals. Additionally, it discusses the Raspberry Pi as an affordable, flexible computing solution suitable for learning and various applications.