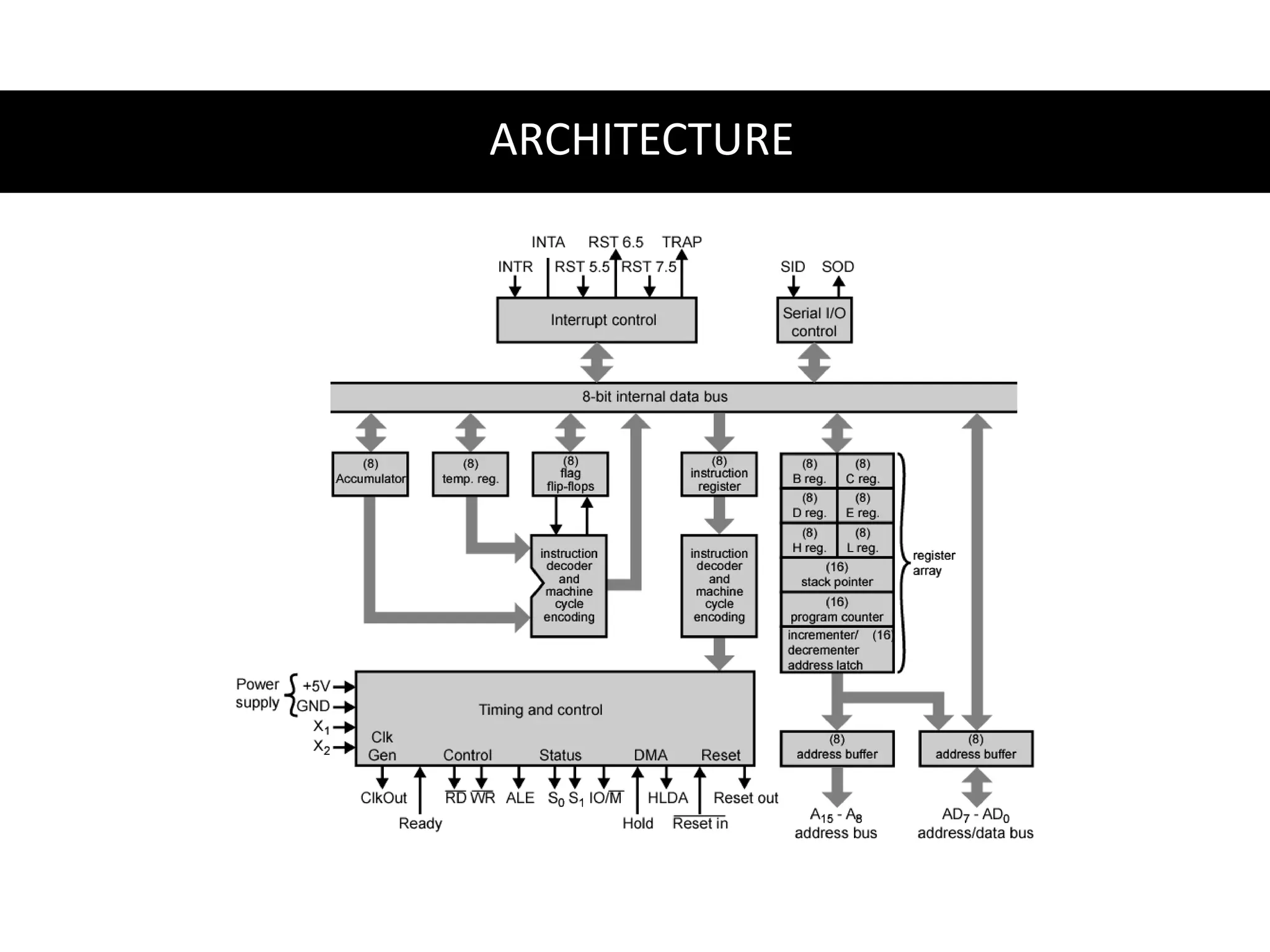
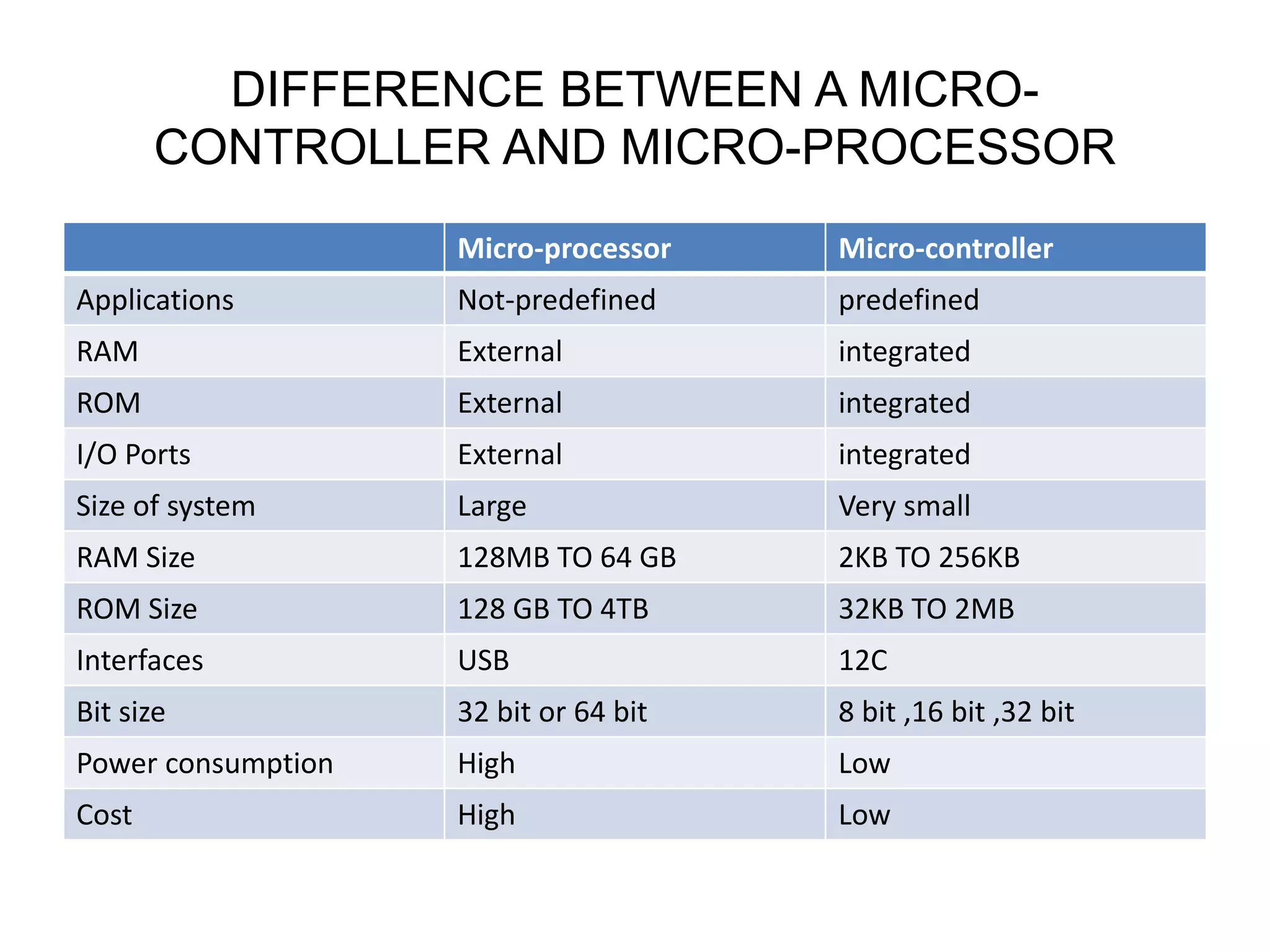
This document compares microprocessors and microcontrollers. It states that a microprocessor is an integrated circuit containing transistors that serves as the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer. A microcontroller, on the other hand, is a highly integrated chip containing a CPU, memory, I/O ports, and timers designed to control a specific system. The key differences are that microprocessors have external memory and interfaces, larger size and power consumption, and are used in non-predefined applications, while microcontrollers have integrated memory and interfaces, smaller size, lower power consumption, and are used in predefined embedded applications.