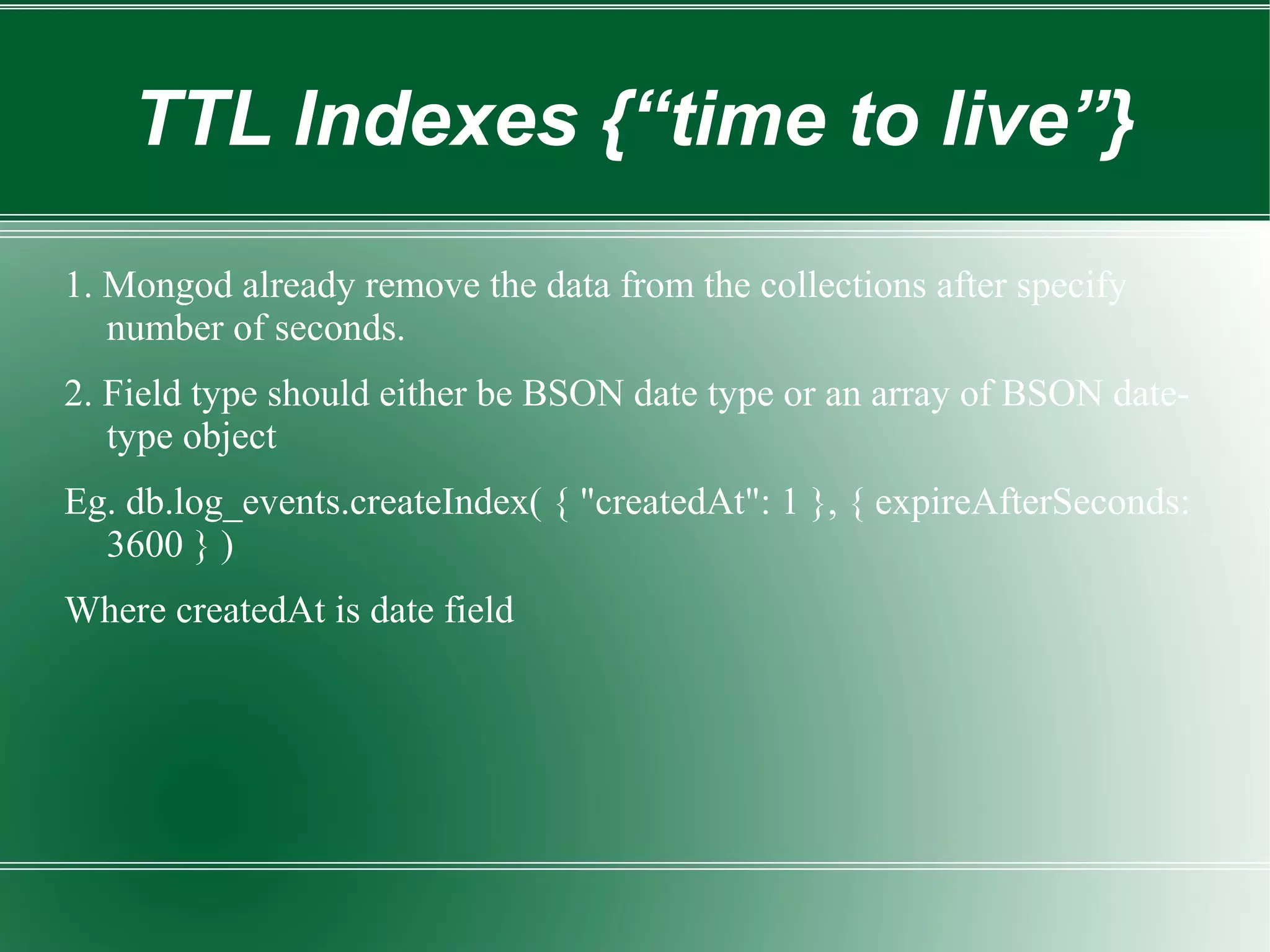
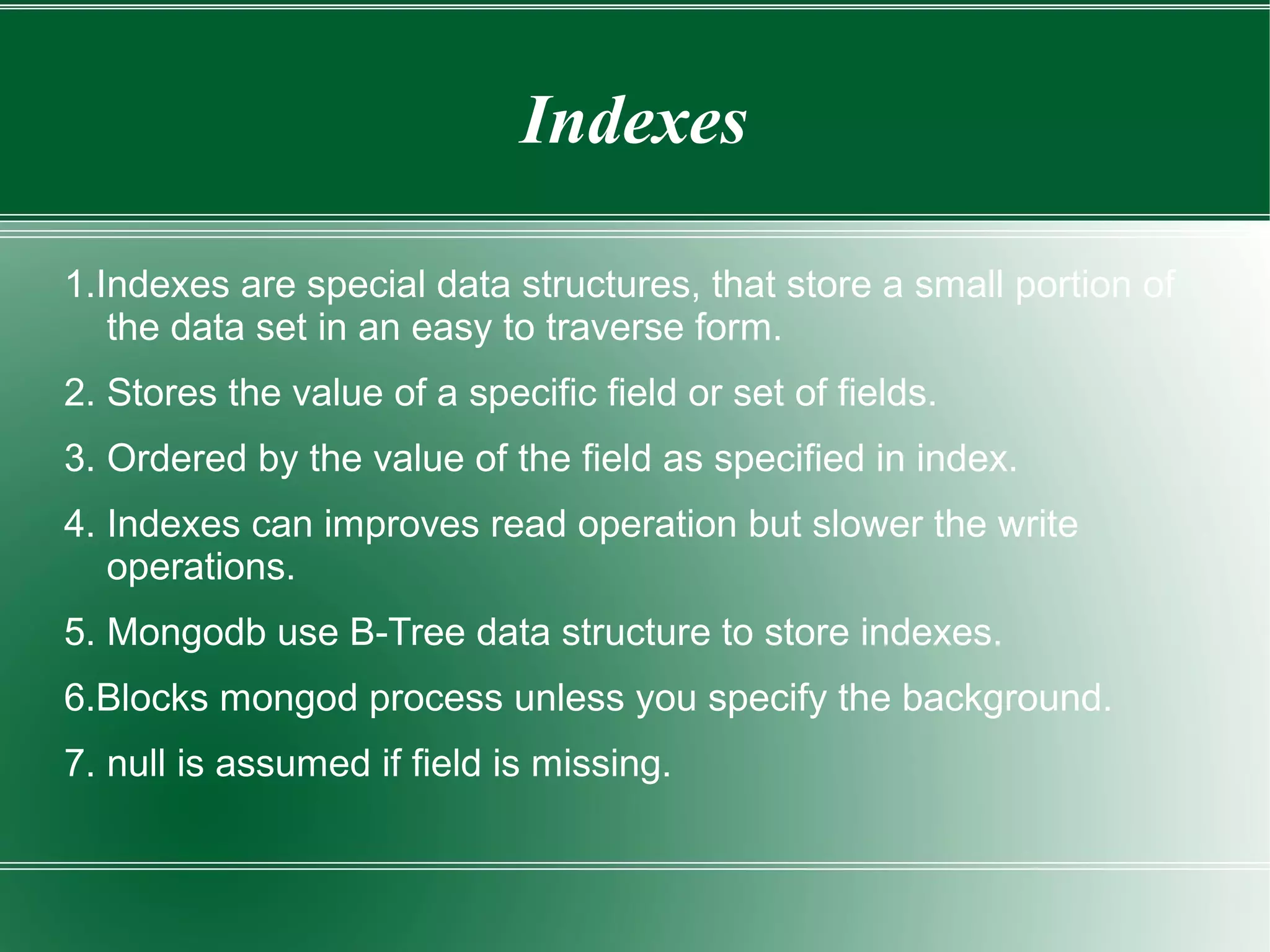
This document provides an introduction to MongoDB, a scalable, high-performance NoSQL database, emphasizing its document-oriented design and ease of use without a predefined schema. It discusses key features like replication, sharding, and indexing, while also highlighting MongoDB's strengths in real-time analytics and content management. Additionally, the document includes practical examples, schema design considerations, and CRUD operations relevant to MongoDB.





![Mongo Schema
{
“_id” : ObjectId("55b1f50899708bec87f96edc")
“title” : “MongoDB Tutorial for beginner”,
“description: “How to start using mongodb”,
“by: Anuj Jain,
“url: “http://mongodbtutorial.com/blog/mongodb”,
“tags” : ['mongodb', 'nosql' ],
“likes” : 200,
“comments” : [
{
“user” : ''MongoUser”,
“message” : “Very Nice Tutorial” ,
“dateCreated” : NumberLong(1437725960469),
“like” : true
}
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbtutorials-150818122125-lva1-app6891/75/Mongo-db-tutorials-11-2048.jpg)





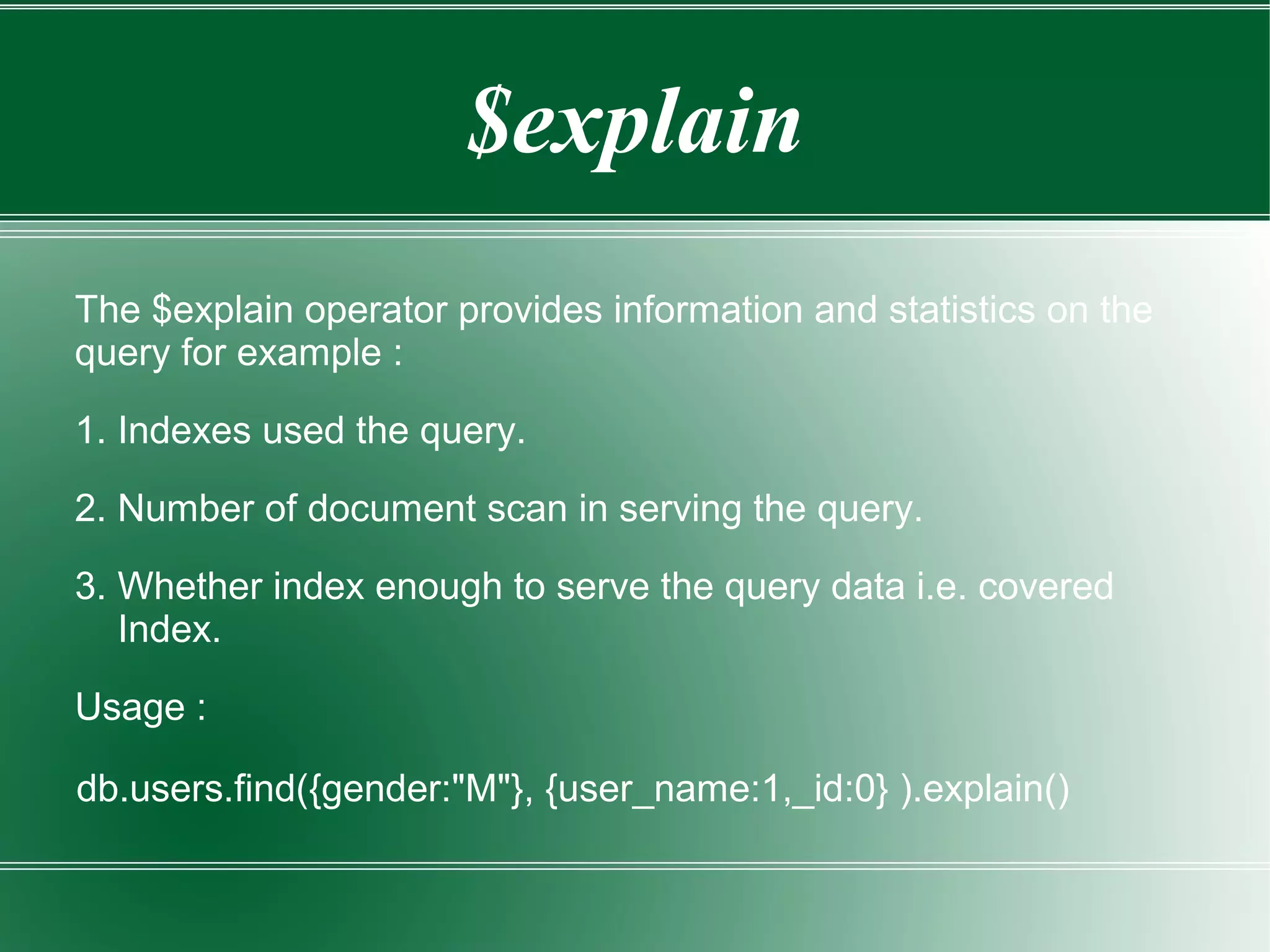
![Covered Indexes
Queries that can be resolved with only the index (does not need to
fetch the original document)
Example: { “name”:”Anuj”,
– “age”:28,
– “gender”:Male,
– “skills”:[“Java”,”Mongo”]
}
db.people.ensureIndex({“name”:1,”age”:1})
db.people.find ({“name”:”Anuj”},{“_id” :0 , “age”:1})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbtutorials-150818122125-lva1-app6891/75/Mongo-db-tutorials-20-2048.jpg)