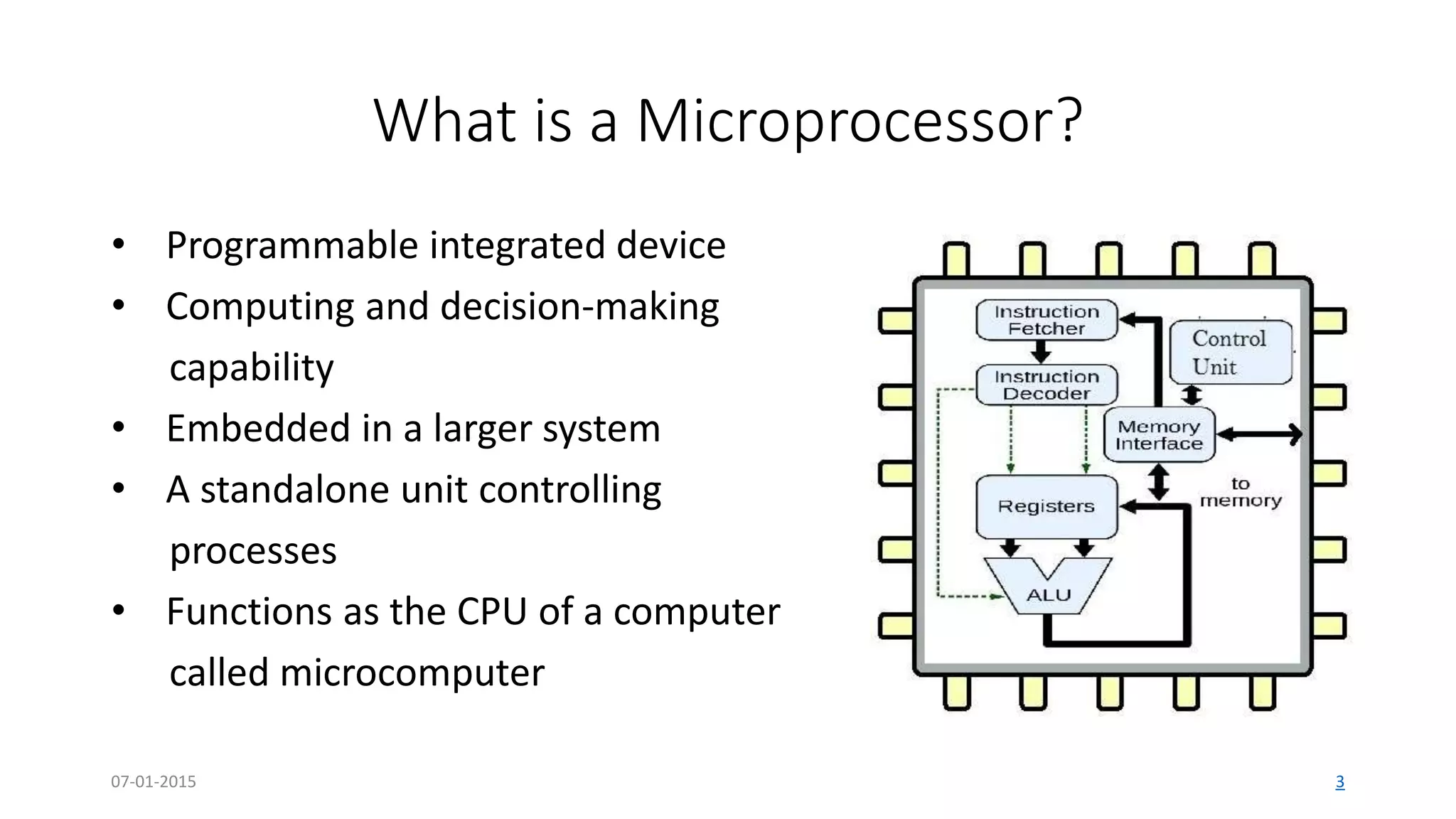
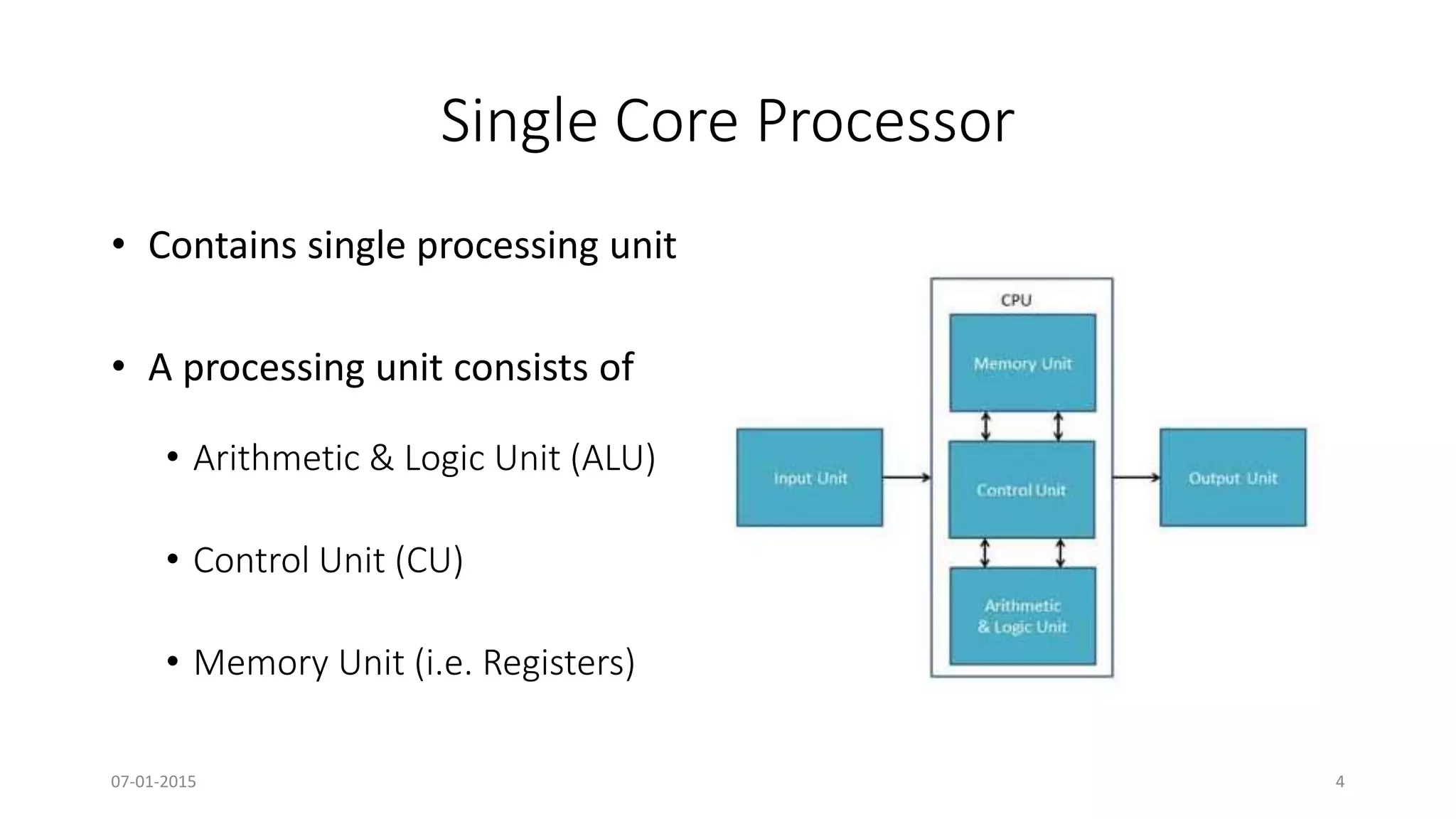
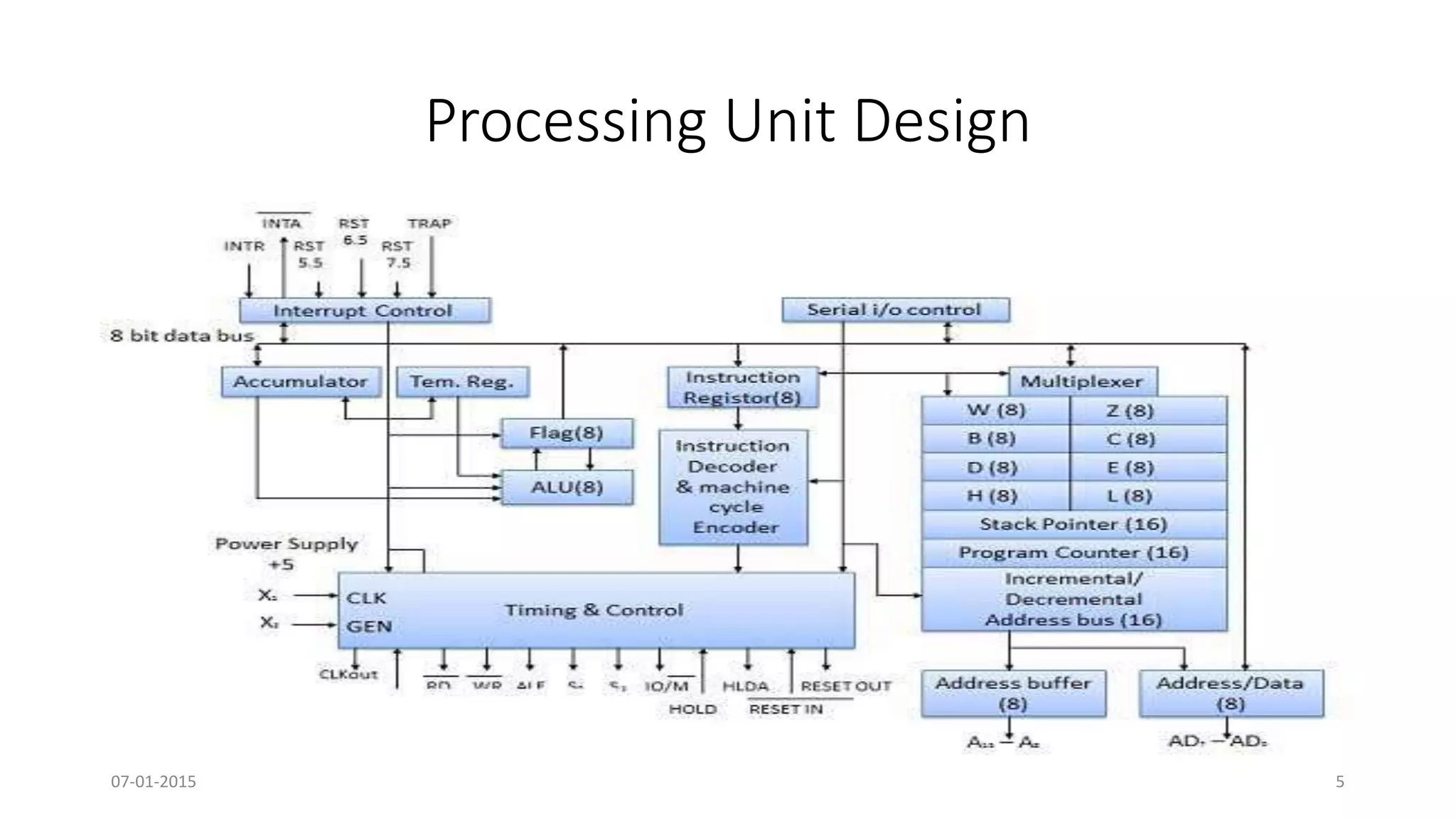
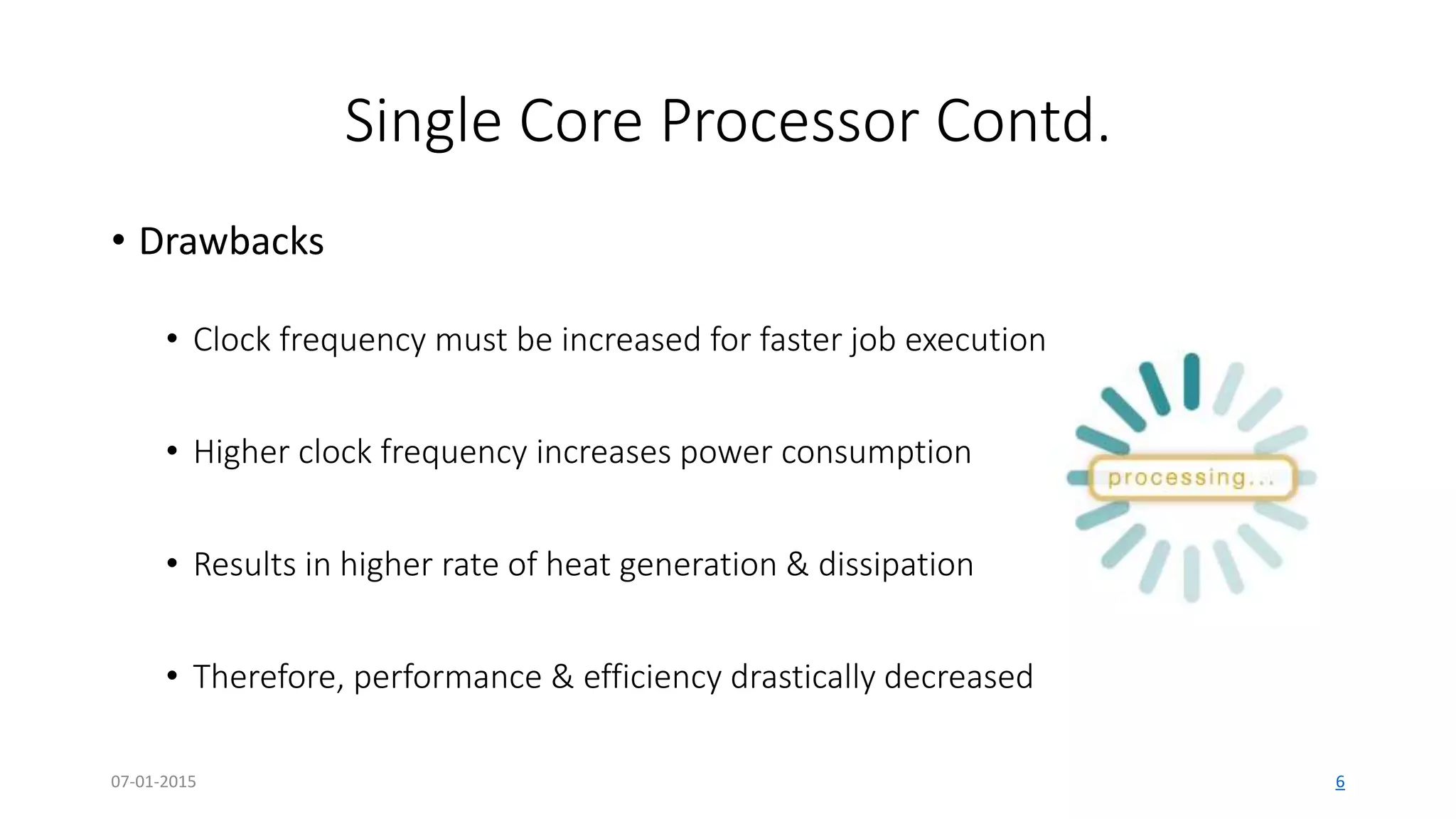
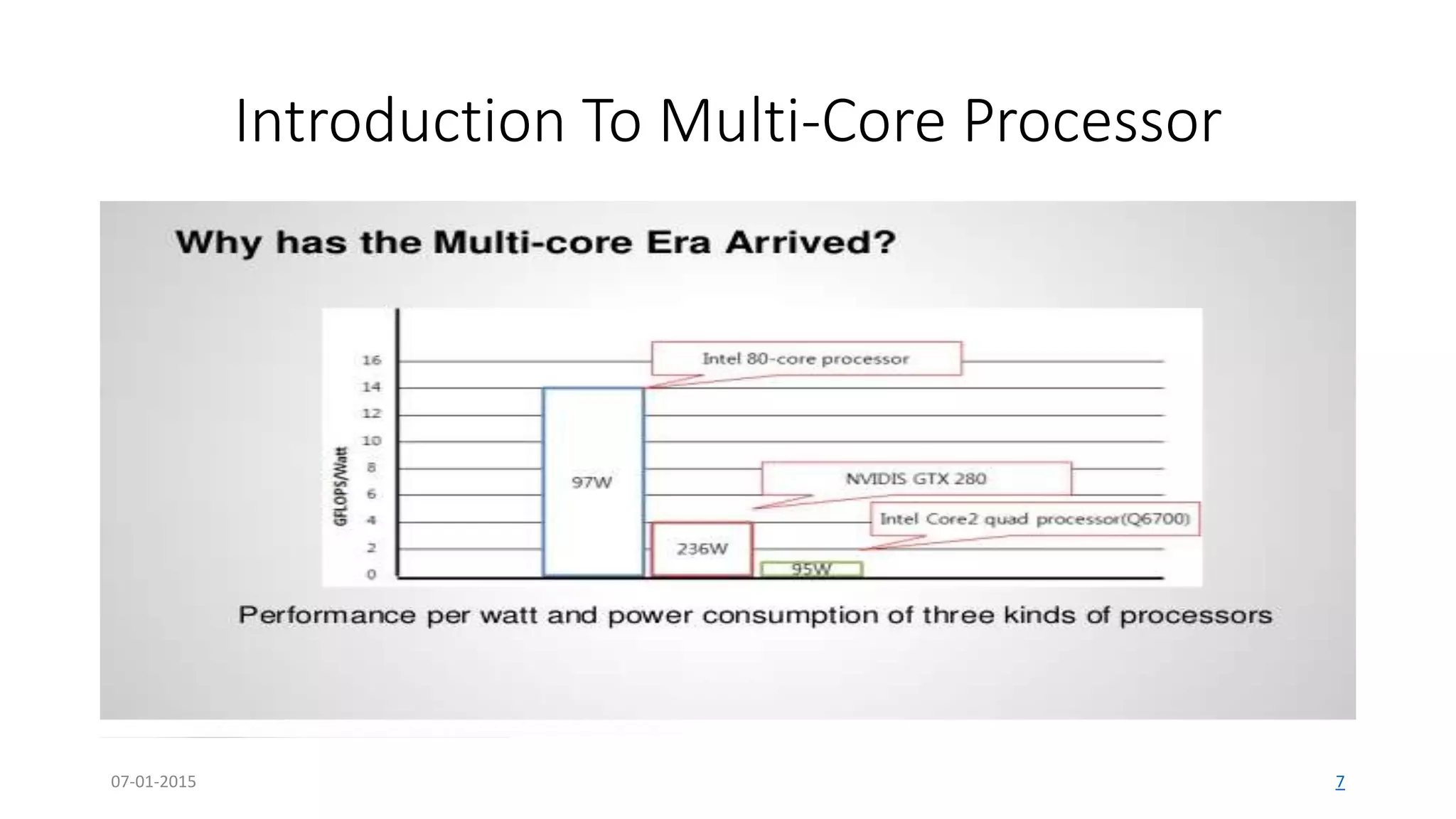
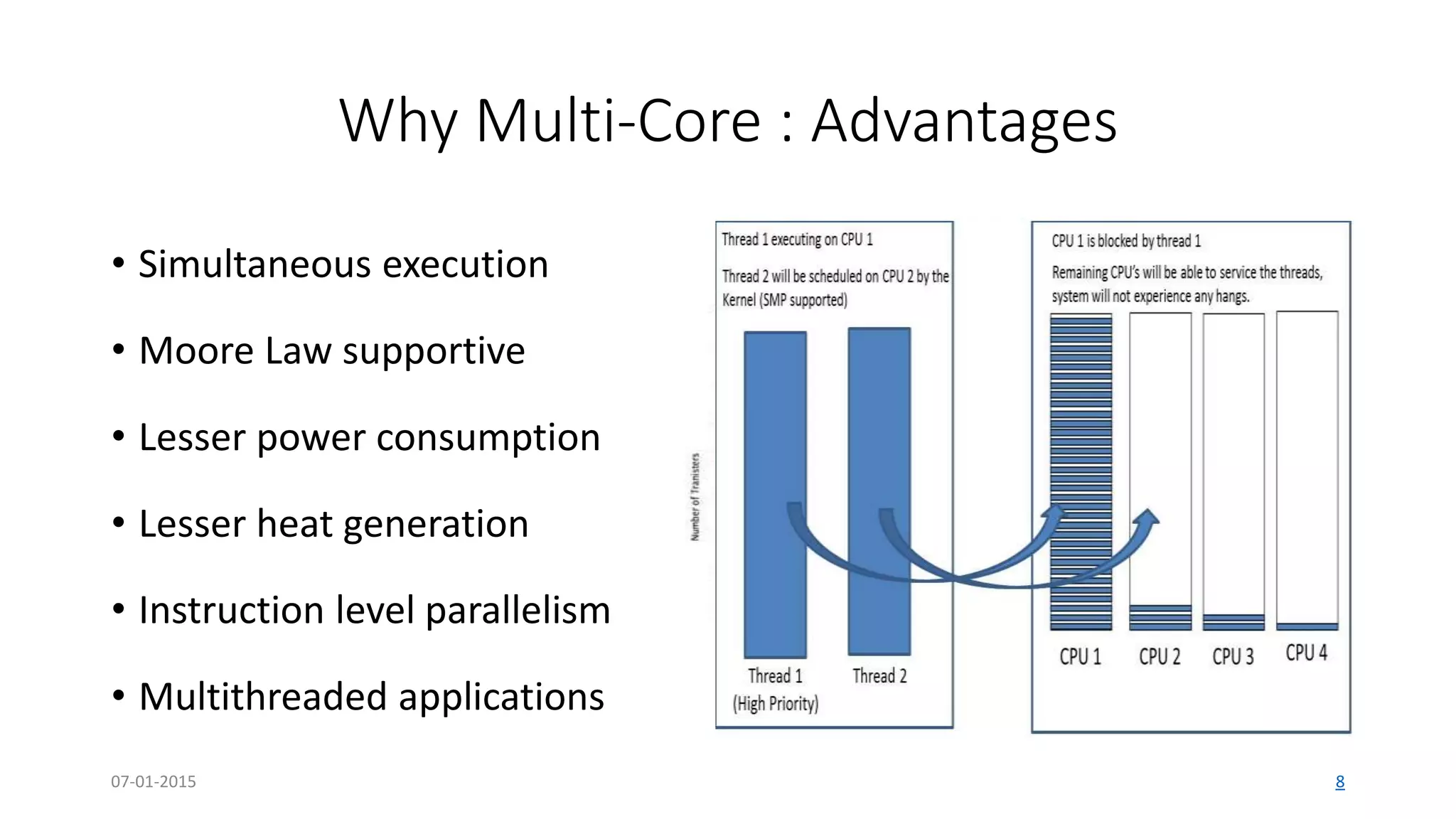
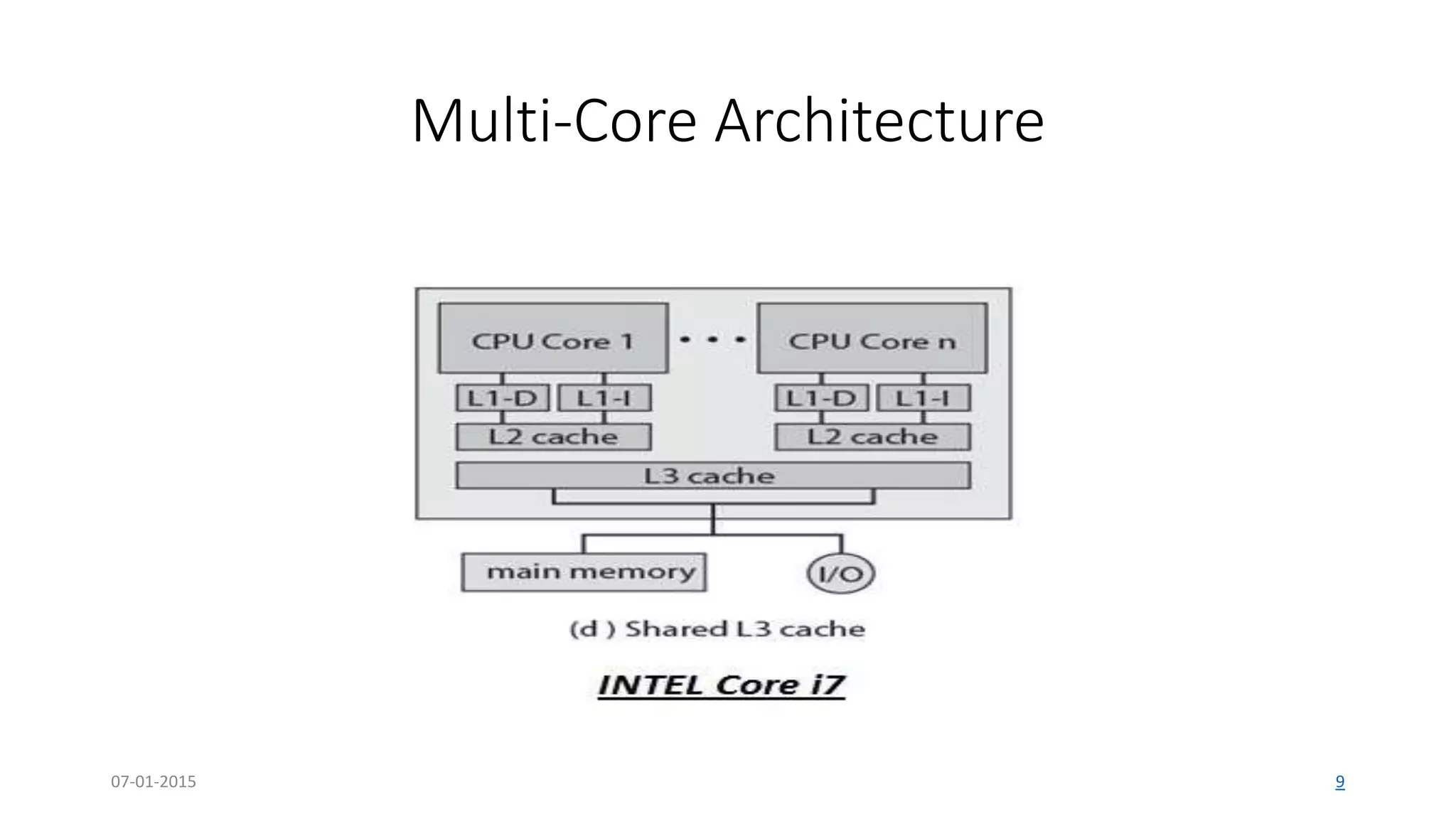
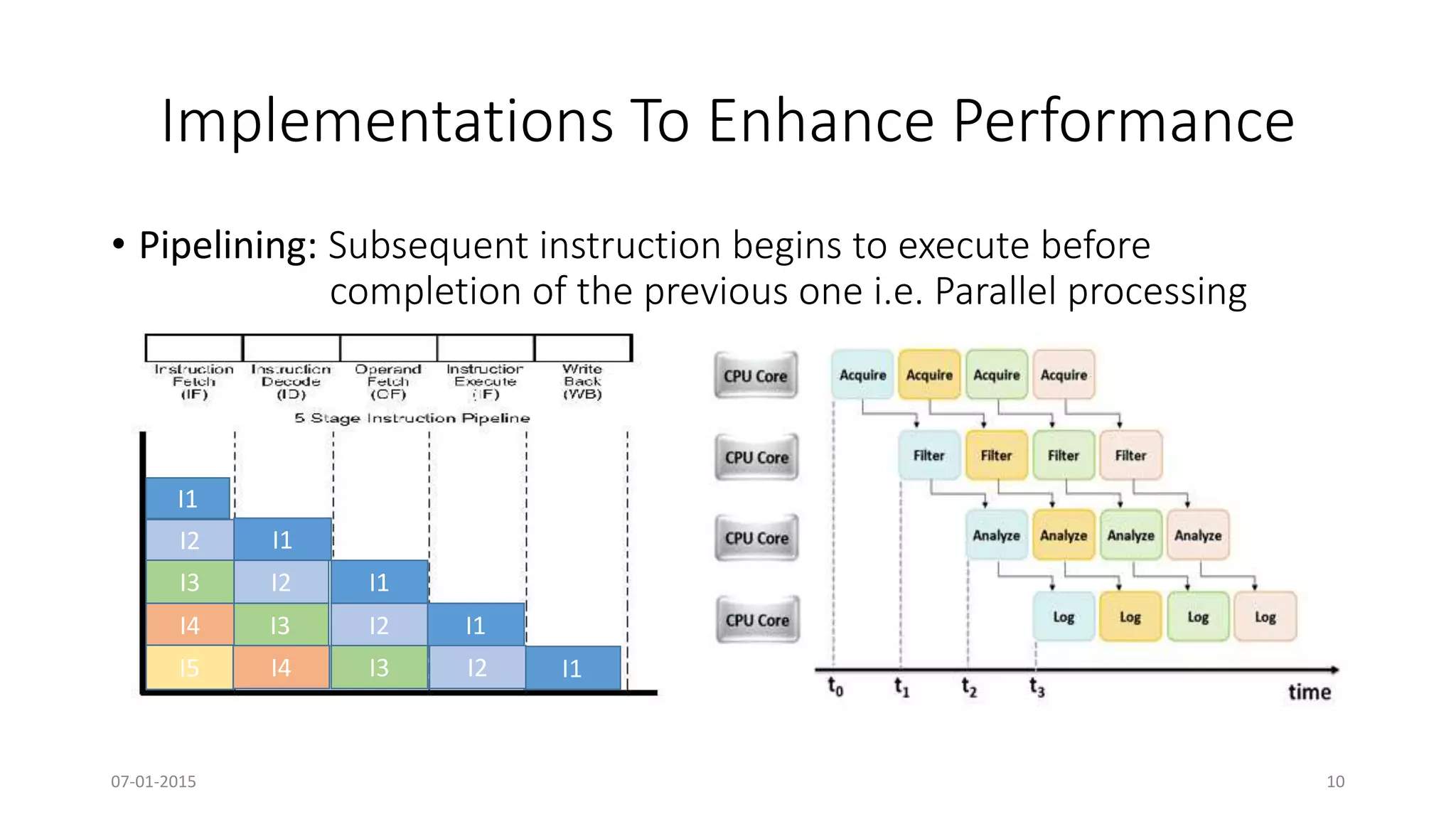
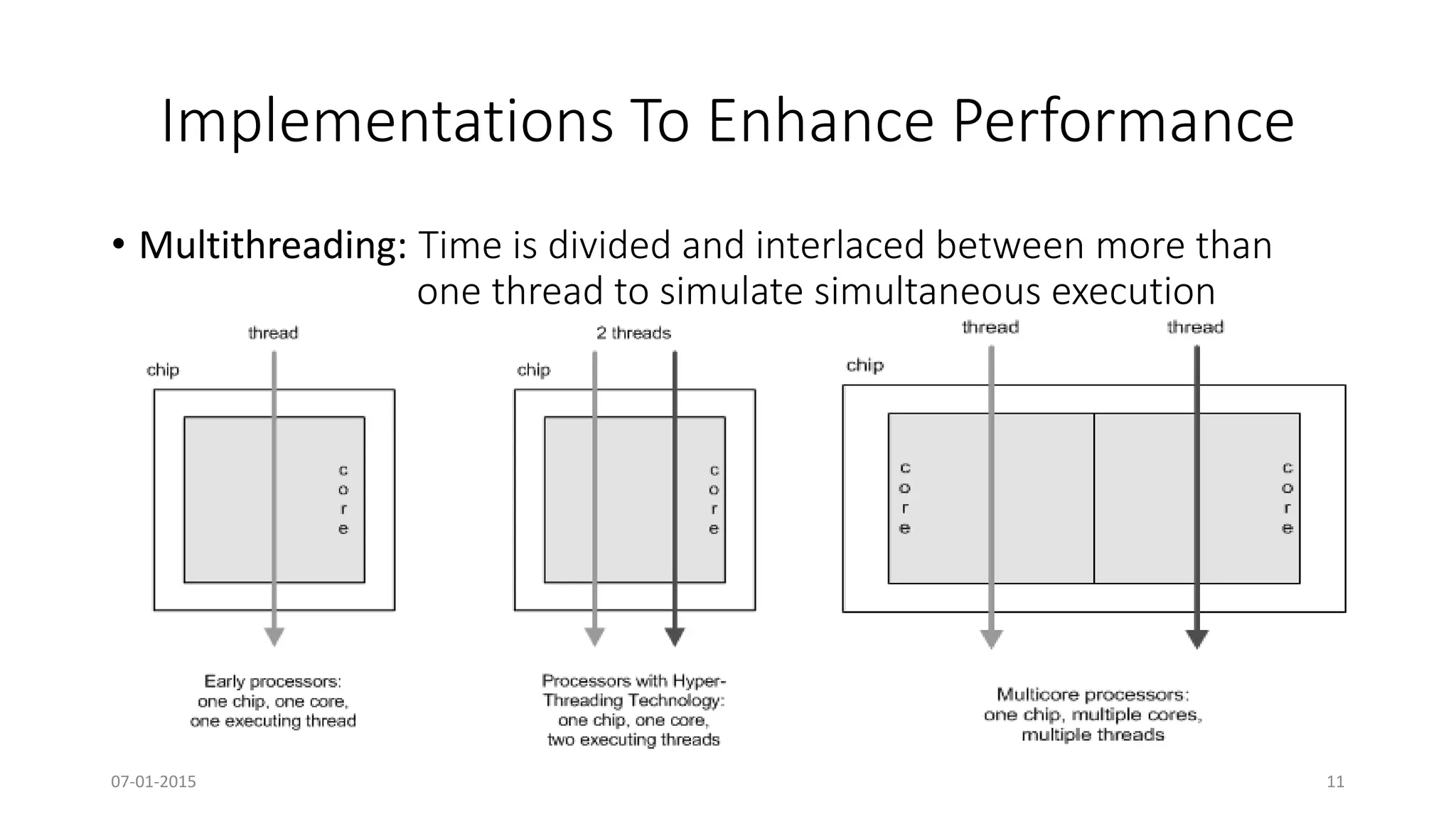
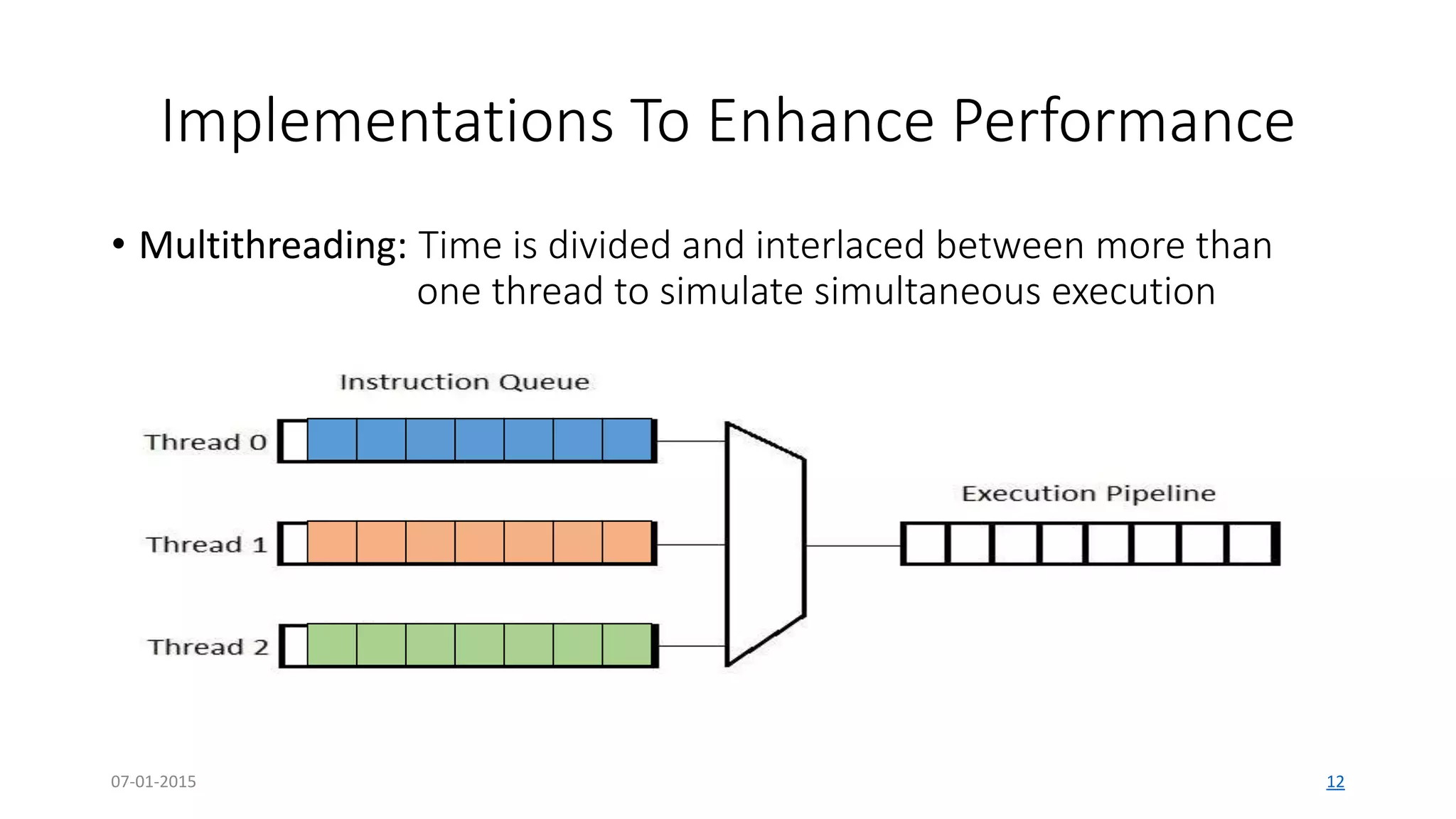
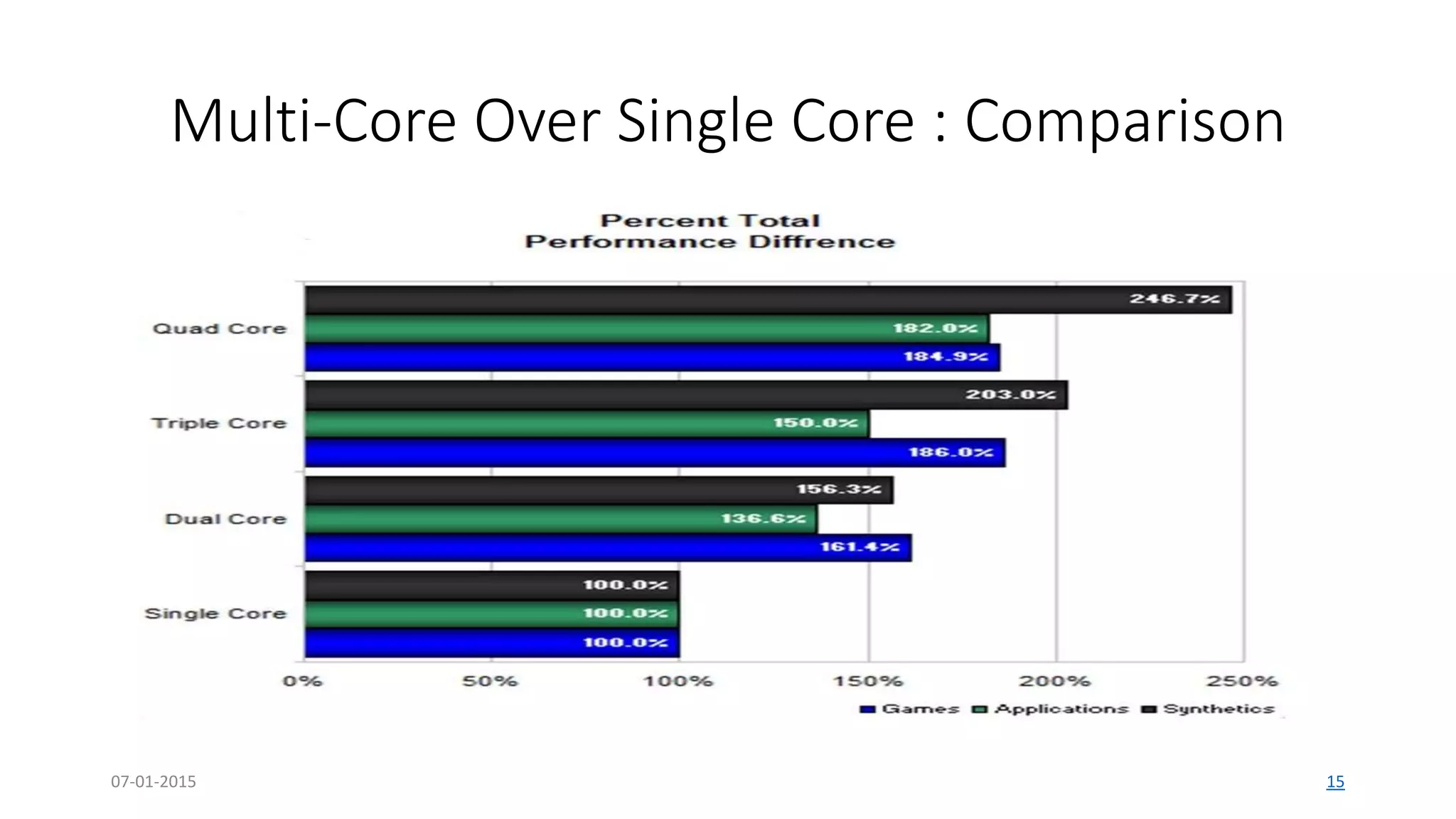
The document provides an overview of multi-core processors, outlining their architecture, advantages, and applications compared to single-core processors. It discusses the performance enhancements they offer and highlights challenges such as costs and software compatibility. The future of multi-core processors is emphasized as critical for advanced computing needs, including AI and pattern recognition.