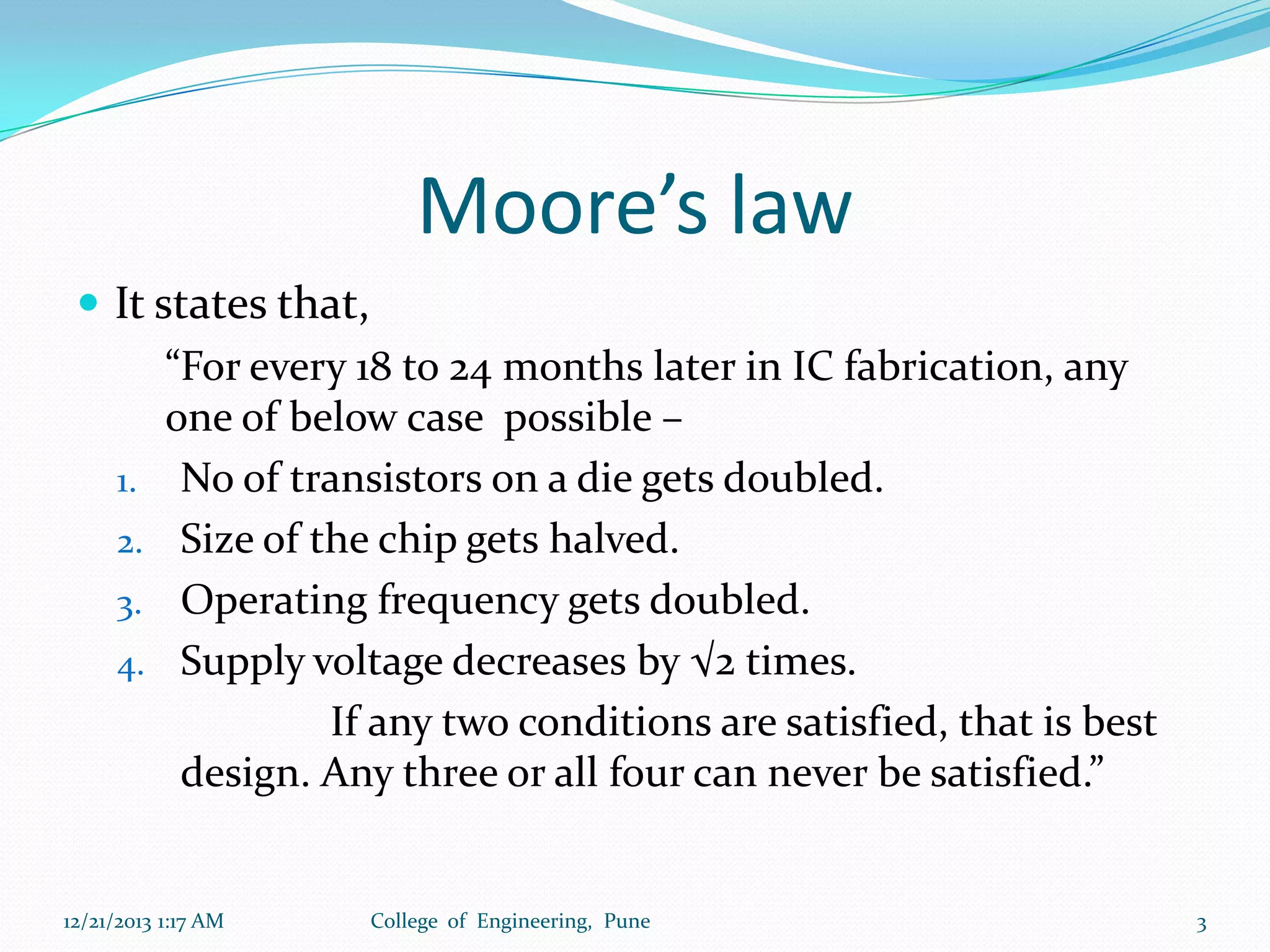
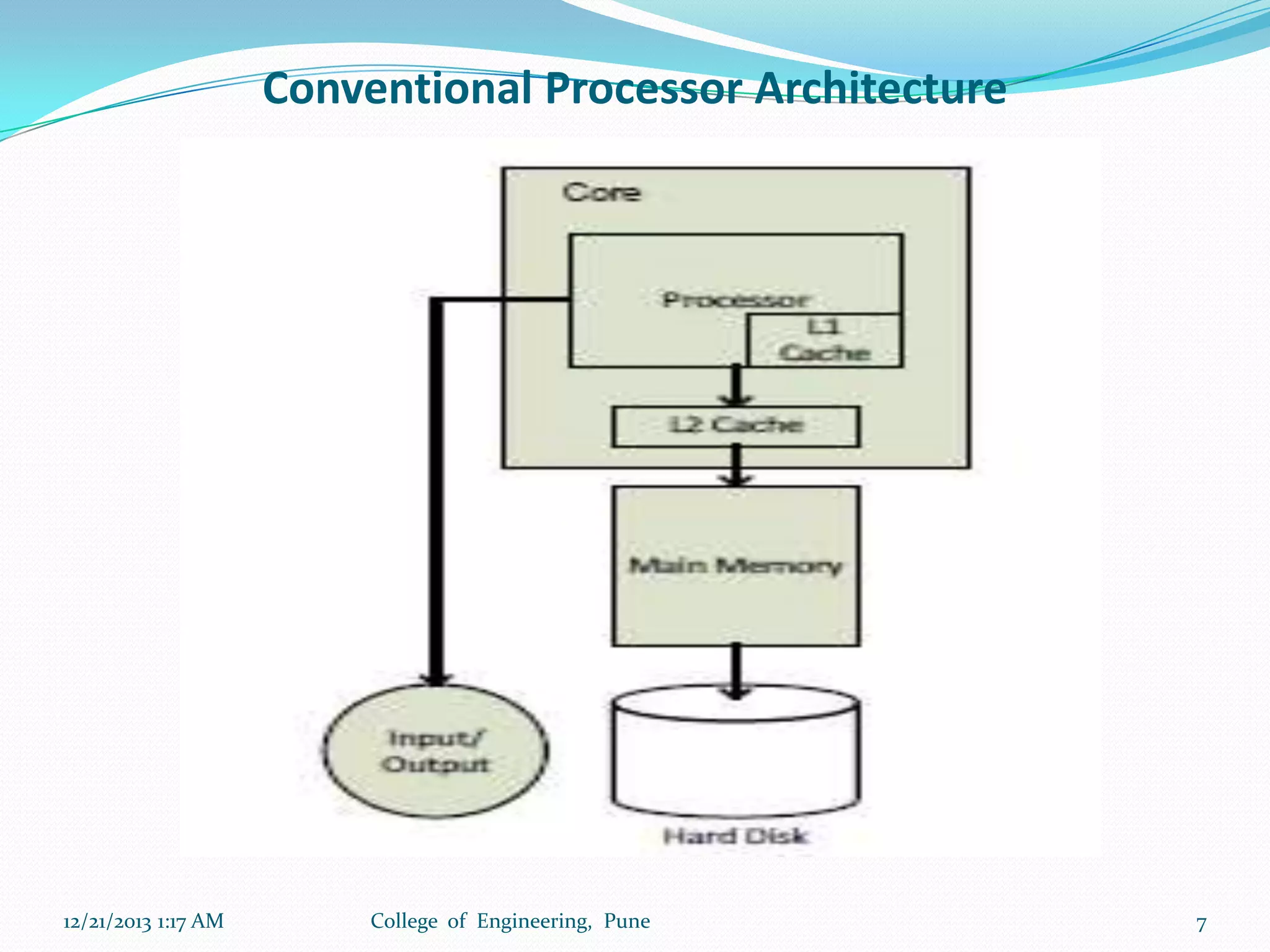
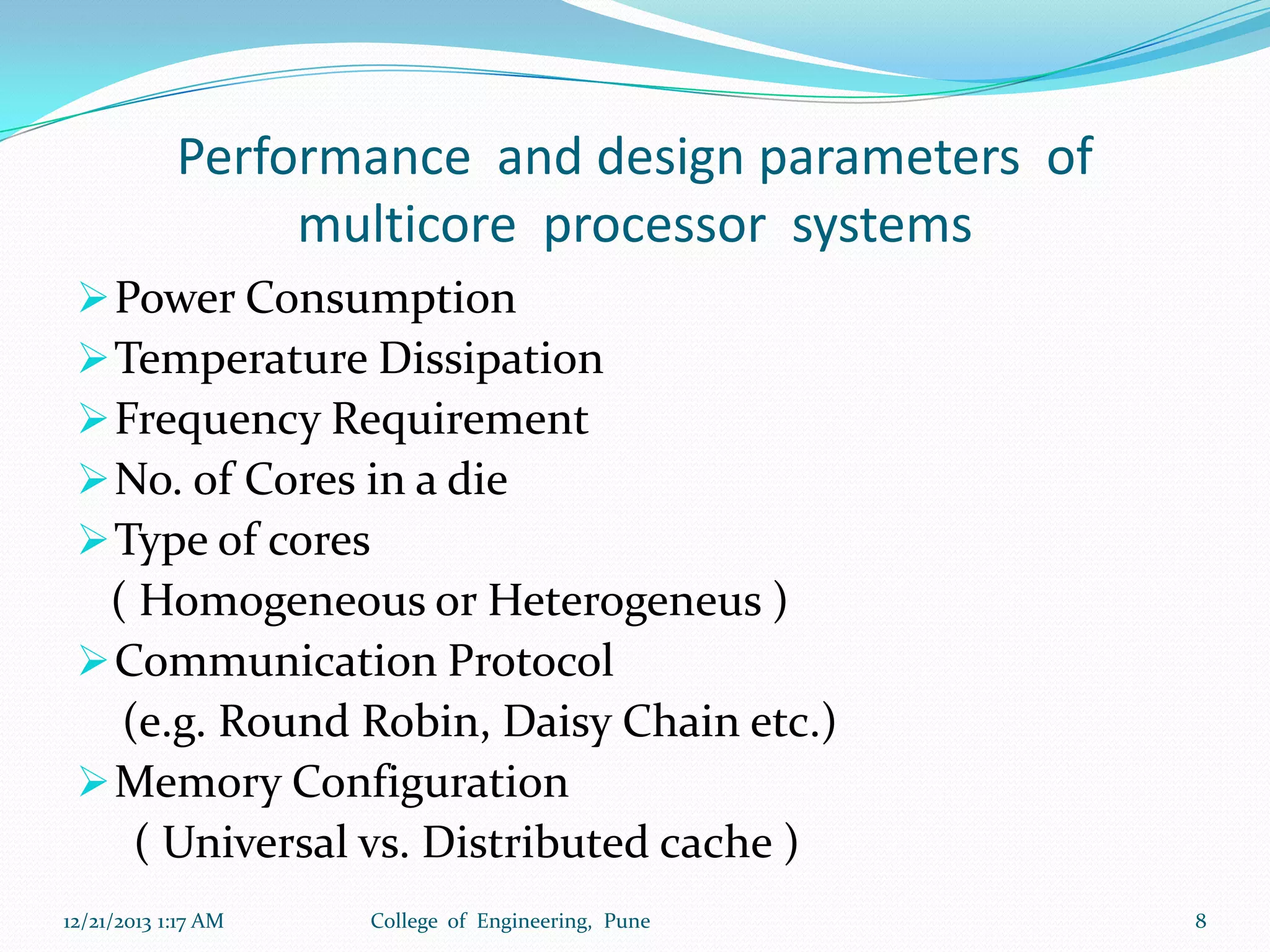
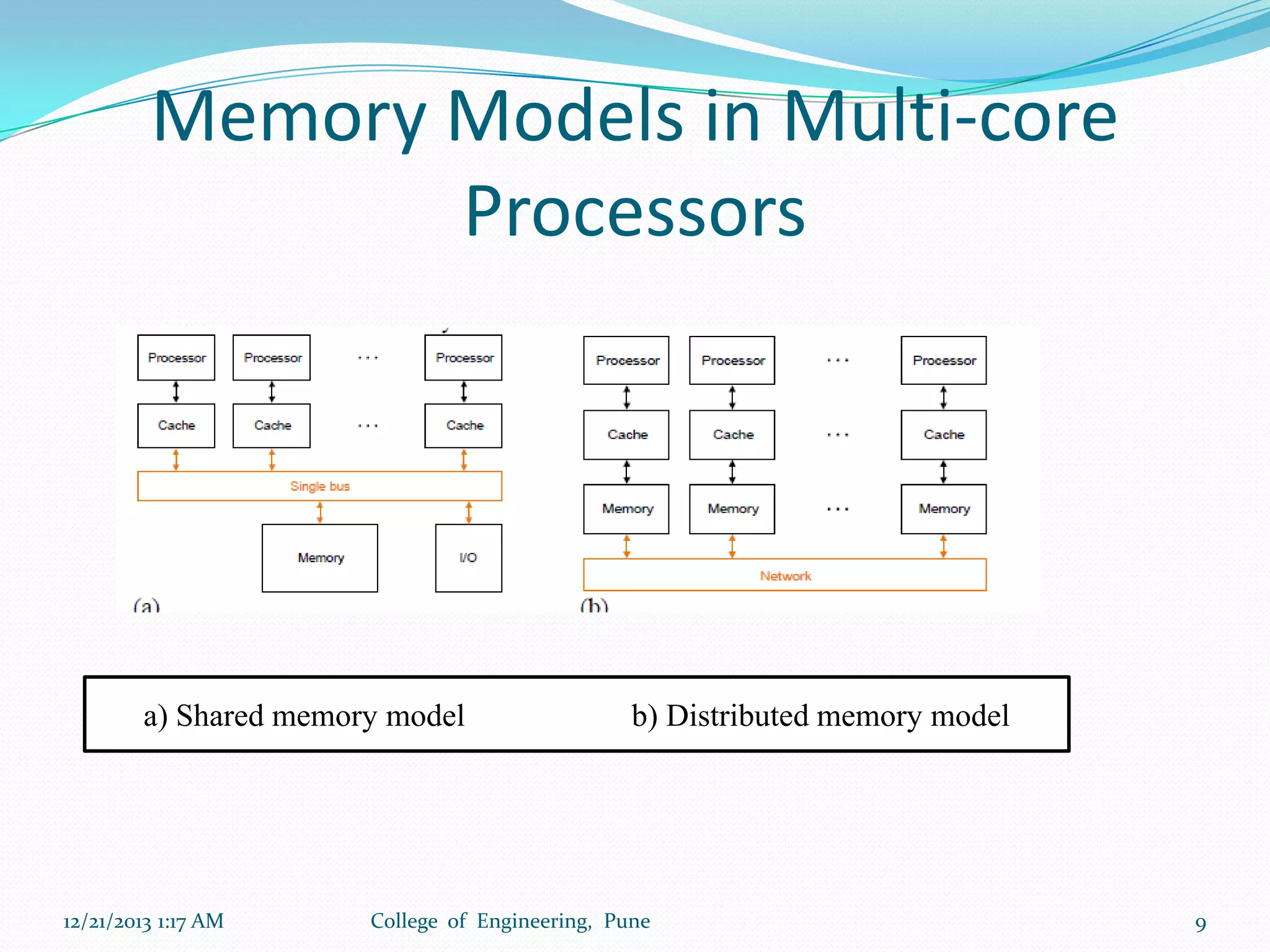
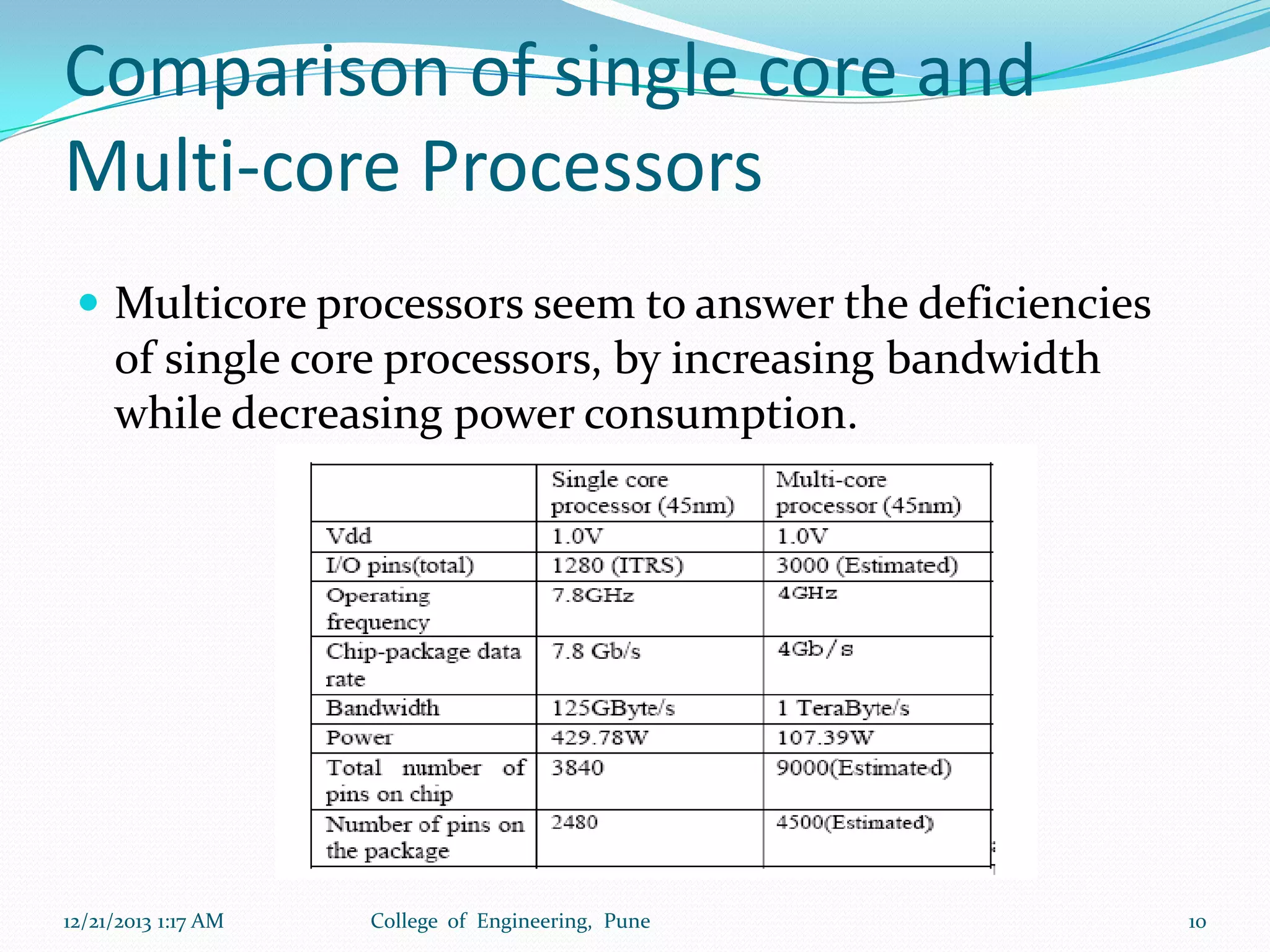
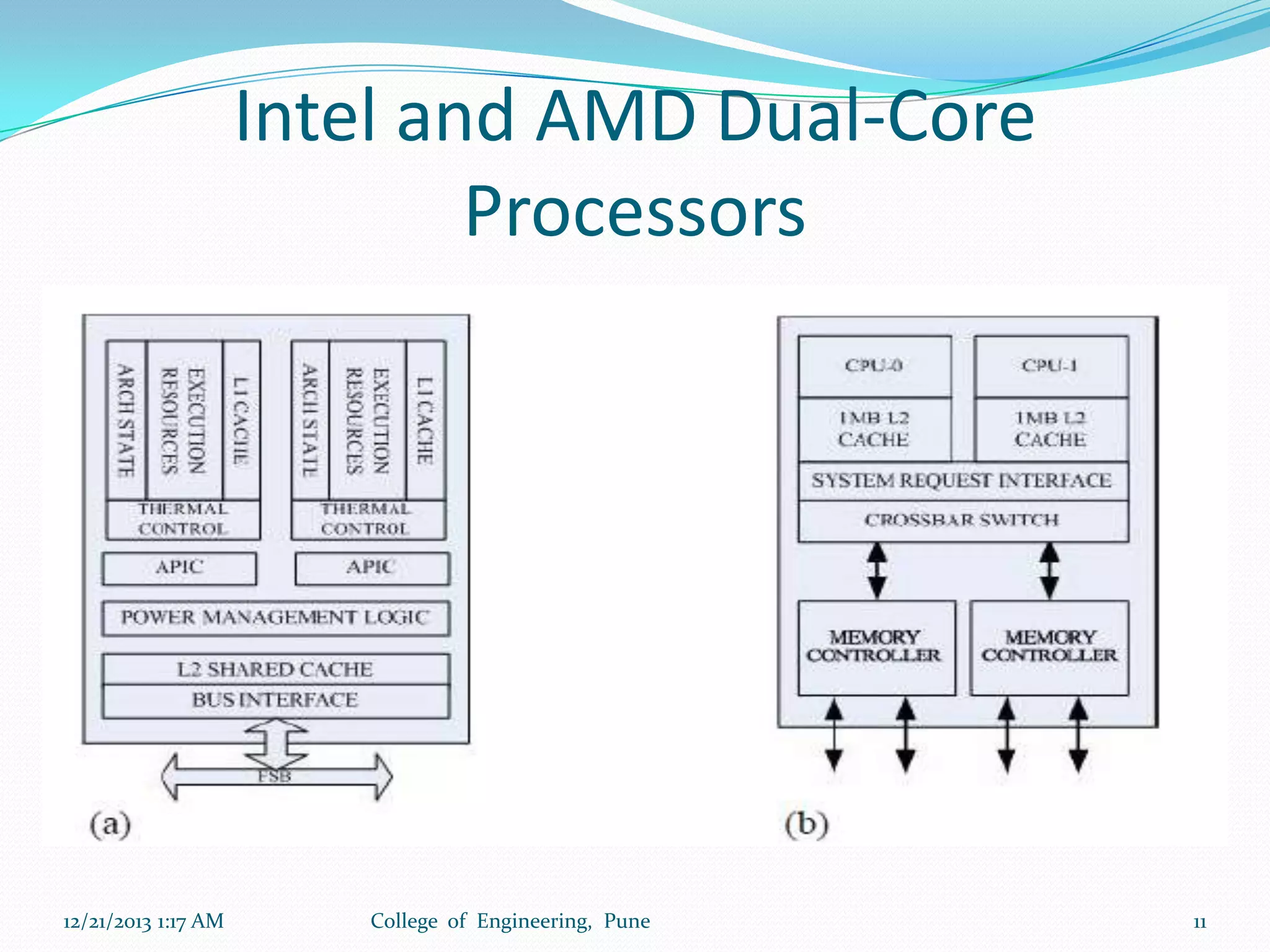
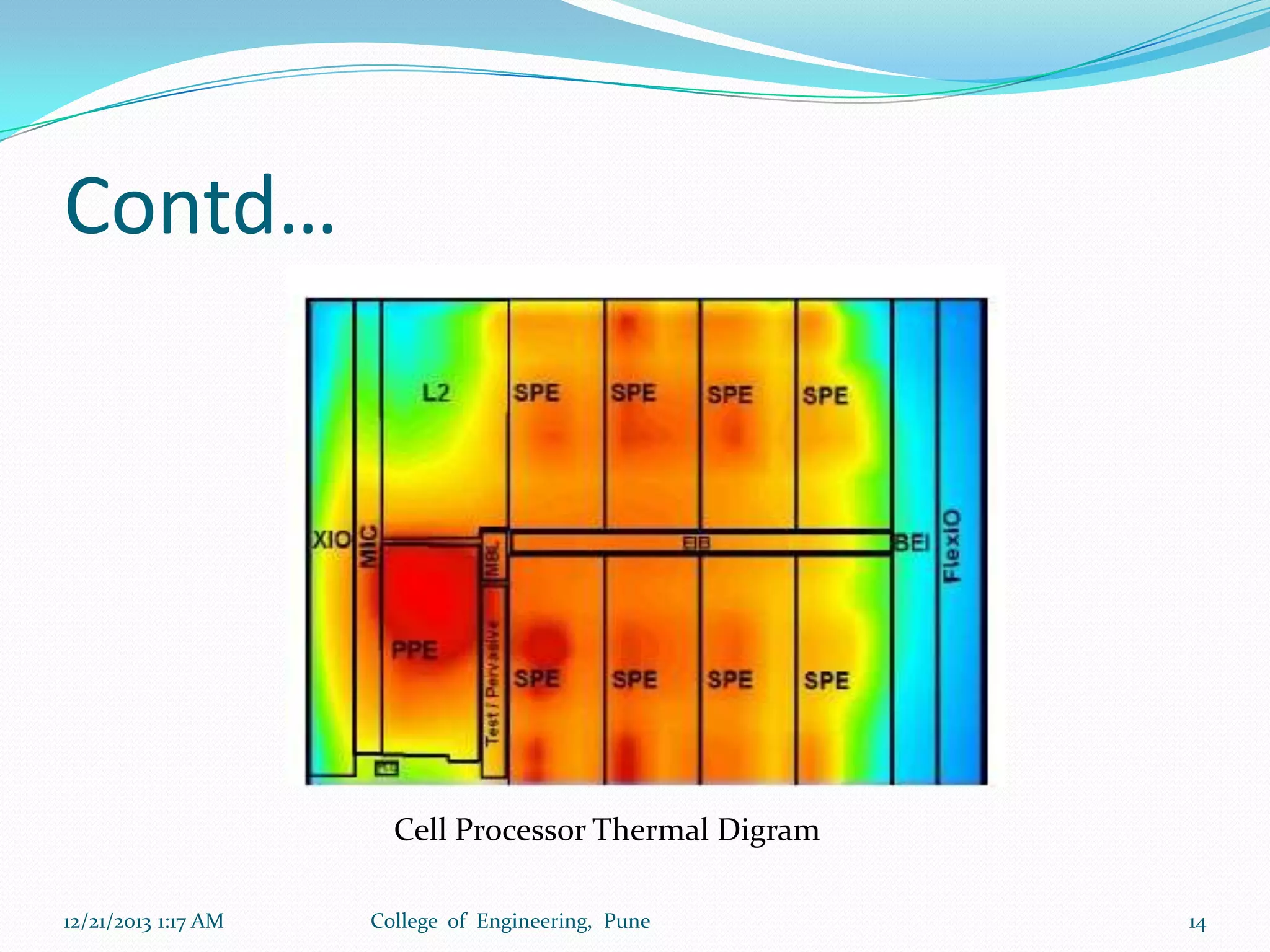
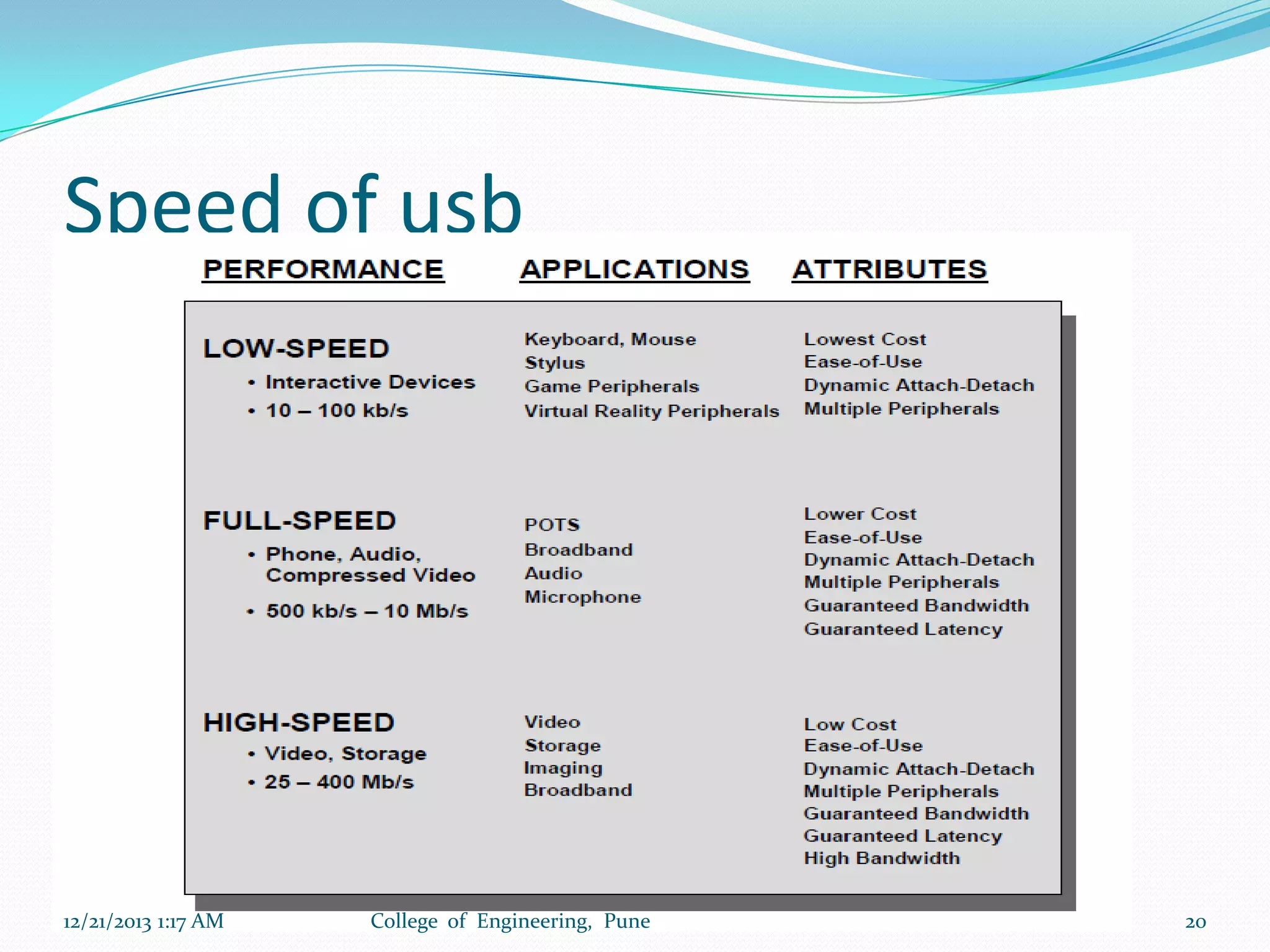
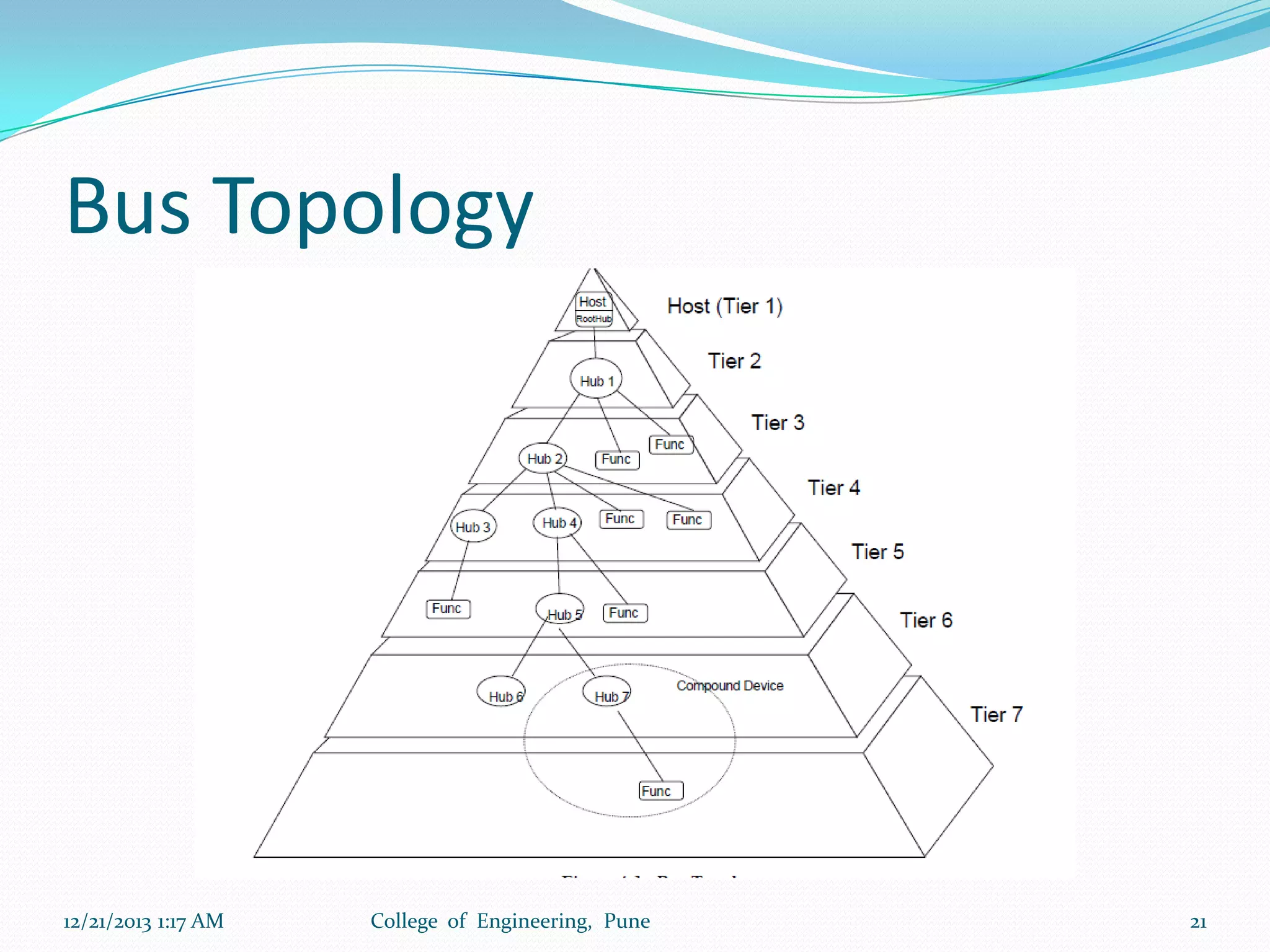
The document discusses advancements in microprocessor technology, focusing on multi-core processing and inbuilt USB connectivity. It highlights Moore's law, the need for multi-core processors to address limitations in single-core designs, and the benefits of reduced power consumption and increased performance. Additionally, it covers challenges such as power and temperature dependence, cache coherence, and multithreading in multicore systems.