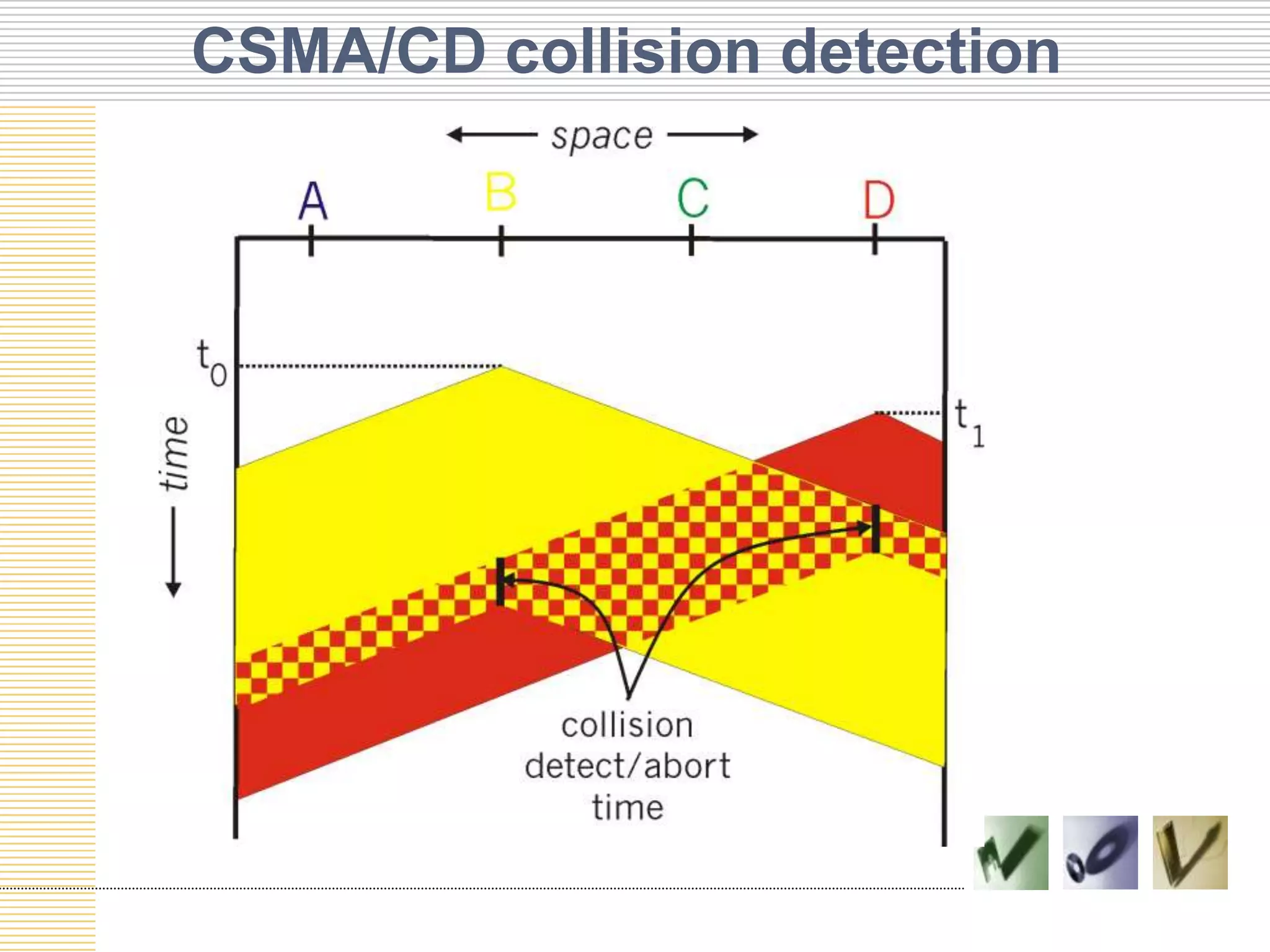
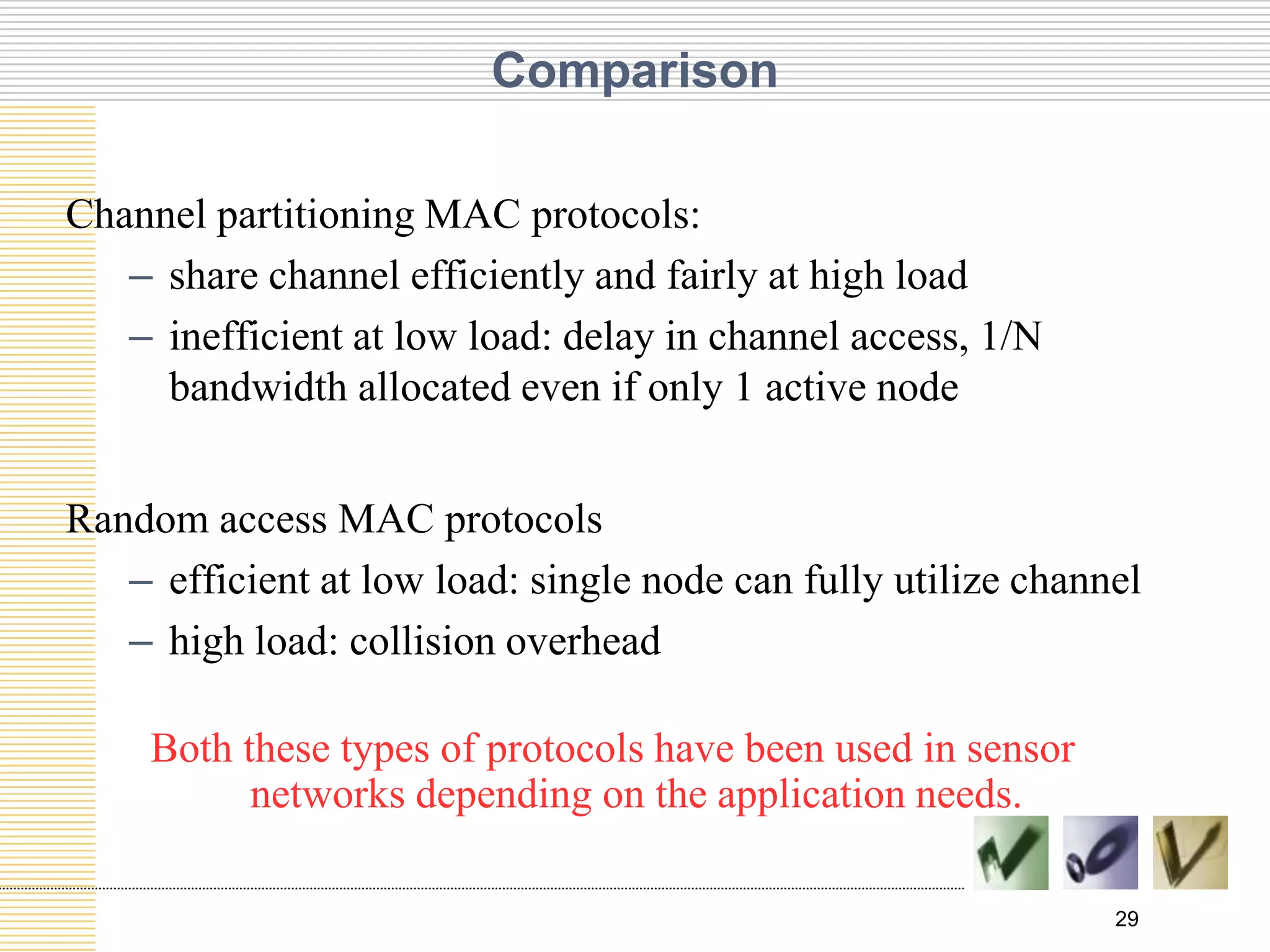
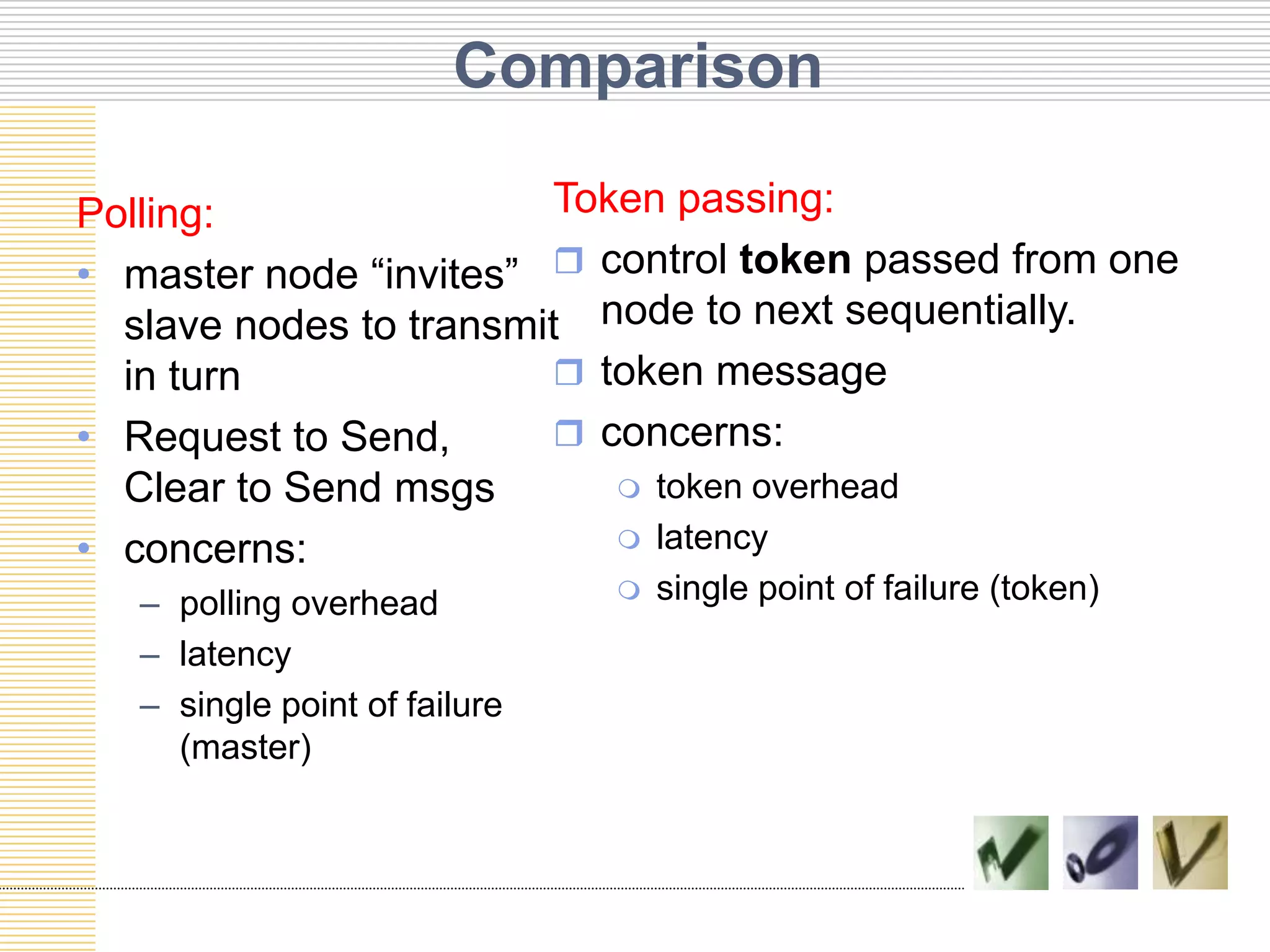
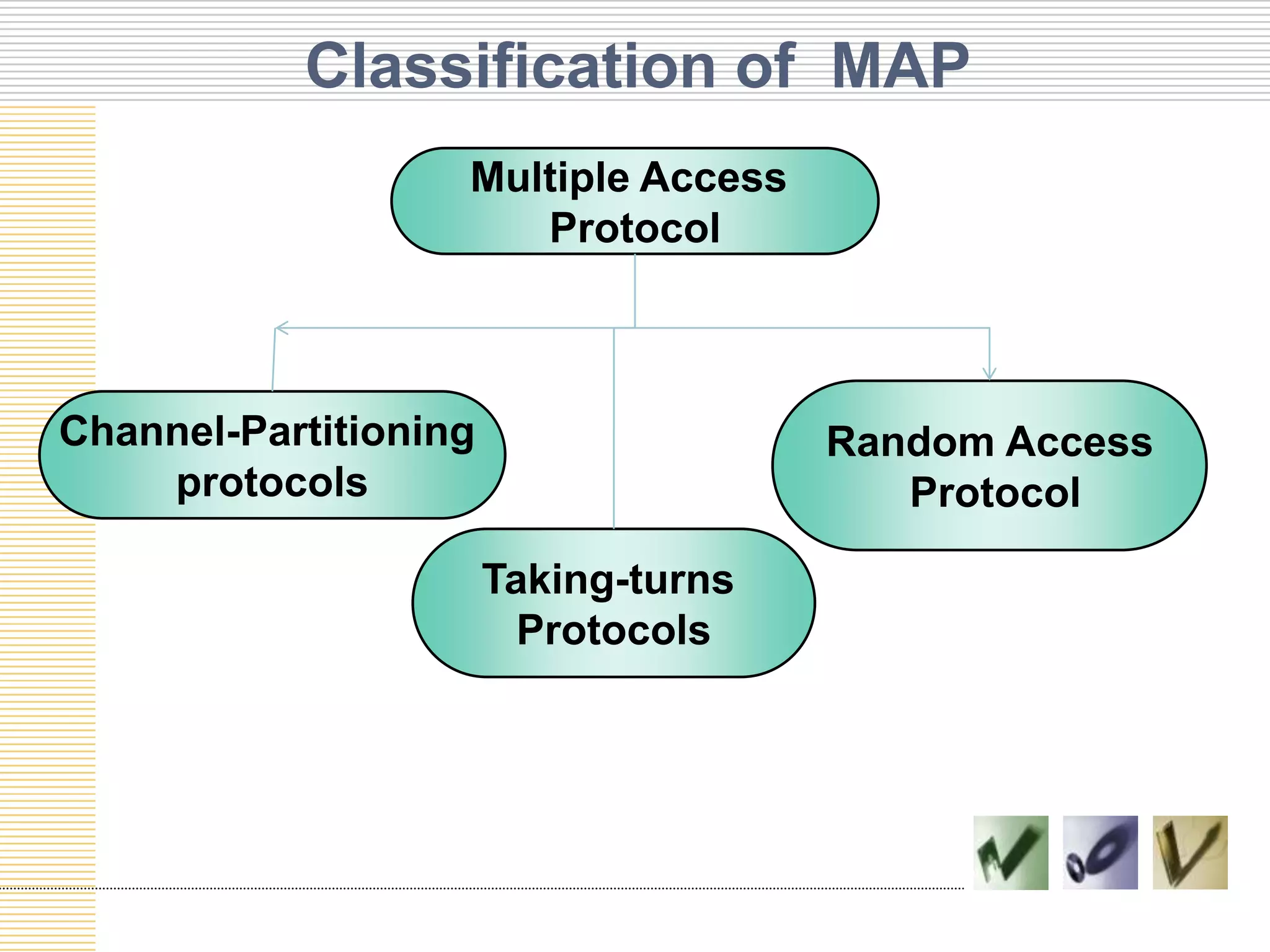
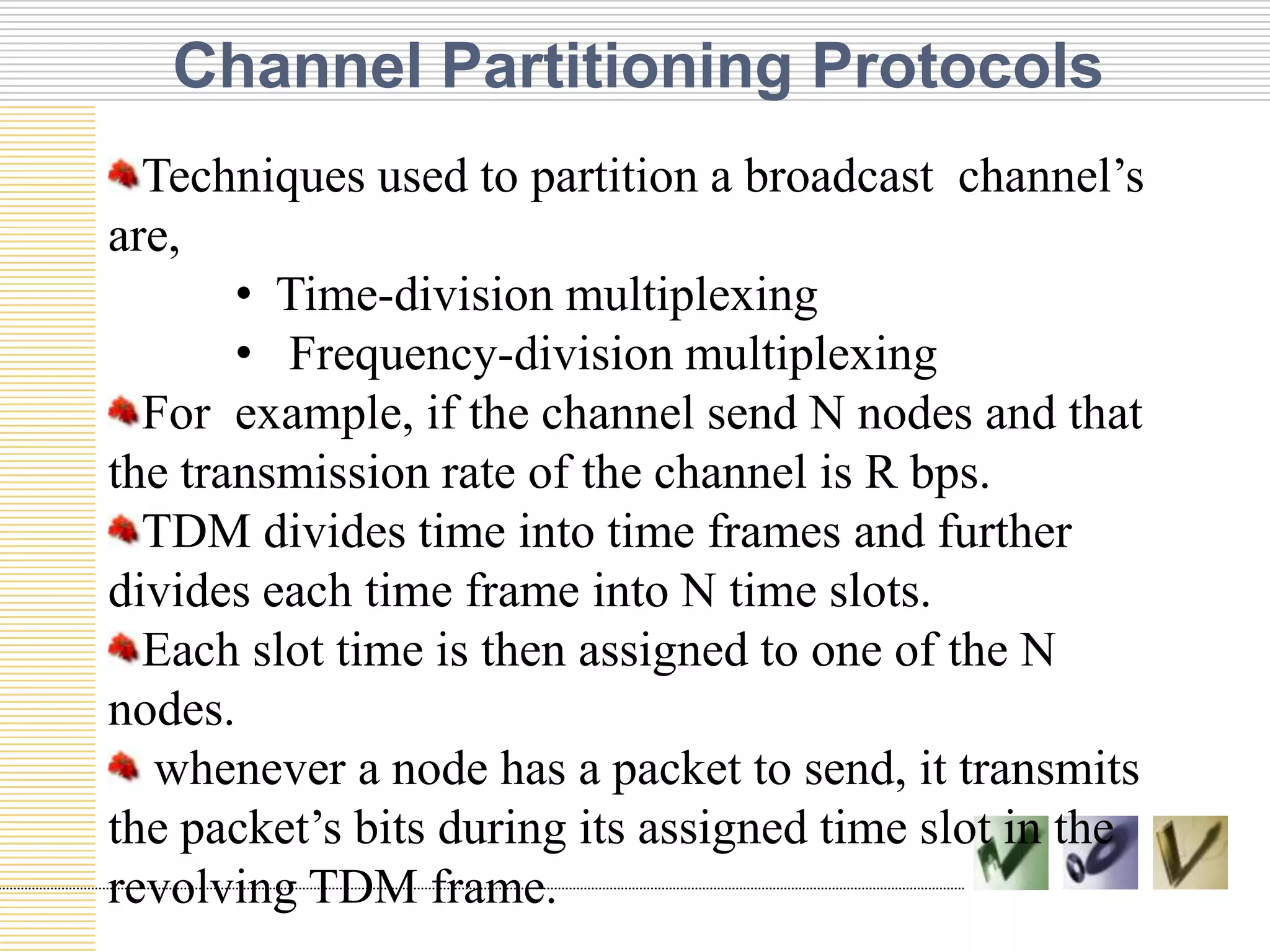
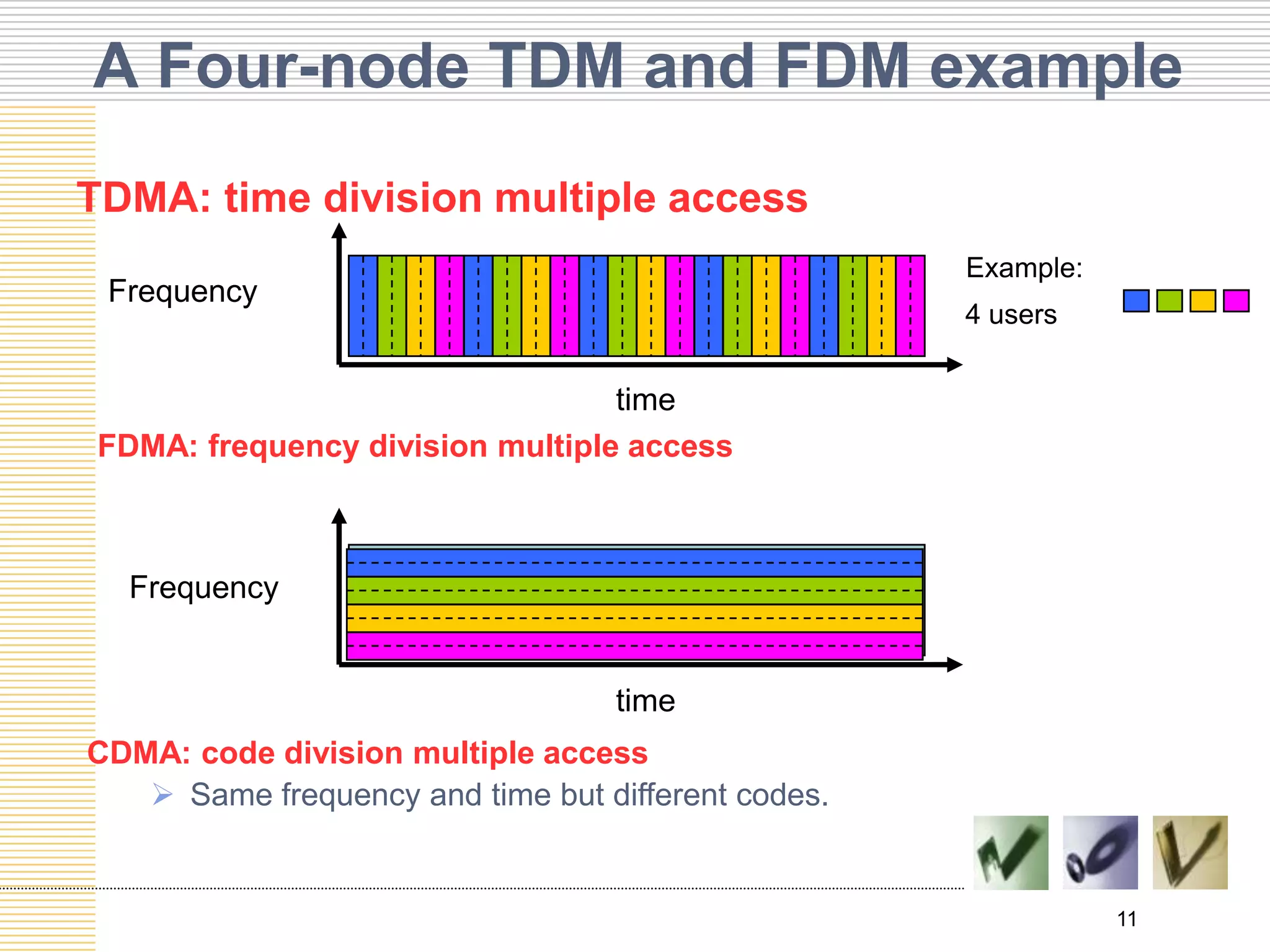
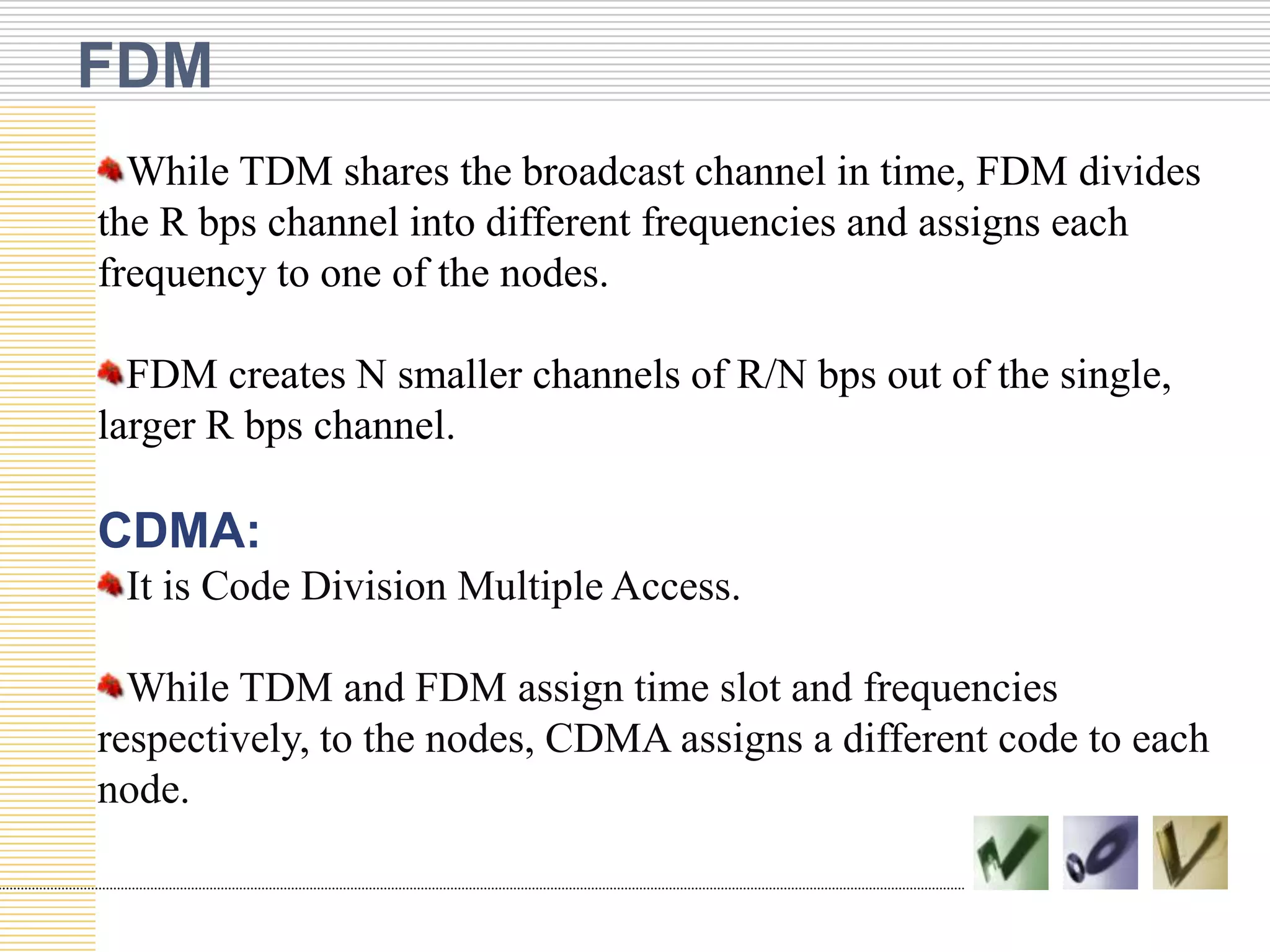
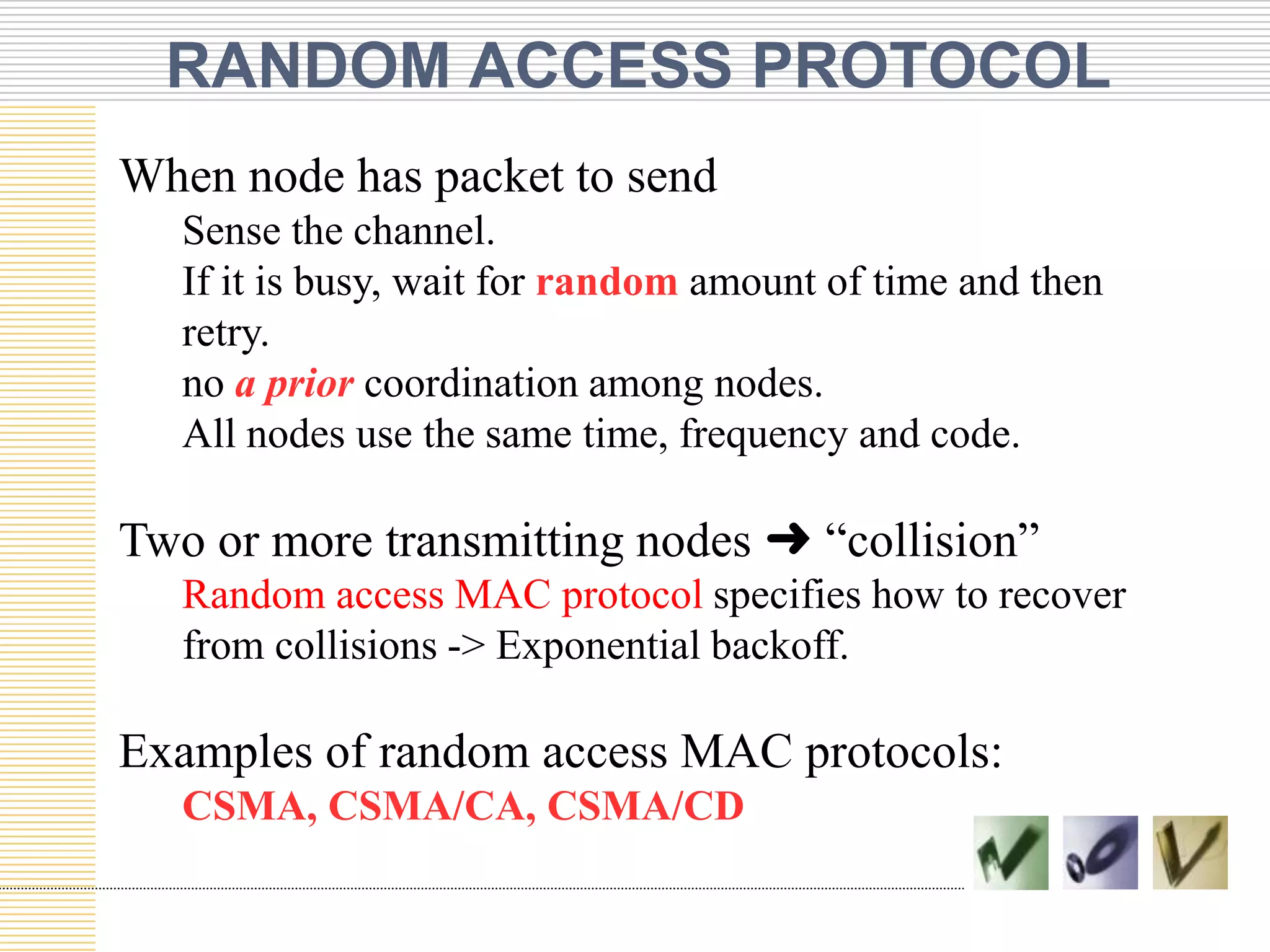
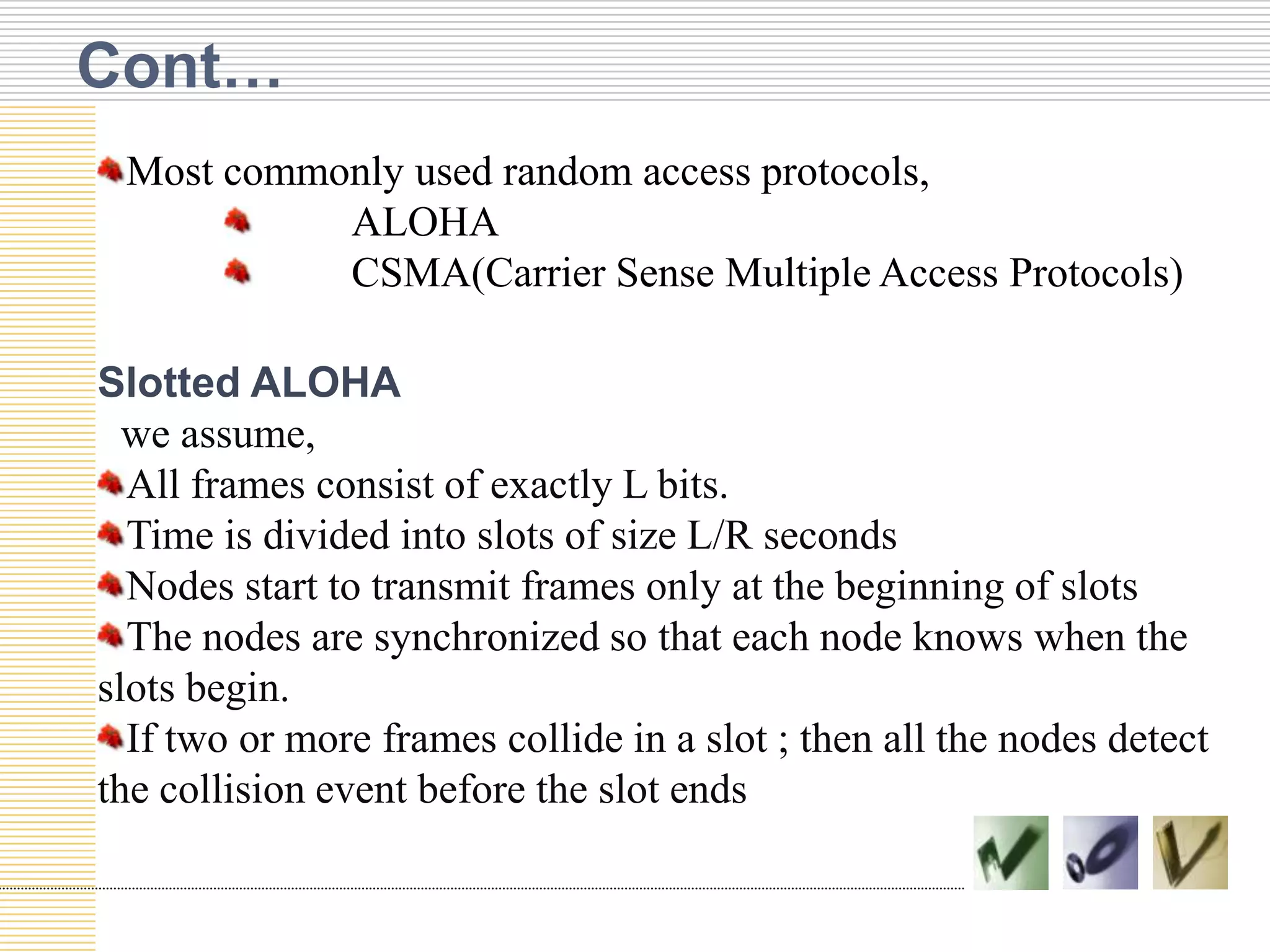
This document discusses multiple access protocols used to coordinate access to shared broadcast channels. It describes various channel partitioning protocols like TDMA and FDMA that divide channels by time or frequency. Random access protocols like ALOHA and CSMA are also covered, which allow nodes to transmit randomly and detect collisions. CSMA/CD improves on CSMA by allowing nodes to detect collisions quickly and abort transmissions. Taking-turns protocols pass control of the channel between nodes either through polling or token passing. The document provides examples and compares the efficiency of different multiple access protocols.






![unsloted Aloha: simpler, no synchronization
when frame first arrives
transmit immediately
collision probability increases:
frame sent at t0 collides with other frames sent in
[t0-1,t0+1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multipleaccessprotocol-140213082552-phpapp02/75/Multiple-access-protocol-20-2048.jpg)
![P(success by given node) = P(node transmits) .
P(no other node transmits in [t0-1,t0] .
P(no other node transmits in [t0,t0+1]
= p . (1-p)N-1 . (1-p)N-1
= p . (1-p)2(N-1)
choosing optimum p and then letting n ->
Efficiency = 1/(2e) = .18
...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multipleaccessprotocol-140213082552-phpapp02/75/Multiple-access-protocol-21-2048.jpg)