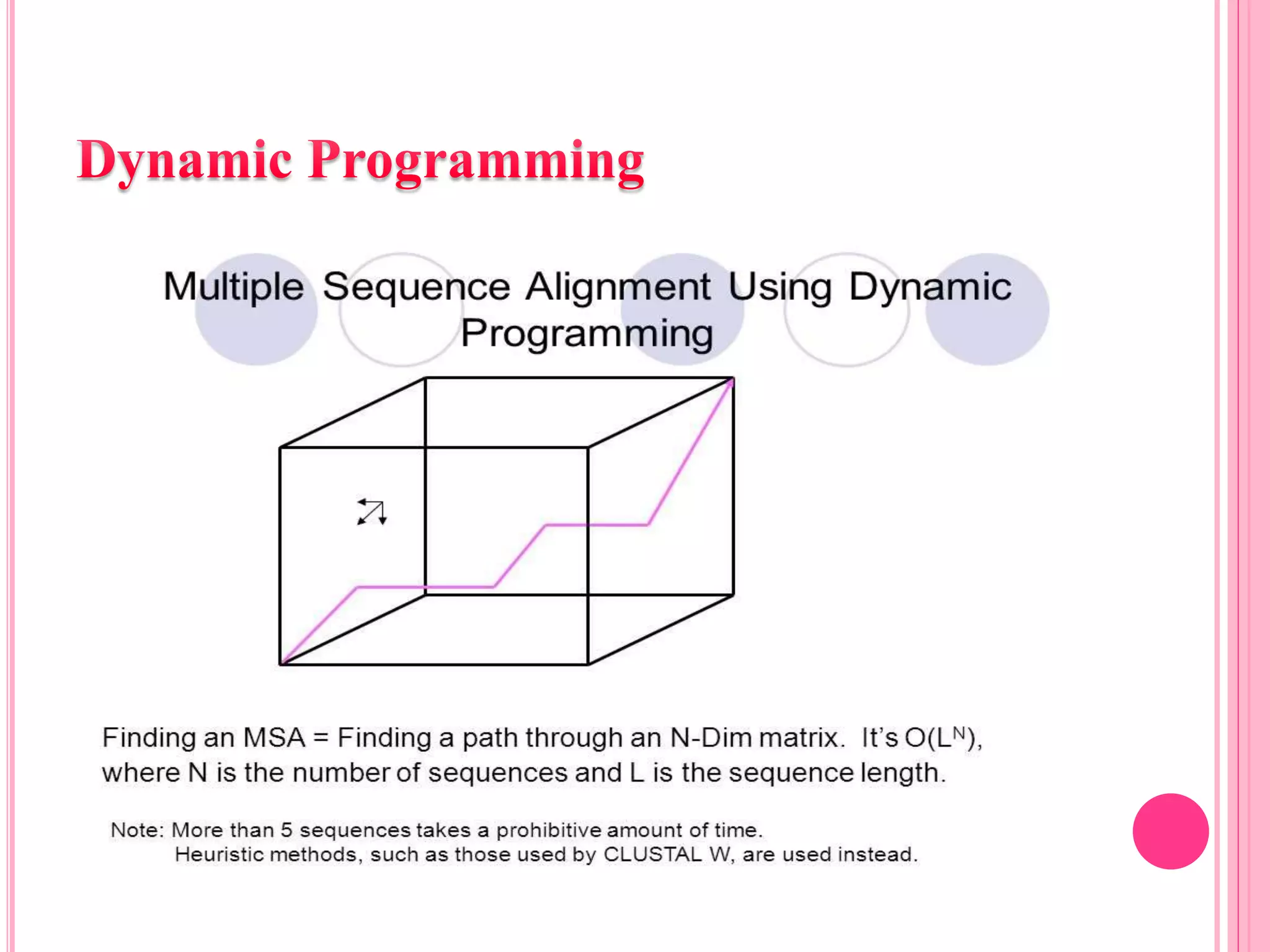
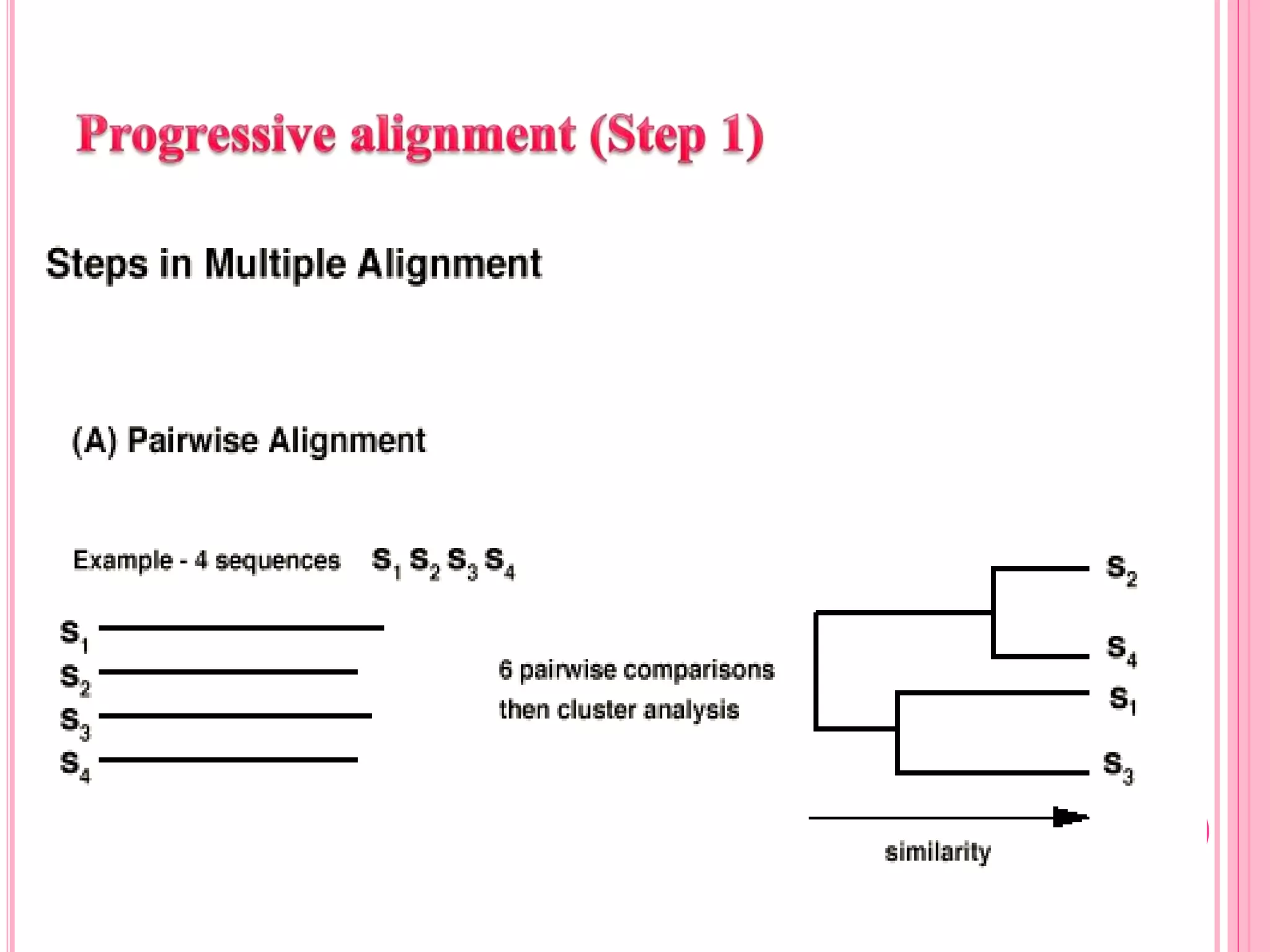
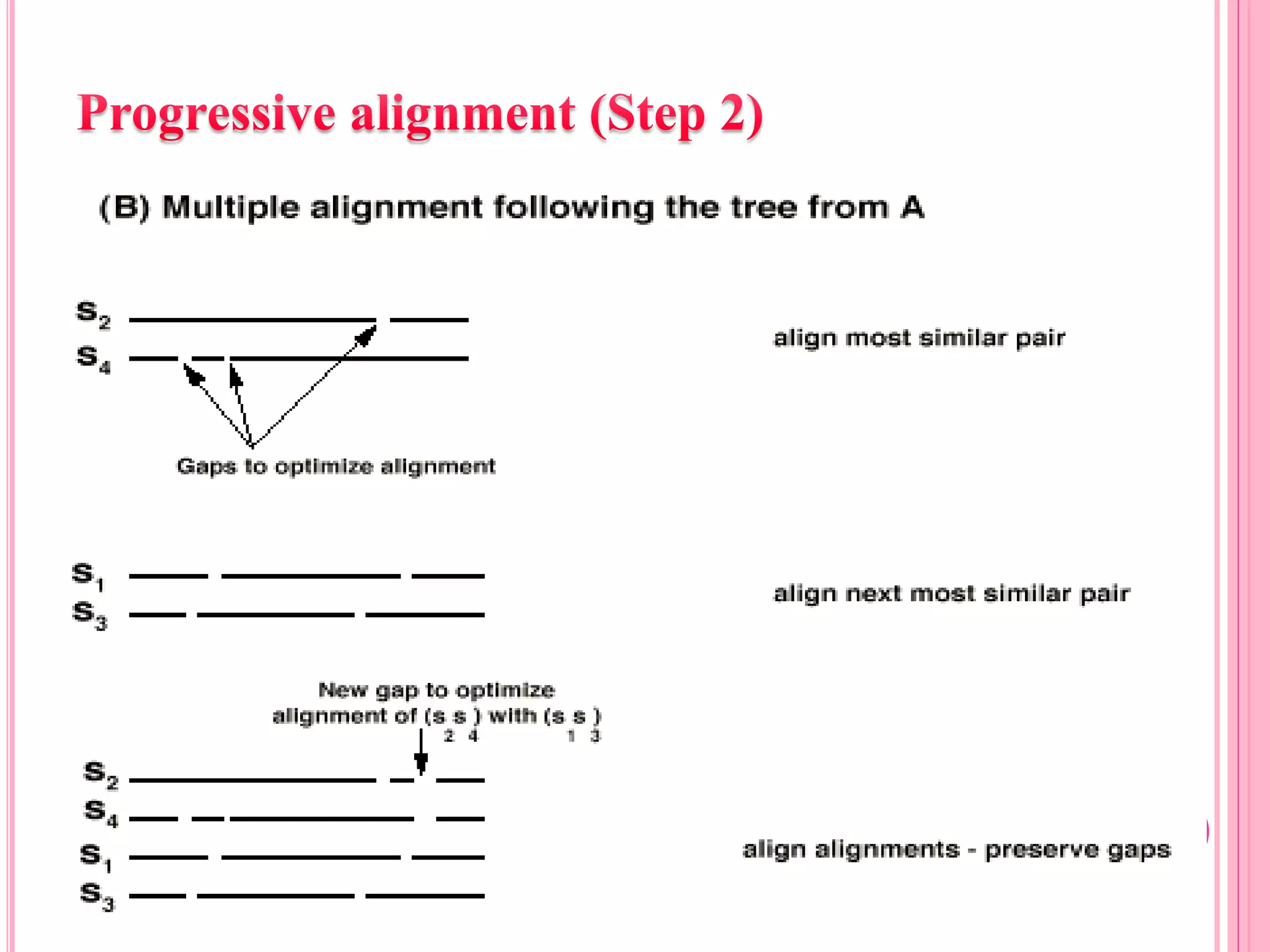
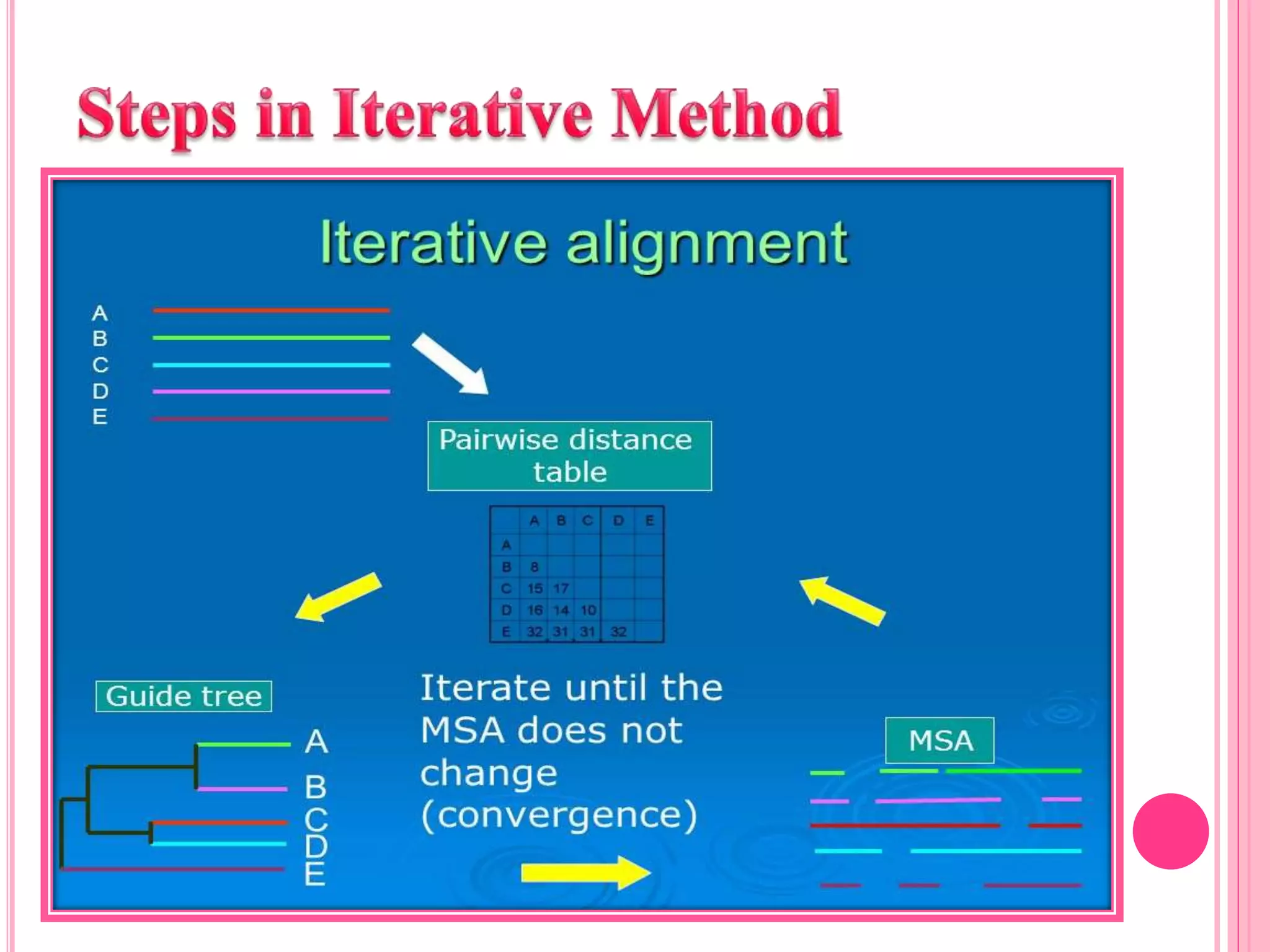
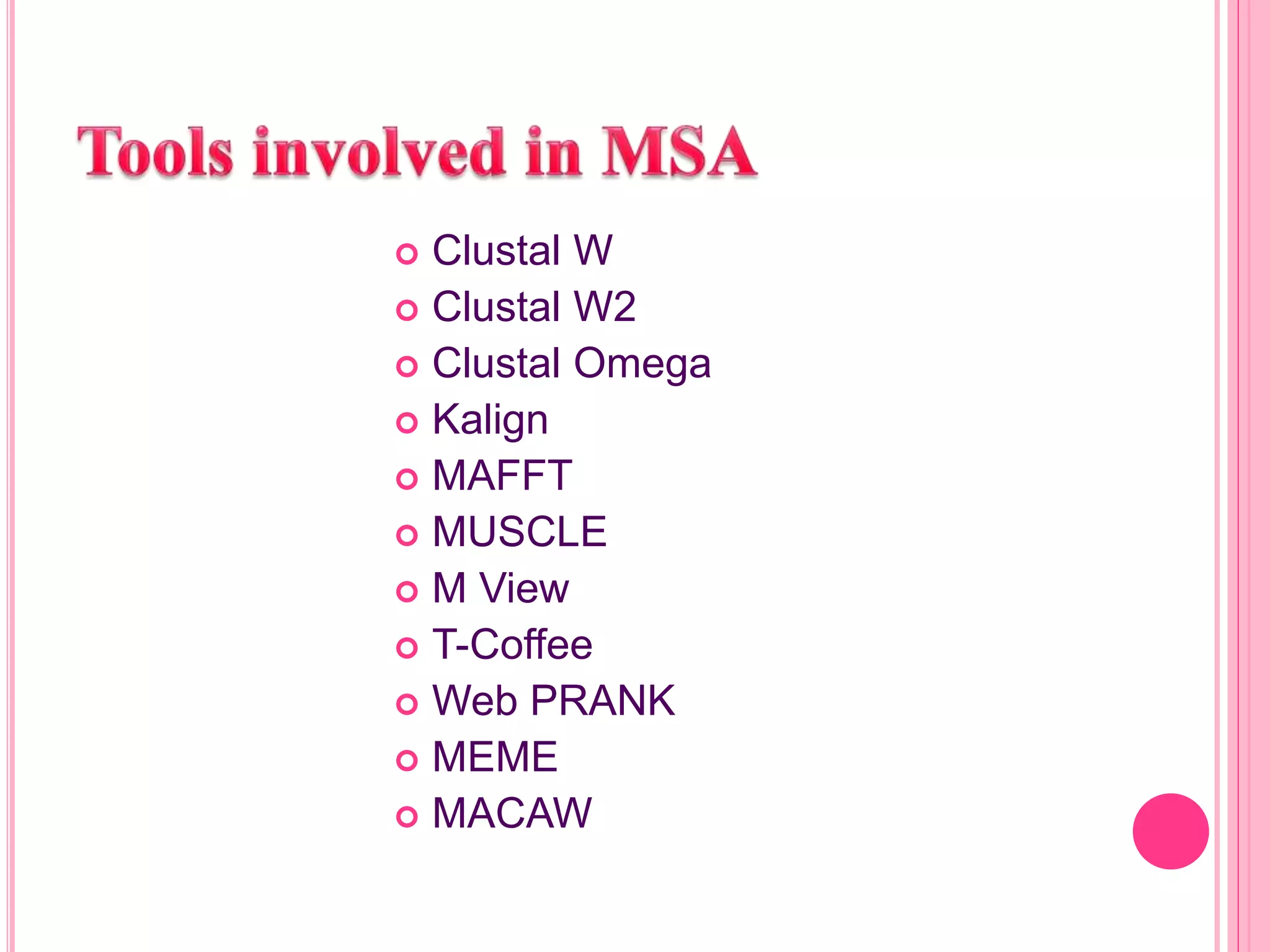
Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) aligns three or more biological sequences, like proteins or nucleic acids, to infer homology and evolutionary relationships. There are three main methods - dynamic programming computes an optimal alignment but has high runtime; progressive alignment first does pairwise alignments and adds sequences; iterative alignment successively improves approximations without pairwise alignments. Popular tools for MSA include Clustal W, MAFFT, MUSCLE, and T-Coffee. MSA helps detect similarities, conserved motifs, and structural homologies between sequences.