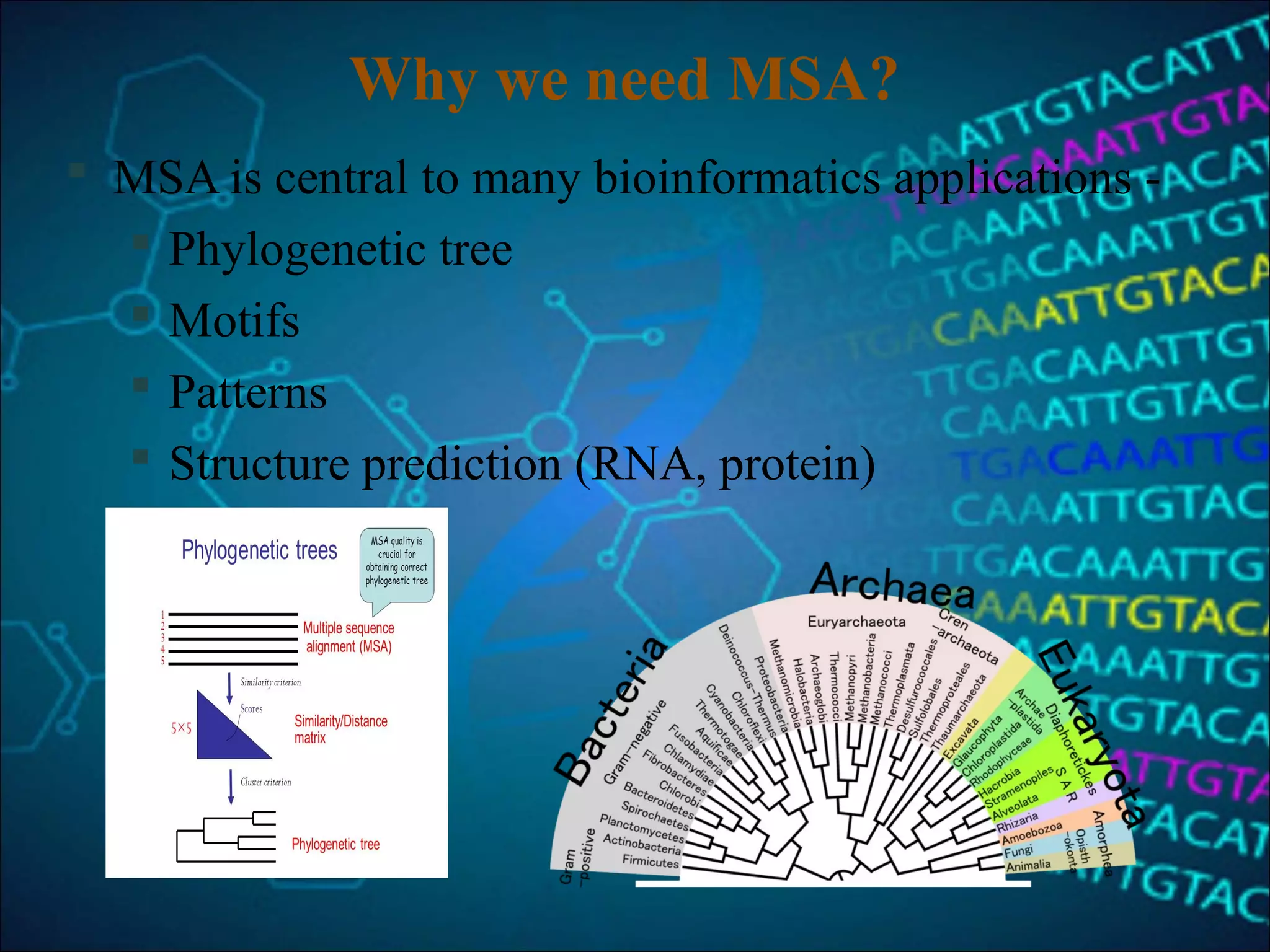
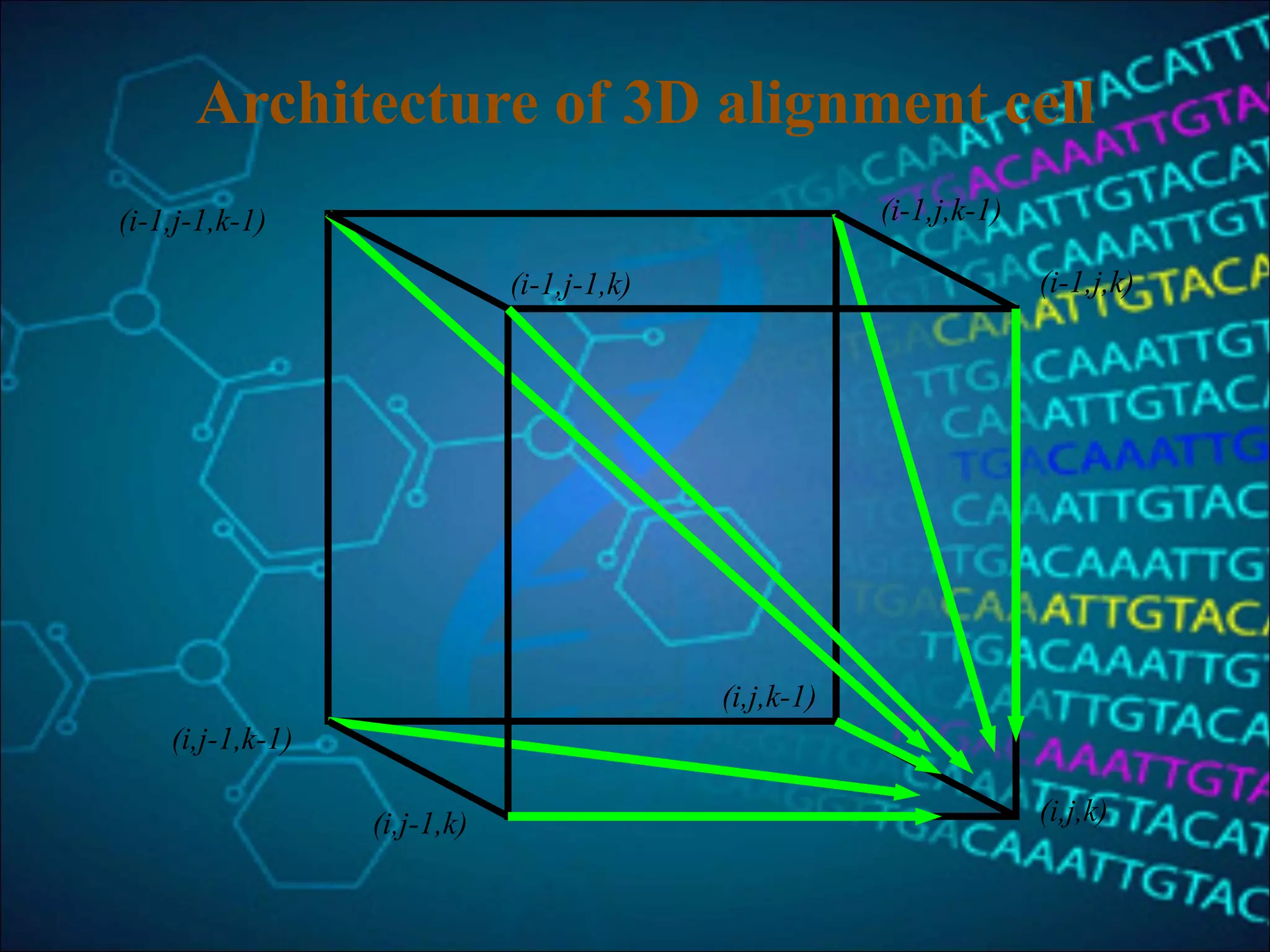
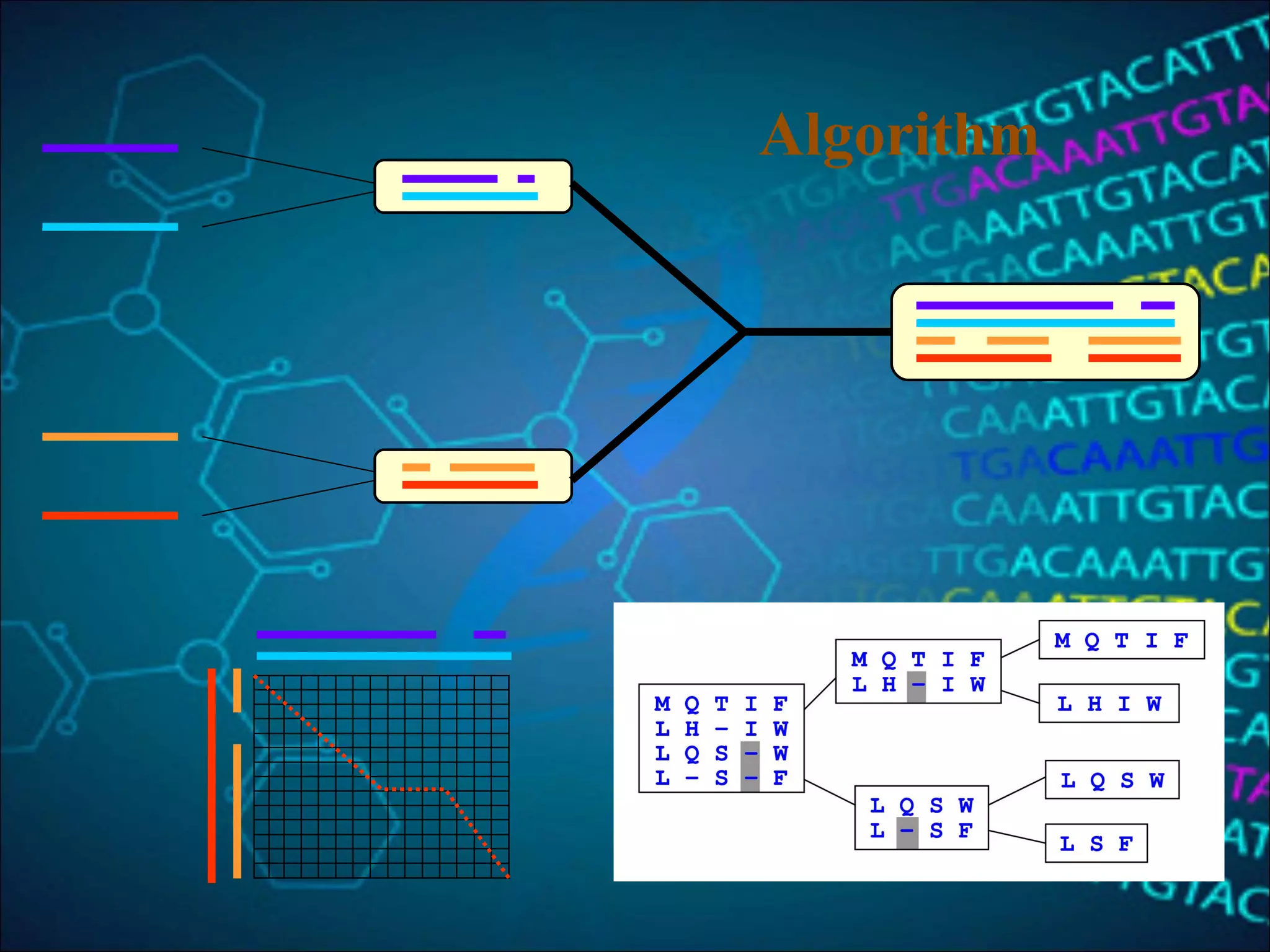
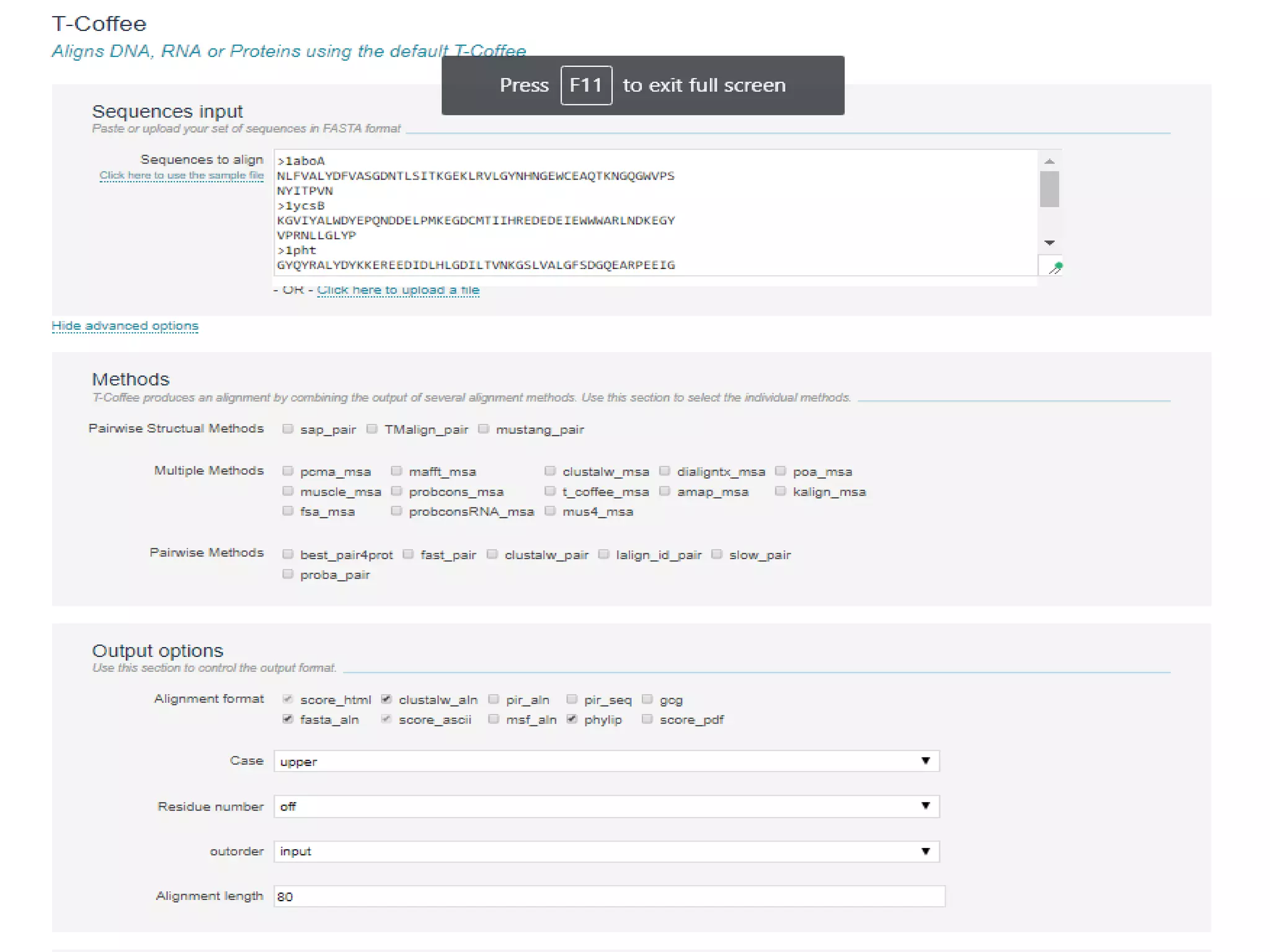
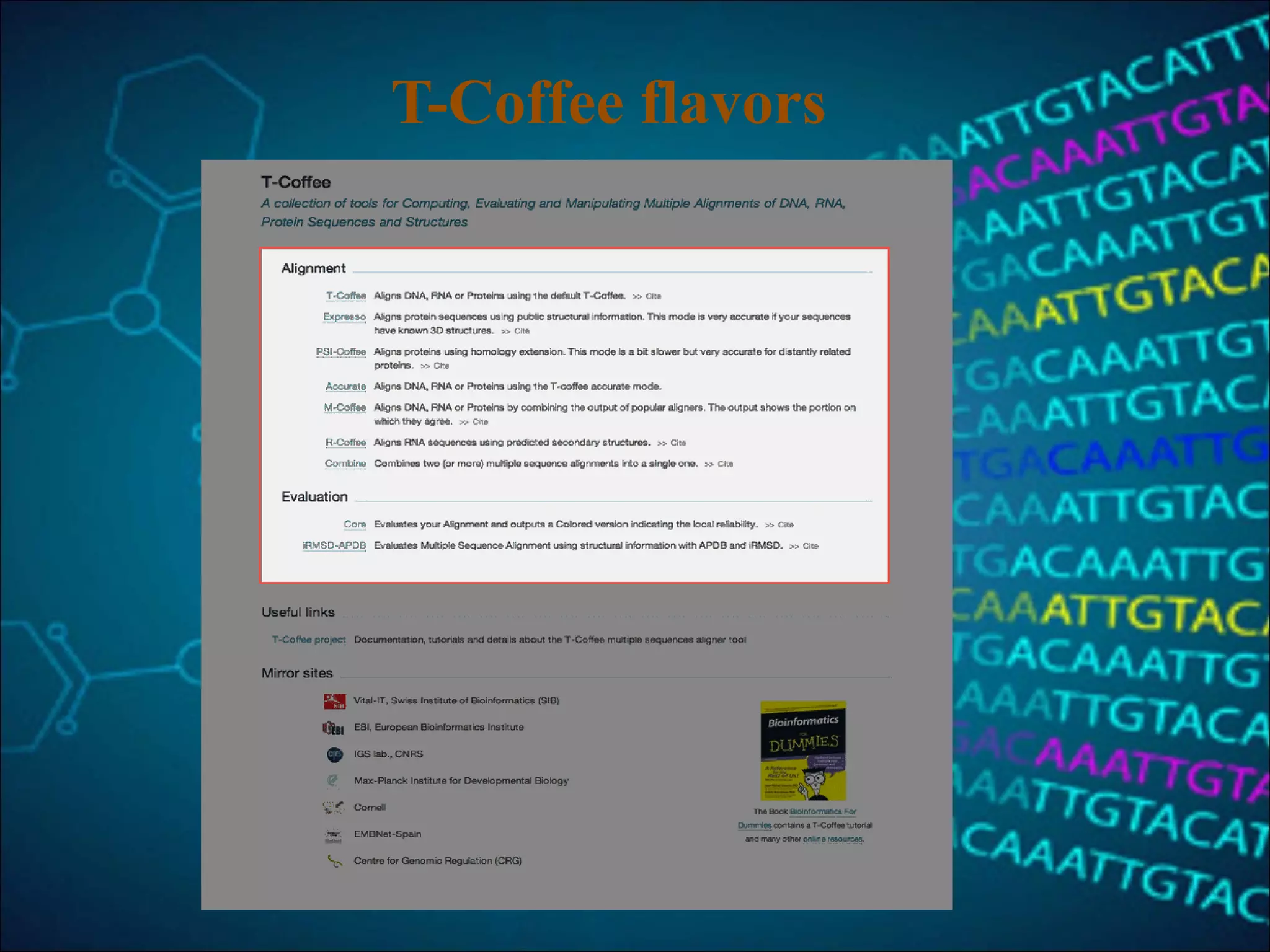
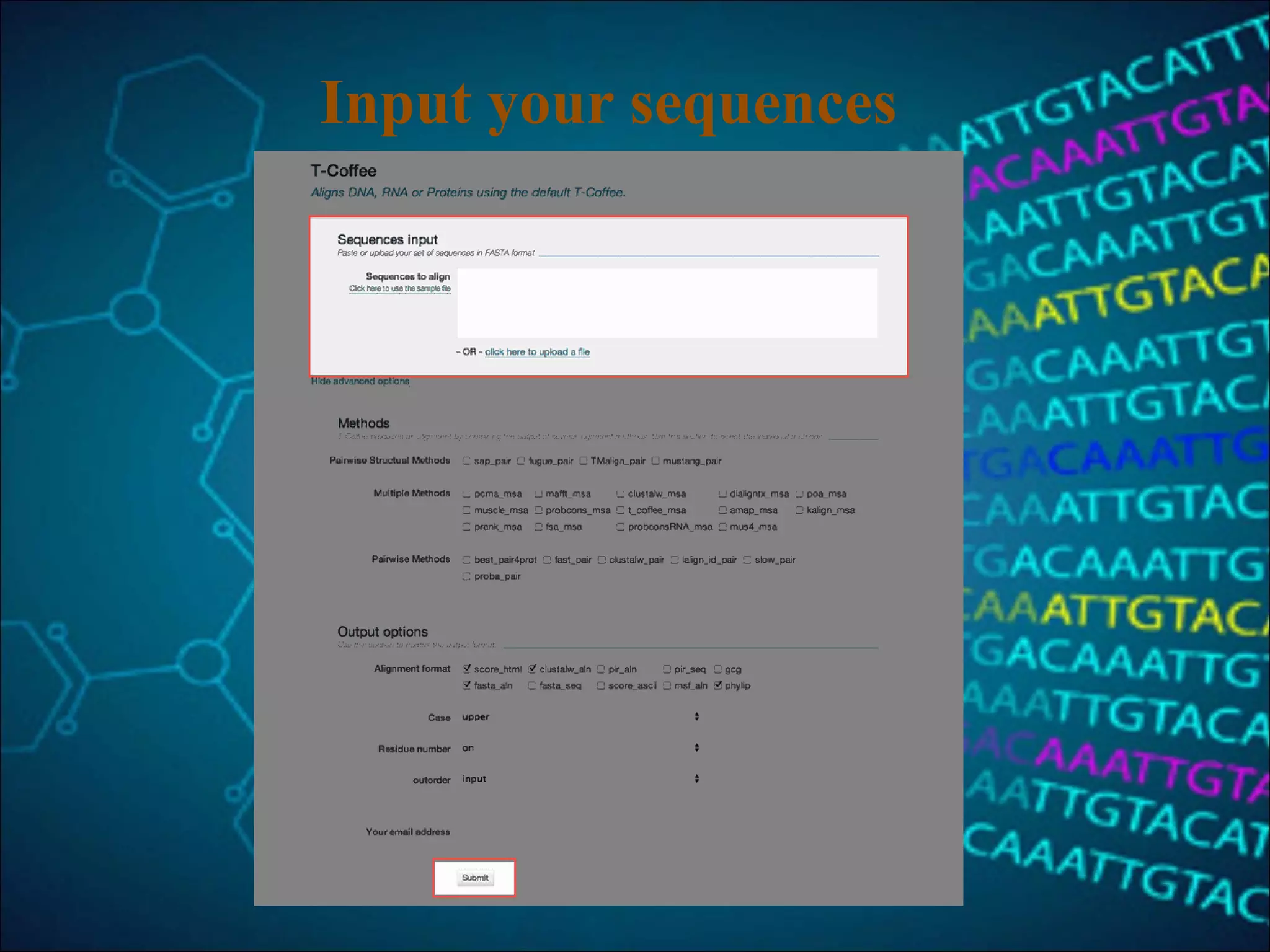
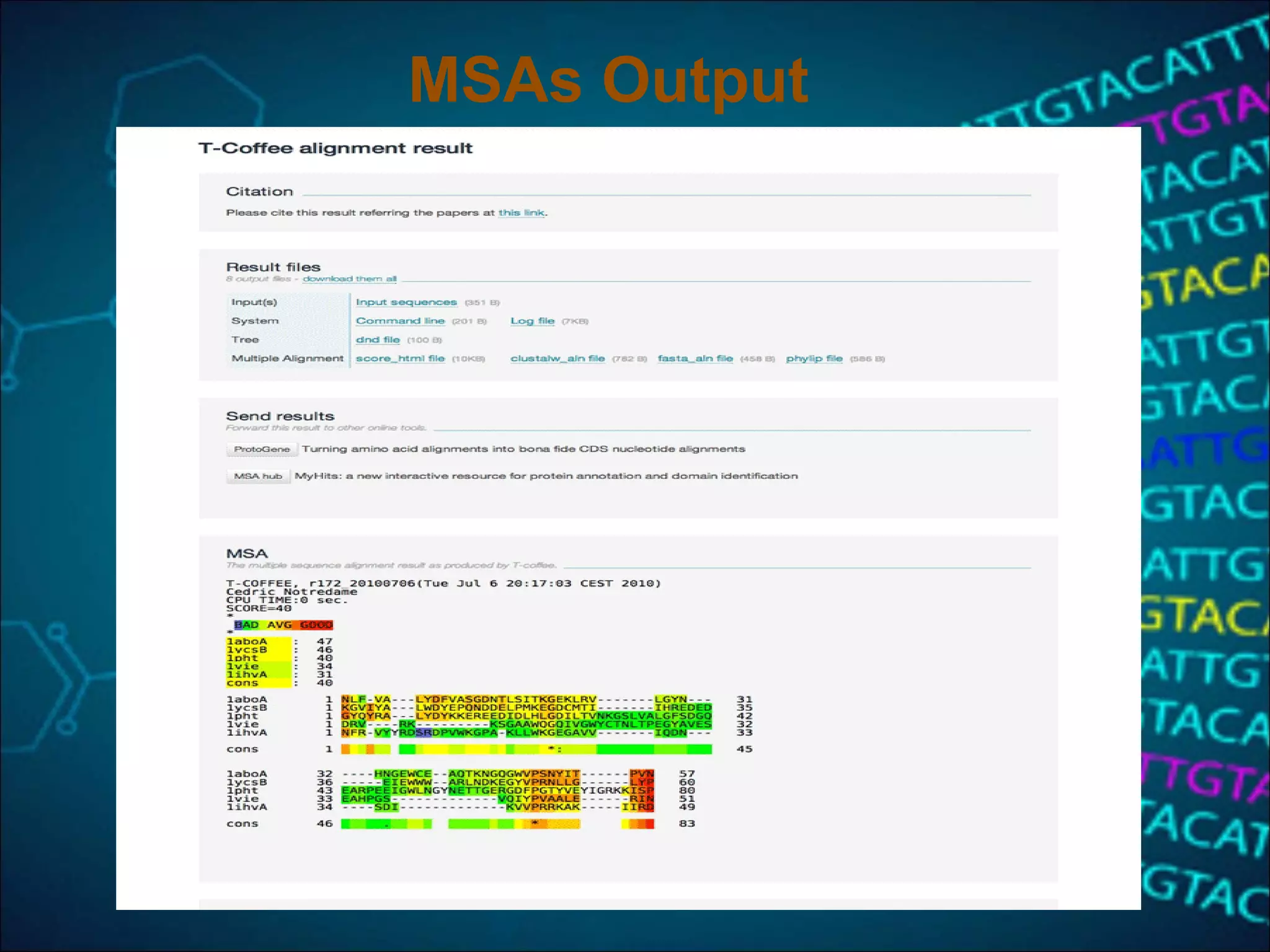
This document discusses multiple sequence alignment (MSA), which aligns three or more biological sequences to infer homology and evolutionary relationships. MSA is central to applications like phylogenetics, motif identification, and structure prediction. The key methods are dynamic programming, progressive alignment, and iterative refining. Dynamic programming uses an N-dimensional matrix for N sequences, with time and memory complexity of O(LN) for N sequences of length L. Progressive alignment first builds a tree guide and then aligns sequences according to the tree, while iterative refining repeatedly realigns sequences to reduce errors. Popular tools include Clustal, MUSCLE, and T-Coffee.