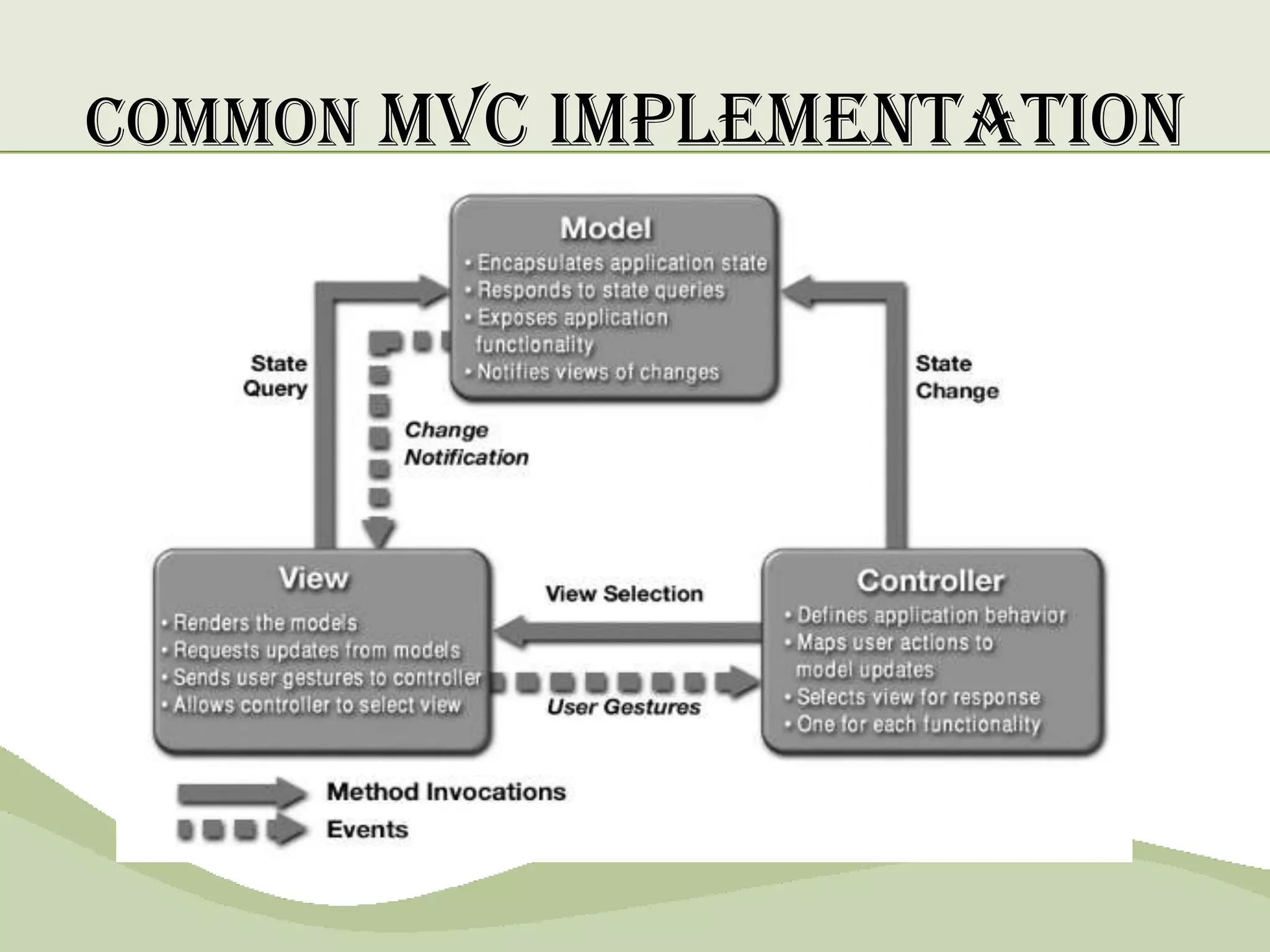
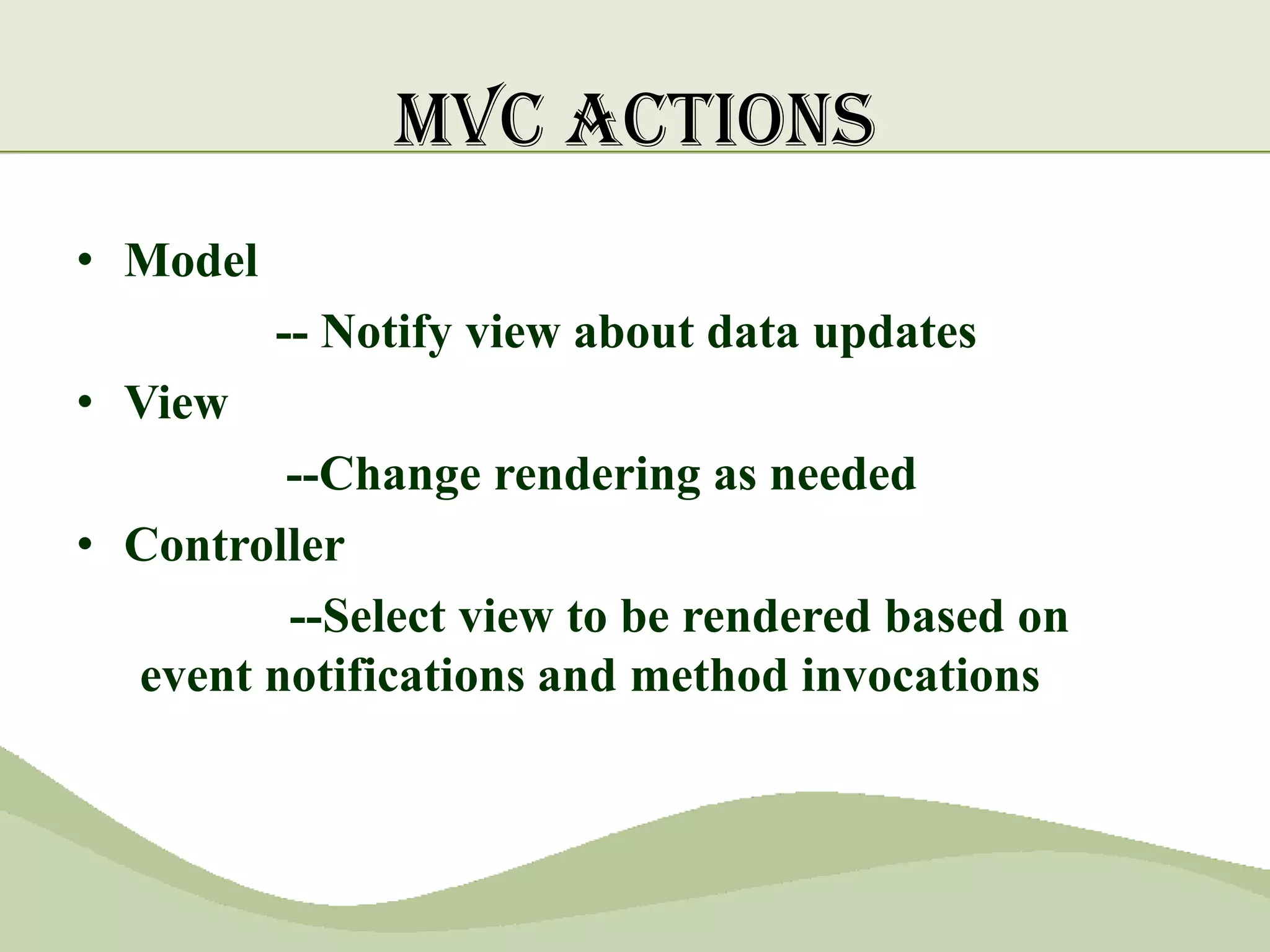
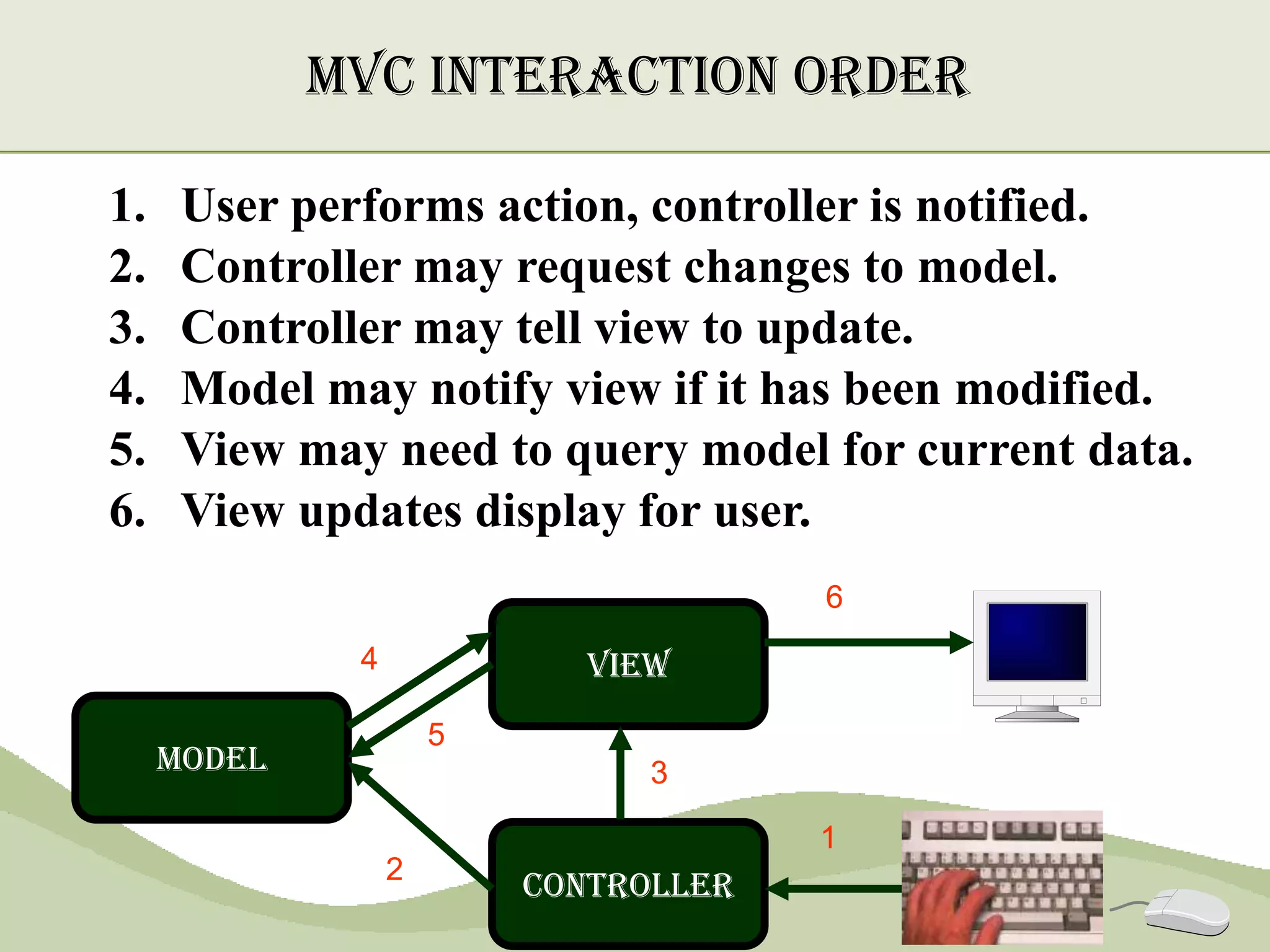
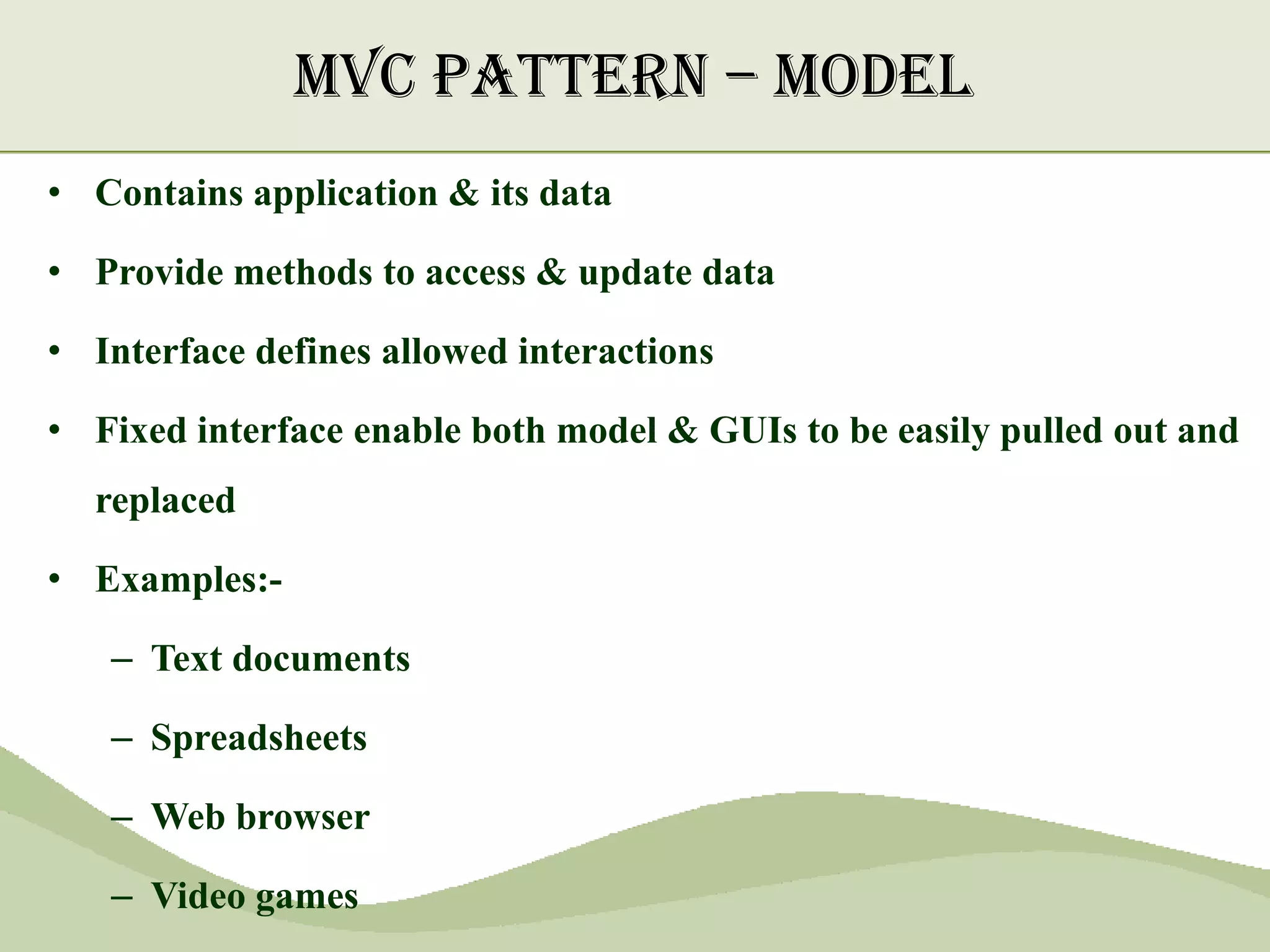
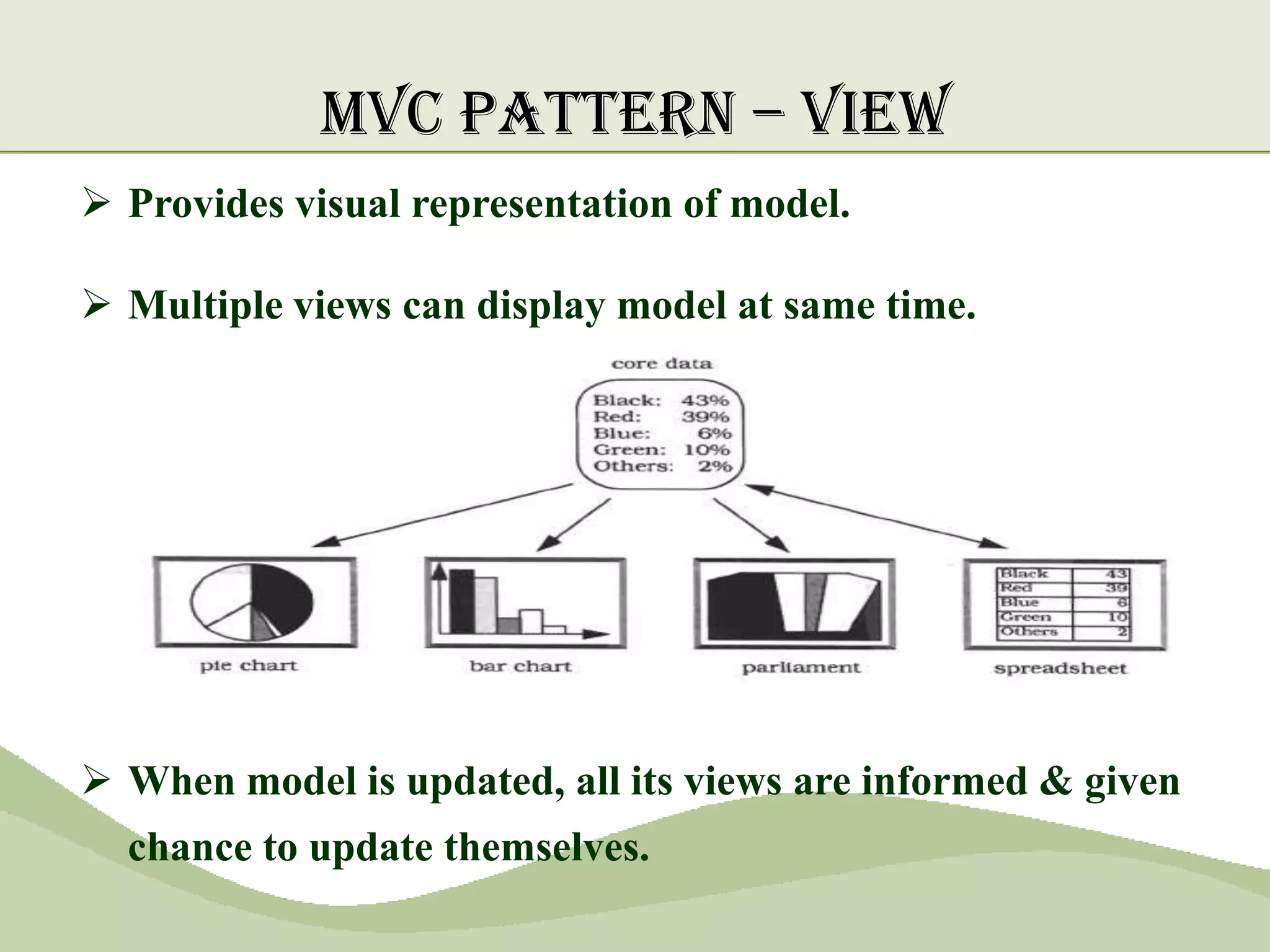
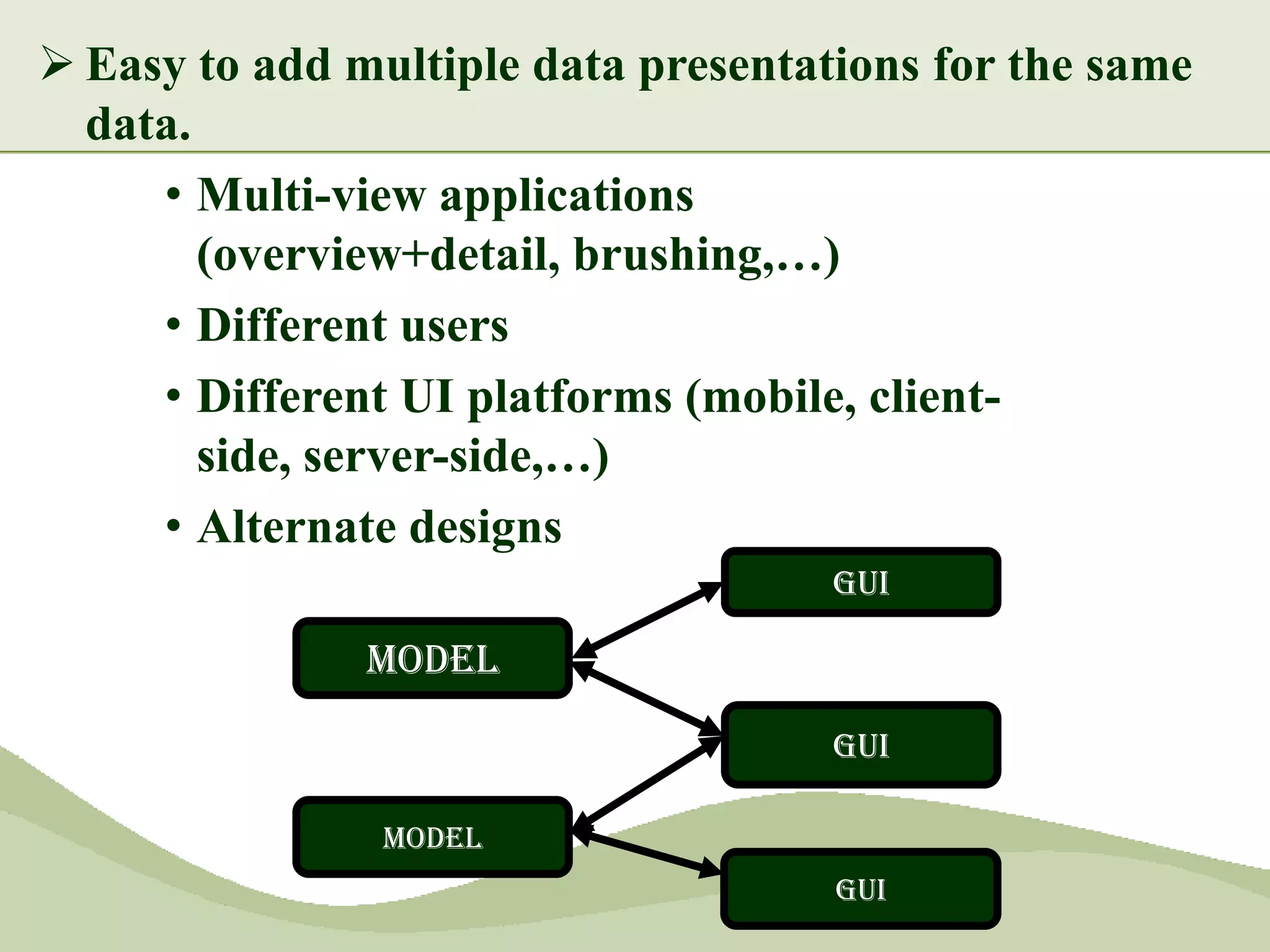
The document discusses the MVC pattern for developing user interfaces, which separates an application into three components - the model manages the core data and logic, the view handles visual presentation of the data to the user, and the controller receives user input and translates it into actions on the model. The MVC pattern promotes separation of concerns, makes the code more modular and reusable, and allows independent development and updating of each component without impacting the others. Common implementations of MVC involve the model notifying subscribed views of any data changes, the controller handling user input to update the model and selecting views, and views updating their presentation when the model changes.