Download as PDF, PPTX



































This document discusses various strategies for optimizing MySQL queries and indexes, including: - Using the slow query log and EXPLAIN statement to analyze slow queries. - Avoiding correlated subqueries and issues in older MySQL versions. - Choosing indexes based on selectivity and covering common queries. - Identifying and addressing full table scans and duplicate indexes. - Understanding the different join types and selecting optimal indexes.














































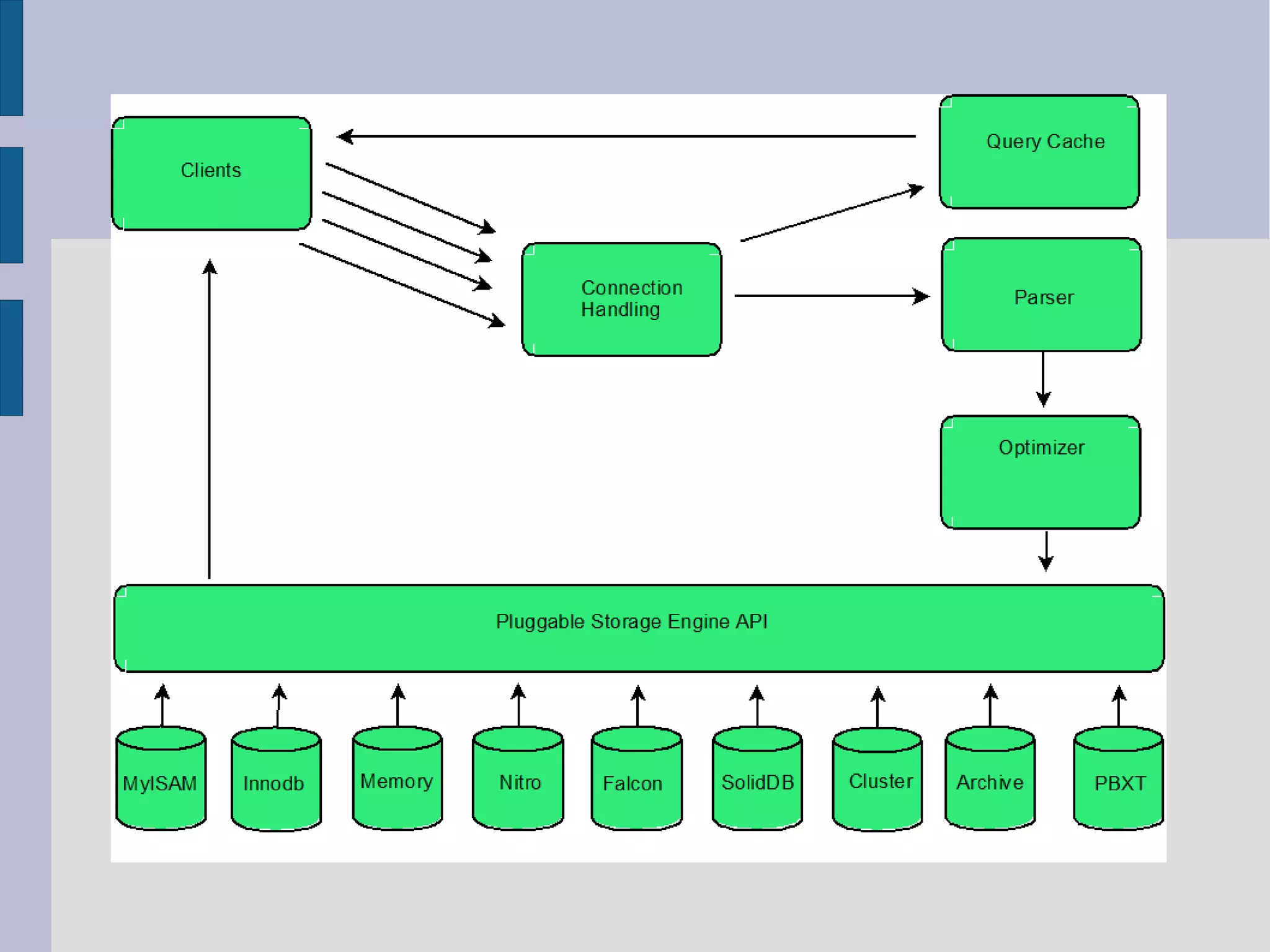
Overview of MySQL query tuning principles including slow query logging, EXPLAIN statement, indexing strategies, and MySQL optimizations.
Explanation of slow query logging and its defaults, including sample outputs and the use of mysqldumpslow command.
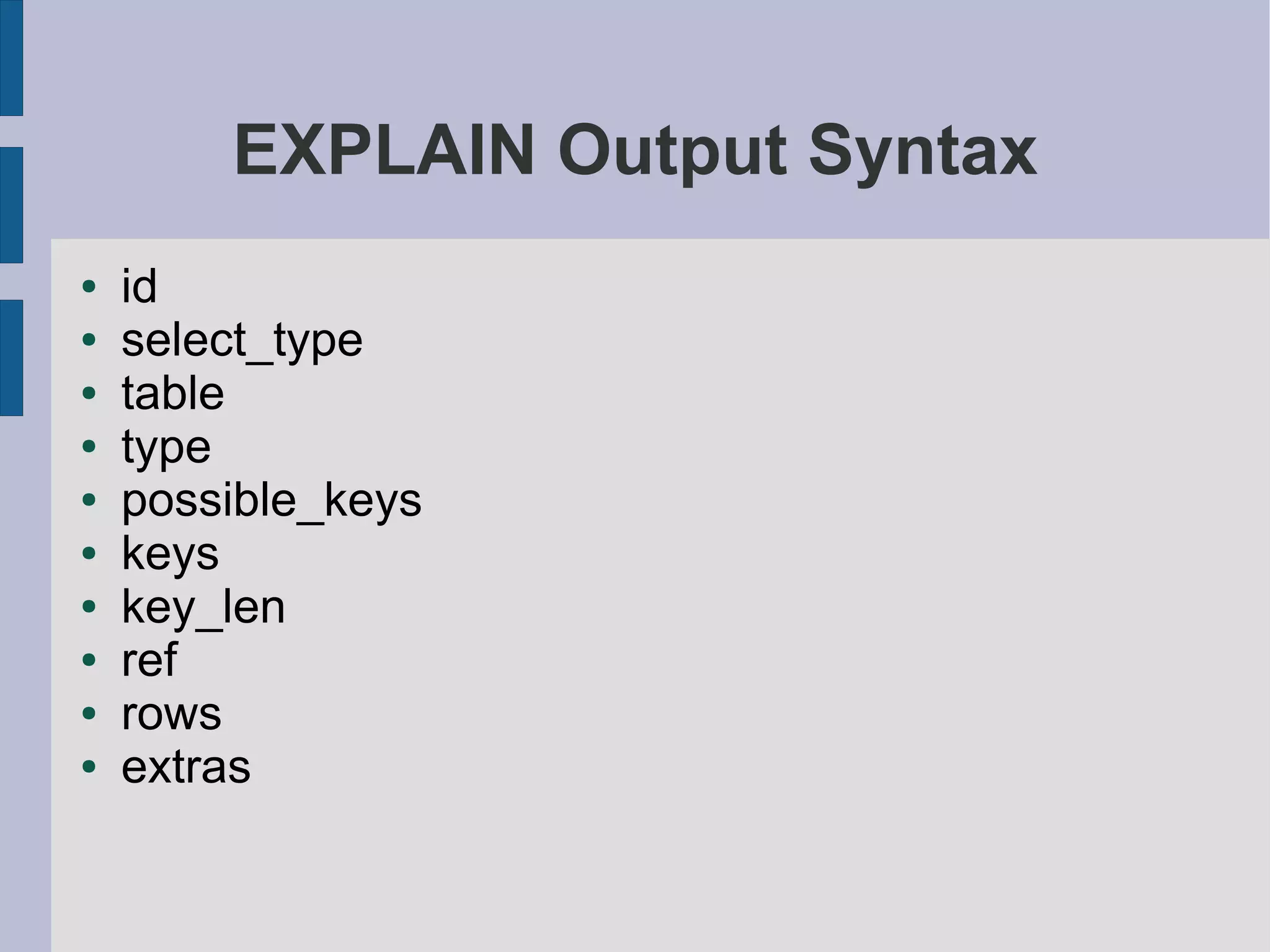
Overview of the EXPLAIN statement format, its components, and the significance of various select types in evaluating query performance.
Explanation of different SQL join types including SIMPLE, PRIMARY, UNION and their usage with examples.
List of common pitfalls in queries to avoid, particularly correlated subqueries and specific version limitations.
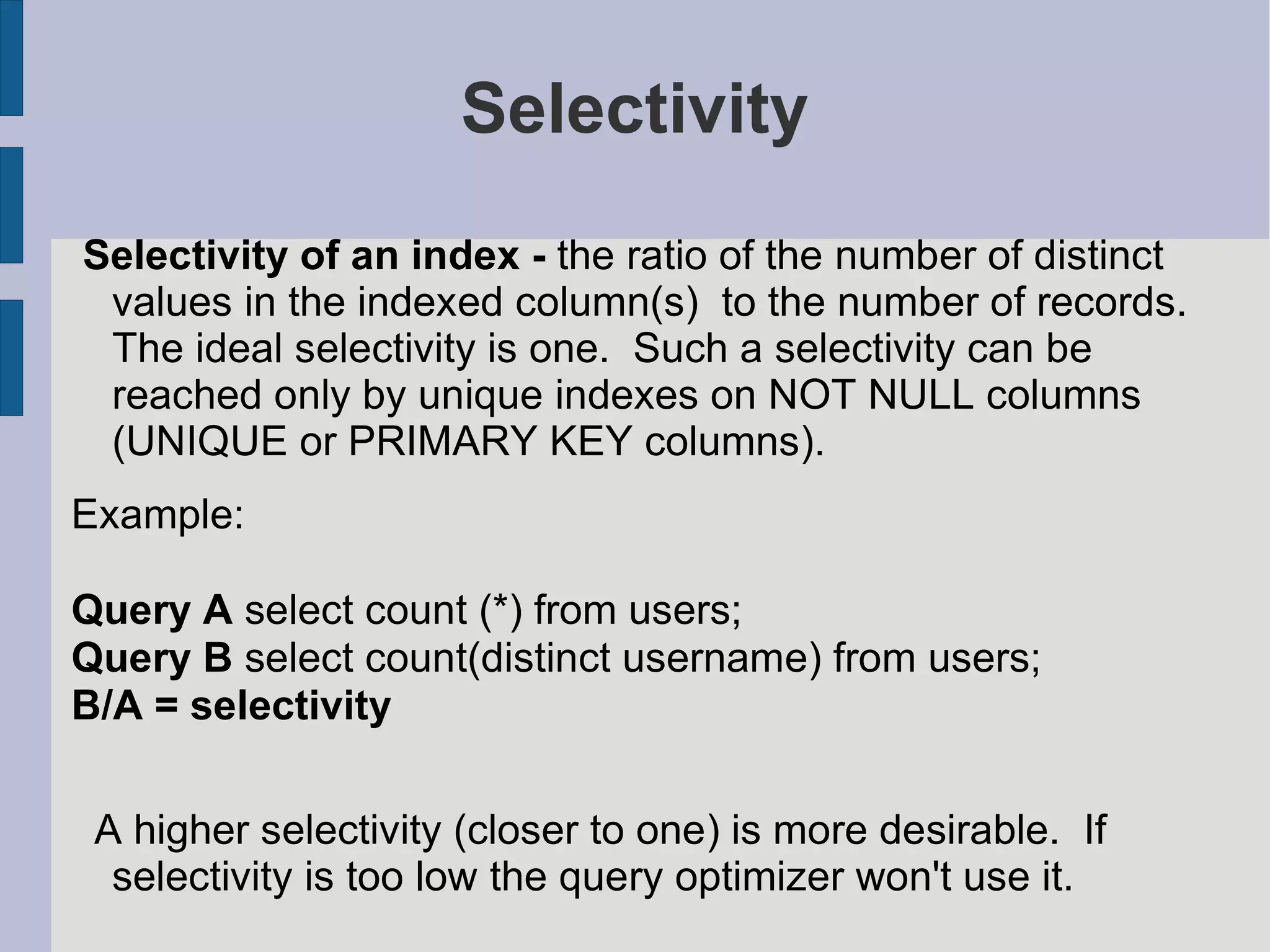
Strategies for indexing tables, defining optimal index usage, and understanding selectivity in indexing.
Discussion on full table scans, reasons for occurrence, and methods to identify them using EXPLAIN.
Insights into covering indexes, their advantages and specific scenarios such as large tables.
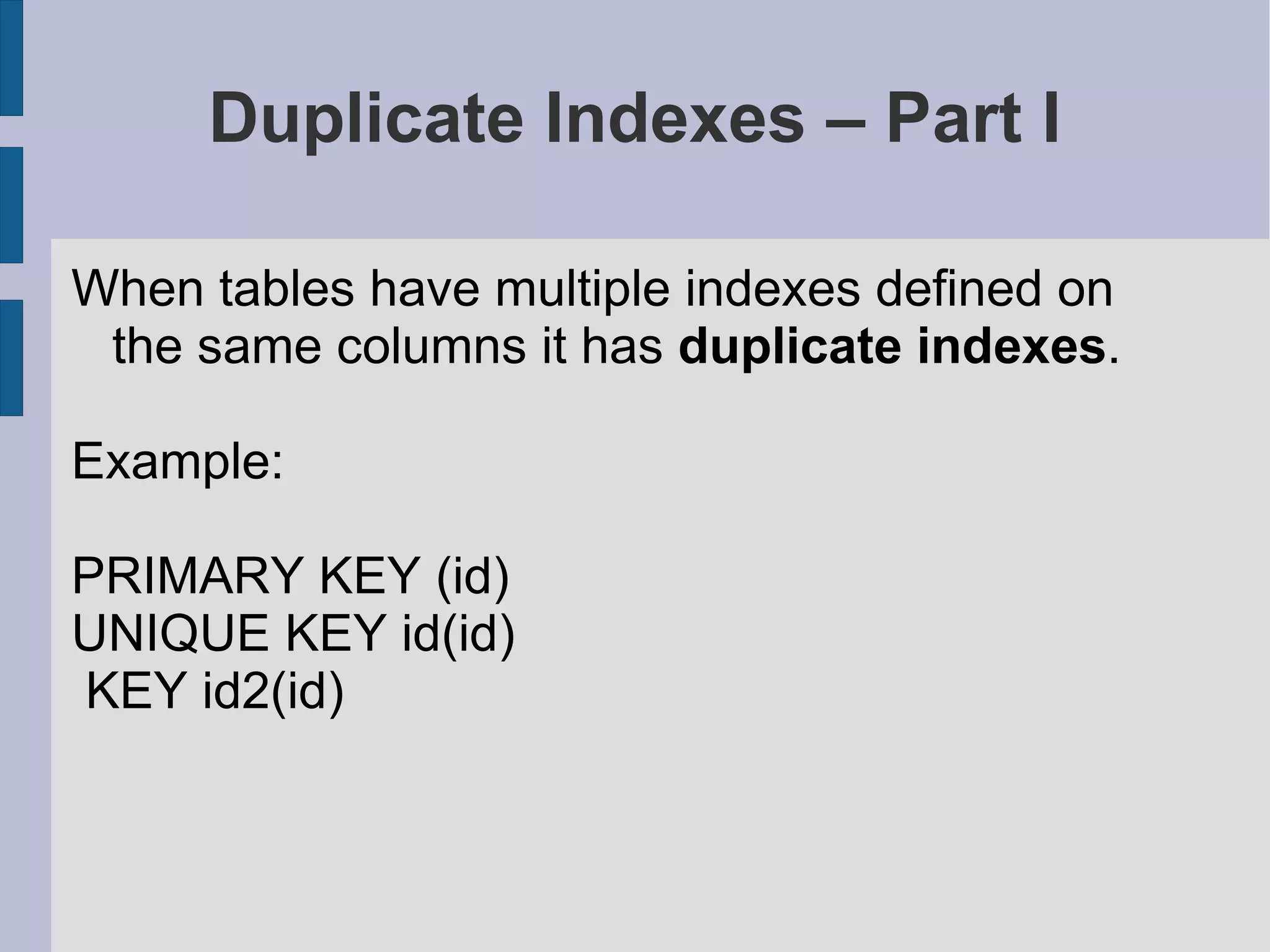
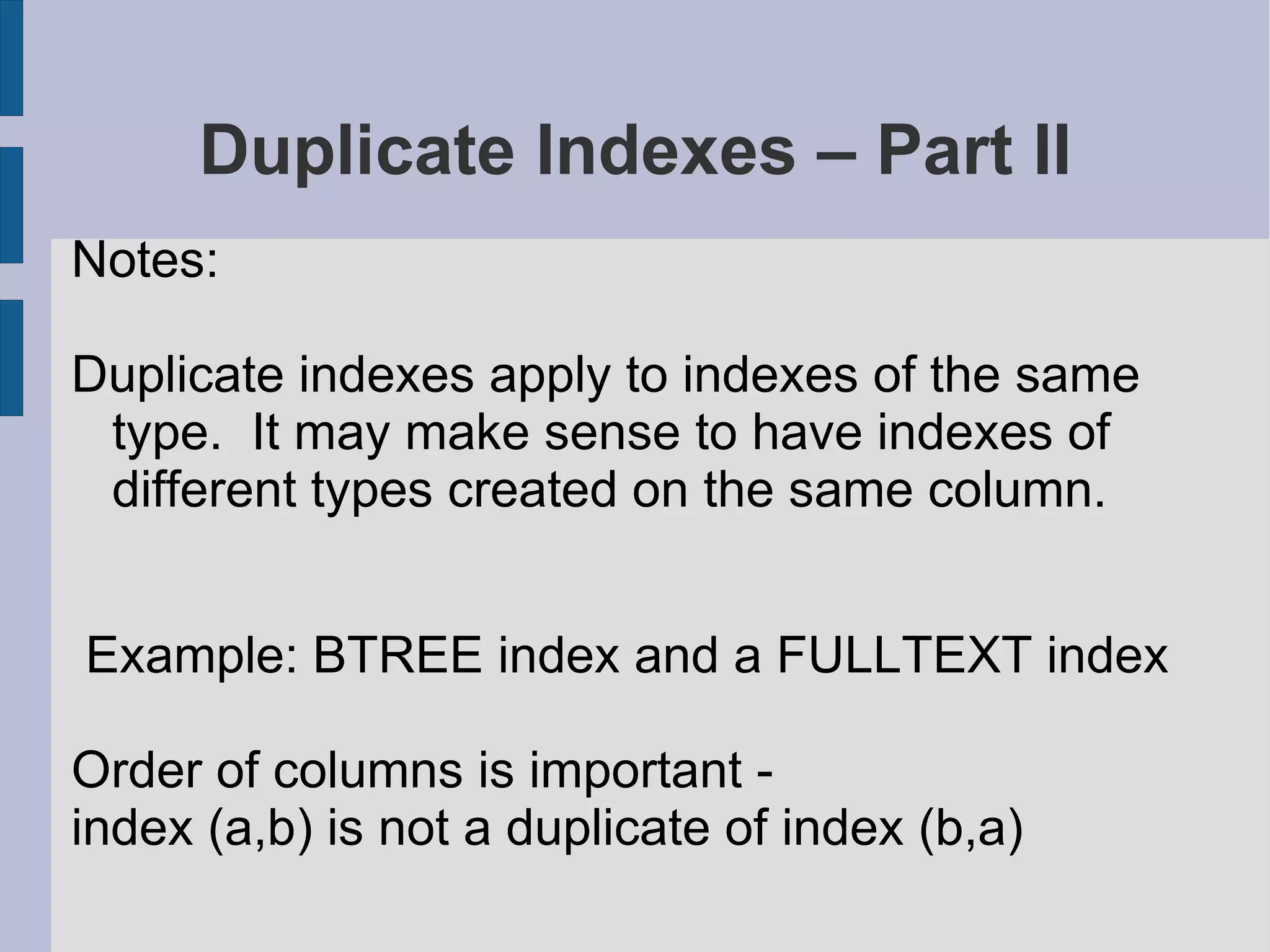
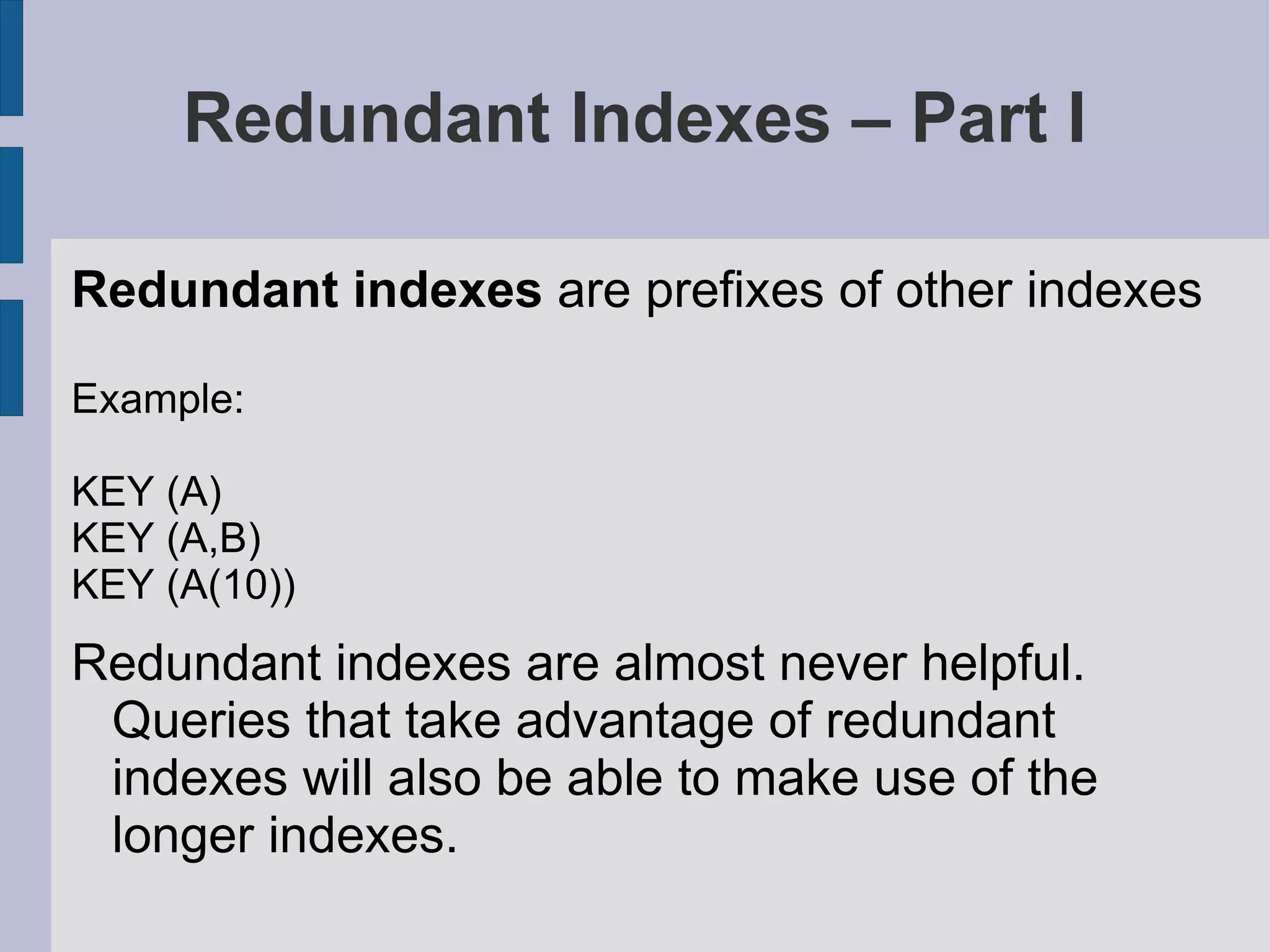
Analysis of duplicate and redundant indexes, including examples and implications for query performance.
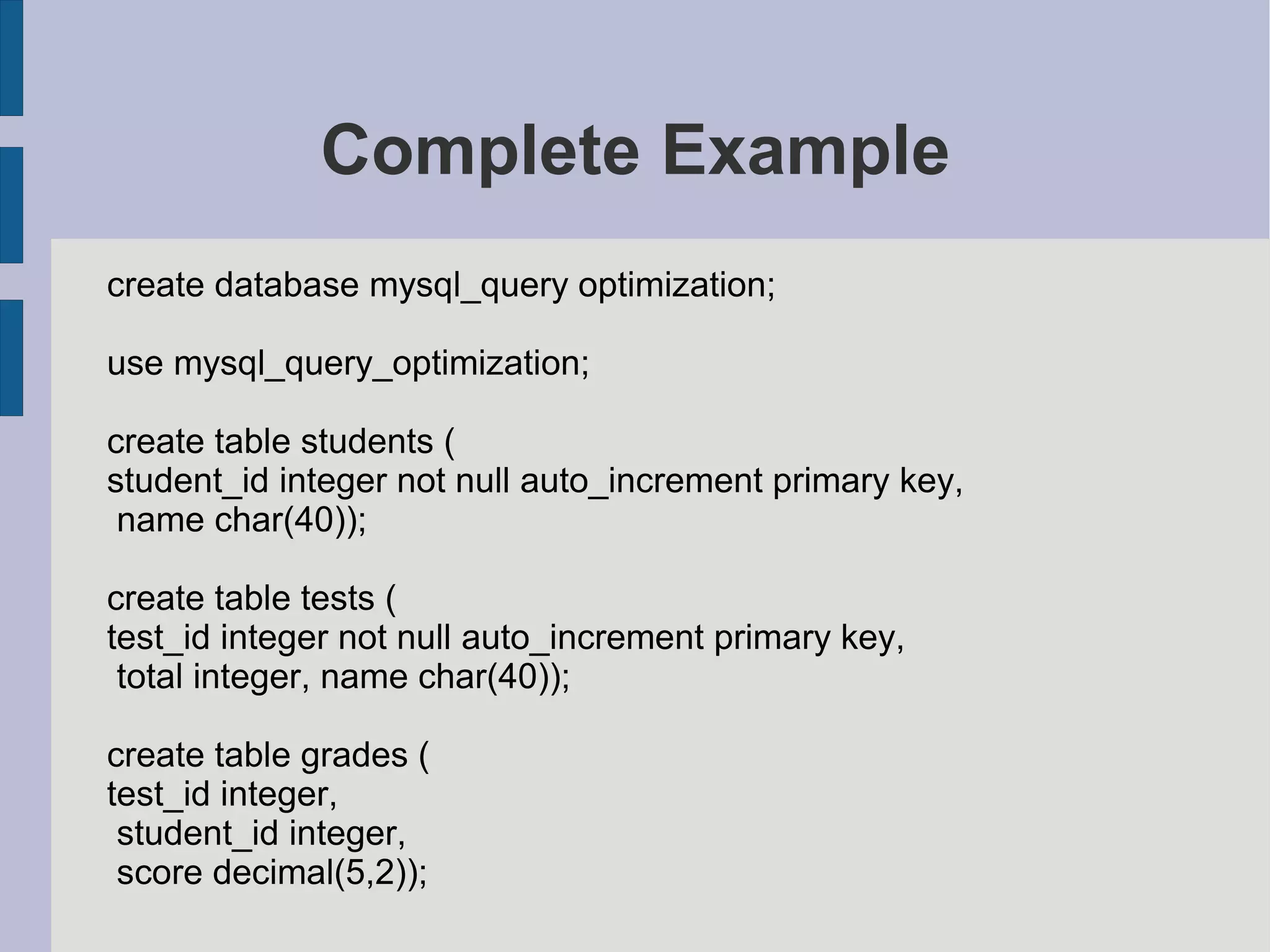
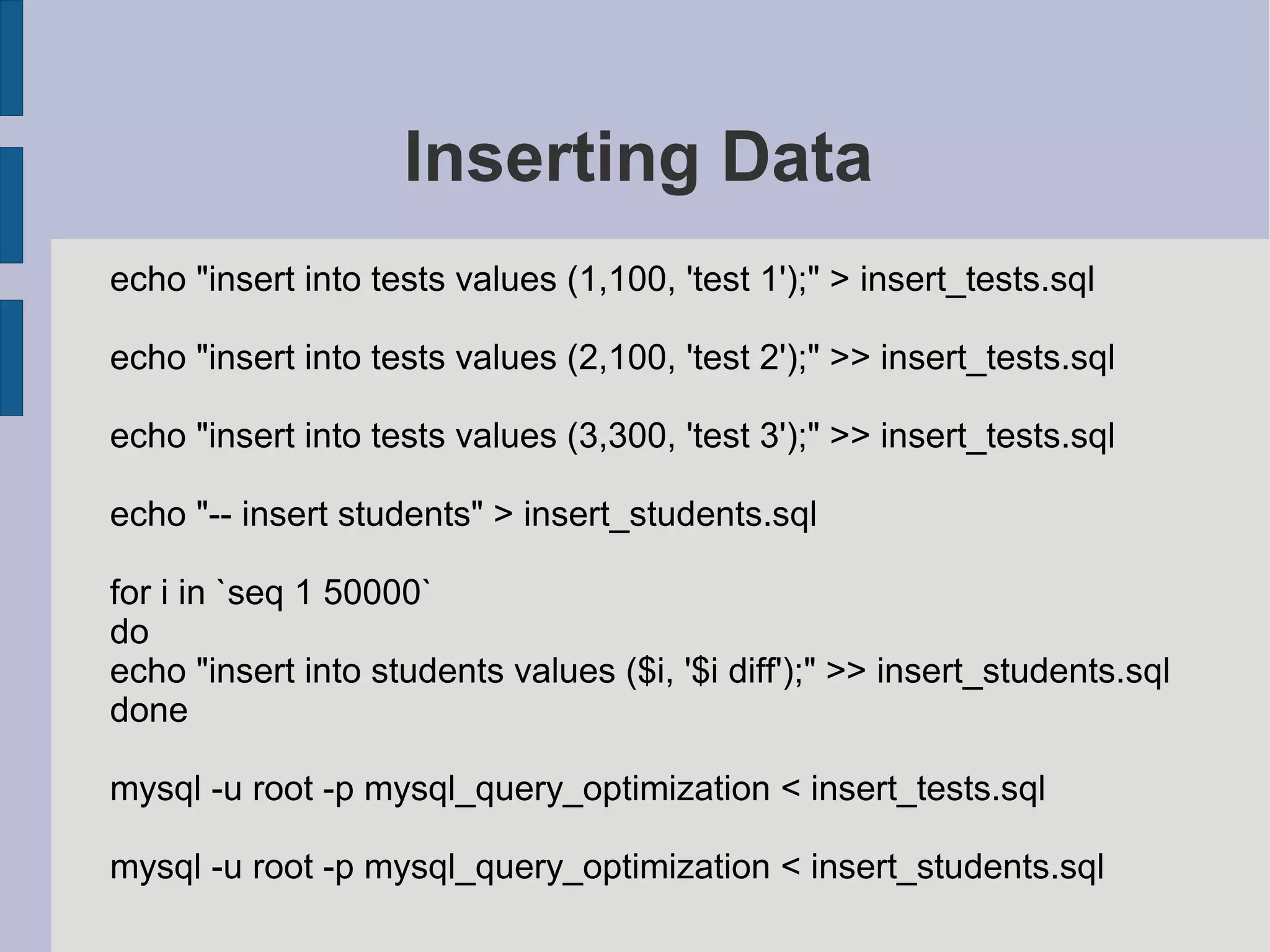
SQL examples for inserting test data into tables for performance testing without indexes.
Demonstration of the impact of indexes on SQL query performance with EXPLAIN outputs before and after indexing.
Overview of MySQL's cost-based and rule-based optimizers, their functionality, and potential pitfalls.
Best practices for schema design, including data type selection and normalization.
Understanding query cache usage and the balance between performance and CPU usage.
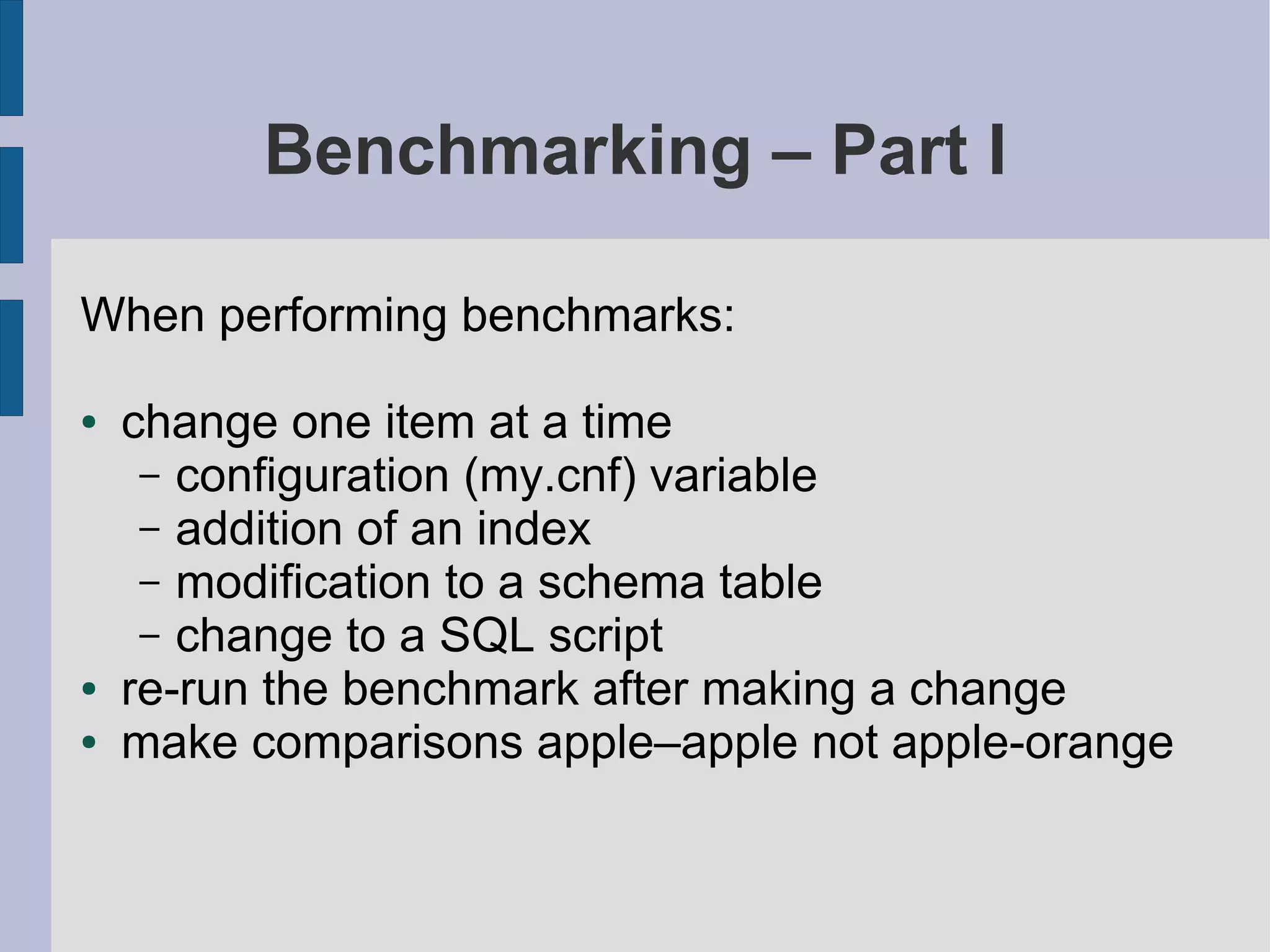
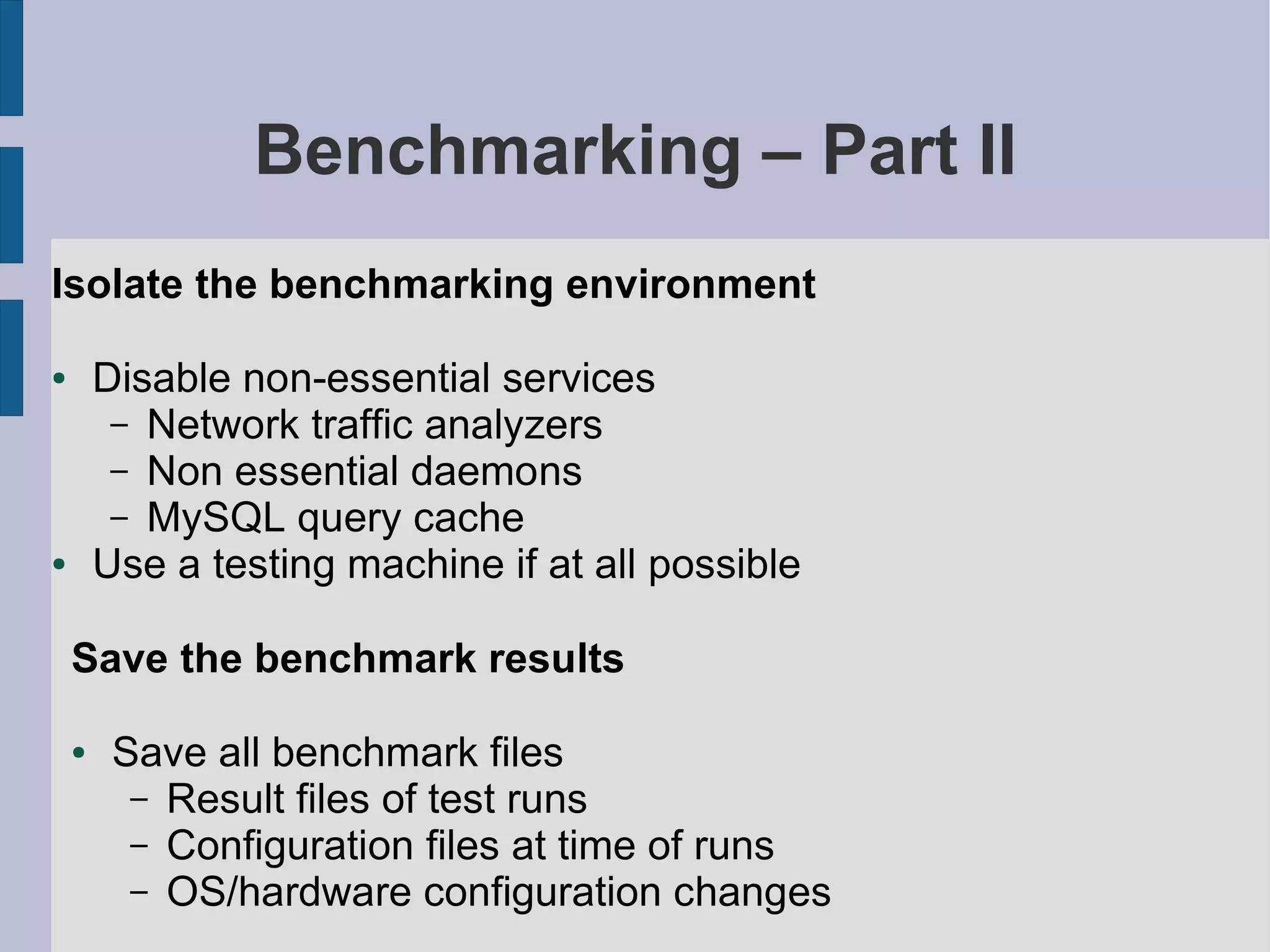
Guidelines for benchmarking MySQL performance, including environmental isolation and tools to use.
Recommended benchmarking tools and resources for SQL tuning and database design.