Numpy_Arrays in python libraries use.pptx
Recommended
PDF
PDF
Essential numpy before you start your Machine Learning journey in python.pdf
PPTX
Introduction to Numpy module in Python.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
NumPy-python-27-9-24-we.pptxNumPy-python-27-9-24-we.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
Numpy in python, Array operations using numpy and so on
PPTX
NUMPY LIBRARY study materials PPT 2.pptx
PDF
PDF
PPTX
Introduction-to-NumPy-in-Python (1).pptx
PPTX
PDF
PDF
Introduction to NumPy (PyData SV 2013)
PDF
PDF
Python_cheatsheet_numpy.pdf
PDF
NumPy__data__anlysis___using__python.pdf
PDF
NumPy__data__anlysis___using__python.pdf
PPTX
Arrays with Numpy, Computer Graphics
PPTX
UNIT-03_Numpy (1) python yeksodbbsisbsjsjsh
PPTX
lec08-numpyIntroduction_to_Matplotlib_Detailed.pptx
PPT
PPT
PPTX
NumPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPpy.pptx
PPT
Introduction to Numpy Foundation Study GuideStudyGuide
PPTX
PDF
ACFrOgAabSLW3ZCRLJ0i-To_2fPk_pA9QThyDKNNlA3VK282MnXaLGJa7APKD15-TW9zT_QI98dAH...
PPTX
L 5 Numpy final learning and Coding
PPTX
Understanding UL Wire Options that Surpass Industry Standards
PPT
23 EL PGS Sec-I (Shared).ppt power generation systems
More Related Content
PDF
PDF
Essential numpy before you start your Machine Learning journey in python.pdf
PPTX
Introduction to Numpy module in Python.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
NumPy-python-27-9-24-we.pptxNumPy-python-27-9-24-we.pptx
PPTX
PPTX
Numpy in python, Array operations using numpy and so on
PPTX
NUMPY LIBRARY study materials PPT 2.pptx
Similar to Numpy_Arrays in python libraries use.pptx
PDF
PDF
PPTX
Introduction-to-NumPy-in-Python (1).pptx
PPTX
PDF
PDF
Introduction to NumPy (PyData SV 2013)
PDF
PDF
Python_cheatsheet_numpy.pdf
PDF
NumPy__data__anlysis___using__python.pdf
PDF
NumPy__data__anlysis___using__python.pdf
PPTX
Arrays with Numpy, Computer Graphics
PPTX
UNIT-03_Numpy (1) python yeksodbbsisbsjsjsh
PPTX
lec08-numpyIntroduction_to_Matplotlib_Detailed.pptx
PPT
PPT
PPTX
NumPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPPpy.pptx
PPT
Introduction to Numpy Foundation Study GuideStudyGuide
PPTX
PDF
ACFrOgAabSLW3ZCRLJ0i-To_2fPk_pA9QThyDKNNlA3VK282MnXaLGJa7APKD15-TW9zT_QI98dAH...
PPTX
L 5 Numpy final learning and Coding
Recently uploaded
PPTX
Understanding UL Wire Options that Surpass Industry Standards
PPT
23 EL PGS Sec-I (Shared).ppt power generation systems
PDF
Somnath Mukherjee_BIM Specialist_Resume.pdf
PPTX
Data types and datatype conversions of python programming.pptx
PPTX
COLLAGE PLACEMENT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM.pptx
PPTX
Introduction to engineering dynamics for structural engineering student
PPTX
Hydrocarbon traps, migration and accumulation of petroleum
PPTX
E waste_management_module 4.pptx_22_scheme_VTU
PPTX
An improved feature extraction algorithm of EEG signals
PDF
energies-14-0ggggggggggggggggg2725-v2.pdf
PPTX
Optimizing Wave Energy Capture: Utilizing Variable-Pitch Turbine Blades in We...
PDF
mariadbwebinardr07301000156458558219.pdf
PPT
Basic electronics concepts like what is resistor , inductor capacitor
PPTX
Basic presentation - architecture pics.pptx
PPTX
All About Introduction to Artificial IntelligenceAI.pptx
PPT
lec0_Introduction_to_cmos_vlsi_design.ppt
PDF
International Journal of Network Security & Its Applications (IJNSA)
PDF
Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP): Unit 4
PPTX
UNIT - IV - Computer aided process planning - part 2.pptx
PPTX
AUV DESIGN and DEVELOPMENT FOR DEEP SEA MINING ( POLYMETALLIC NODULES) in MRC...
Numpy_Arrays in python libraries use.pptx 1. 2. What is NumPy?
• NumPy (Numerical Python) is a library for
numerical operations.
• - Supports multi-dimensional arrays
• - Efficient and fast operations
• - Used in ML, data science, and scientific
computing
3. Creating Arrays
• 1D Array:
np.array([1, 2, 3]) → [1 2 3]
• 2D Array:
np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]]) → [[1 2]
[3 4]]
4. 5. 6. Array Range and Linspace
• np.arange(0, 10, 2) → [0 2 4 6 8]
• np.linspace(0, 1, 5) → [0. 0.25 0.5 0.75 1. ]
7. 8. 9. 10. Mathematical Operations
• a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
• b = np.array([4, 5, 6])
• a + b → [5 7 9]
• a * b → [4 10 18]
• np.sqrt(a) → [1. 1.41 1.73]
11. Aggregate Functions
• a = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
• a.sum() → 10
• a.mean() → 2.5
• a.min() → 1
• a.max() → 4
• a.sum(axis=0) → [4 6]
12. Broadcasting
• a = np.array([[1], [2], [3]])
• b = np.array([10, 20])
• a + b → [[11 21]
• [12 22]
• [13 23]]
13. Copy vs View
• a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
• b = a.view() → Shares memory
• c = a.copy() → New memory
• Changing b affects a; changing c does not
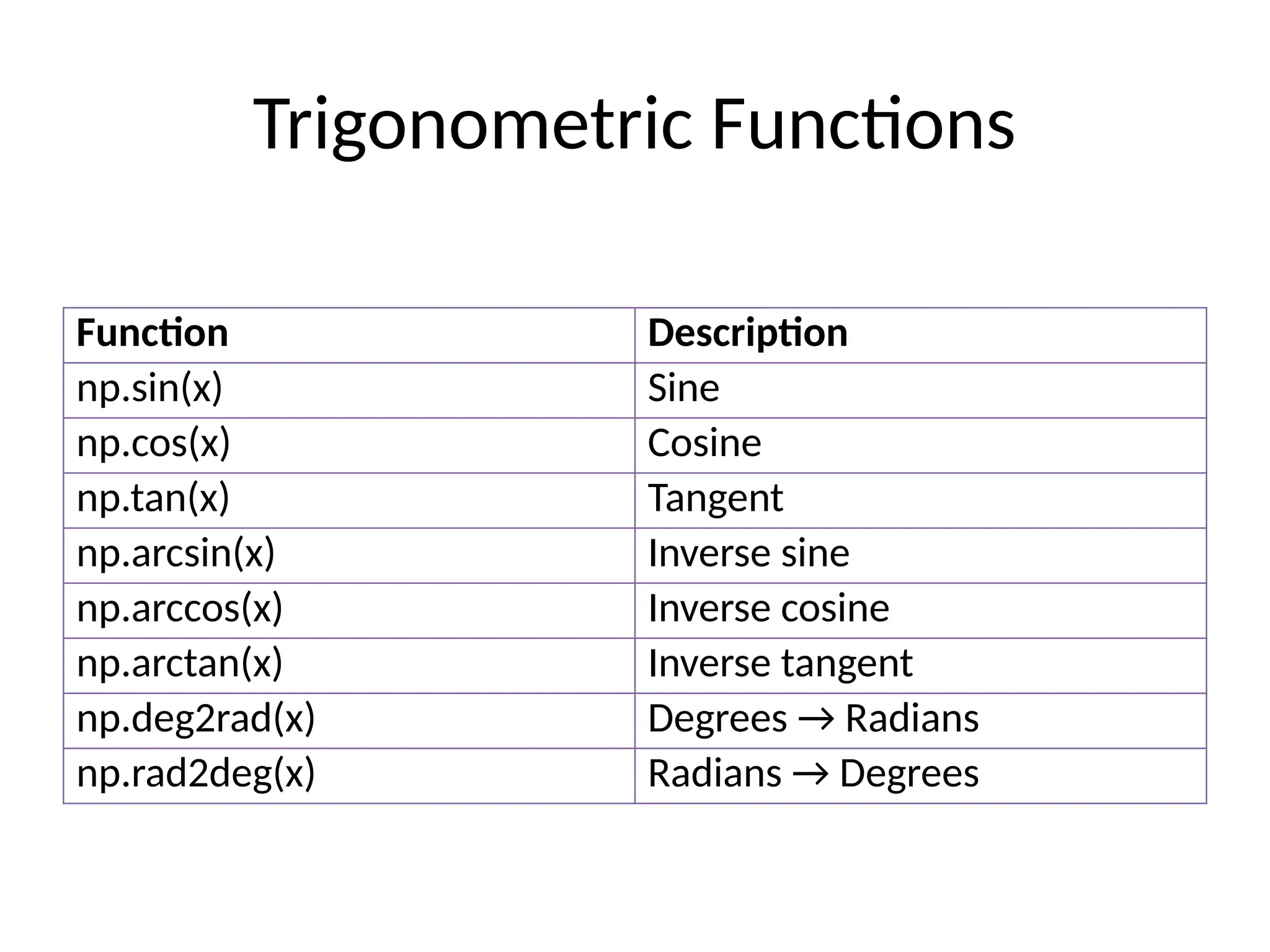
14. 15. Example
import numpy as np
angle_deg = 45
angle_rad = np.deg2rad(angle_deg)
print("sin(45°):", np.sin(angle_rad))
print("cos(45°):", np.cos(angle_rad))
print("tan(45°):", np.tan(angle_rad))
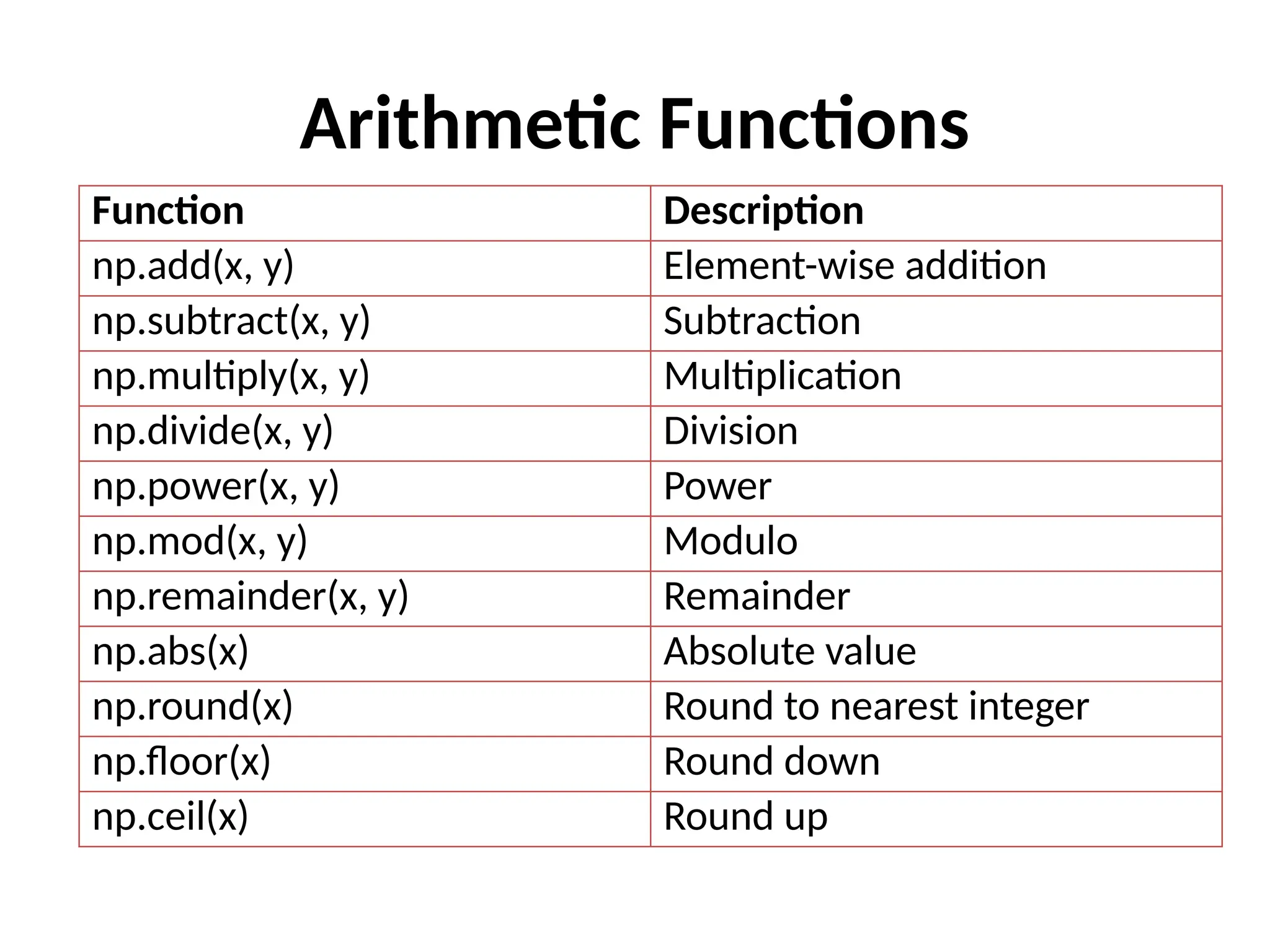
16. 17. 18. 19. 20. Arithmetic Functions
Function Description
np.add(x, y) Element-wise addition
np.subtract(x, y) Subtraction
np.multiply(x, y) Multiplication
np.divide(x, y) Division
np.power(x, y) Power
np.mod(x, y) Modulo
np.remainder(x, y) Remainder
np.abs(x) Absolute value
np.round(x) Round to nearest integer
np.floor(x) Round down
np.ceil(x) Round up
21. Example
a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
b = np.array([4, 5, 6])
print("a + b:", np.add(a, b))
print("a * b:", np.multiply(a, b))
print("a^2:", np.power(a, 2))
print("abs([-3, -5]):", np.abs([-3, -5]))


![Creating Arrays
• 1D Array:
np.array([1, 2, 3]) → [1 2 3]
• 2D Array:
np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]]) → [[1 2]
[3 4]]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numpyarrays-250714081049-a867897a/75/Numpy_Arrays-in-python-libraries-use-pptx-3-2048.jpg)

![Array Creation Functions
• np.zeros((2,2)) → [[0. 0.]
[0. 0.]]
• np.ones((2,2)) → [[1. 1.]
[1. 1.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numpyarrays-250714081049-a867897a/75/Numpy_Arrays-in-python-libraries-use-pptx-5-2048.jpg)
![Array Range and Linspace
• np.arange(0, 10, 2) → [0 2 4 6 8]
• np.linspace(0, 1, 5) → [0. 0.25 0.5 0.75 1. ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numpyarrays-250714081049-a867897a/75/Numpy_Arrays-in-python-libraries-use-pptx-6-2048.jpg)

![Indexing and Slicing
• a = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
• a[0,1] → 2
• a[:,0] → [1 3]
• a[1,:] → [3 4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numpyarrays-250714081049-a867897a/75/Numpy_Arrays-in-python-libraries-use-pptx-8-2048.jpg)
![Reshaping and Flattening
• a = np.arange(6).reshape(2, 3) → [[0 1 2]
• [3 4 5]]
• a.flatten() → [0 1 2 3 4 5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numpyarrays-250714081049-a867897a/75/Numpy_Arrays-in-python-libraries-use-pptx-9-2048.jpg)
![Mathematical Operations
• a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
• b = np.array([4, 5, 6])
• a + b → [5 7 9]
• a * b → [4 10 18]
• np.sqrt(a) → [1. 1.41 1.73]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numpyarrays-250714081049-a867897a/75/Numpy_Arrays-in-python-libraries-use-pptx-10-2048.jpg)
![Aggregate Functions
• a = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
• a.sum() → 10
• a.mean() → 2.5
• a.min() → 1
• a.max() → 4
• a.sum(axis=0) → [4 6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numpyarrays-250714081049-a867897a/75/Numpy_Arrays-in-python-libraries-use-pptx-11-2048.jpg)
![Broadcasting
• a = np.array([[1], [2], [3]])
• b = np.array([10, 20])
• a + b → [[11 21]
• [12 22]
• [13 23]]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numpyarrays-250714081049-a867897a/75/Numpy_Arrays-in-python-libraries-use-pptx-12-2048.jpg)
![Copy vs View
• a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
• b = a.view() → Shares memory
• c = a.copy() → New memory
• Changing b affects a; changing c does not](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numpyarrays-250714081049-a867897a/75/Numpy_Arrays-in-python-libraries-use-pptx-13-2048.jpg)



![Example
a = np.array([1, 2, 3])
b = np.array([4, 5, 6])
print("a + b:", np.add(a, b))
print("a * b:", np.multiply(a, b))
print("a^2:", np.power(a, 2))
print("abs([-3, -5]):", np.abs([-3, -5]))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/numpyarrays-250714081049-a867897a/75/Numpy_Arrays-in-python-libraries-use-pptx-21-2048.jpg)