This document provides an overview of object-oriented programming concepts in Java, including classes, objects, constructors, and accessing object data and methods. It defines a class as a template for creating objects, with data fields and behaviors like constructors and methods. Constructors are used to construct (create) objects from a class by initializing their data fields. Objects are then accessed by calling their methods, such as a toString() method to return the object's data as a string. The document also notes that Java is a pure object-oriented programming language and many other languages also use OOP.





![Constructors (2)
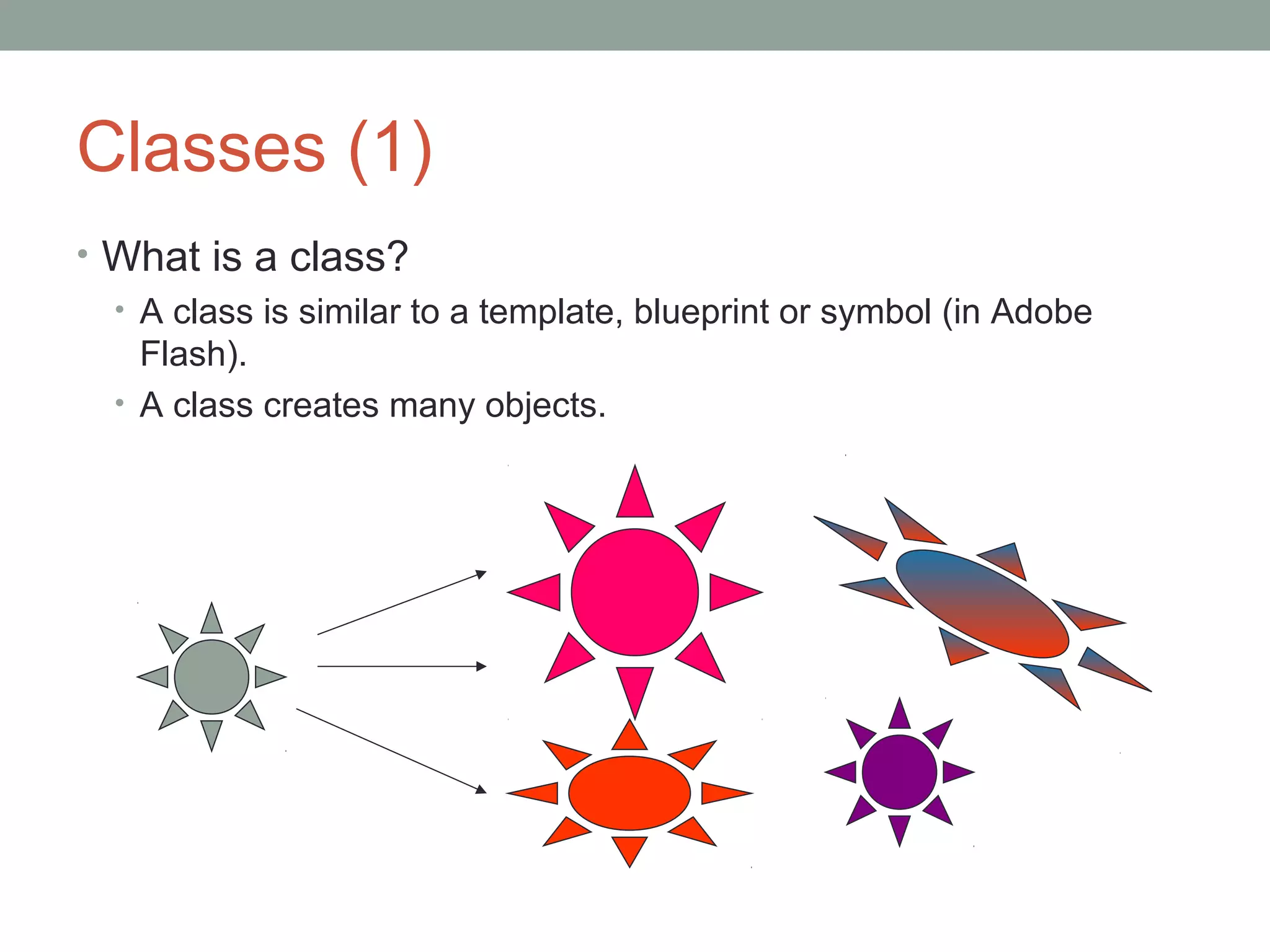
• How to construct objects?
• Usually, we have many classes in a projects. So the student class
will be created in other classes.
• To construct objects from student class:
public class TestStudent {
public static void main(String[] args){
Student stu;
//To construct an object
stu = new Student();
System.out.println(stu.toString());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter6-ooprevision-151019085622-lva1-app6892/75/Objected-Oriented-Programming-with-Java-7-2048.jpg)
![Access Object’s Data and Methods
• To access method:
public class TestStudent {
public static void main(String[] args){
Student stu;
//To construct an object
stu = new Student(“123”,”Veasna”);
System.out.println(stu.toString());
}
}
• To access data:
• Usually, We don’t access the data. If you like, you can do like :
stu.id = 123 in case id is not private.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter6-ooprevision-151019085622-lva1-app6892/75/Objected-Oriented-Programming-with-Java-8-2048.jpg)

