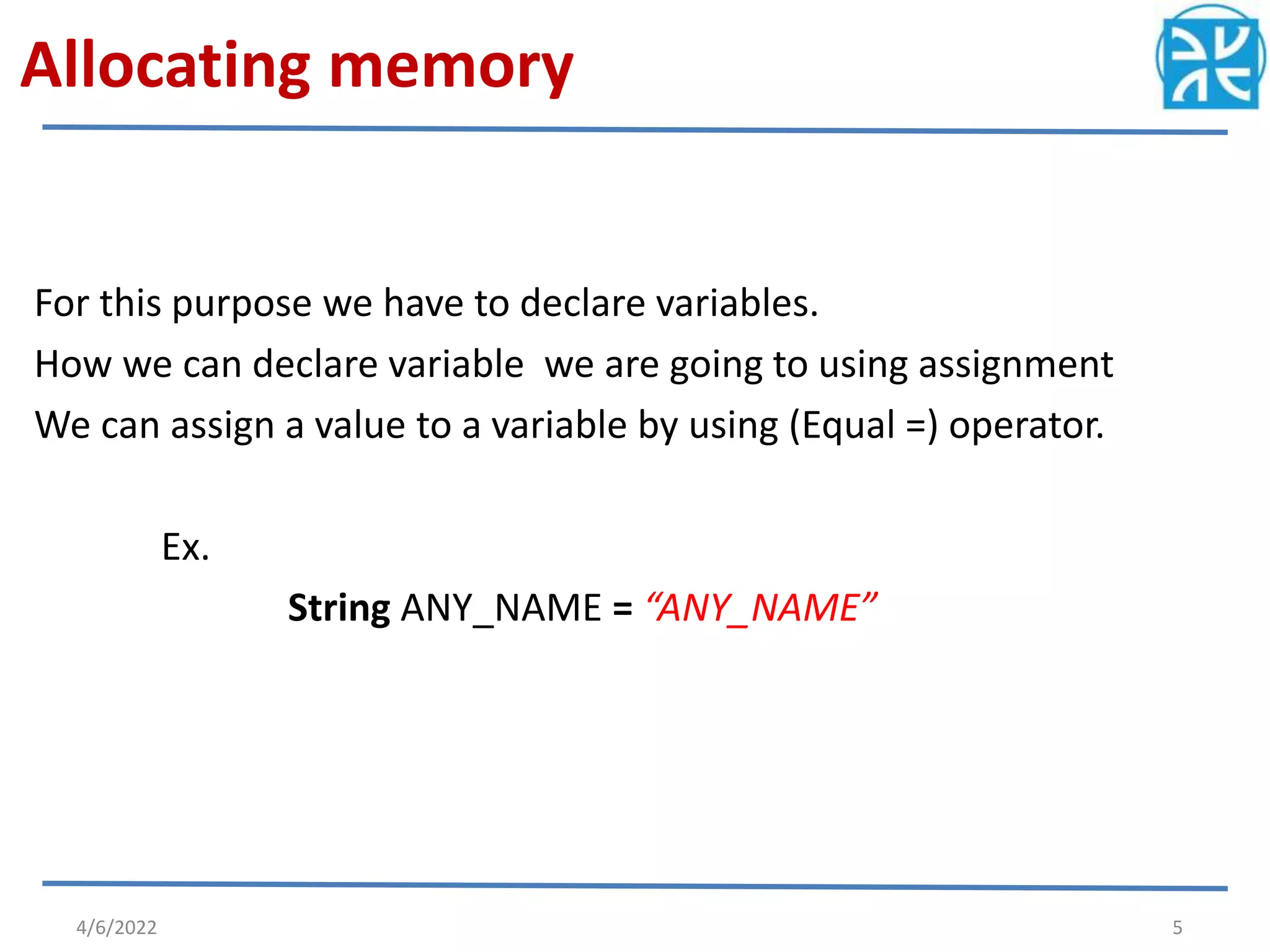
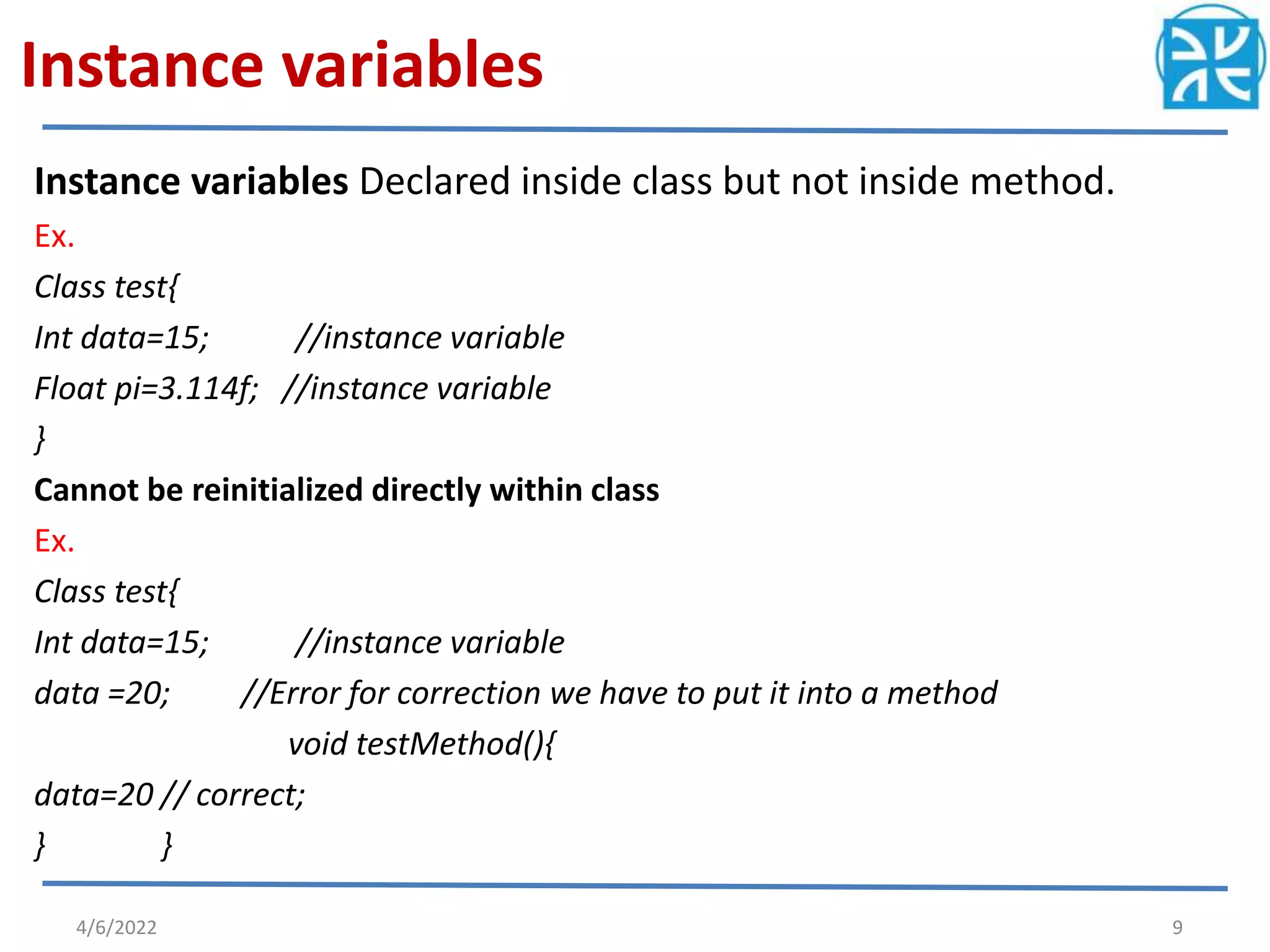
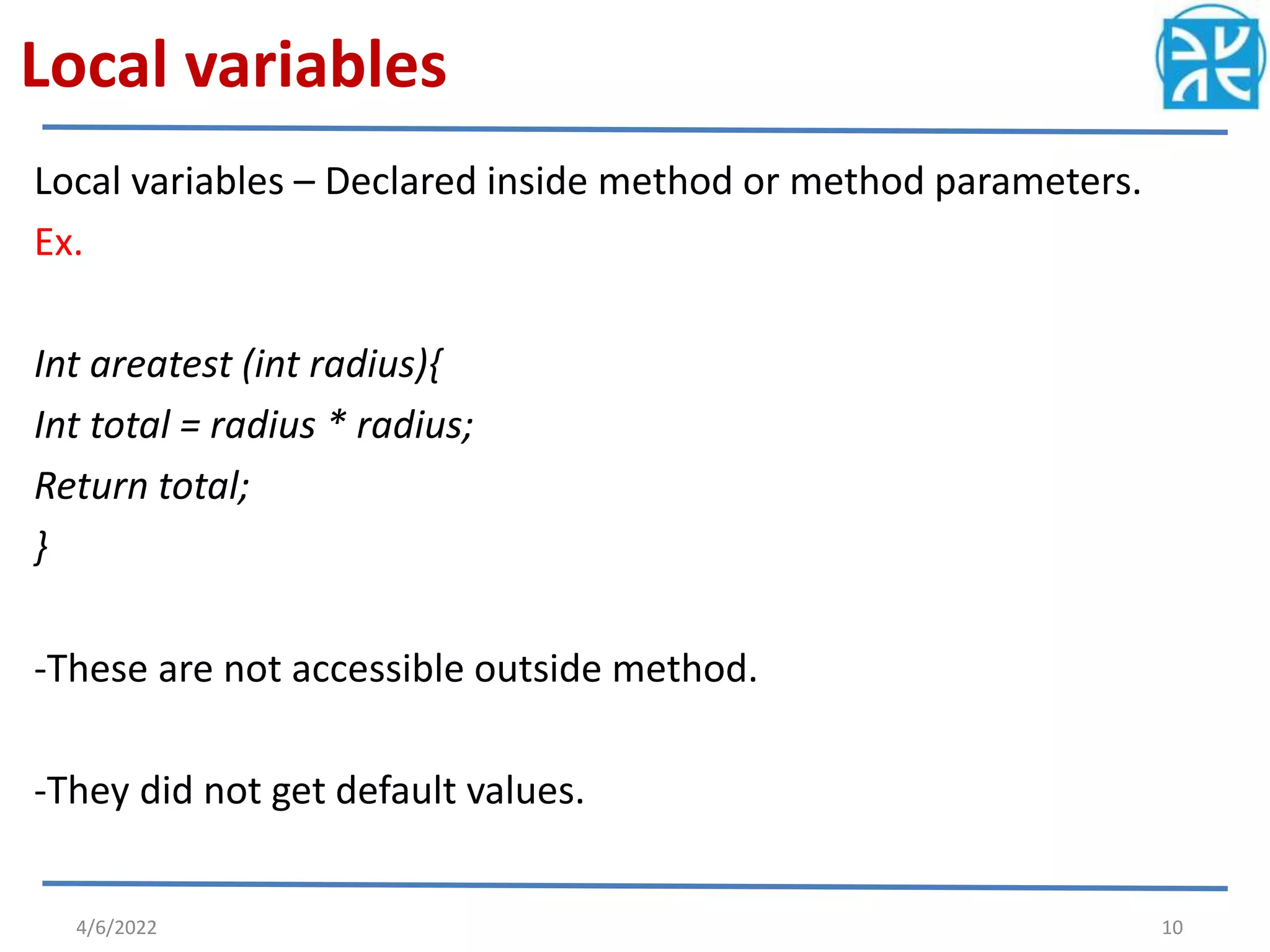
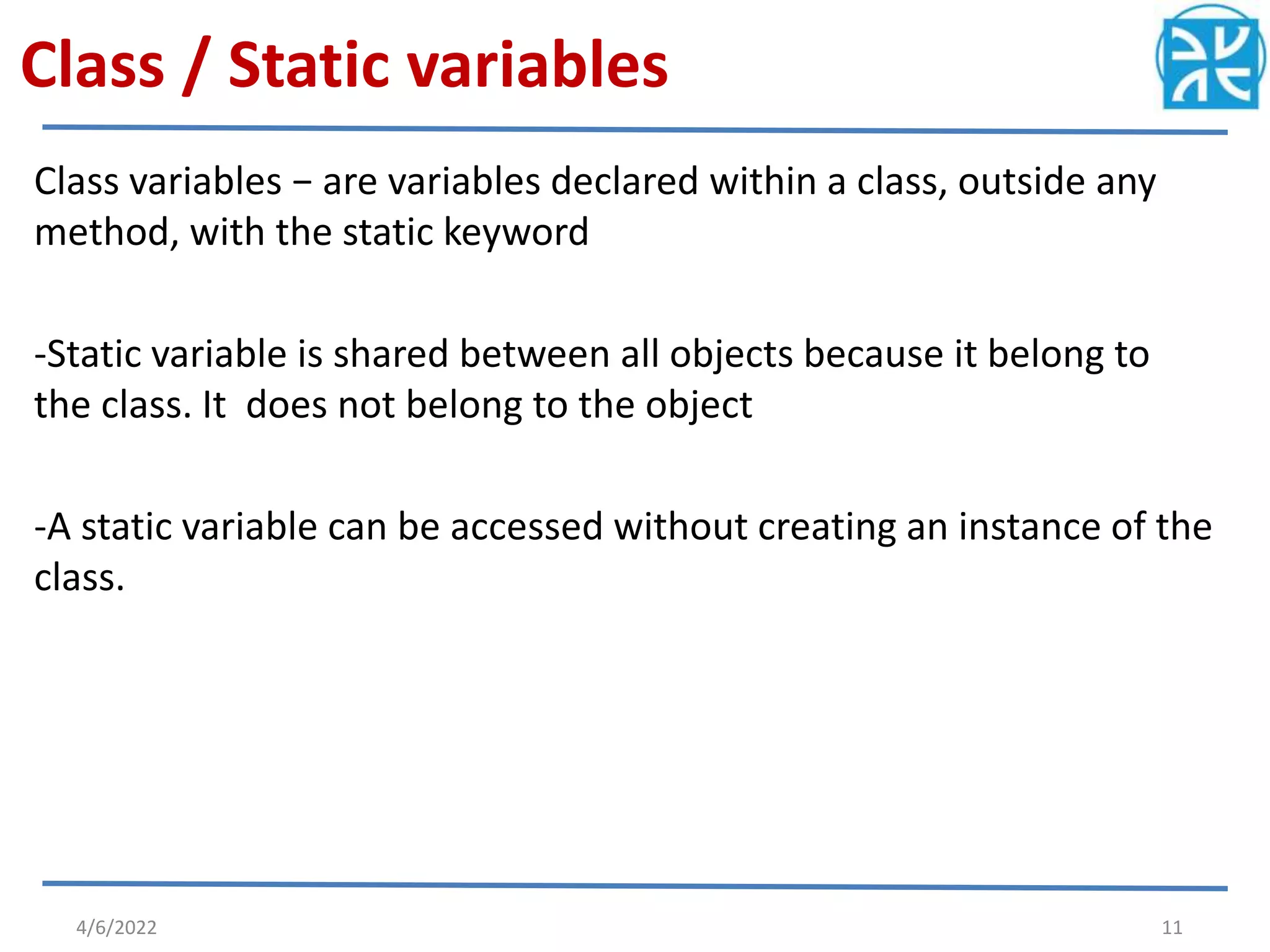
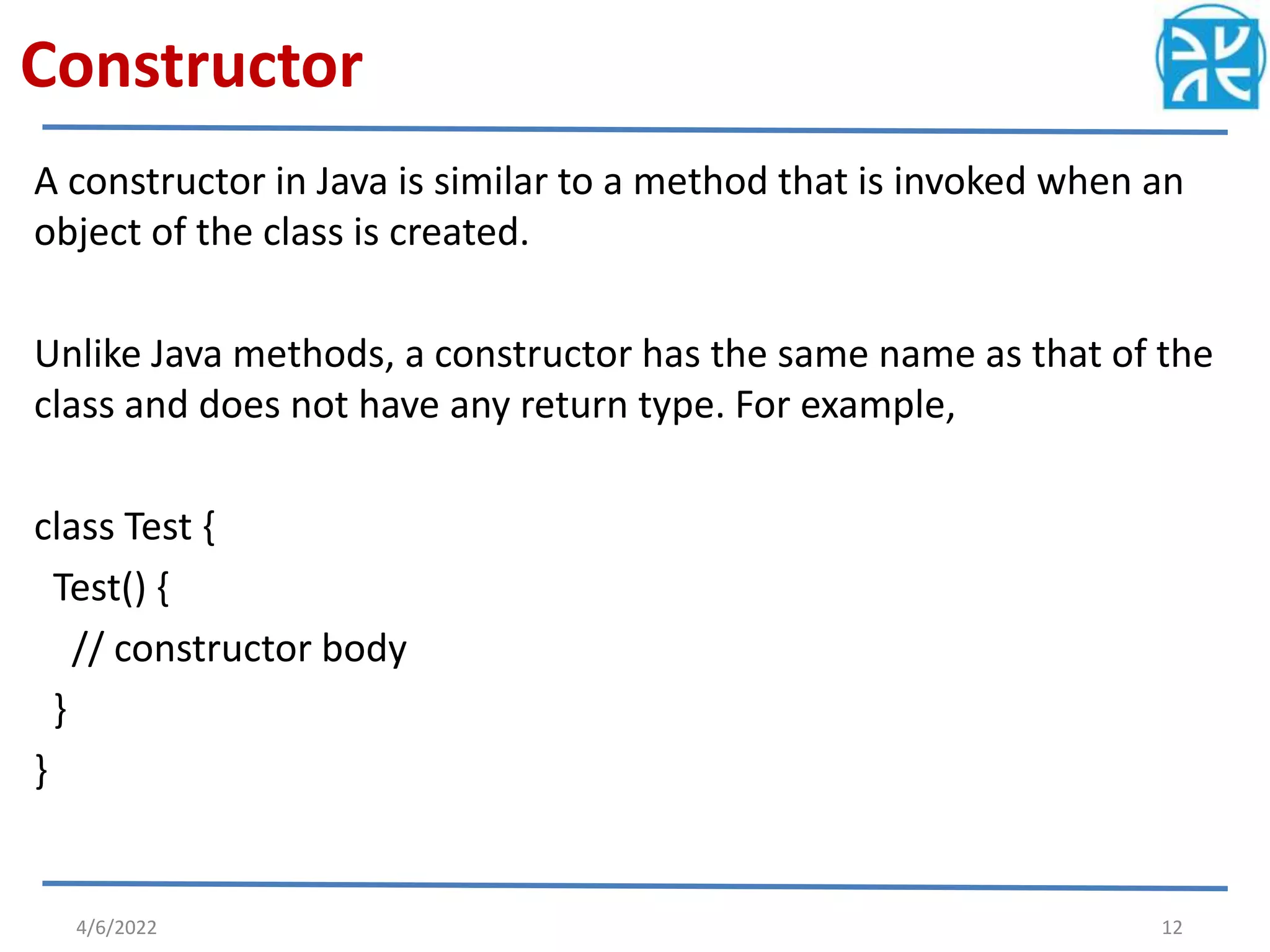
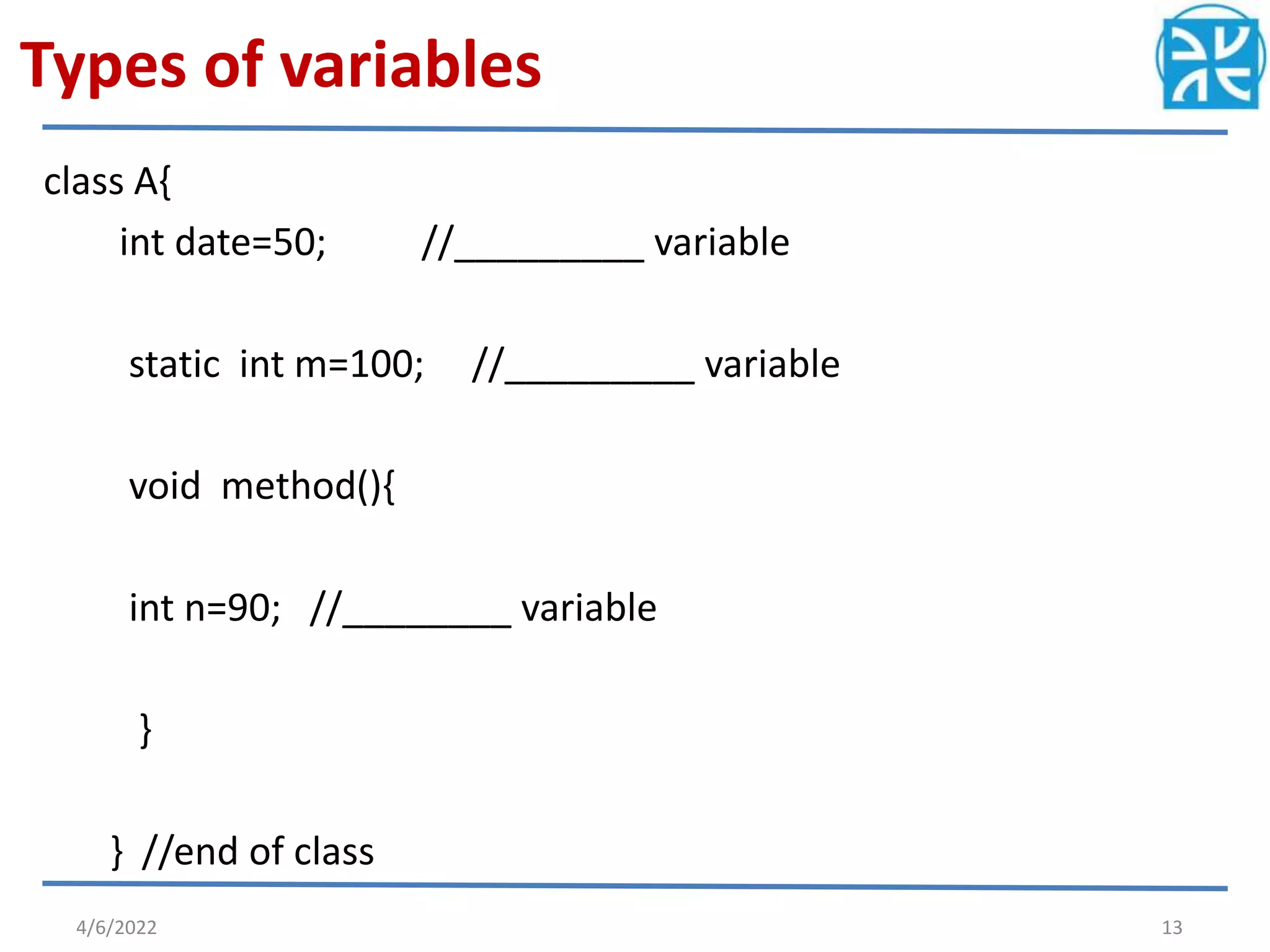
The document provides an overview of variables in Java, including their definition, memory allocation, and types such as instance, local, and class (static) variables. It explains how to declare variables and emphasizes the role of constructors in object creation. Key points include the importance of reinitializing variables within methods and the shared nature of static variables among class instances.