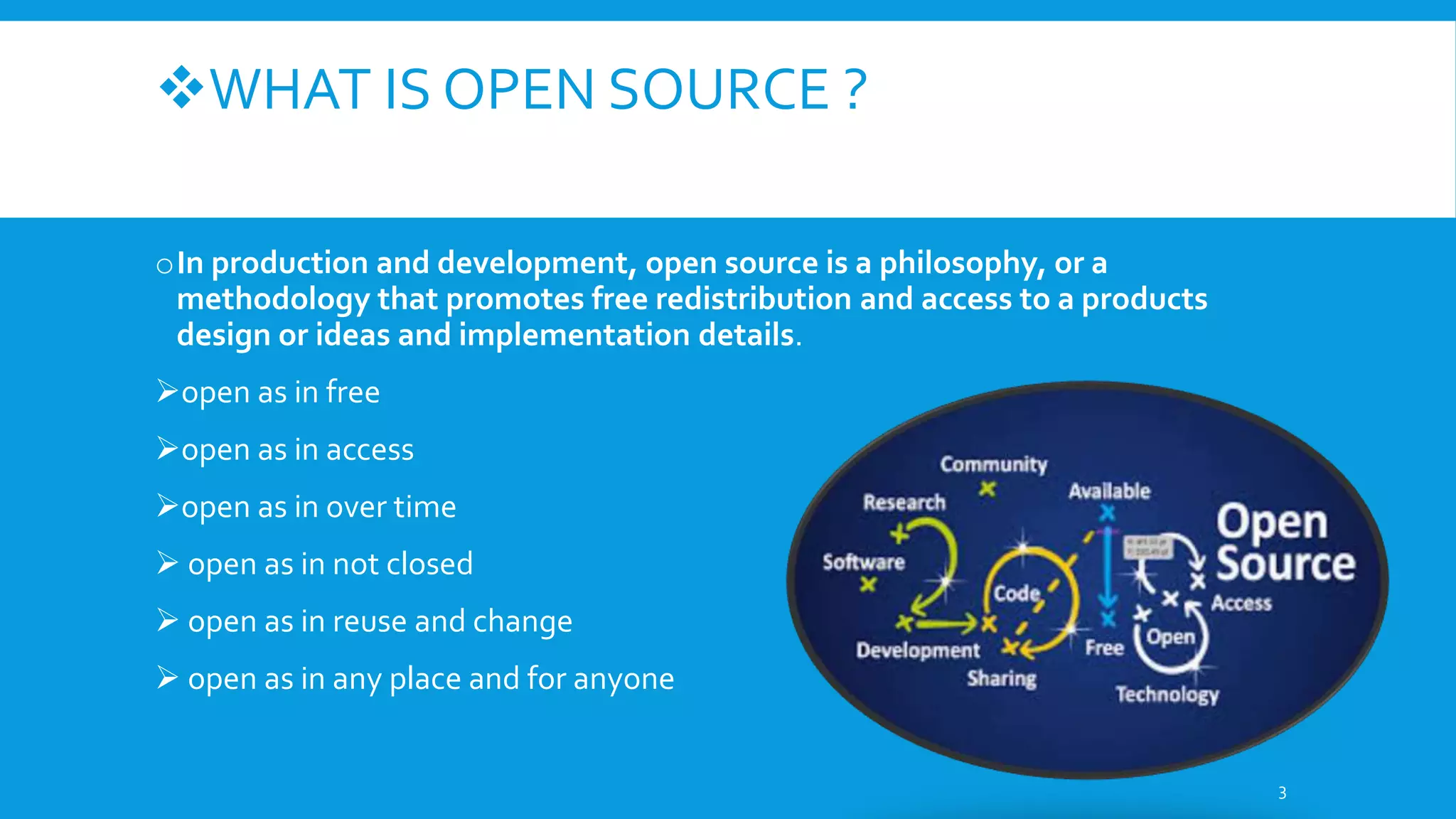
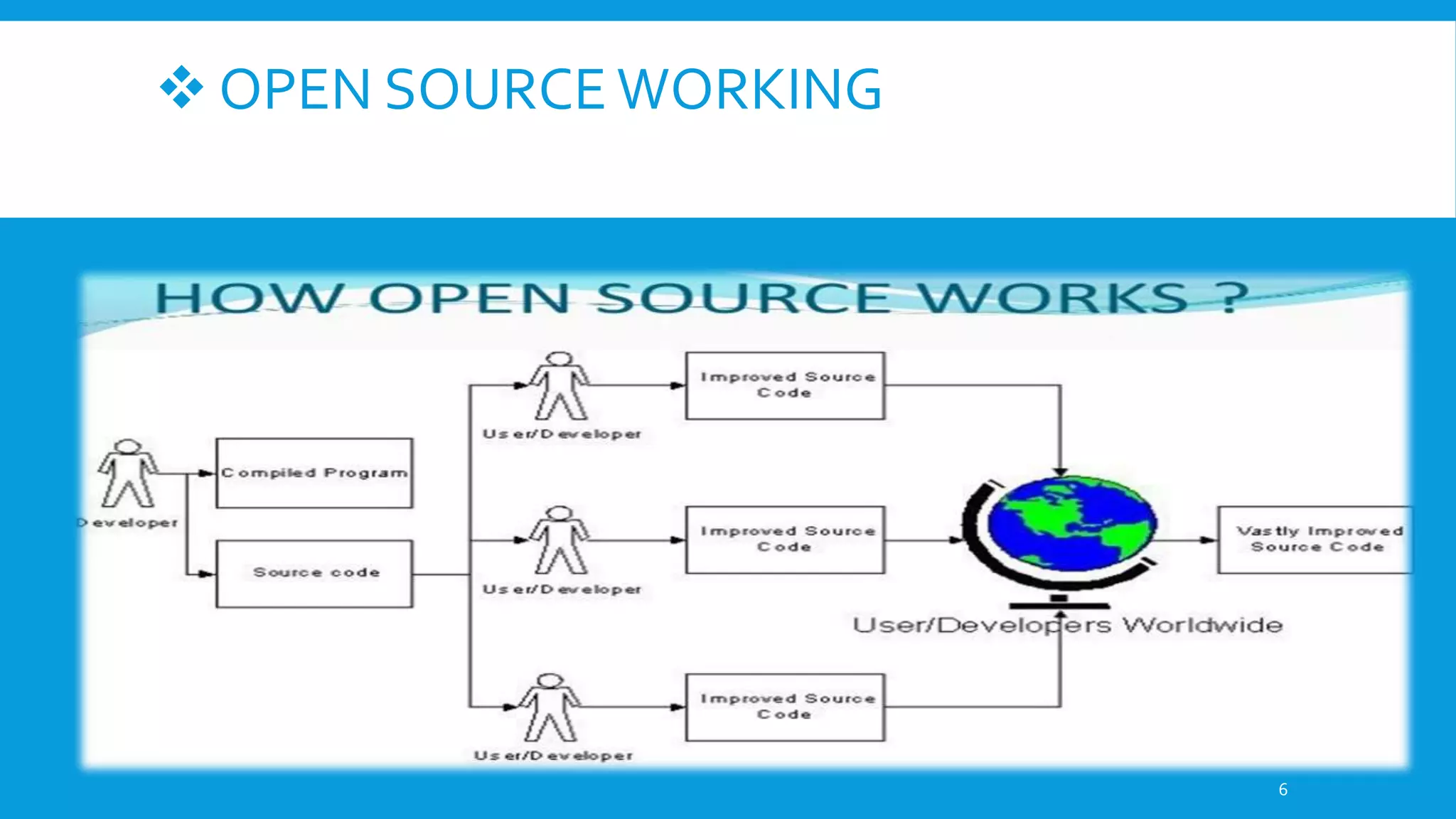
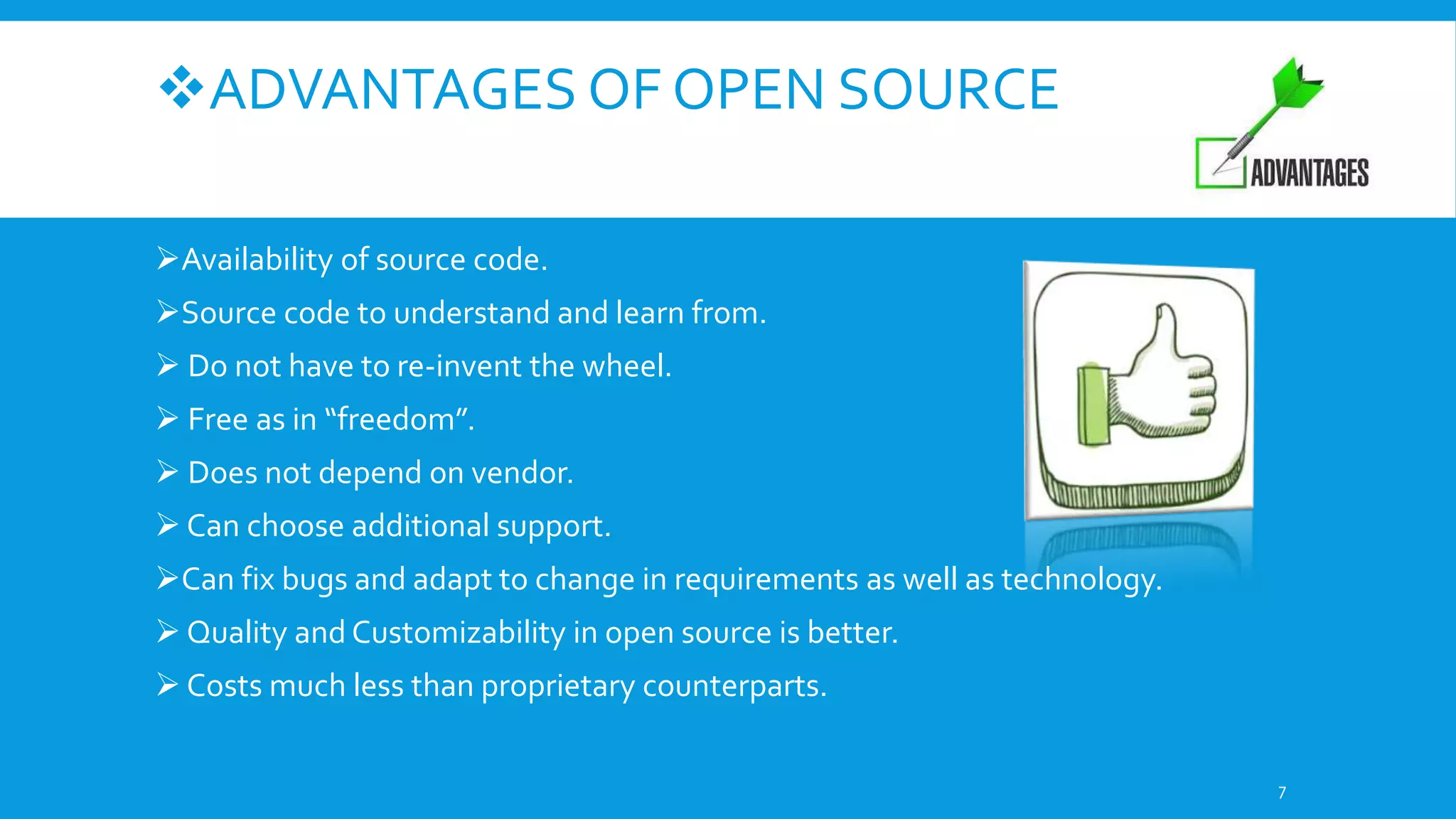
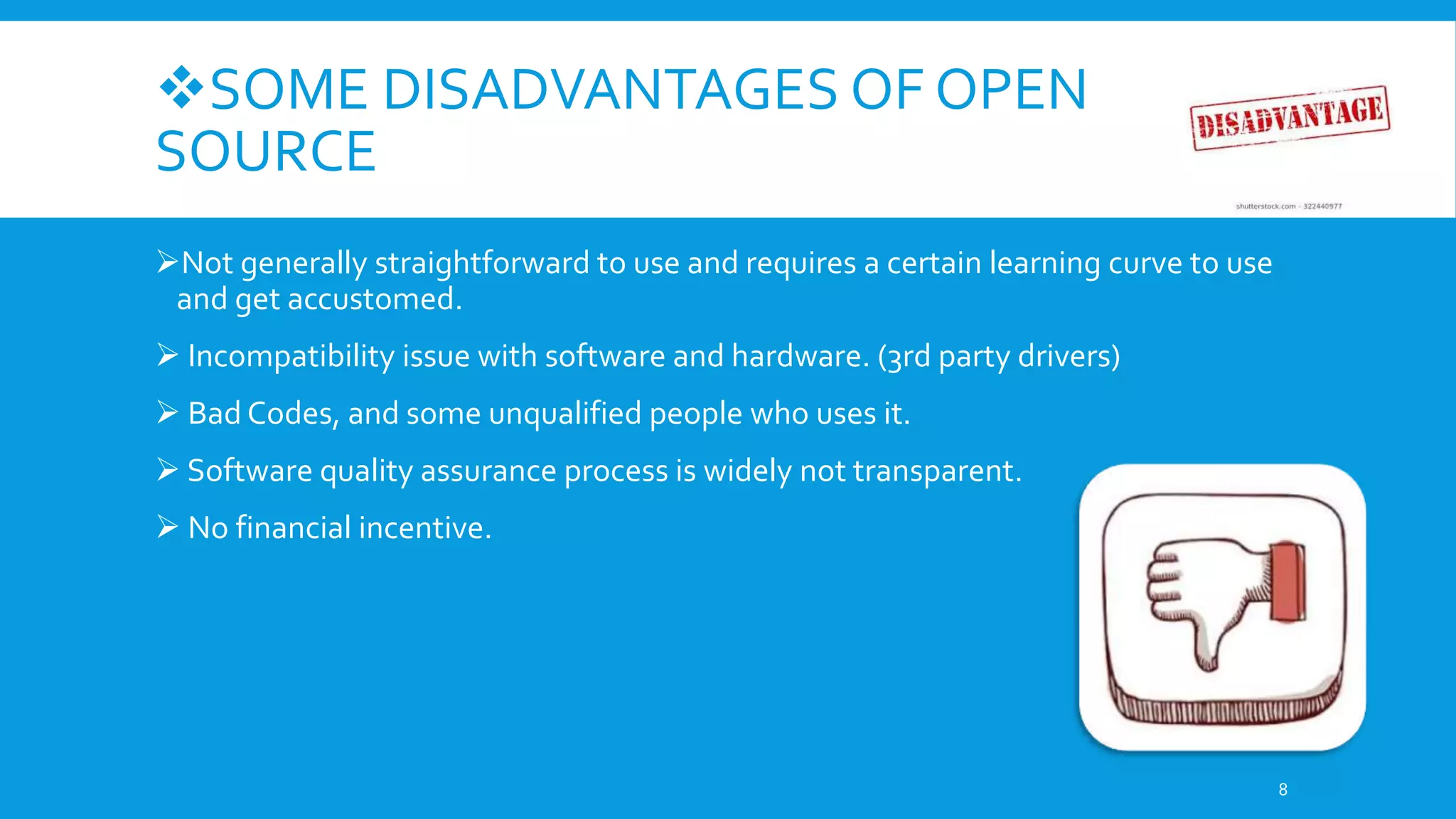
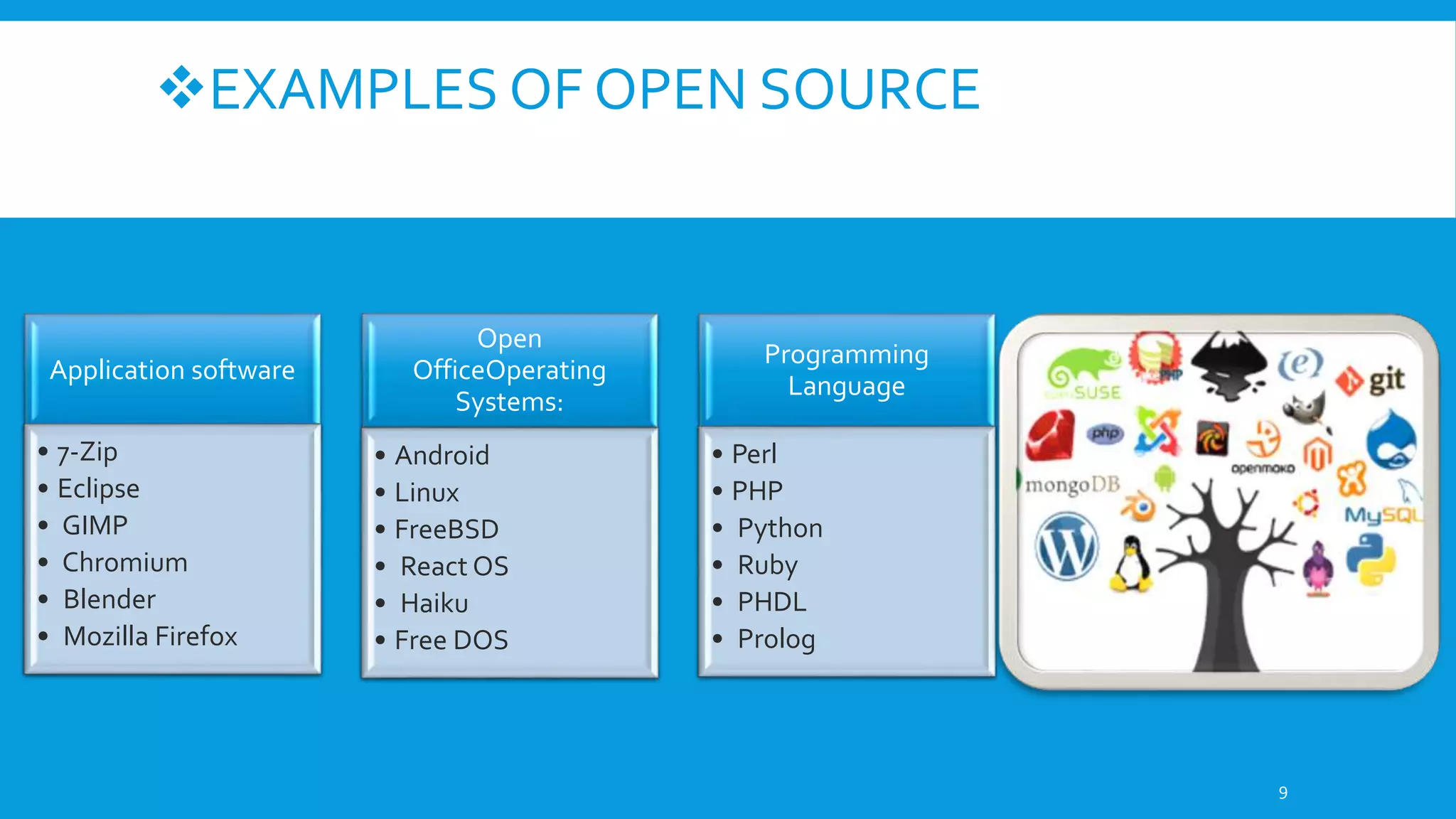
This document discusses open source software. It defines open source as software with source code that is freely available and may be redistributed and modified. The criteria for open source include availability of source code, allowing derivatives, free redistribution, and non-discriminatory licensing. Some advantages are availability of source code to learn from, freedom from vendor lock-in, ability to fix bugs and customize. Examples given are operating systems like Linux and Android as well as applications like Firefox, LibreOffice, and Blender. Common open source licenses are discussed including the GPL and LGPL.