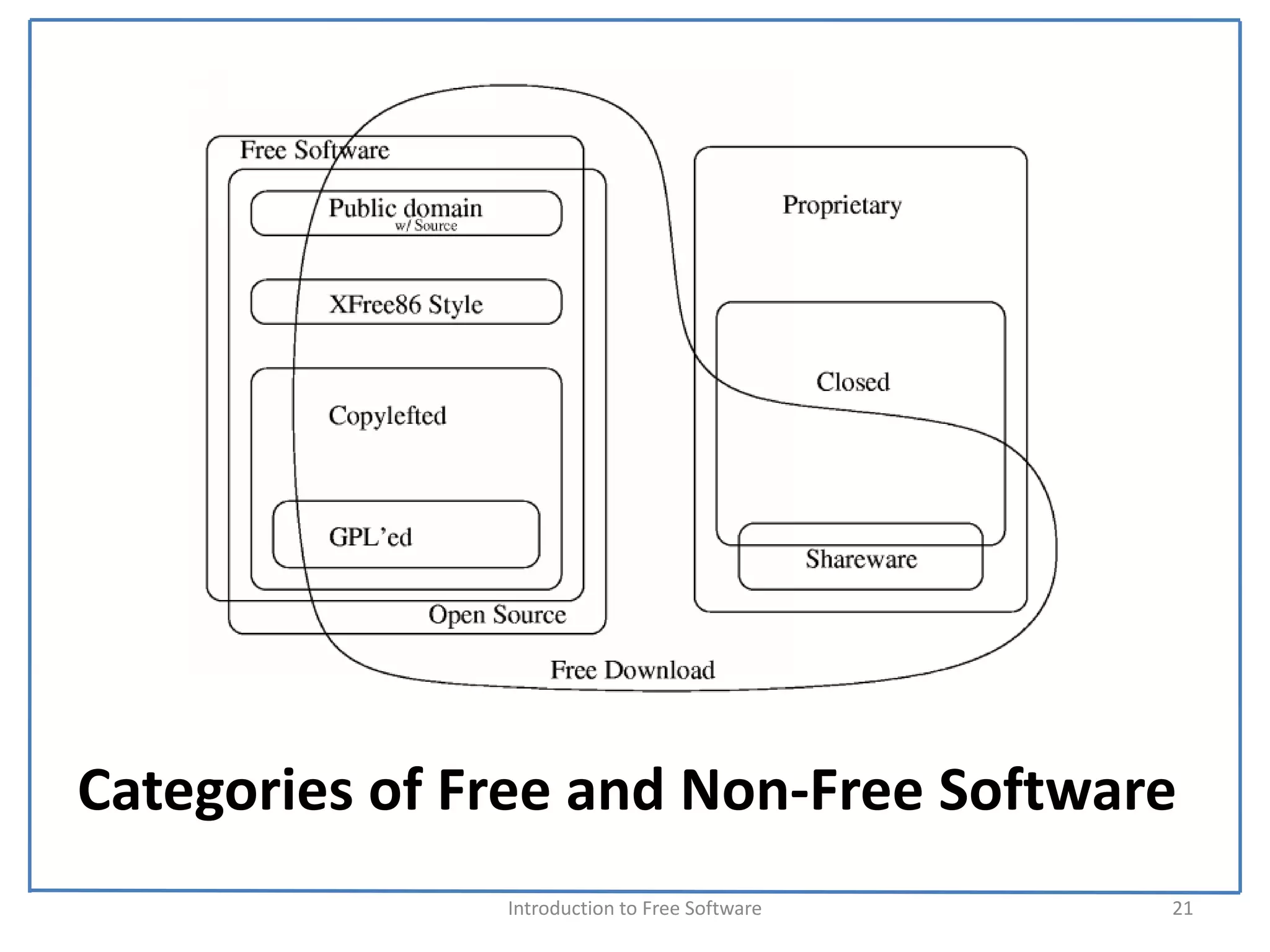
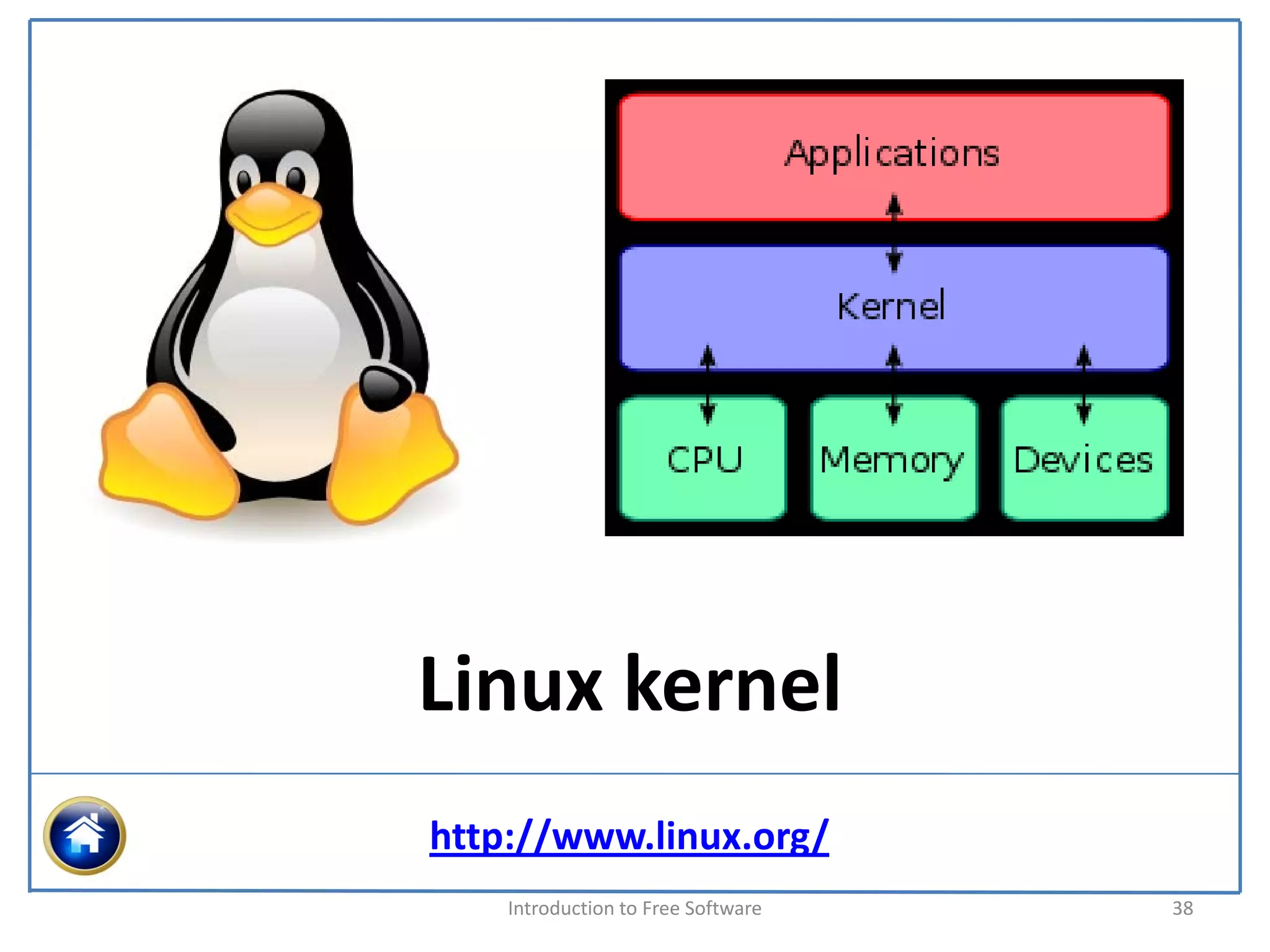
The document introduces free software and discusses its key concepts. It defines software and explores the meanings of "free" as it relates to software freedom rather than cost. The four essential freedoms of free software are explained as the freedom to use, study, share, and modify software. A program is considered free software if it grants users all four of these freedoms. The free software movement was started by Richard Stallman in 1983 to promote these ideals of software freedom. Major organizations that support the development and distribution of free software like the Free Software Foundation are also discussed.