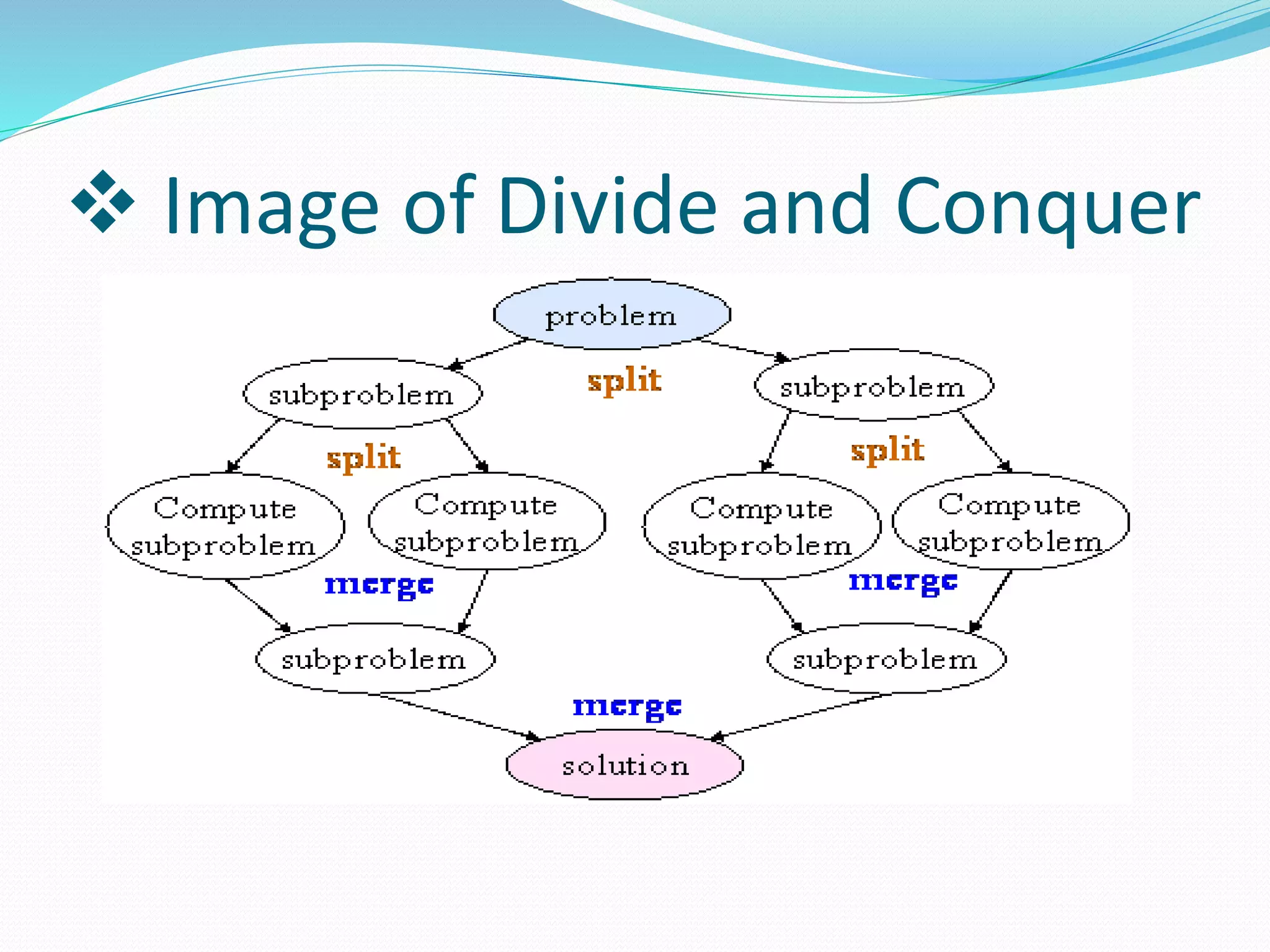
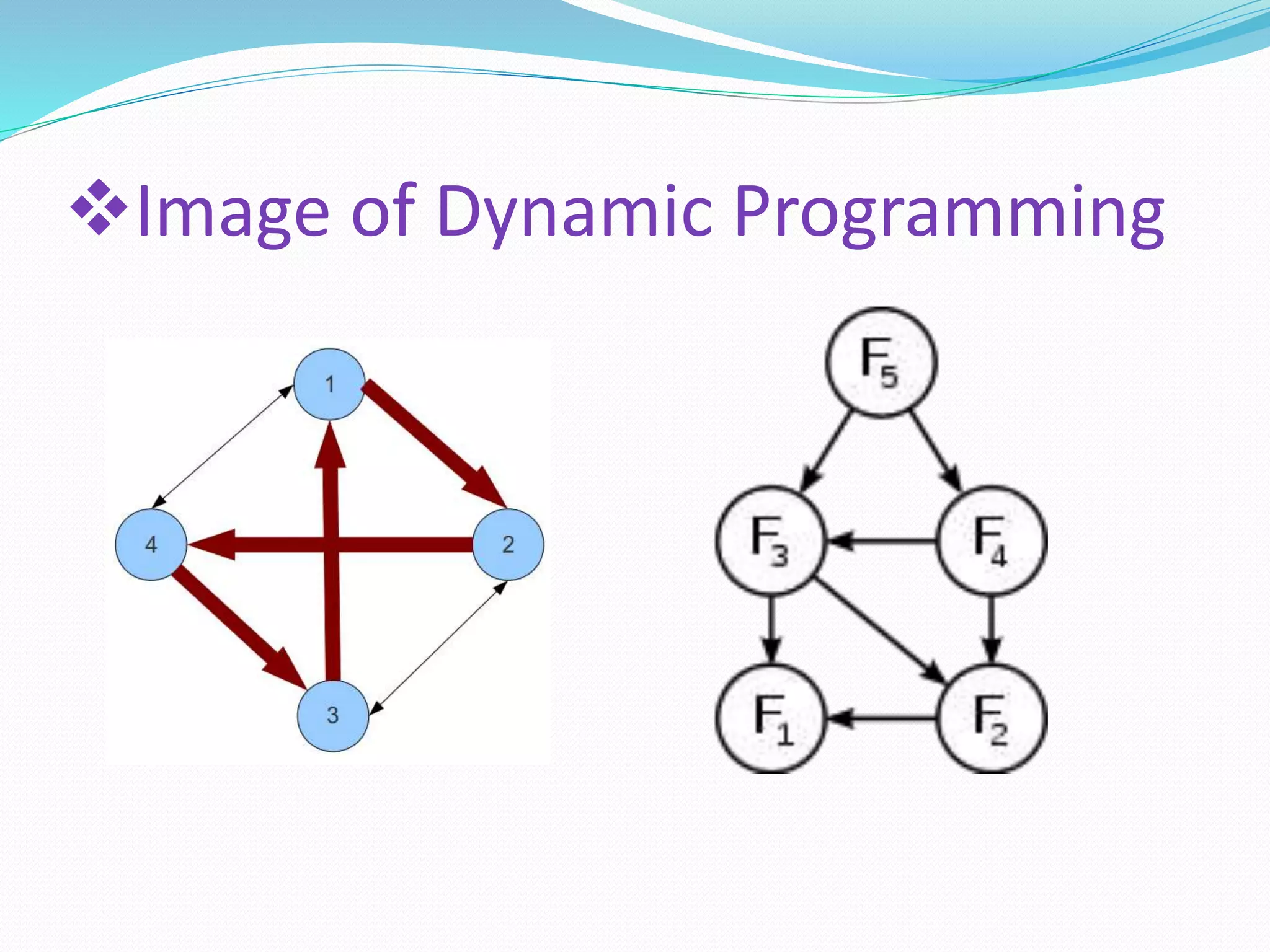
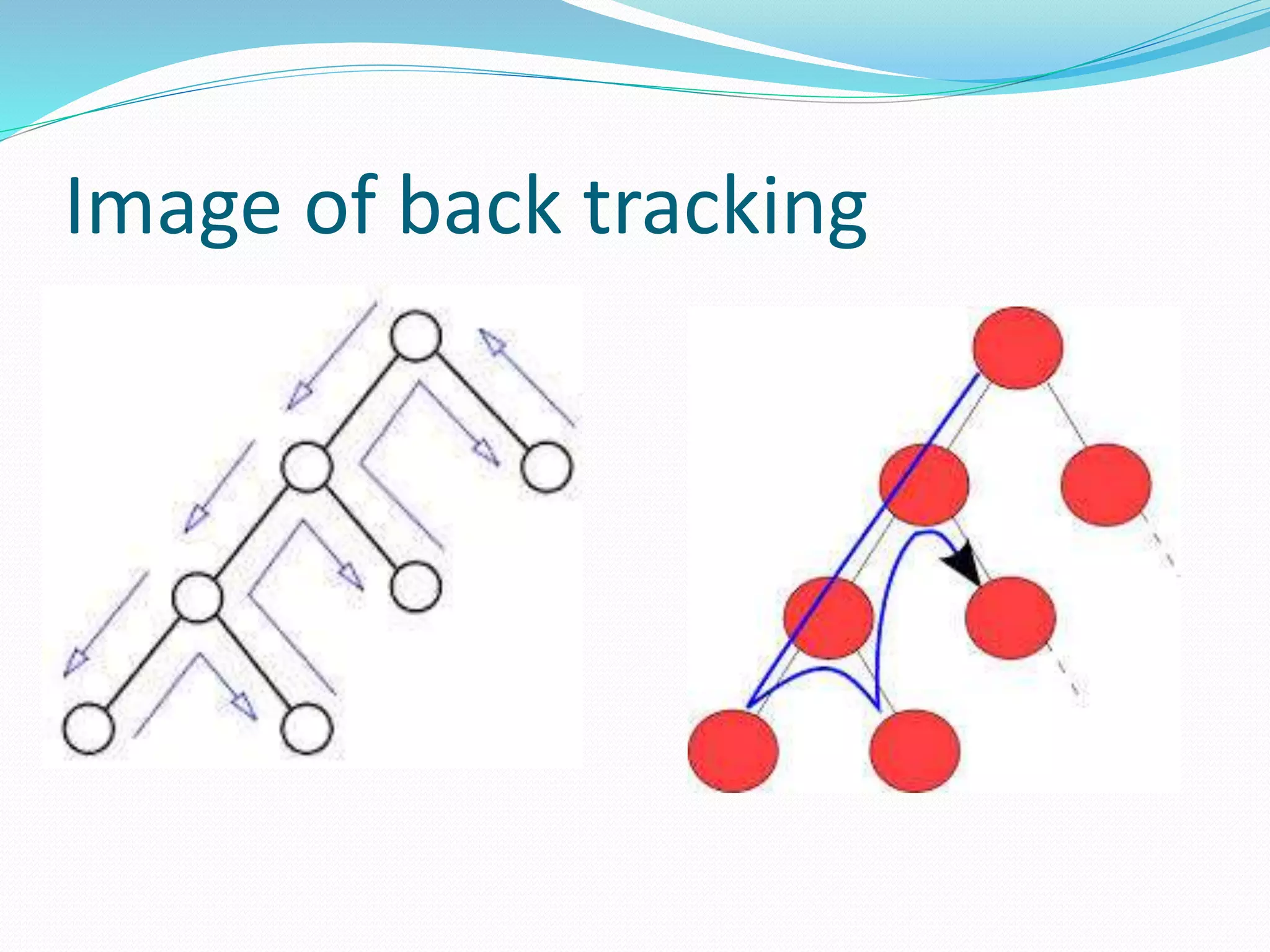
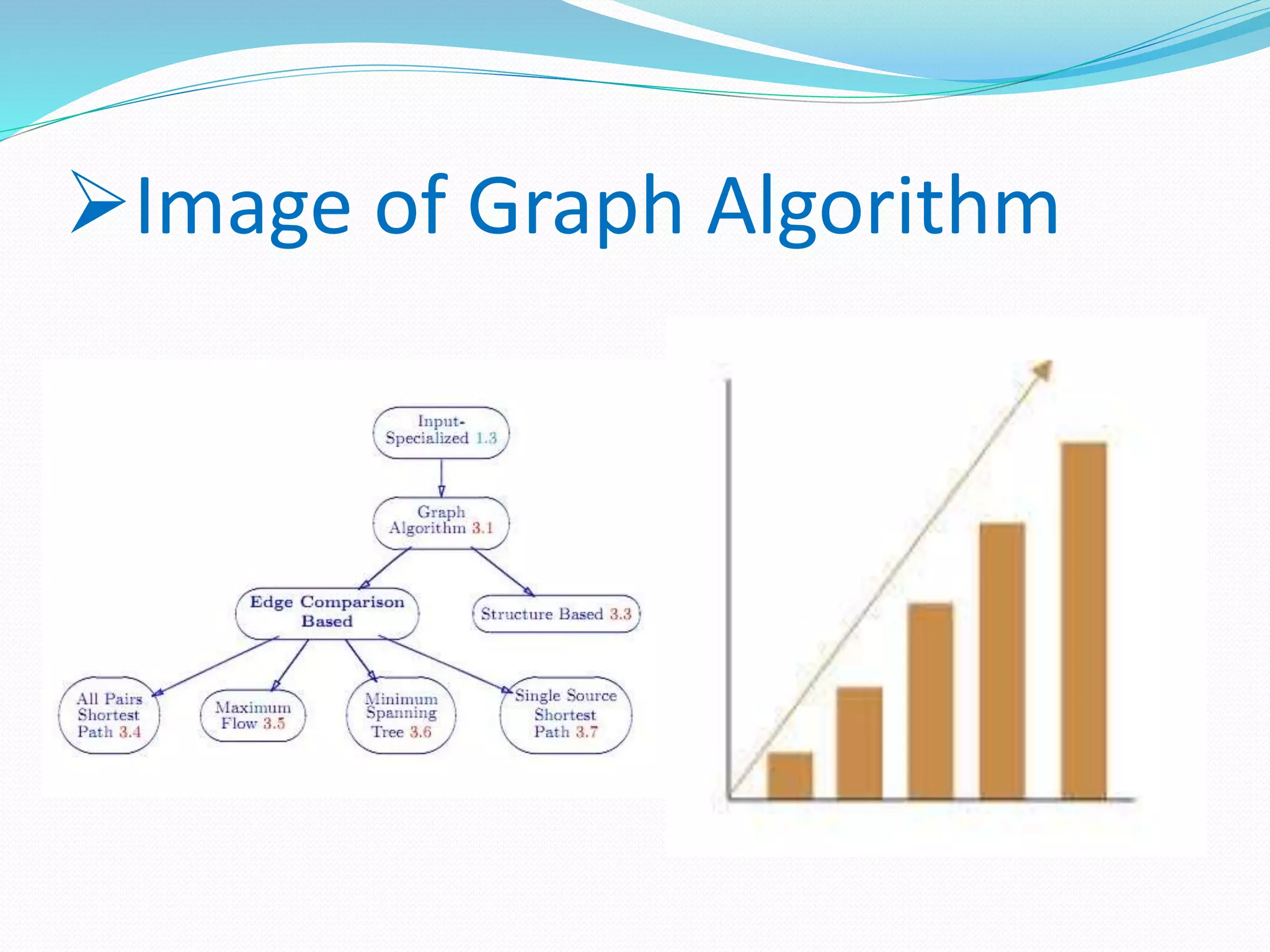
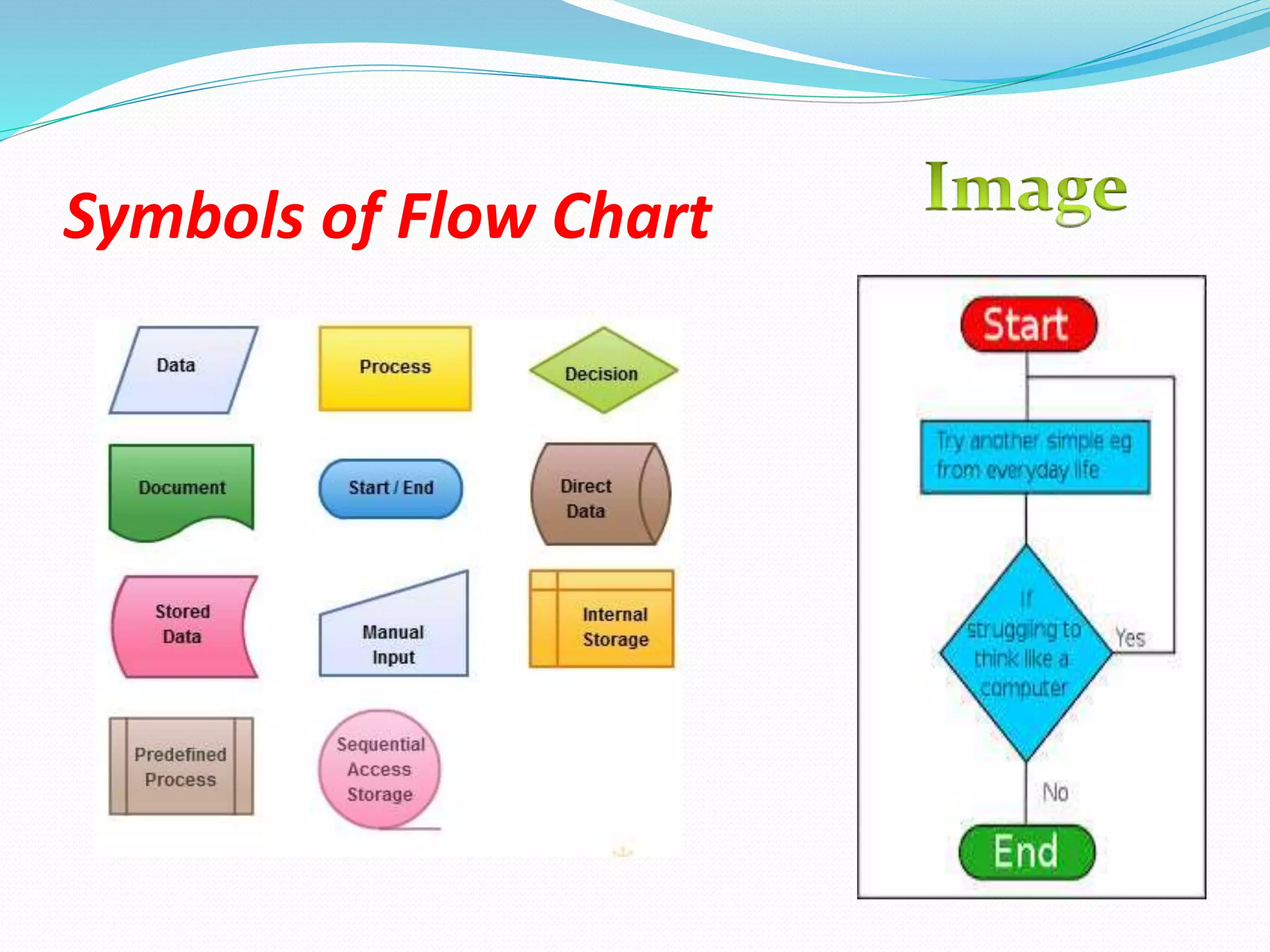
The document discusses algorithm design. It defines an algorithm as a step-by-step solution to a mathematical or computer problem. Algorithm design is the process of creating such mathematical solutions. The document outlines several approaches to algorithm design, including greedy algorithms, divide and conquer, dynamic programming, and backtracking. It also discusses graph algorithms, flowcharts, and the importance of algorithm design in solving complex problems efficiently.