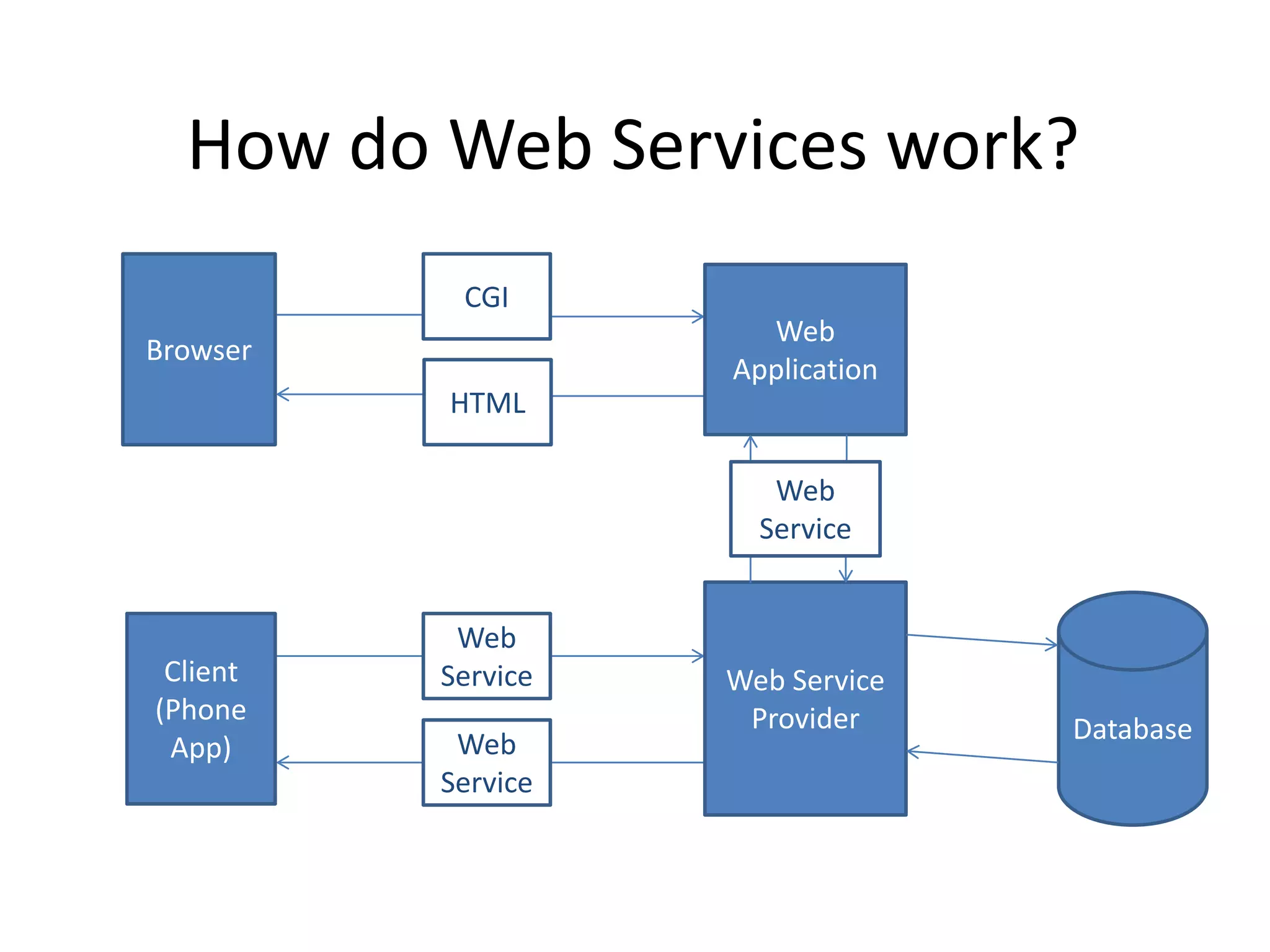
This document provides an overview of web services and compares SOAP and RESTful web services. It defines web services as application components that provide useful functionality via standard Internet protocols. SOAP is a protocol for sending messages in an XML format, while REST is an architectural style using resources identified by URLs and HTTP methods. The document explains how web services work and key concepts for both SOAP and REST like WSDL, UDDI, requests, and responses.