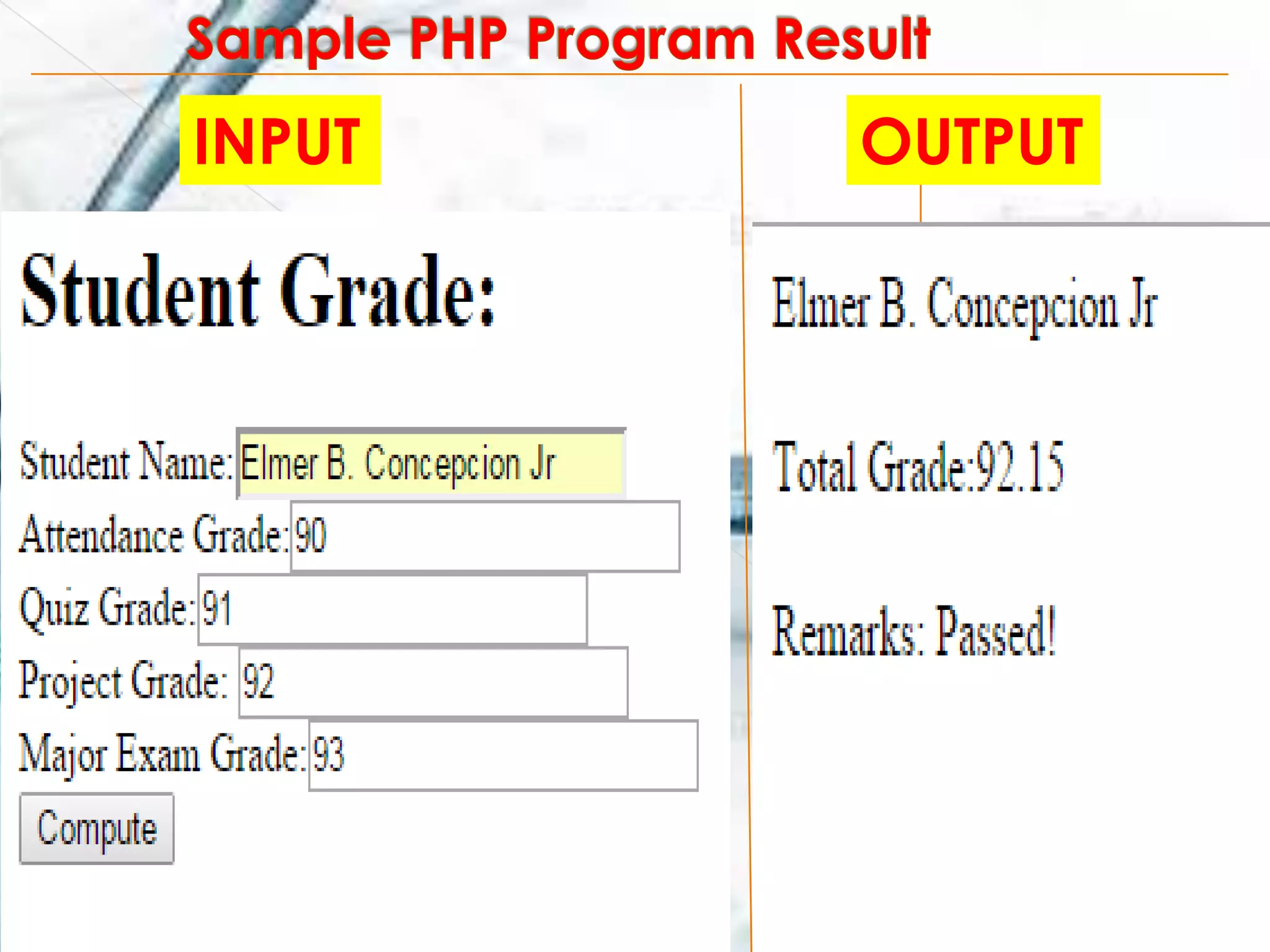
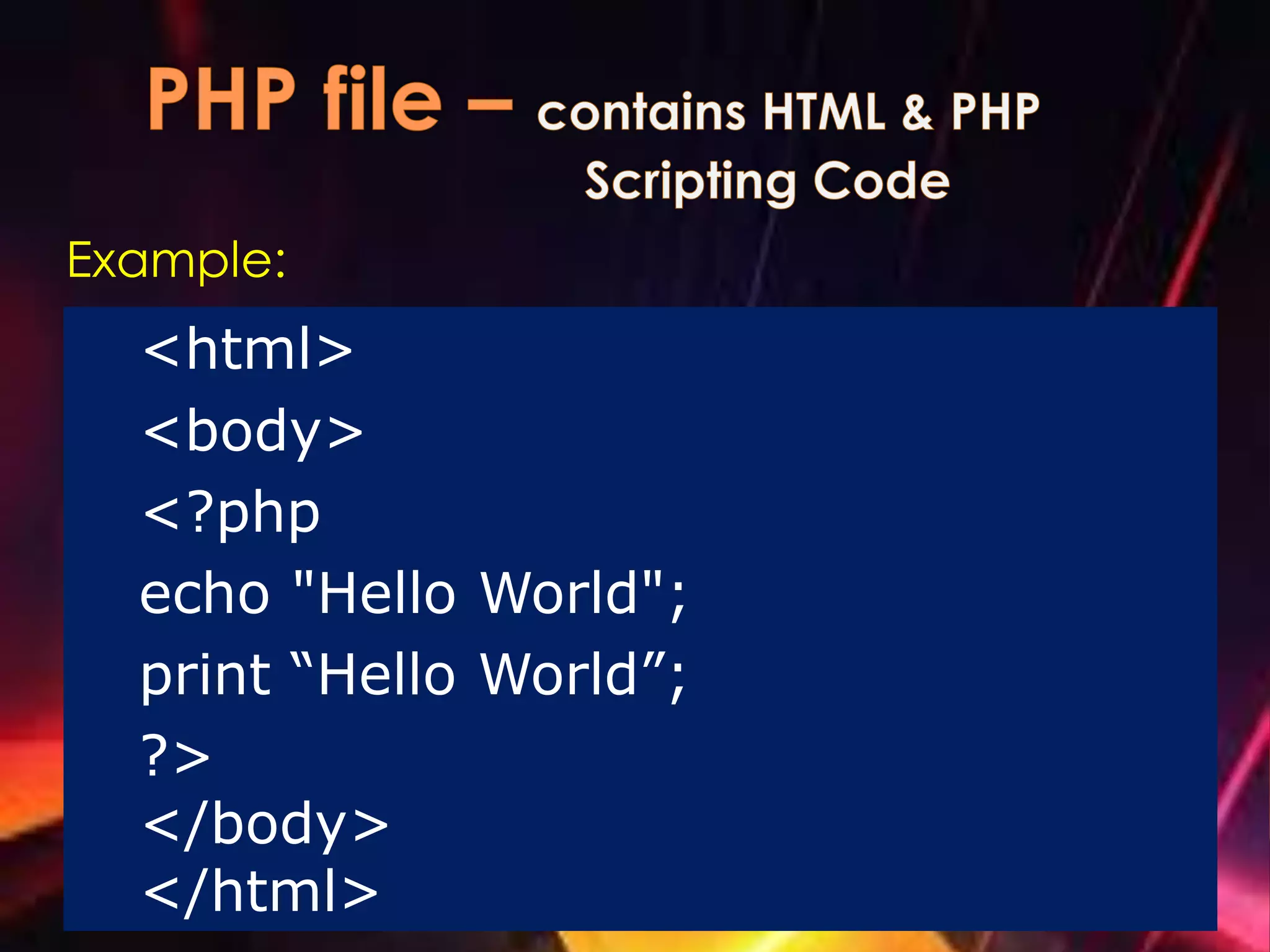
The document explains PHP, a server scripting language widely used for creating dynamic web pages, originally created in 1995. It covers PHP's syntax, variable declaration rules, conditional statements, and user-defined functions, providing examples of each. Additionally, it includes steps for installing PHP using XAMPP, creating PHP files, and handling form submissions using the $_POST function.






















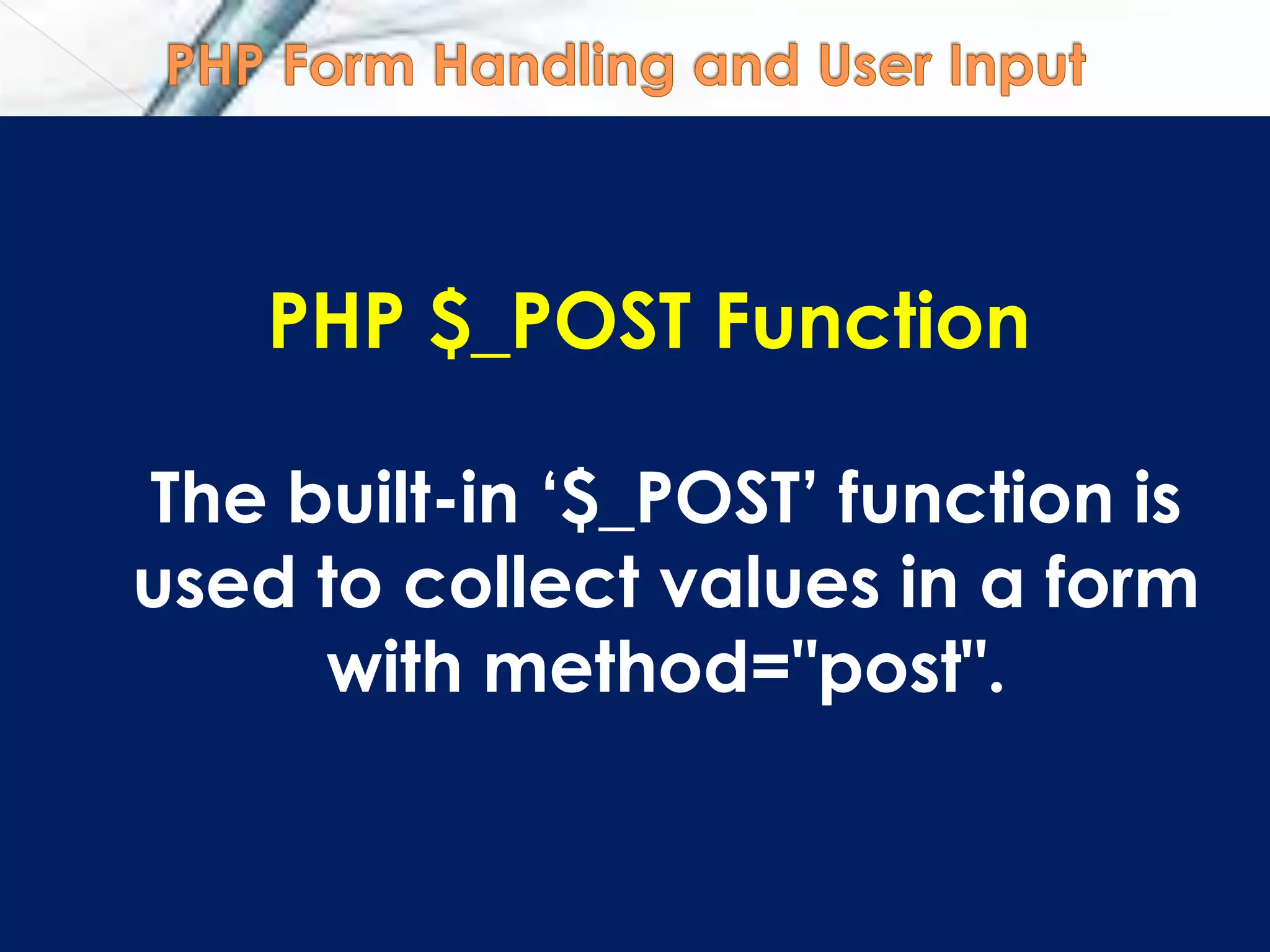
![PHP $_POST Function
Example:
<form action="welcome.php" method="post">
Name: <input type="text" name="fname" />
Age: <input type="text" name="age" />
<input type="submit" />
</form>
When the user clicks the "Submit" button, the
"welcome.php" file can now use the $_POST function to
collect form data
Welcome <?php echo $_POST["fname"]; ?>!<br />
You are <?php echo $_POST["age"]; ?> years old.
Output could be something like this:
Welcome John!
You are 28 years old.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-adynamicwebscriptinglanguage-151217011420/75/Php-a-dynamic-web-scripting-language-29-2048.jpg)

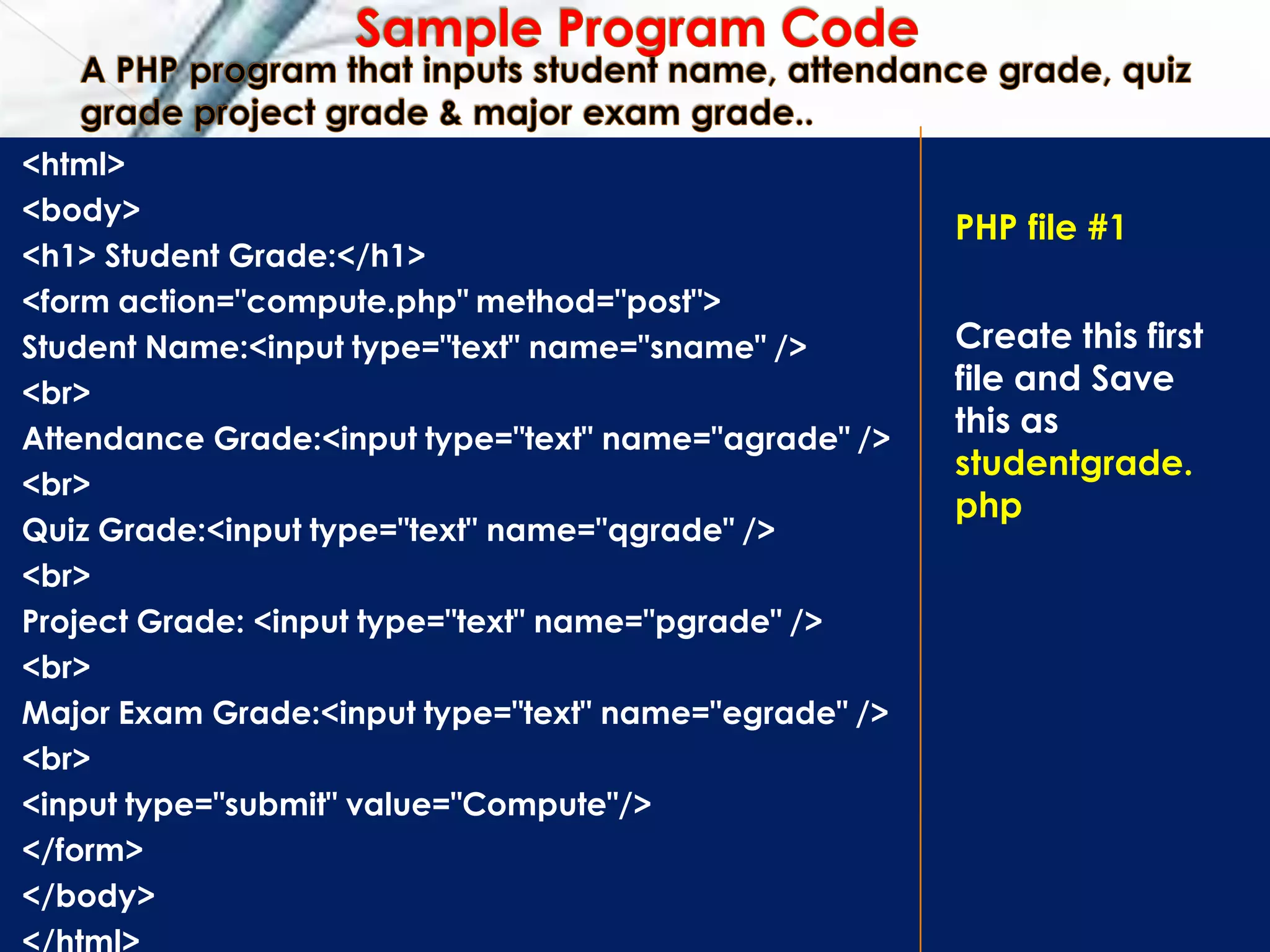
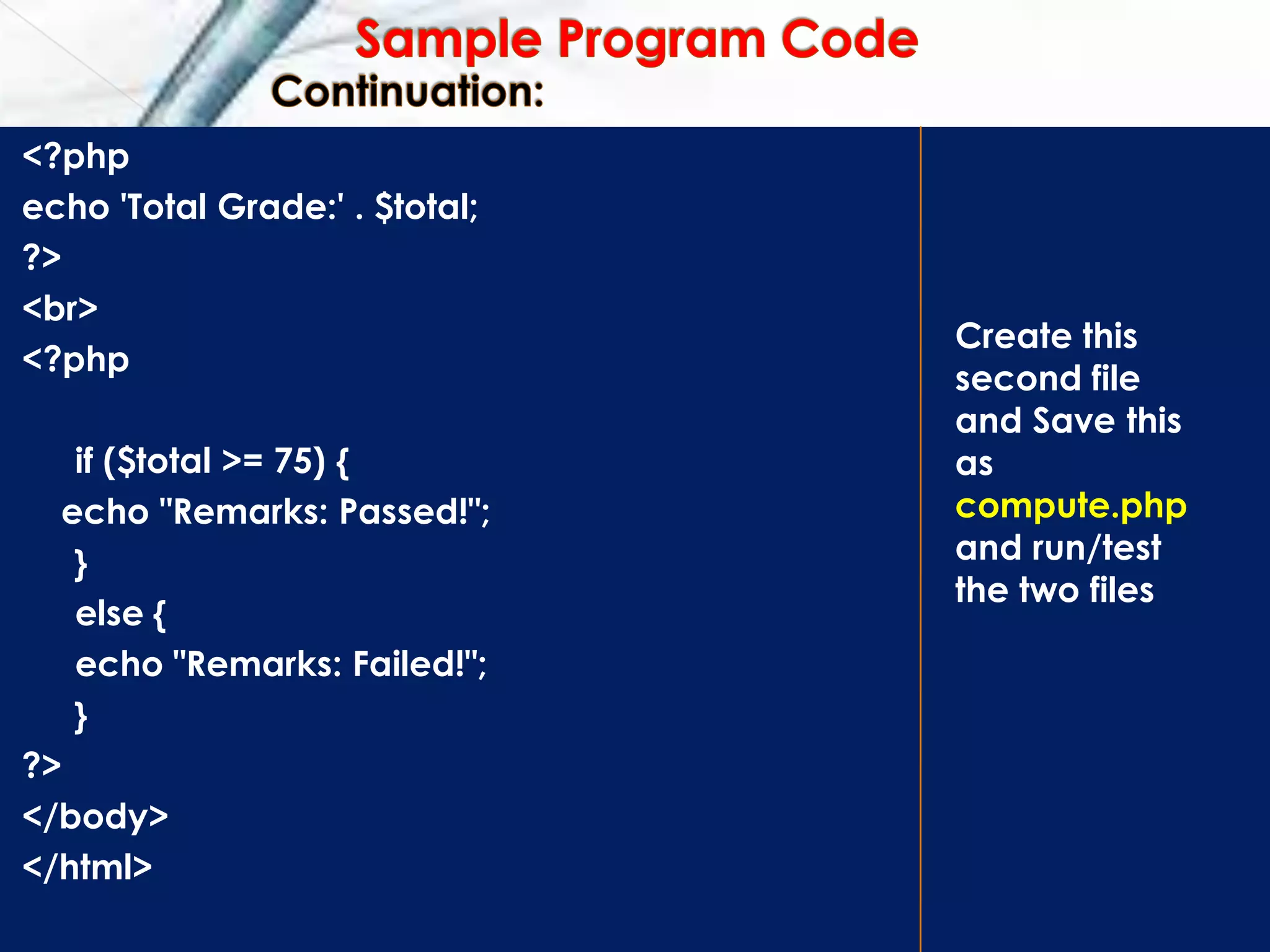
![<html>
<body>
<?php
echo $_POST["sname"];
?>
<br>
<?php
$attgrade = $_POST['agrade'];
$quizgrade = $_POST['qgrade'];
$prograde = $_POST['pgrade'];
$megrade = $_POST['egrade'];
$total = ($attgrade * 0.10) + ($quizgrade * 0.15) + ($prograde * 0.25)
+ ($megrade * 0.50);
?>
<br>
PHP file #2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-adynamicwebscriptinglanguage-151217011420/75/Php-a-dynamic-web-scripting-language-32-2048.jpg)