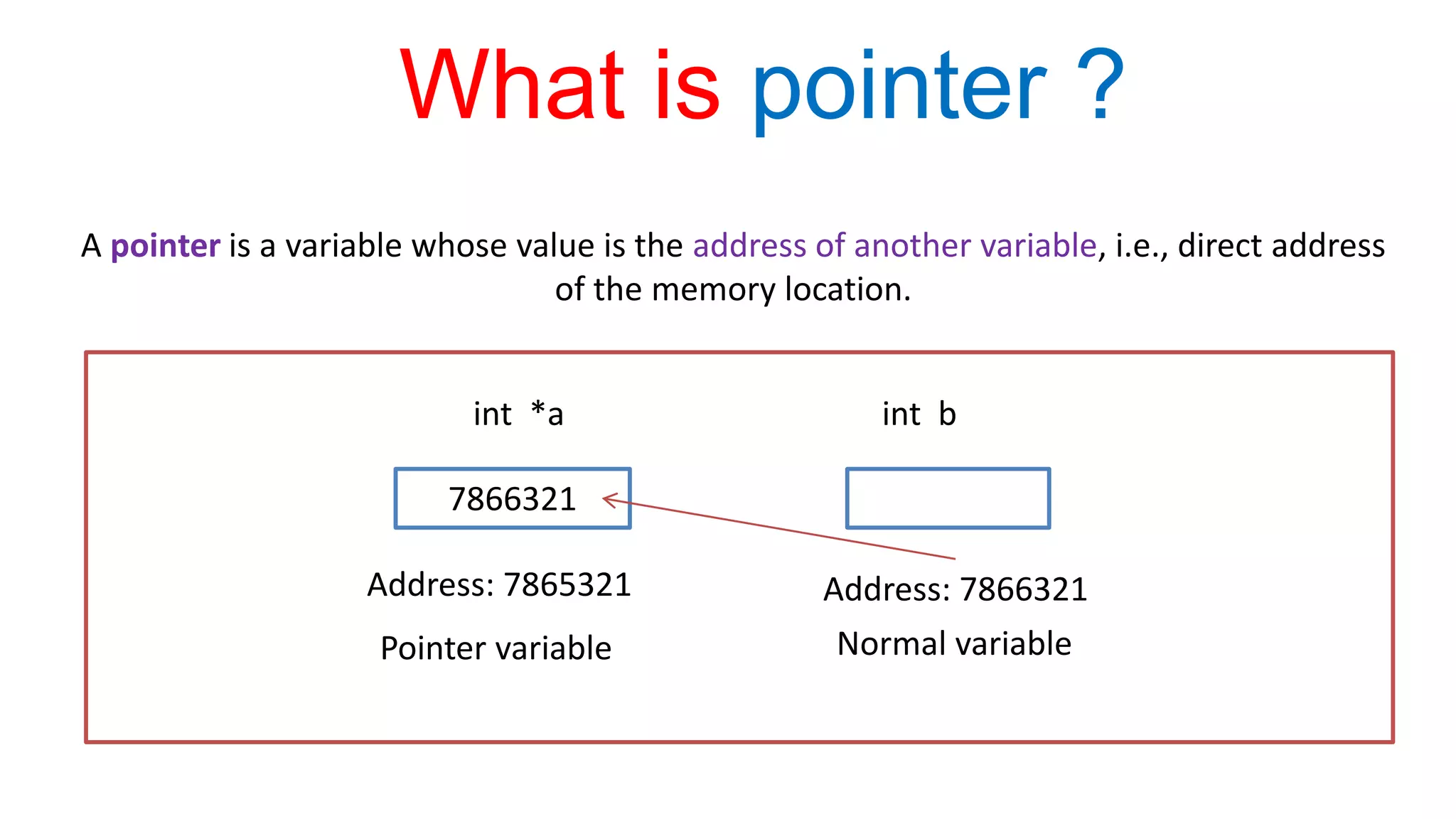
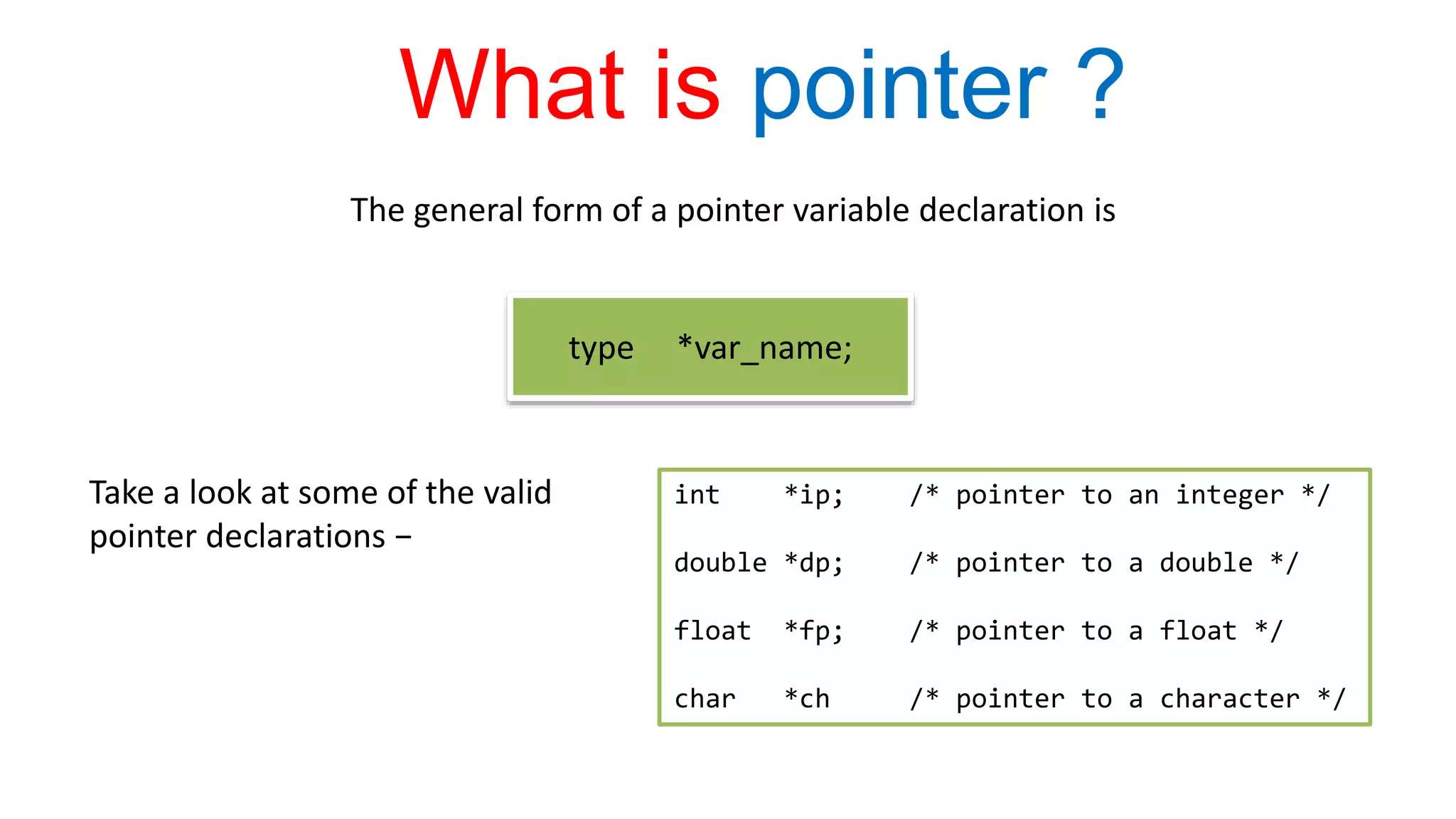
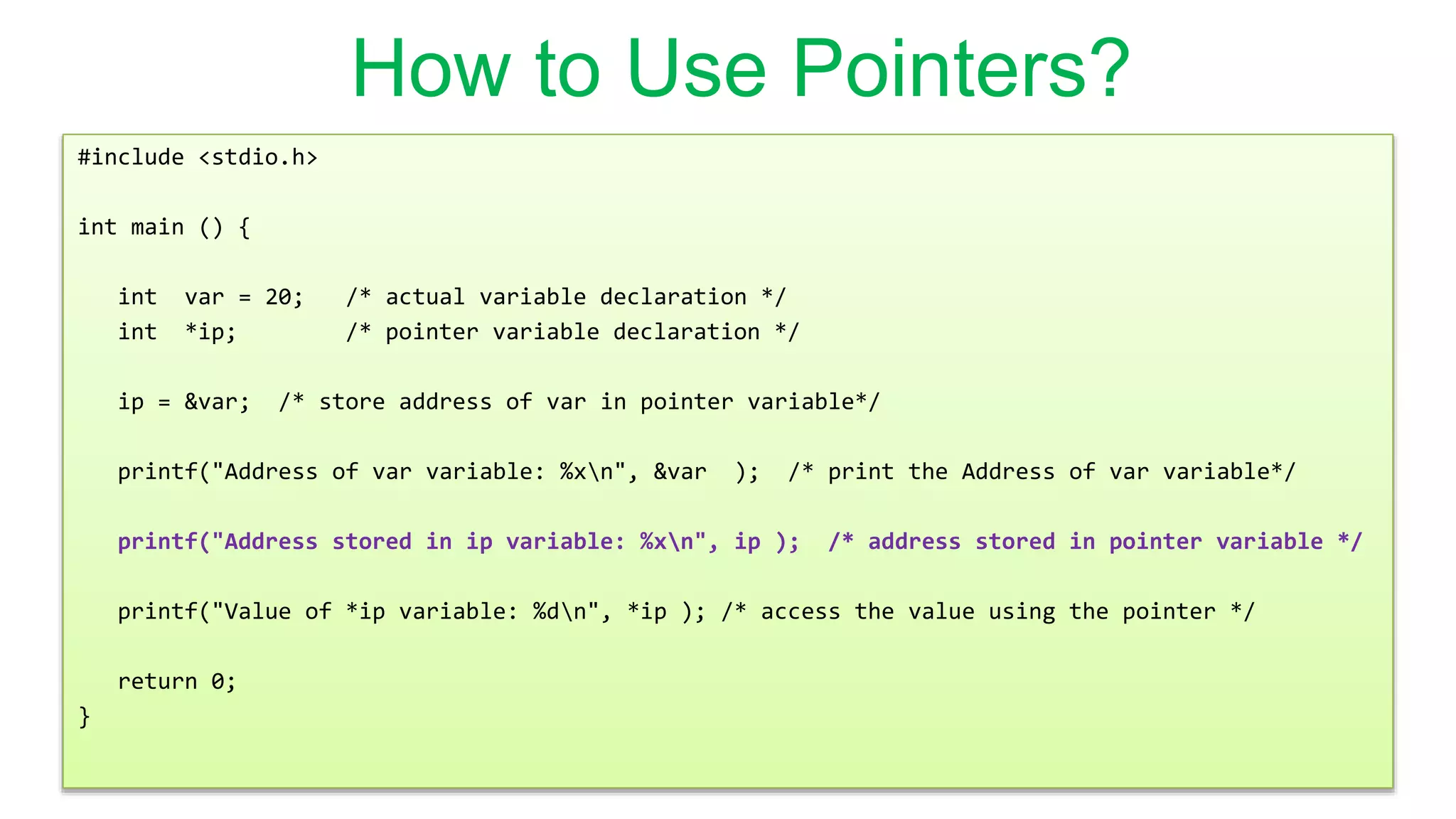
A pointer in C is a variable that stores the address of another variable. It allows a program to indirectly access the memory location that a variable is stored in. Pointers are declared with a * before the variable name. The & operator returns the address of its operand and is used to initialize a pointer variable. The * operator dereferences a pointer to access the value at the address it contains.