The document explains arrays as fundamental data structures in programming for storing and organizing elements of the same type, detailing their declaration, initialization, and common operations. It also covers passing arrays to functions, sorting algorithms, and searching techniques, including linear and binary search. Additionally, the document introduces multidimensional arrays, highlighting their applications and the syntax for accessing their elements.


![Declaring and Creating Arrays
Declaring Arrays
To declare an array in C, you
need to specify the data type,
the name of the array, and
the size (or length) of the
array. The general syntax is:
data_type
array_name[size];
For example, to declare an
array of 10 integers, you
would use:
int numbers[10];
Initializing Arrays
Arrays can be initialized in
several ways, such as by
providing a comma-
separated list of values
enclosed in curly braces, or
by using a loop to assign
values. For example:
int numbers[5] = {1,
2, 3, 4, 5};
This initializes the 'numbers'
array with the values 1, 2, 3,
4, and 5.
Dynamic Allocation
In some cases, you may
need to dynamically allocate
memory for an array at
runtime. This can be done
using the 'malloc()' function.
For example:
int *numbers =
(int*)
malloc(sizeof(int) *
10);
This creates a dynamically
allocated array of 10 integers,
which can be useful when the
size of the array is not known
until runtime.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptonarrays1-240418174559-4e3f072f/75/ppt-on-arrays-in-c-programming-language-pptx-5-2048.jpg)
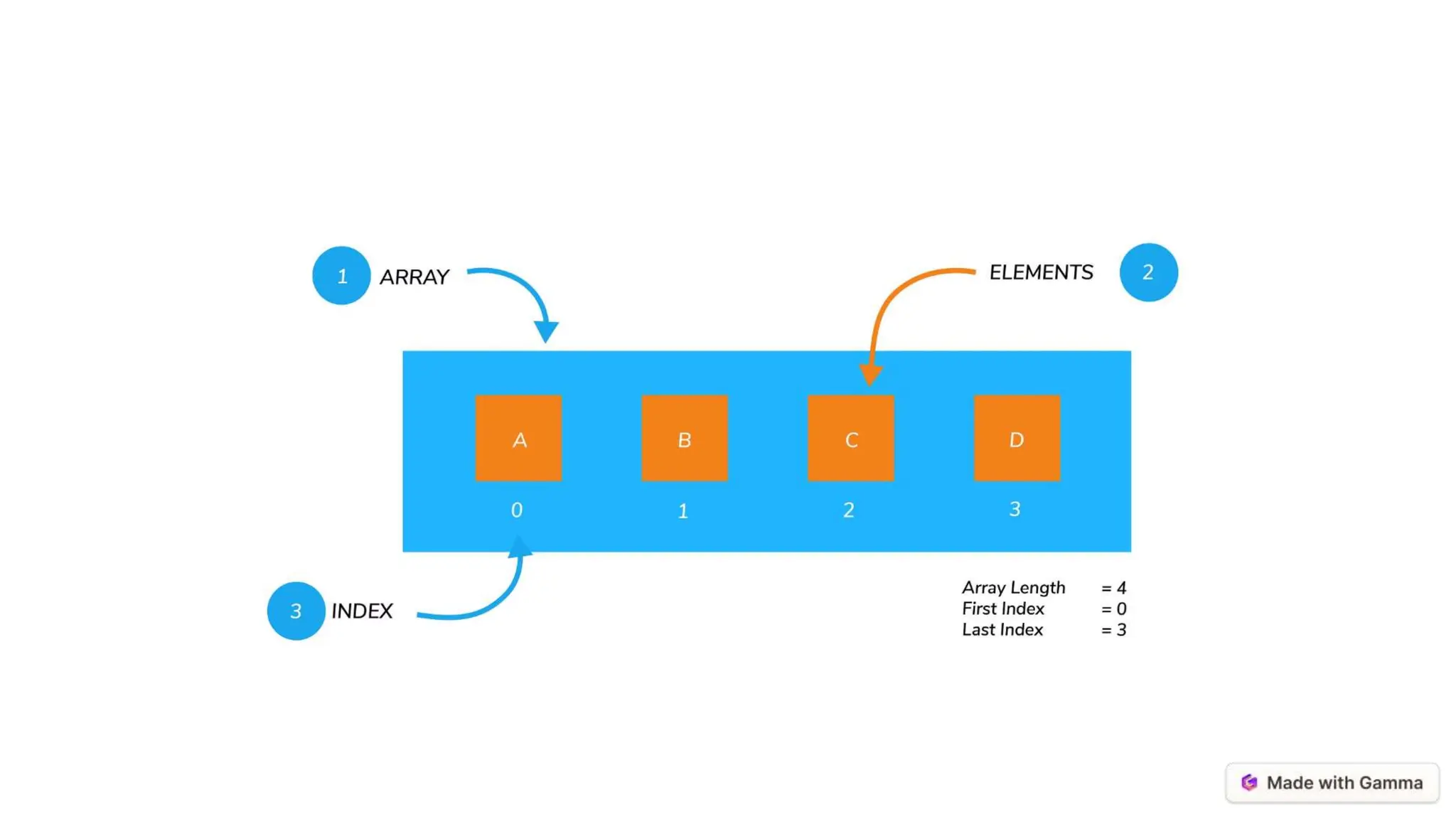
![Examples Using Arrays
1 Storing and
Accessing Data
Arrays allow you to store
and access data using
index values. For
example, you can assign
a value to an array
element using the index:
numbers[0] = 10;
And you can retrieve the
value of an array
element using the index:
int value =
numbers[3];
2 Iterating Over
Arrays
You can use loops to
iterate over the elements
of an array. This is
commonly done using a
'for' loop and the array's
index:
for (int i = 0;
i < 10; i++) {
printf("%d
", numbers[i]);
}
This will print all the
elements of the
'numbers' array.
3 Common Array
Operations
Arrays support a variety
of common operations,
such as finding the
minimum or maximum
value, calculating the
sum or average of the
elements, and more.
These operations can be
implemented using
loops and conditional
statements.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptonarrays1-240418174559-4e3f072f/75/ppt-on-arrays-in-c-programming-language-pptx-6-2048.jpg)




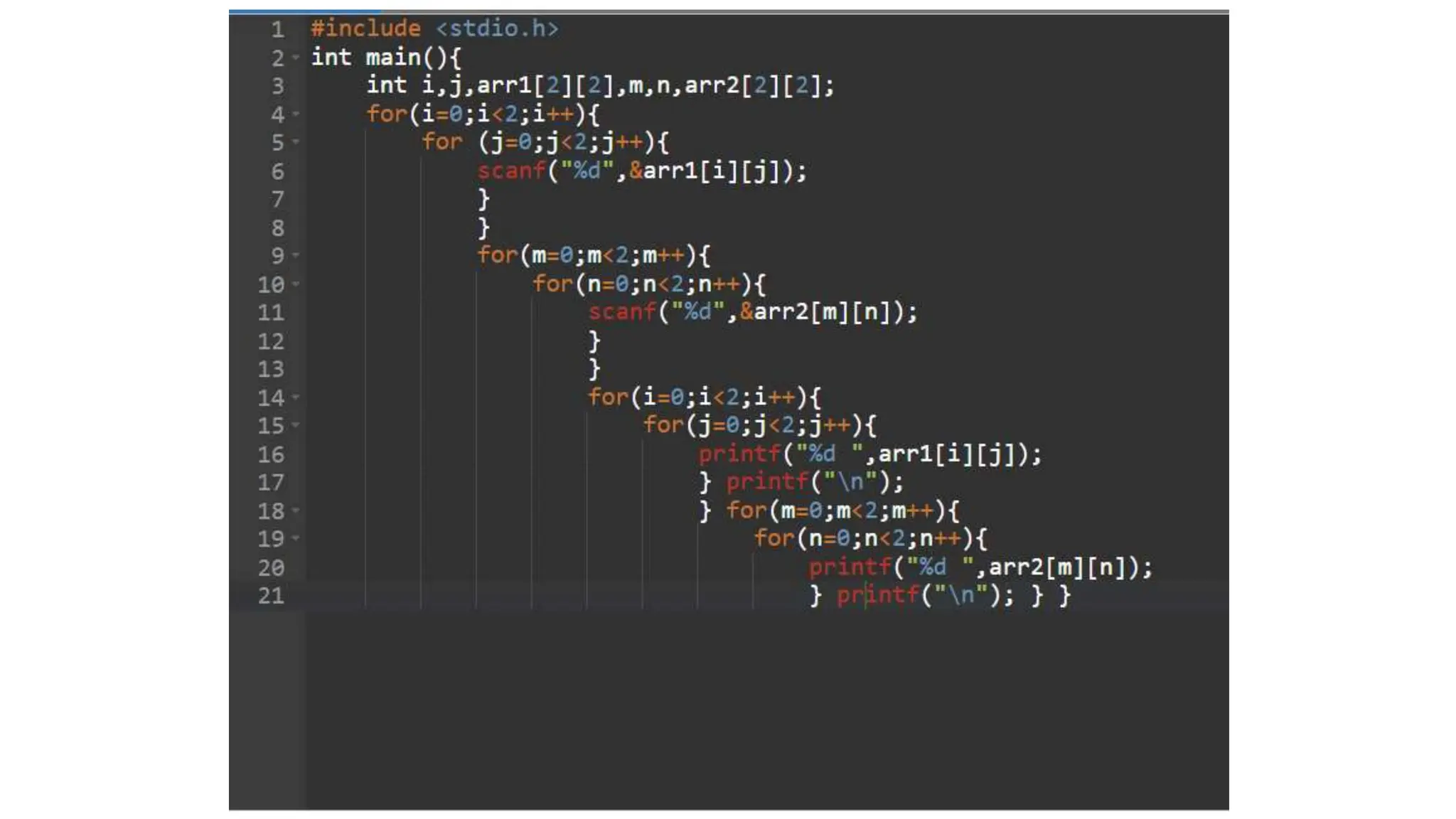
![Multidimensional Arrays
2D Arrays
Multidimensional arrays in C can have
more than one dimension. The most
common type is the 2D array, which
can be thought of as a grid or table of
values. To declare a 2D array, you
specify the number of rows and
columns, like this:
int matrix[3][4];
Accessing
Elements
Accessing elements in a multidimensional
array is done by specifying the indices for
each dimension. For example, to access an
element in a 2D array, you would use:
matrix[row][column];
Multidimensional arrays allow you to
represent and manipulate complex data
structures, making them a powerful tool
in many C programming applications.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptonarrays1-240418174559-4e3f072f/75/ppt-on-arrays-in-c-programming-language-pptx-12-2048.jpg)