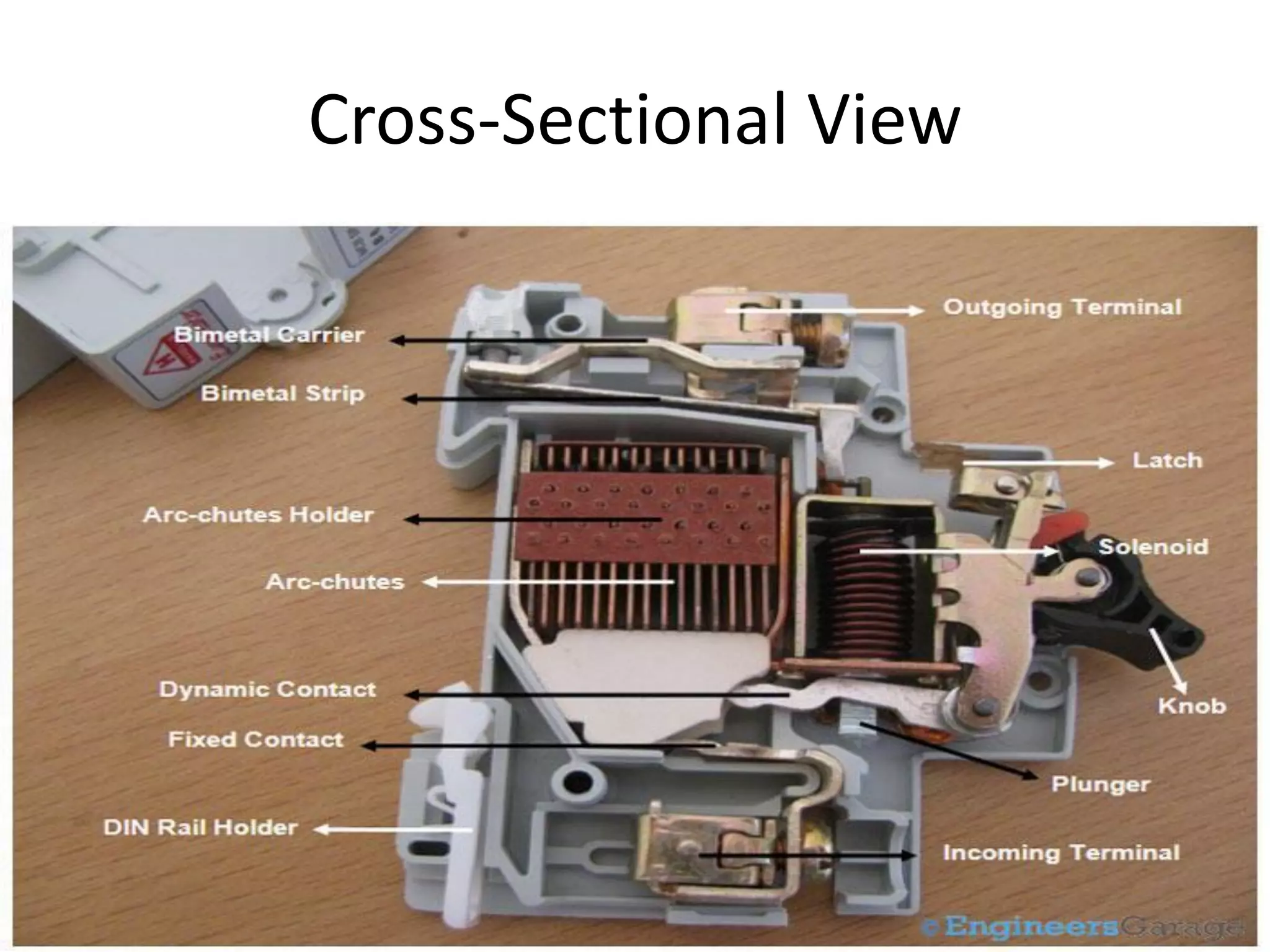
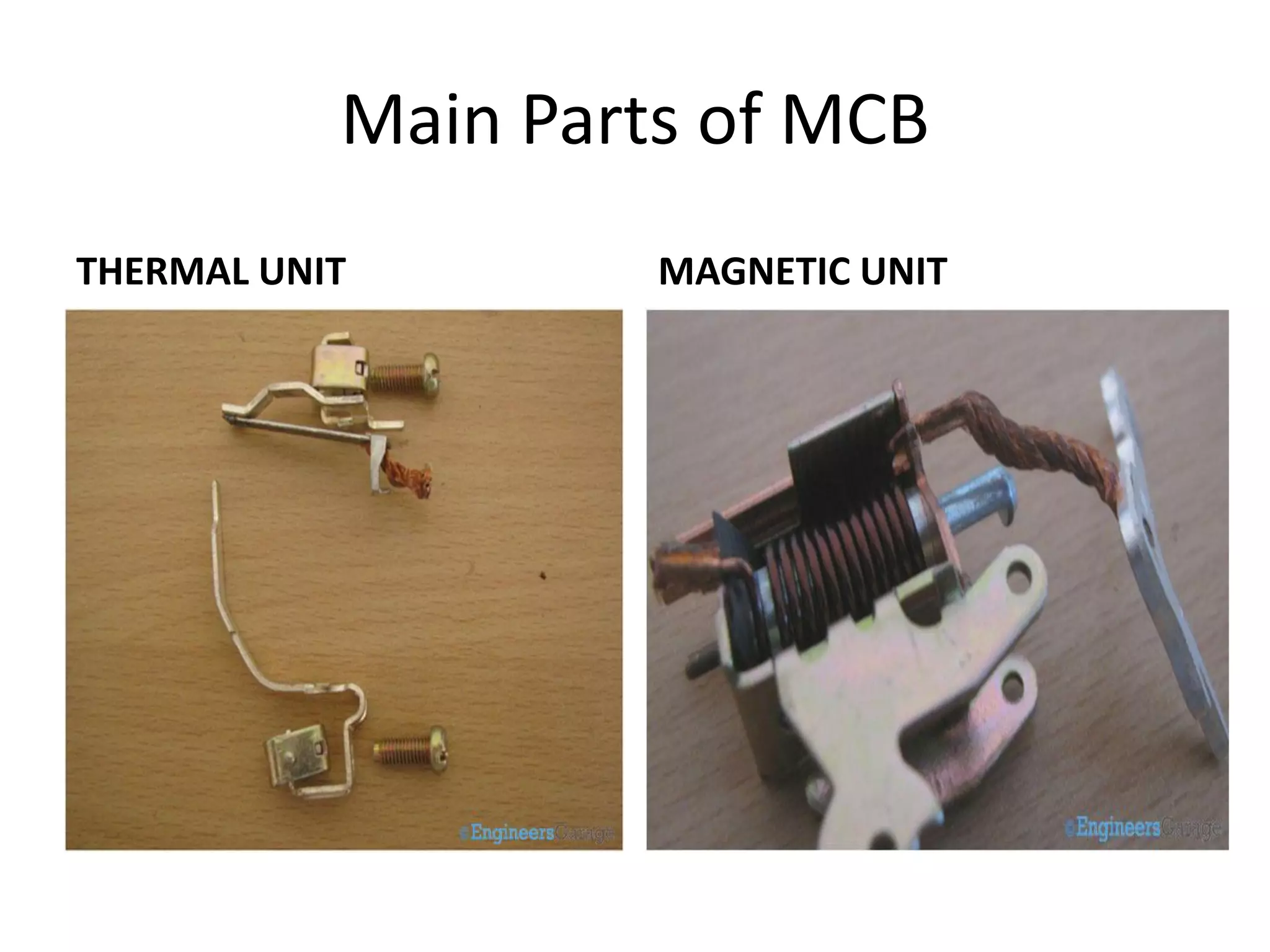
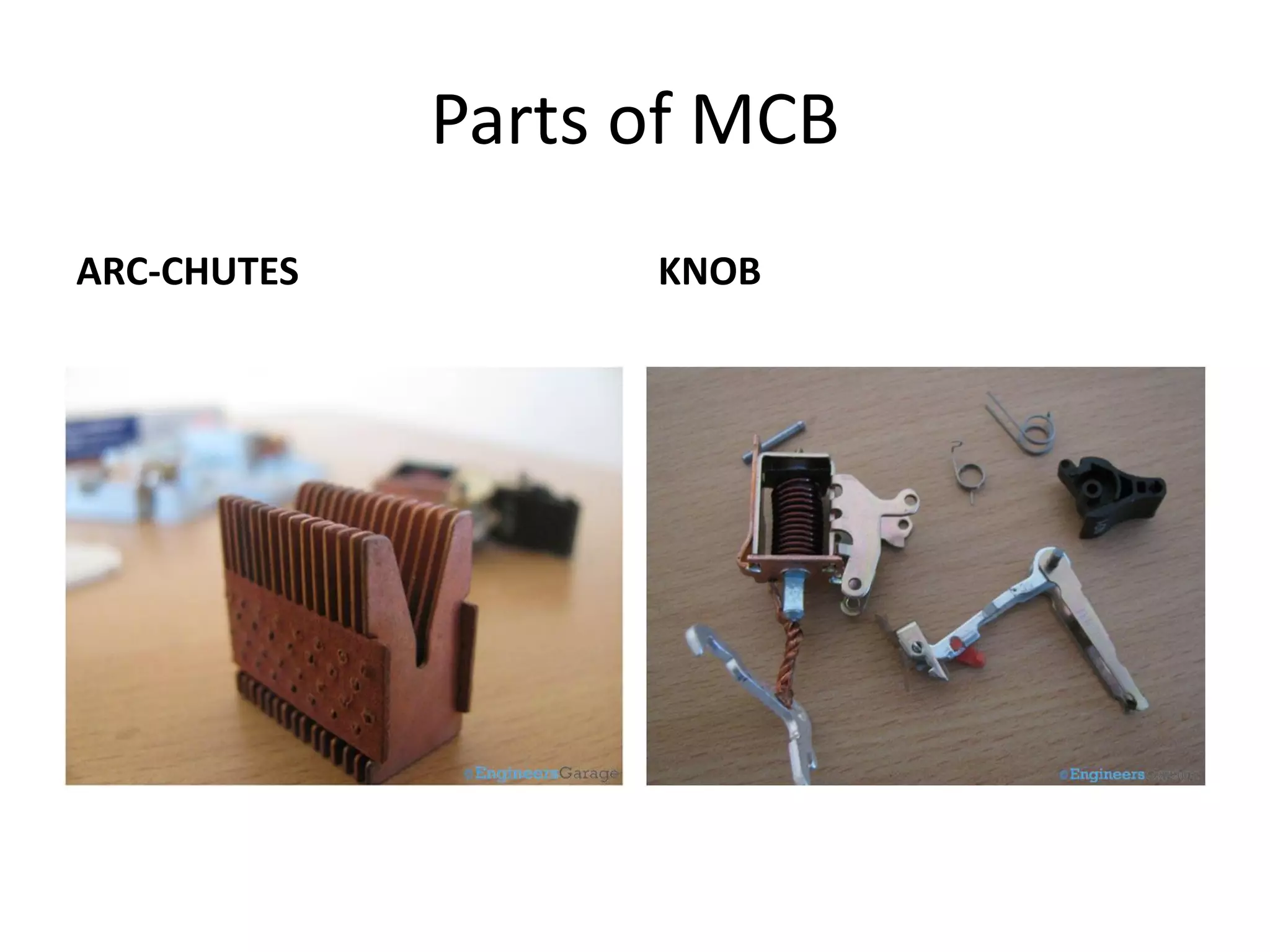
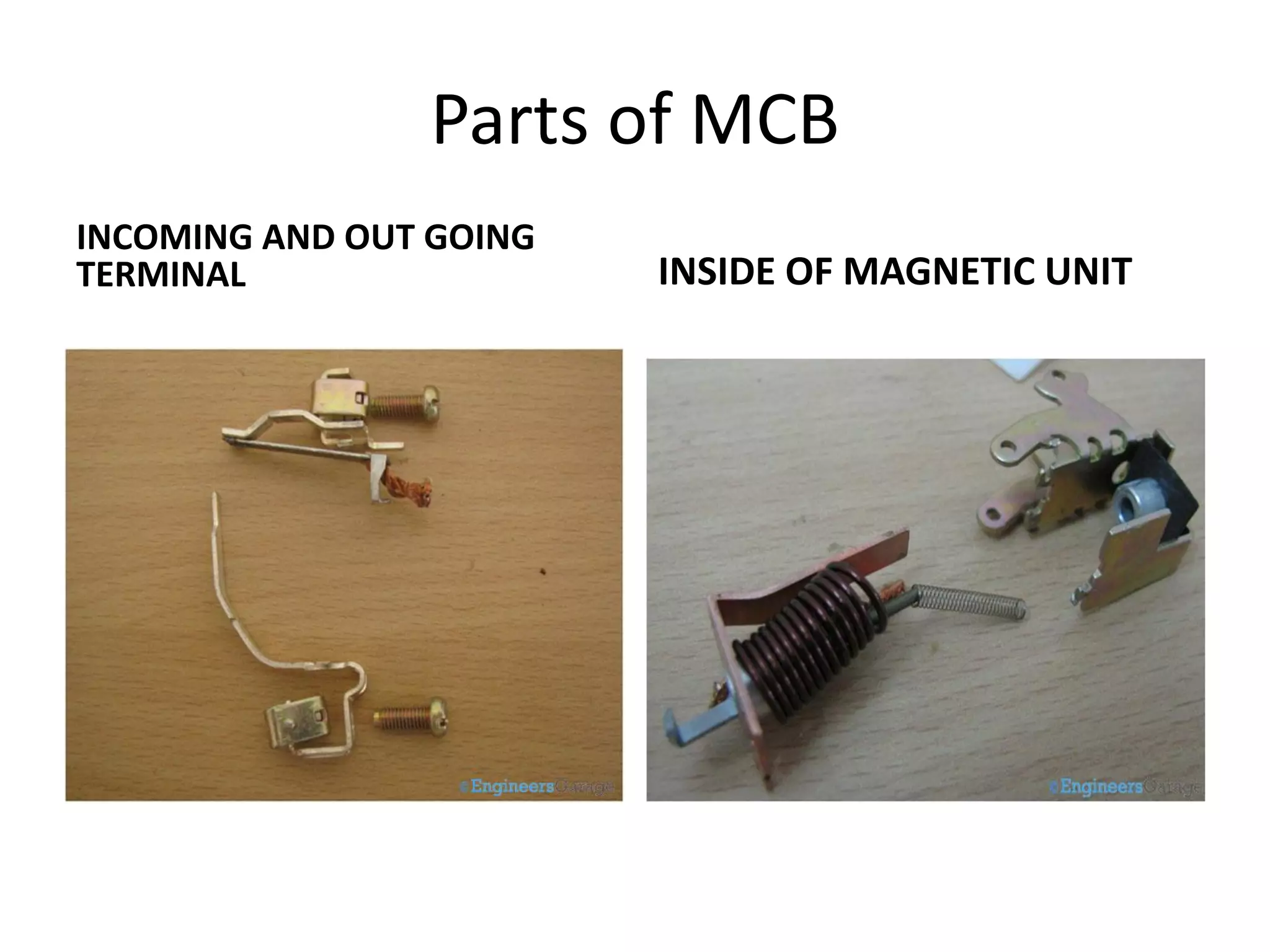
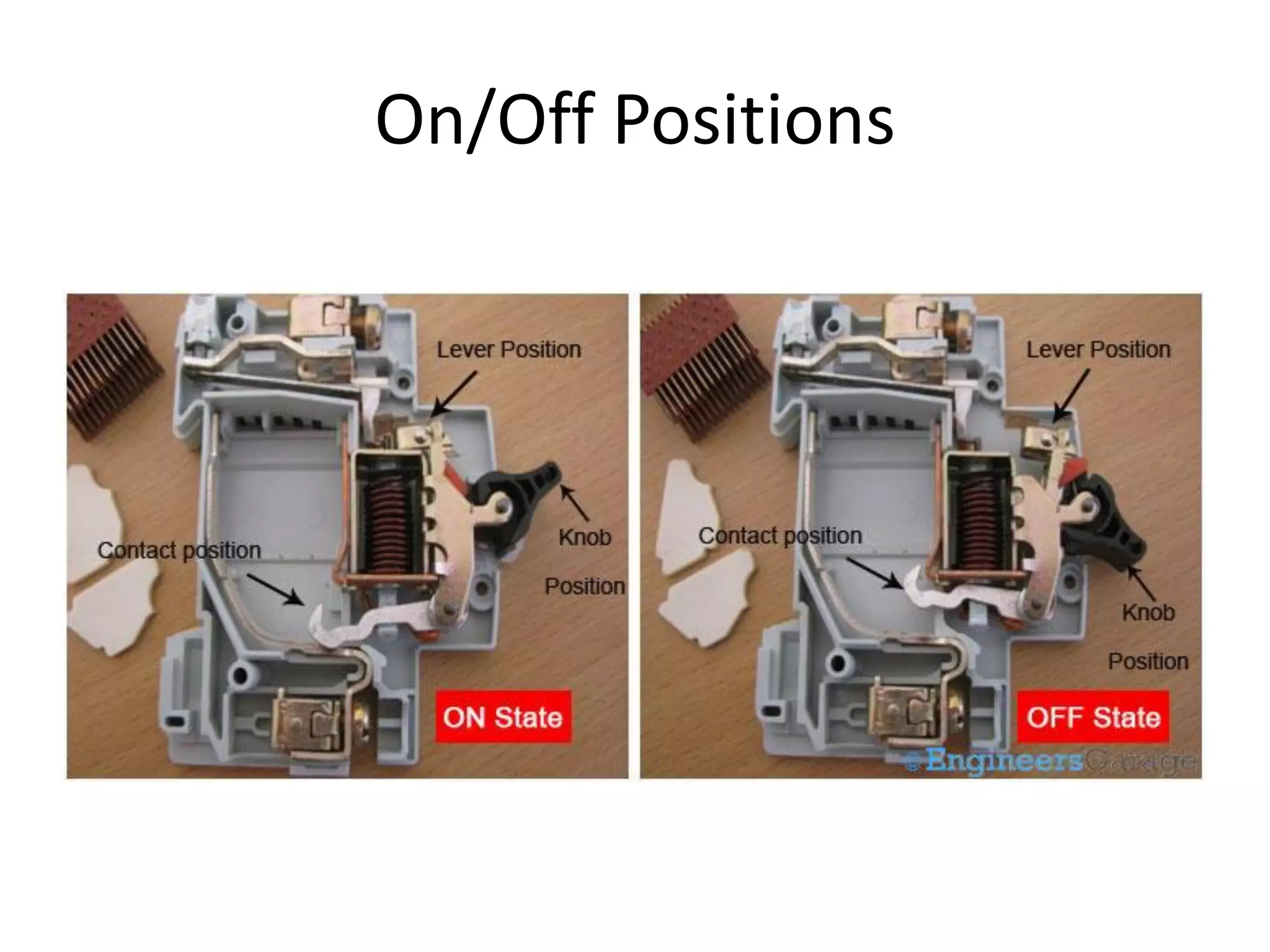
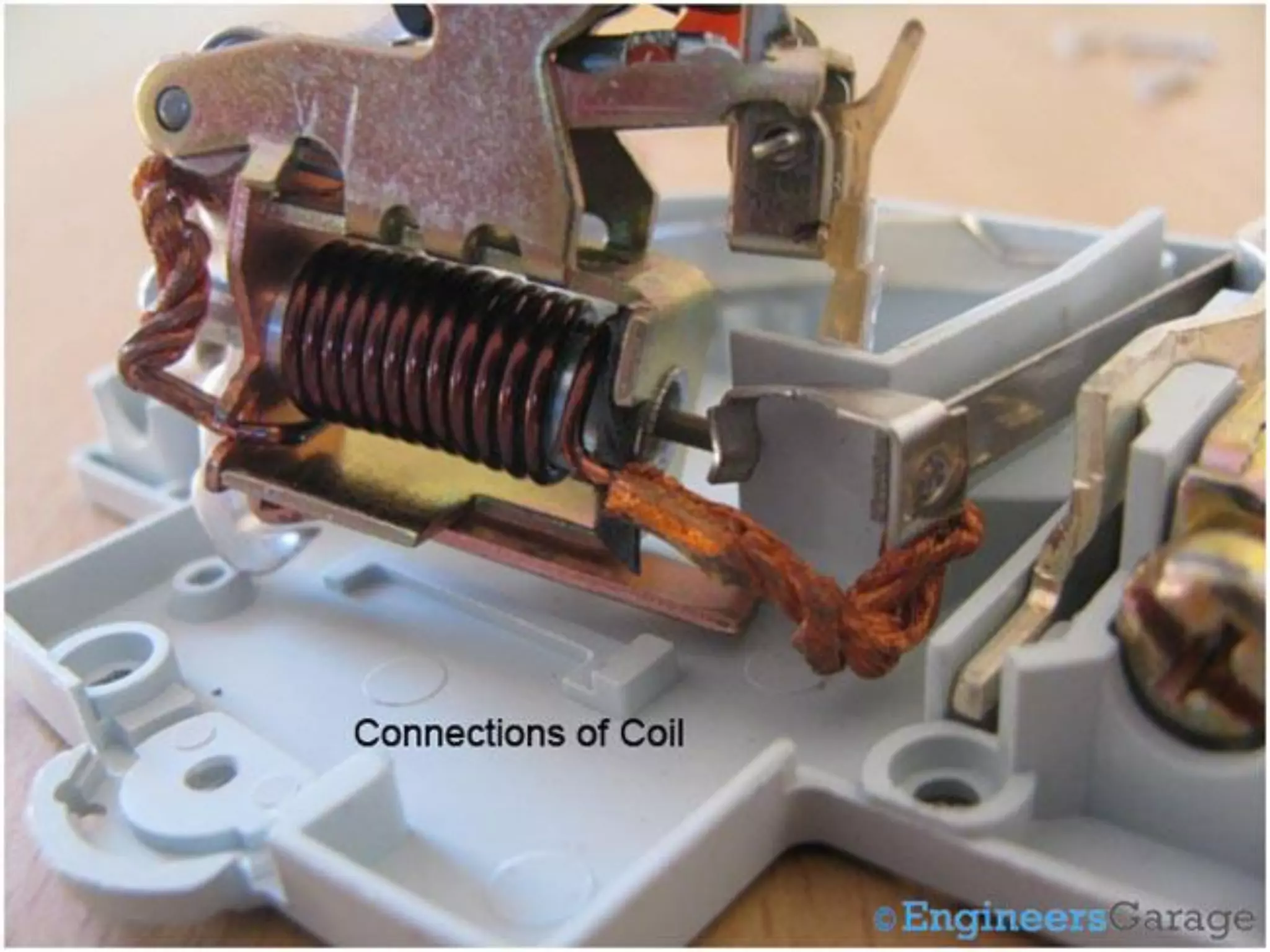
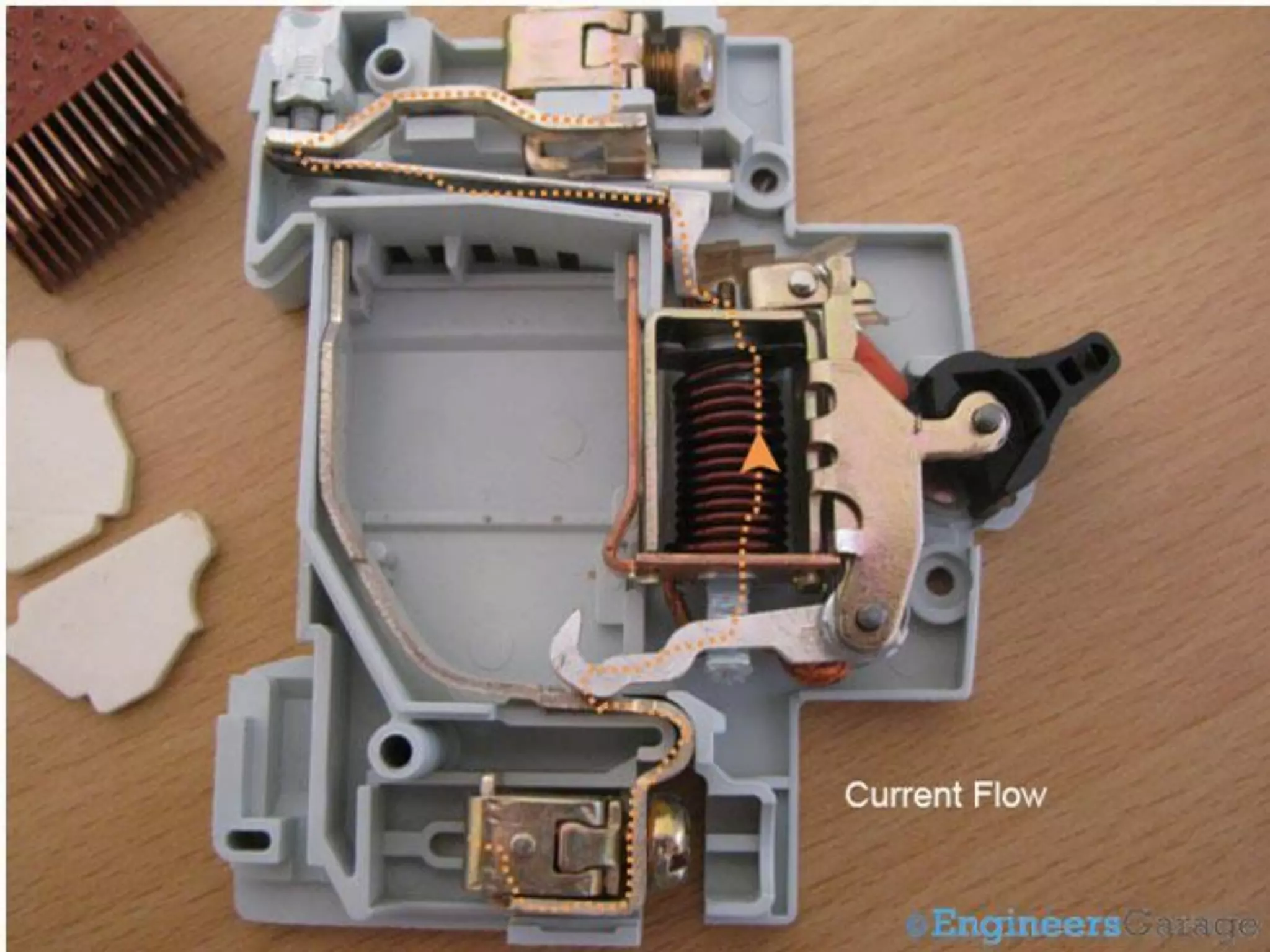
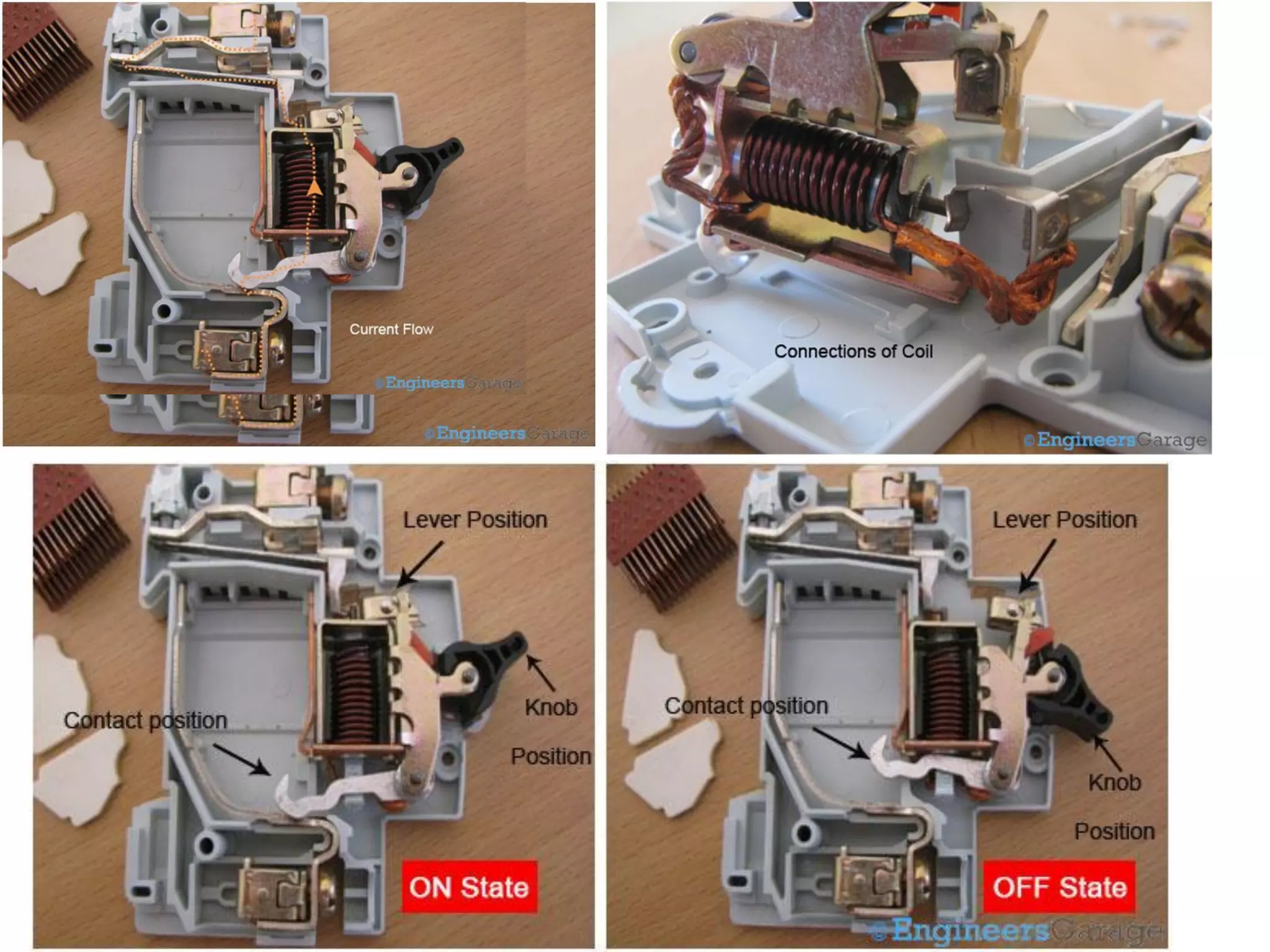
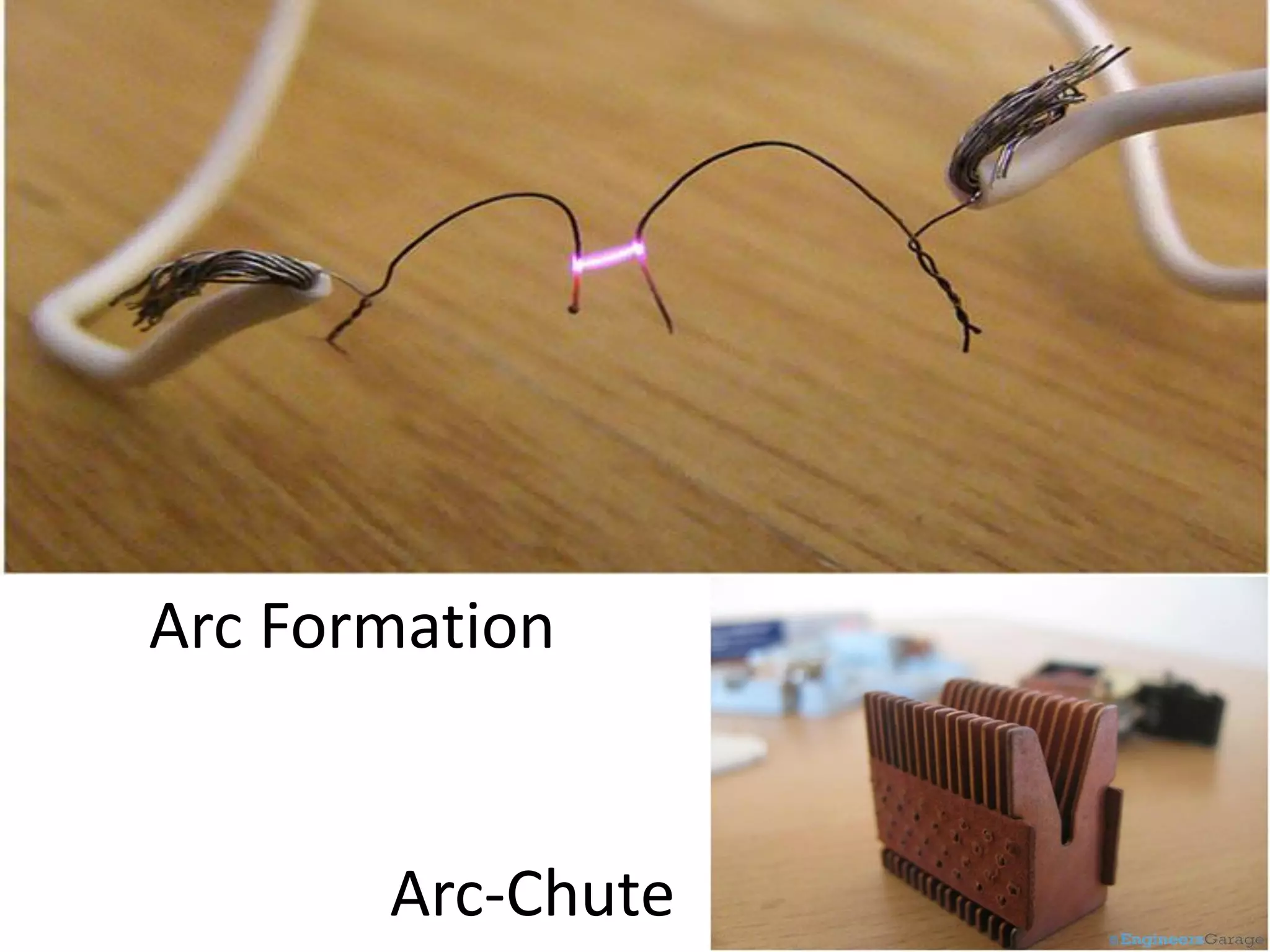
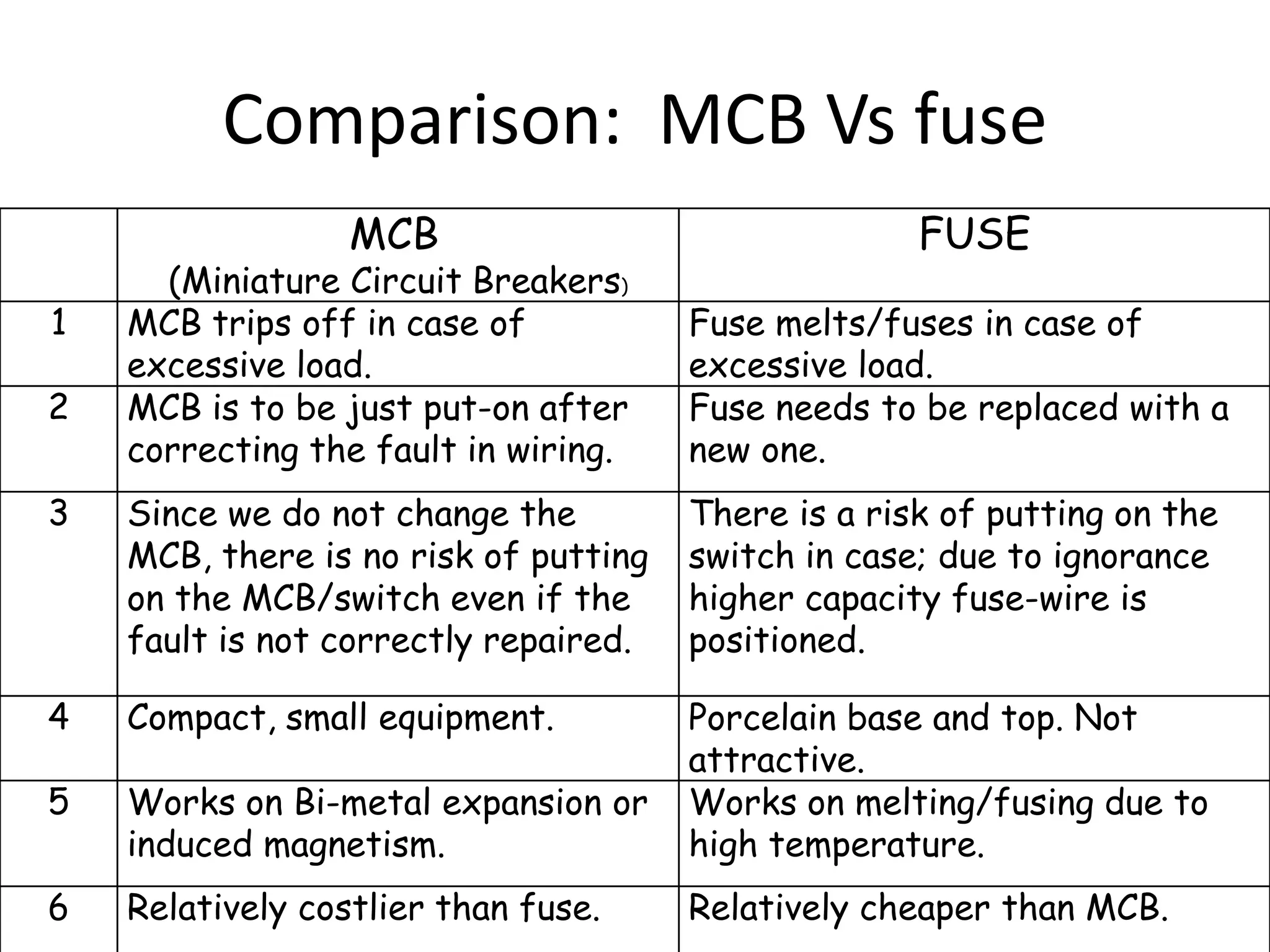
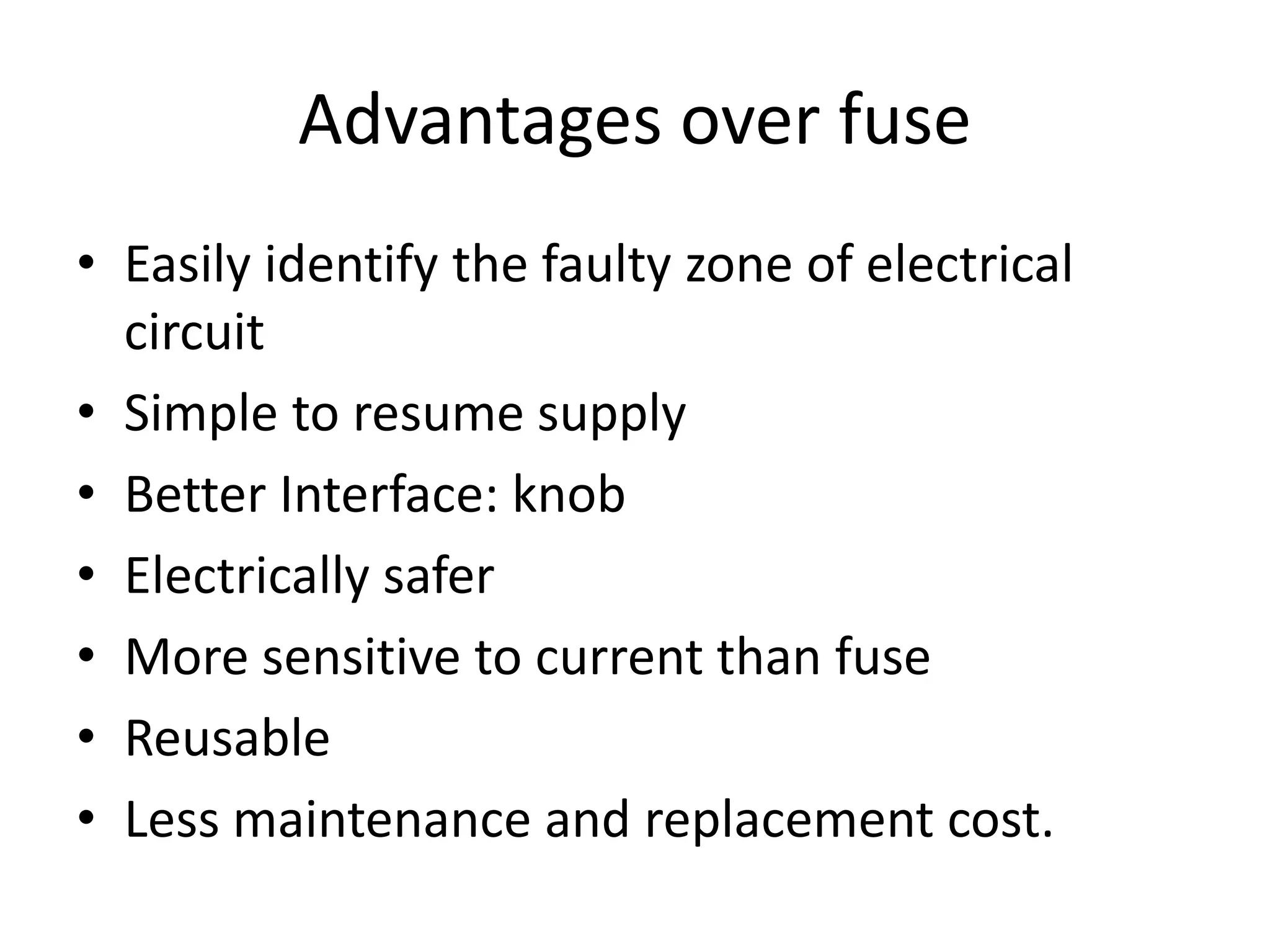
Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) provide overcurrent protection in electrical circuits. MCBs have replaced traditional fuses in many applications. MCBs have three main components: a thermal unit to sense overloads, a magnetic unit to sense short circuits, and arc chutes to suppress arcs. When too much current flows, the bimetal in the thermal unit bends and trips the circuit. For short circuits, a magnetic field trips the circuit. MCBs can be reset by flipping the switch after a fault is corrected, while fuses must be replaced. MCBs are more compact, reusable, and provide easier fault identification than fuses.