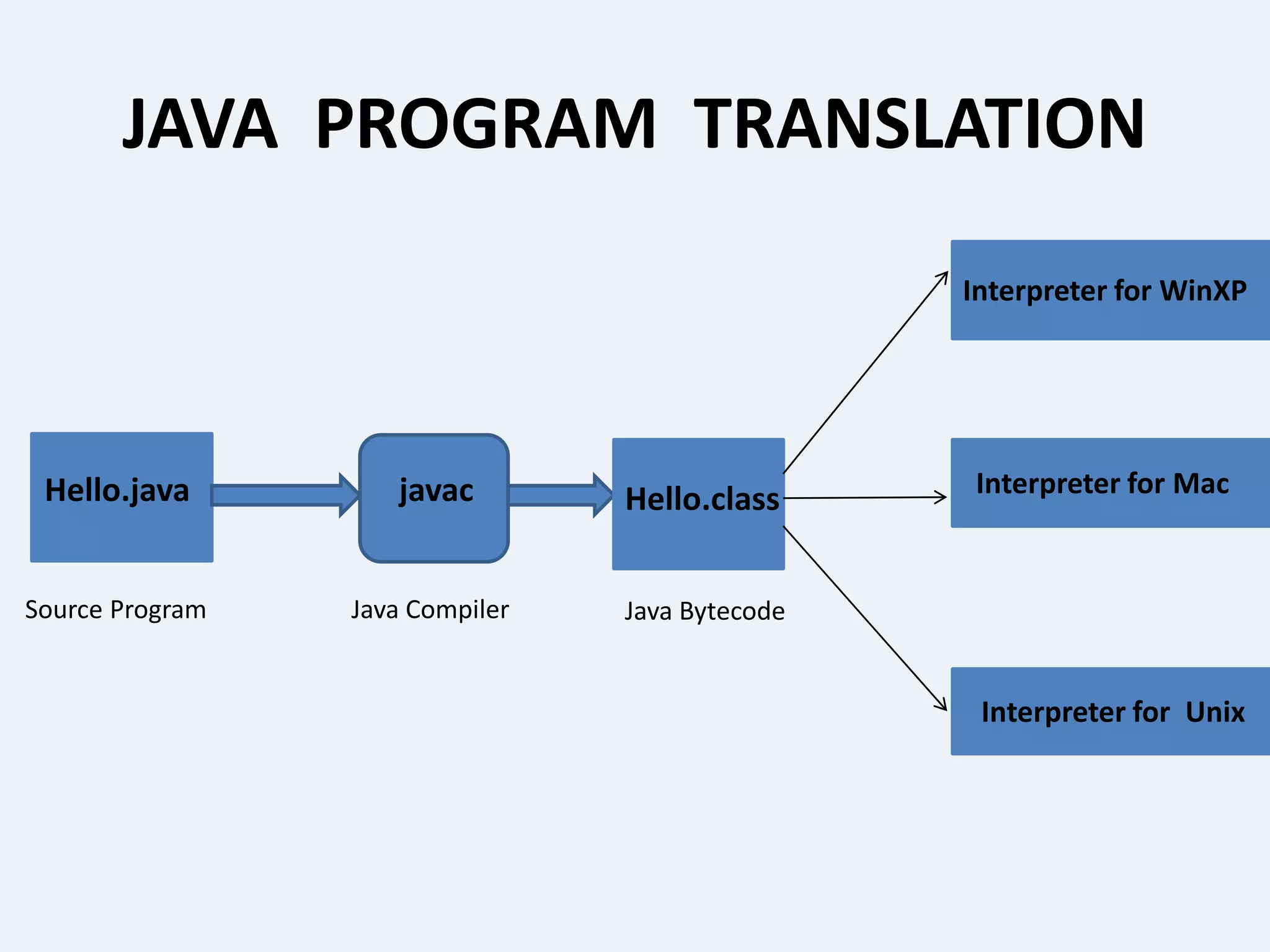
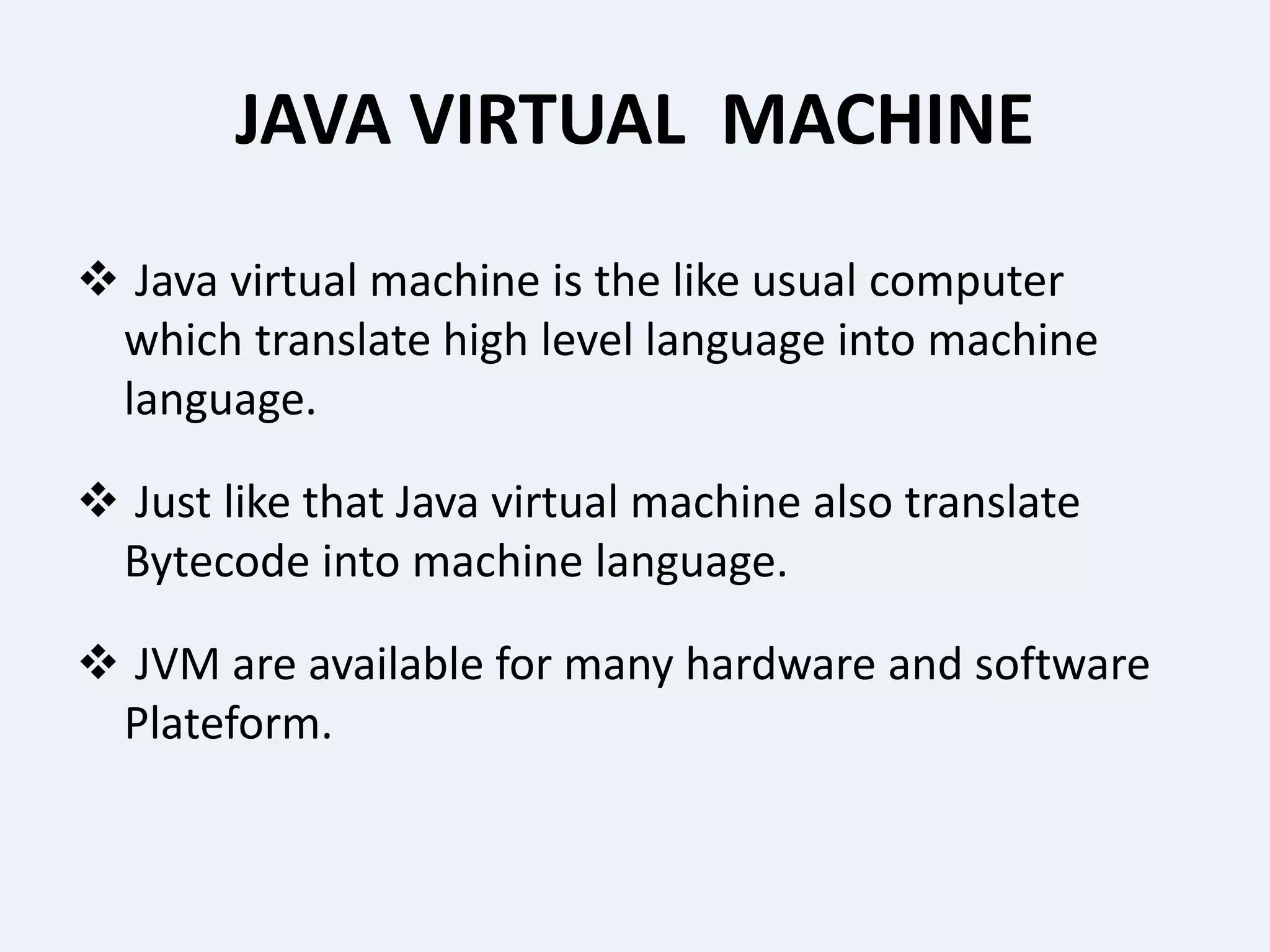
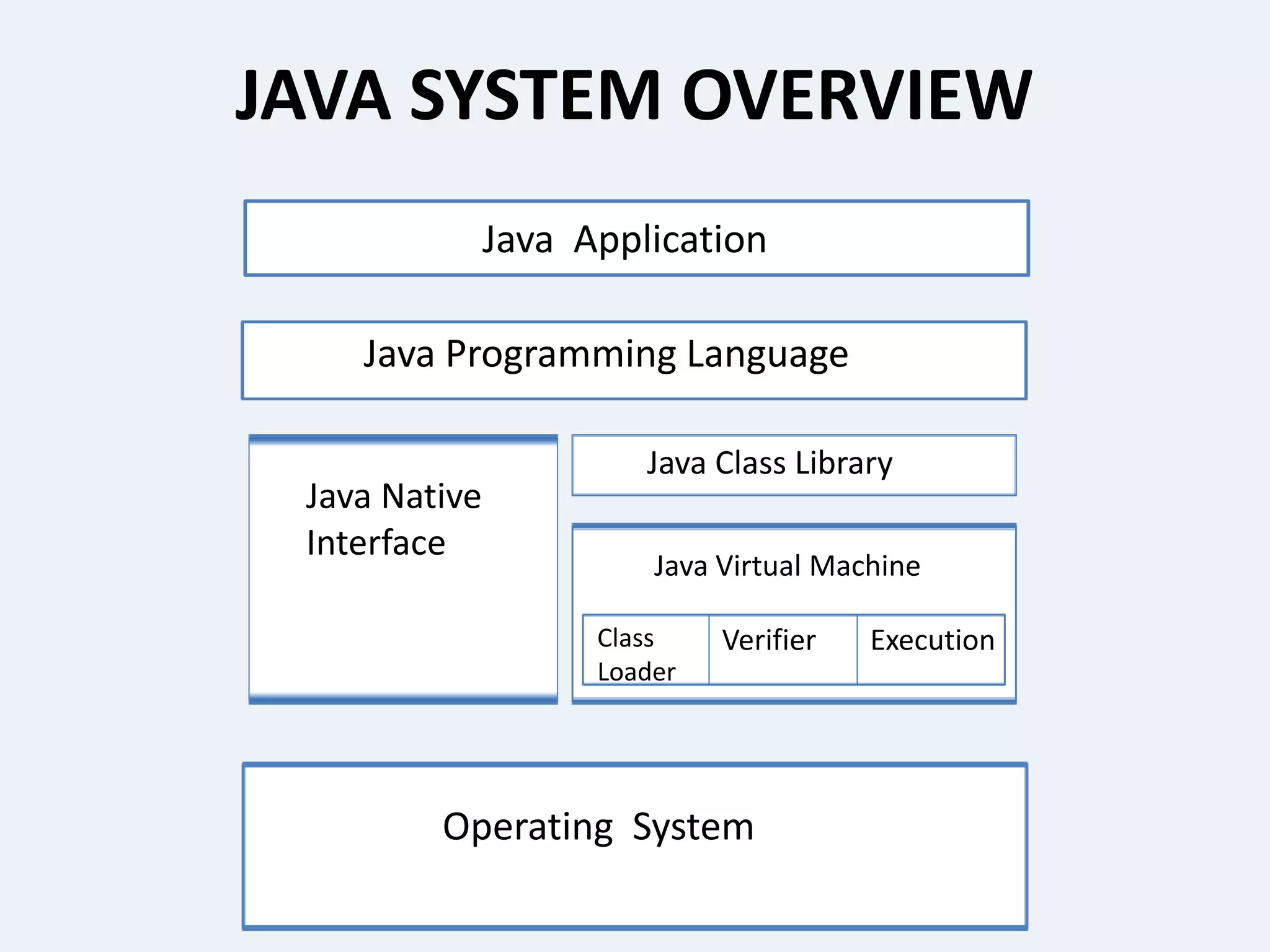
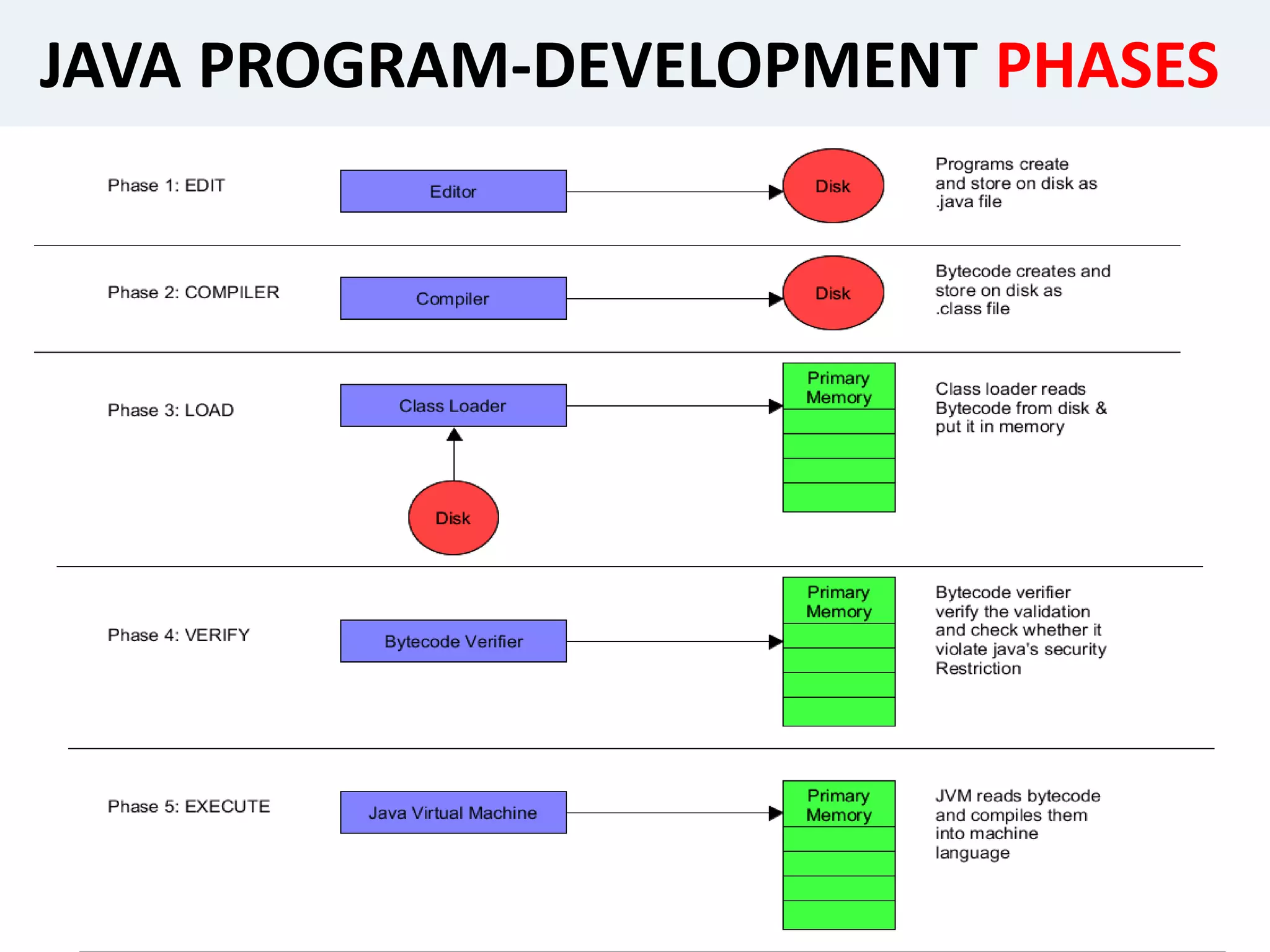
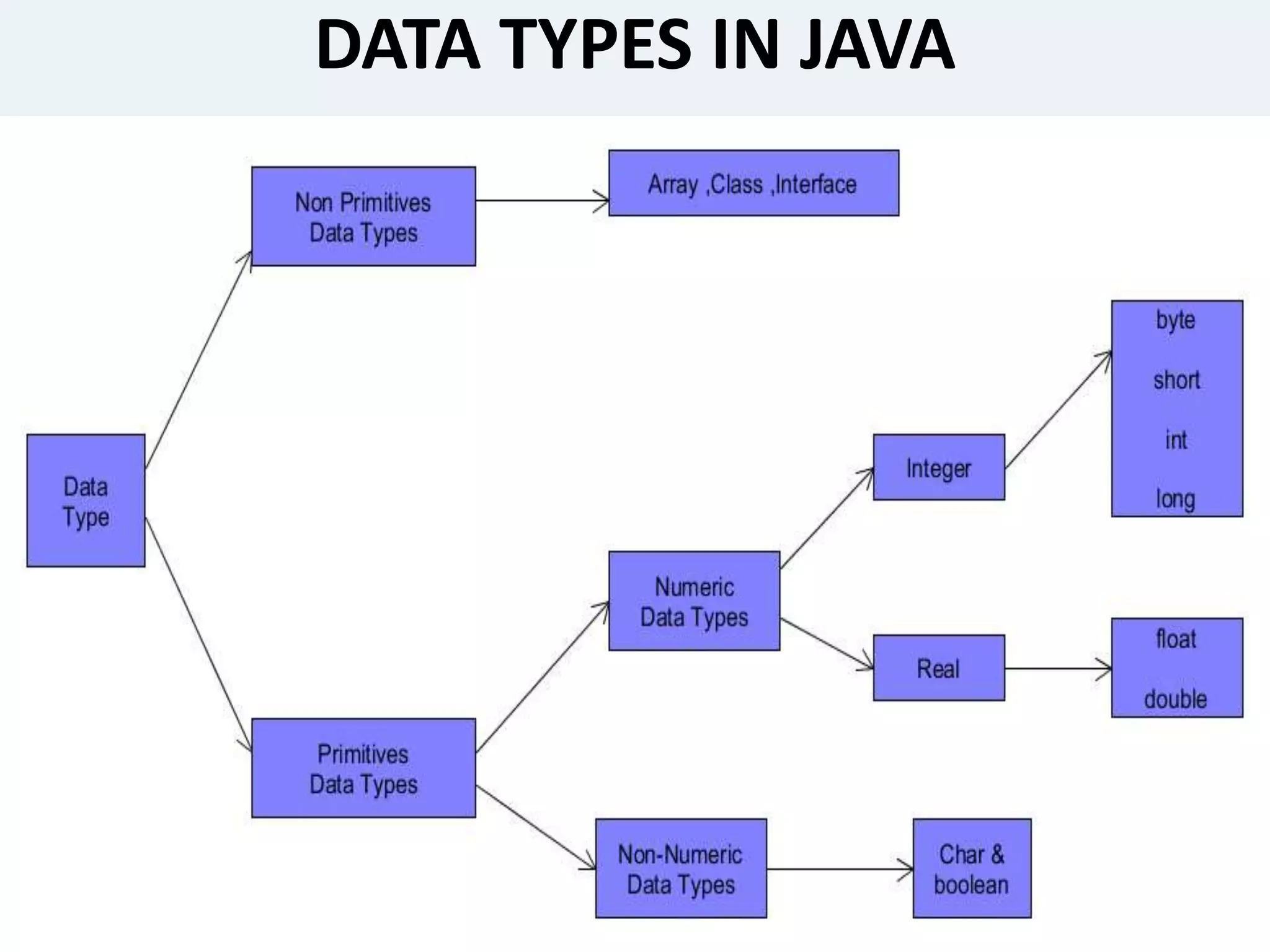
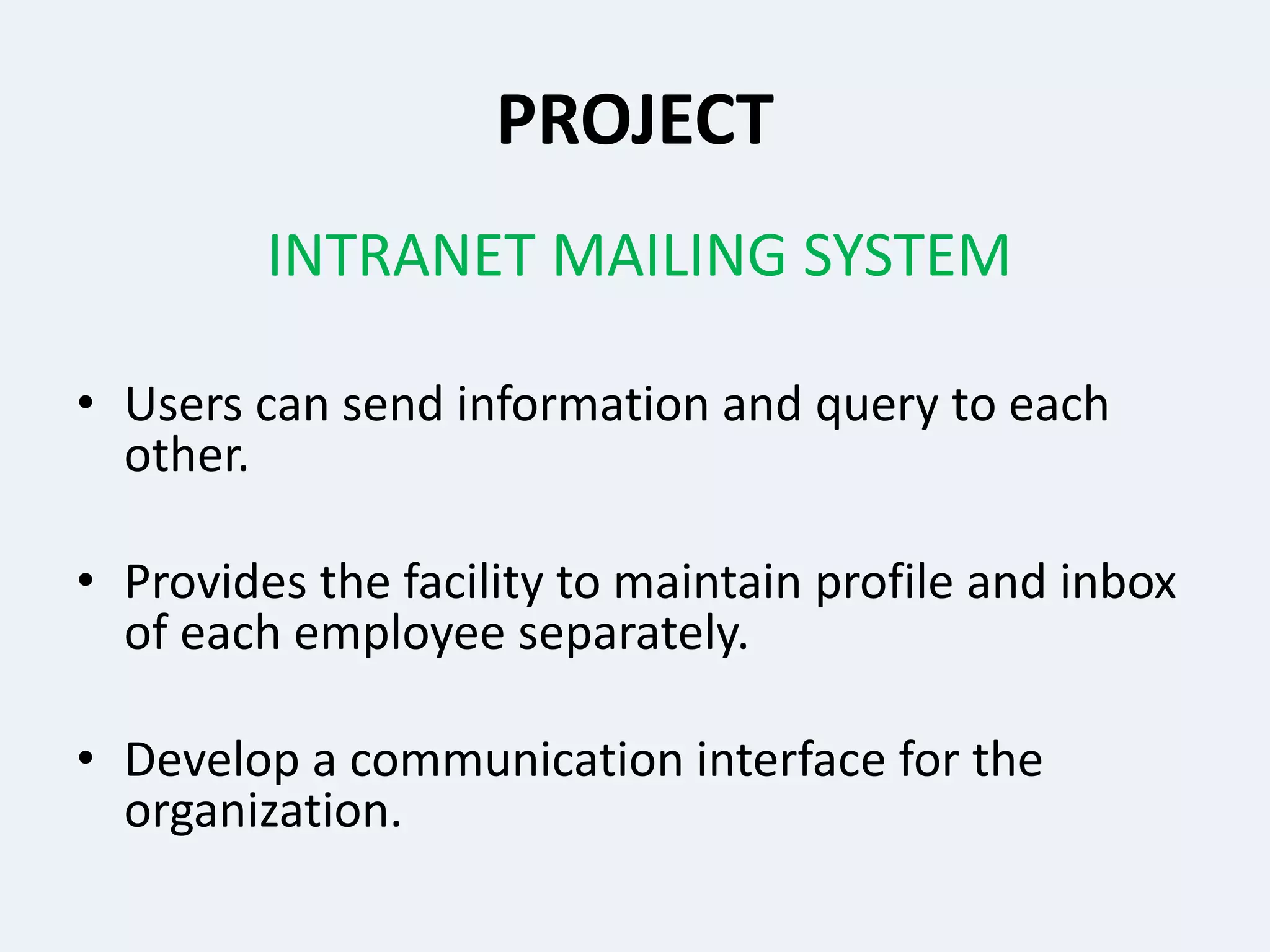
This presentation provides an overview of the Java programming language. It discusses what Java is, where it is used, its features, how Java programs are translated and run on the Java Virtual Machine. It also covers Java concepts like object-oriented programming, data types in Java, garbage collection, and the development phases of a Java program. Finally, it proposes a project idea of developing an intranet mailing system and concludes by thanking the audience and asking if there are any questions.