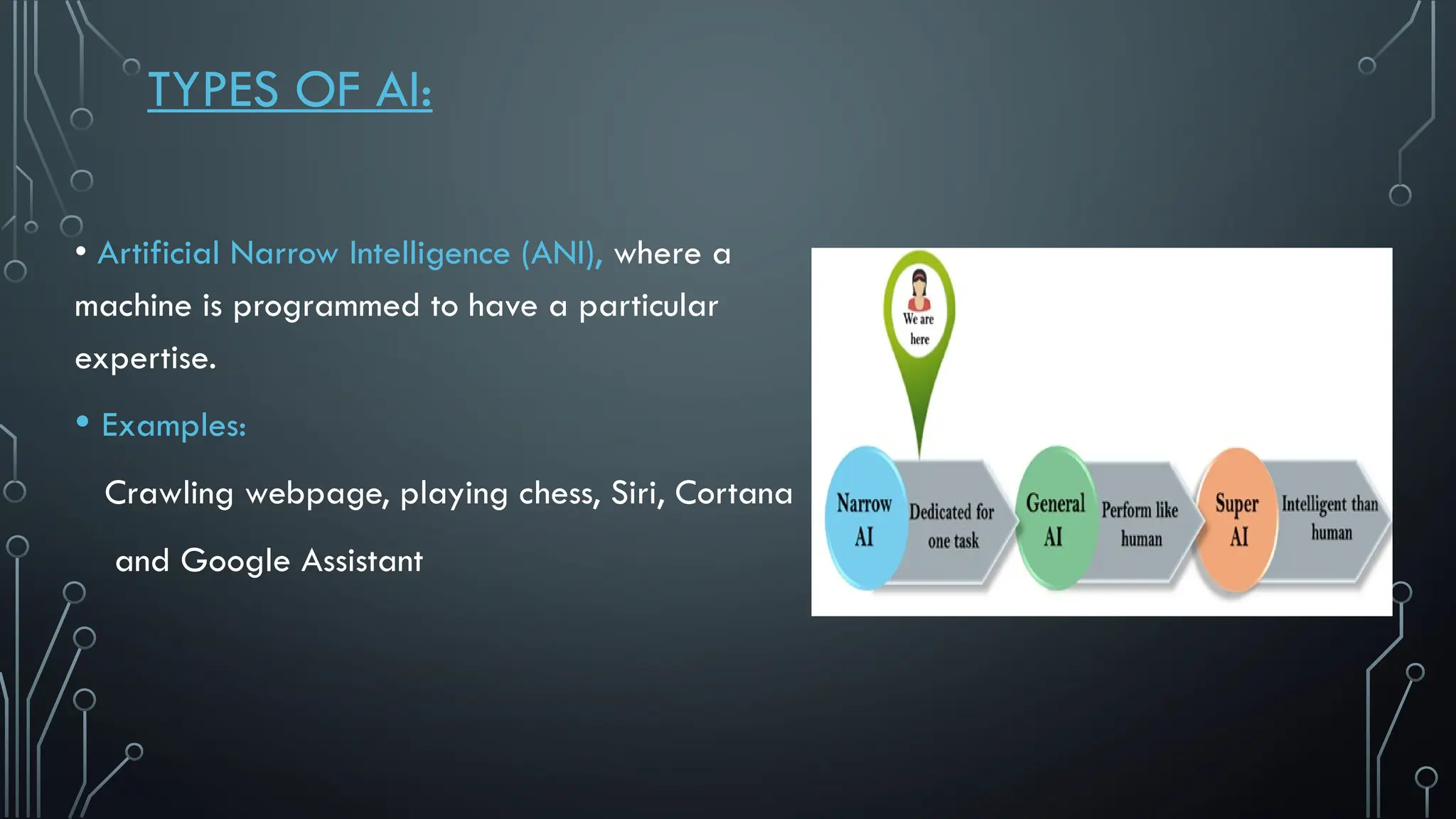
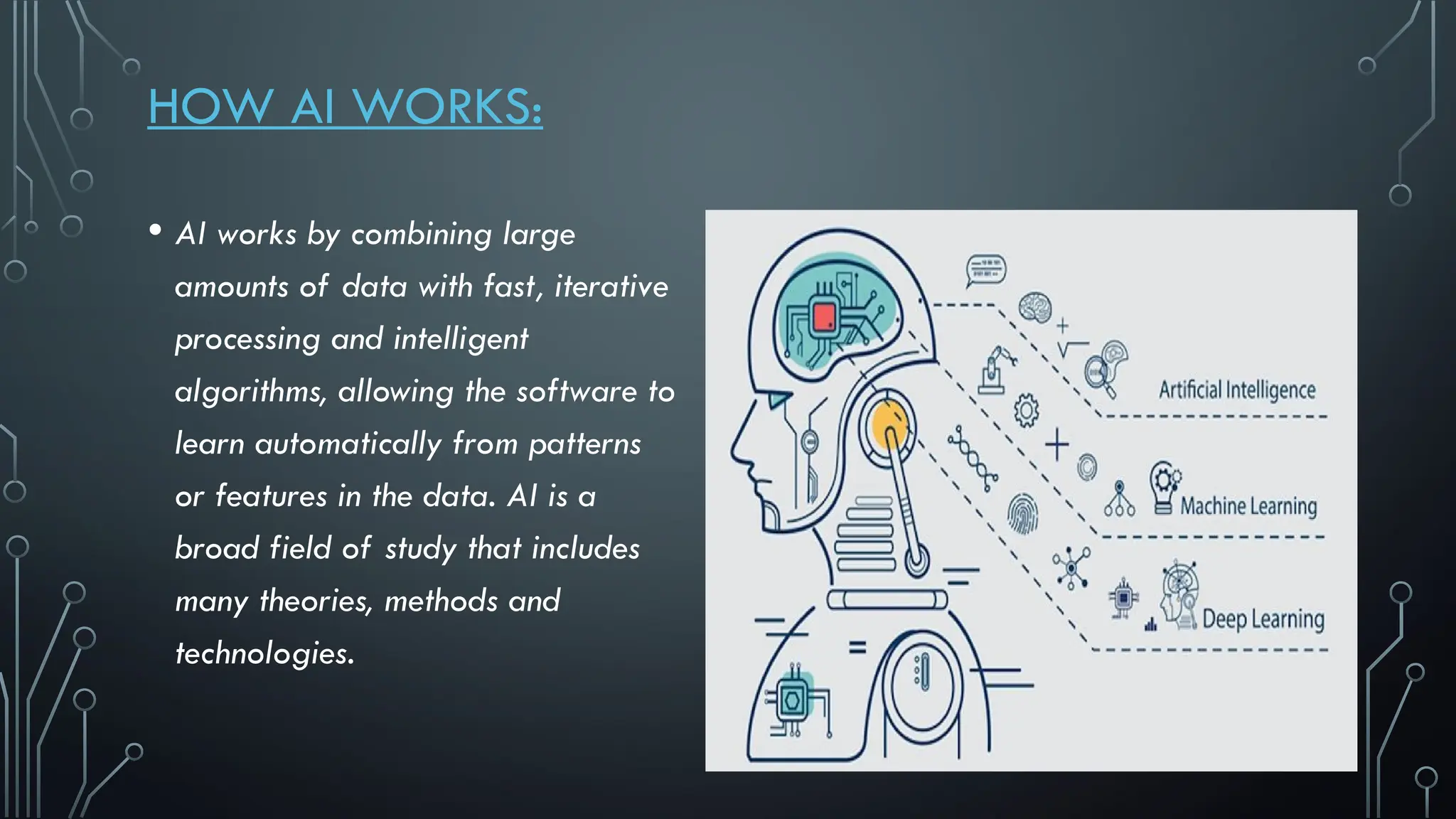
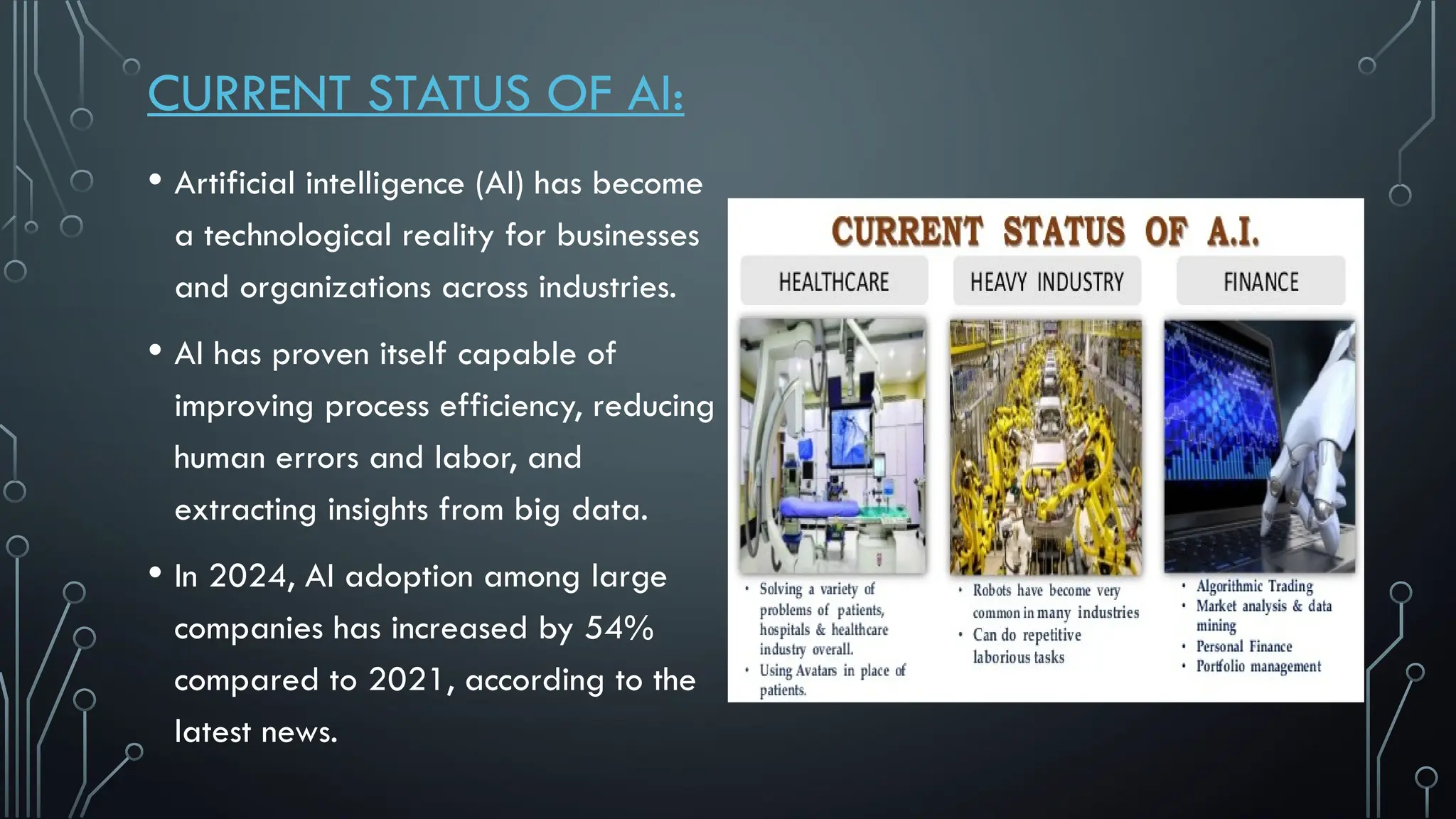
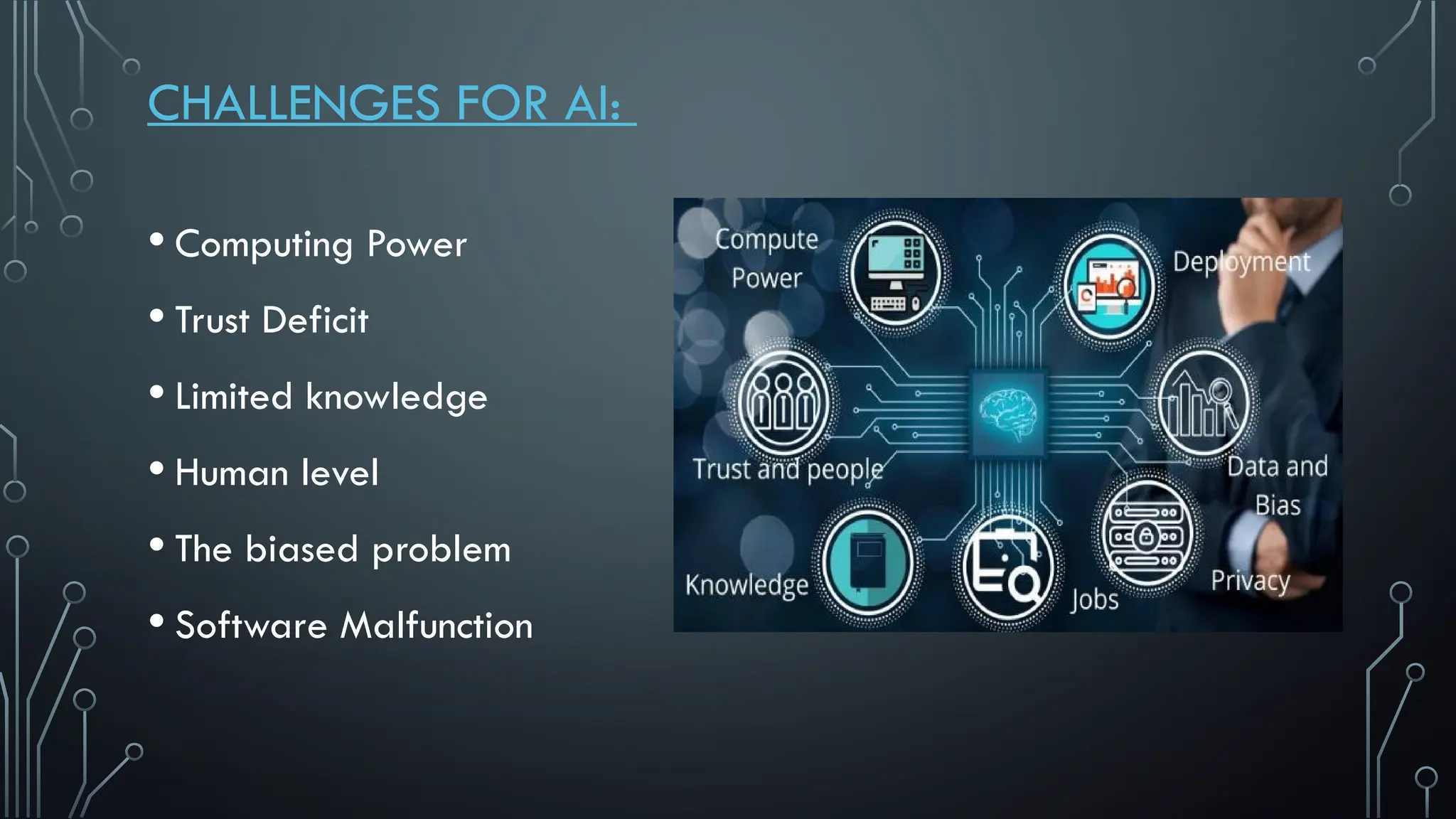
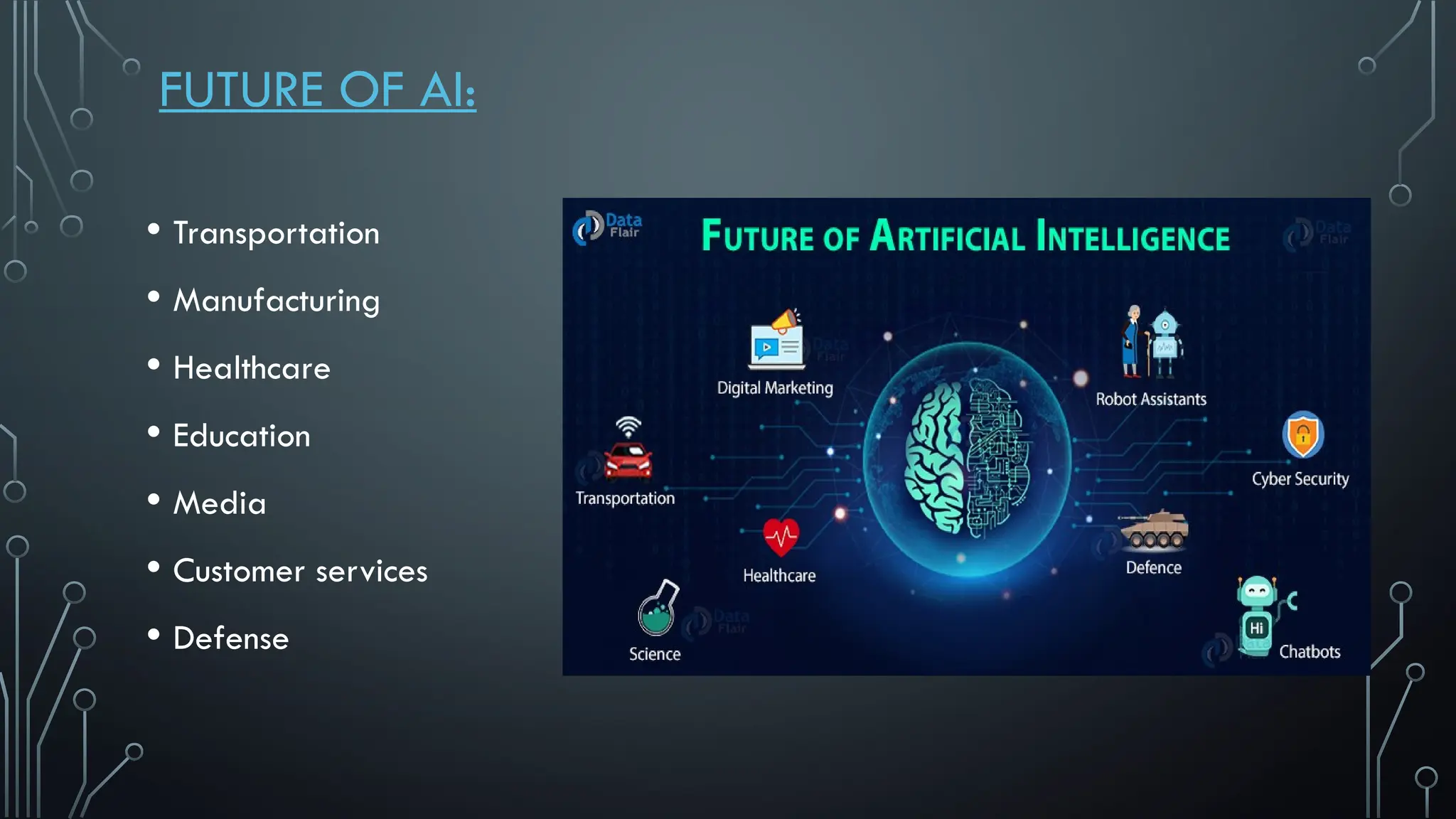
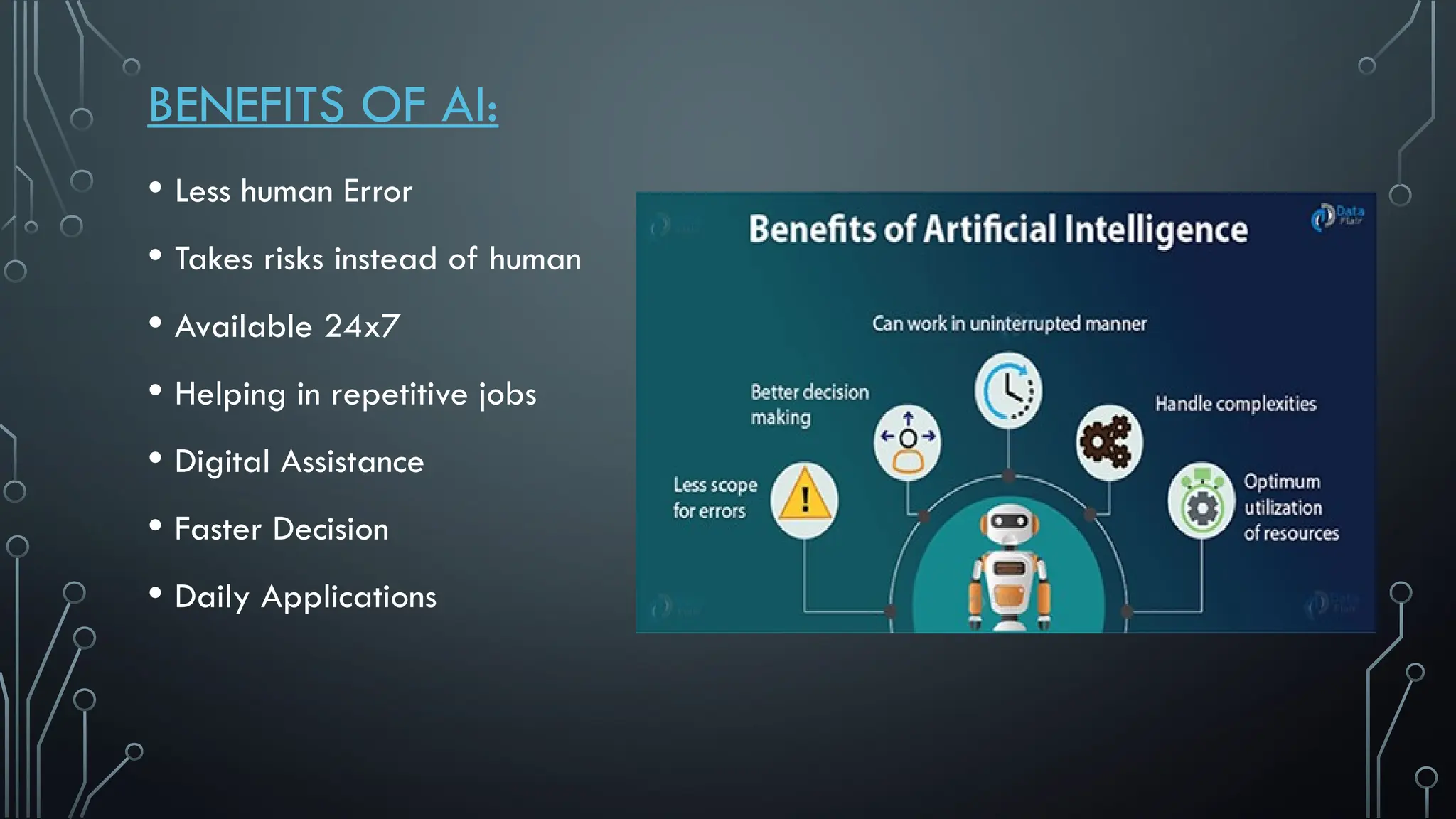
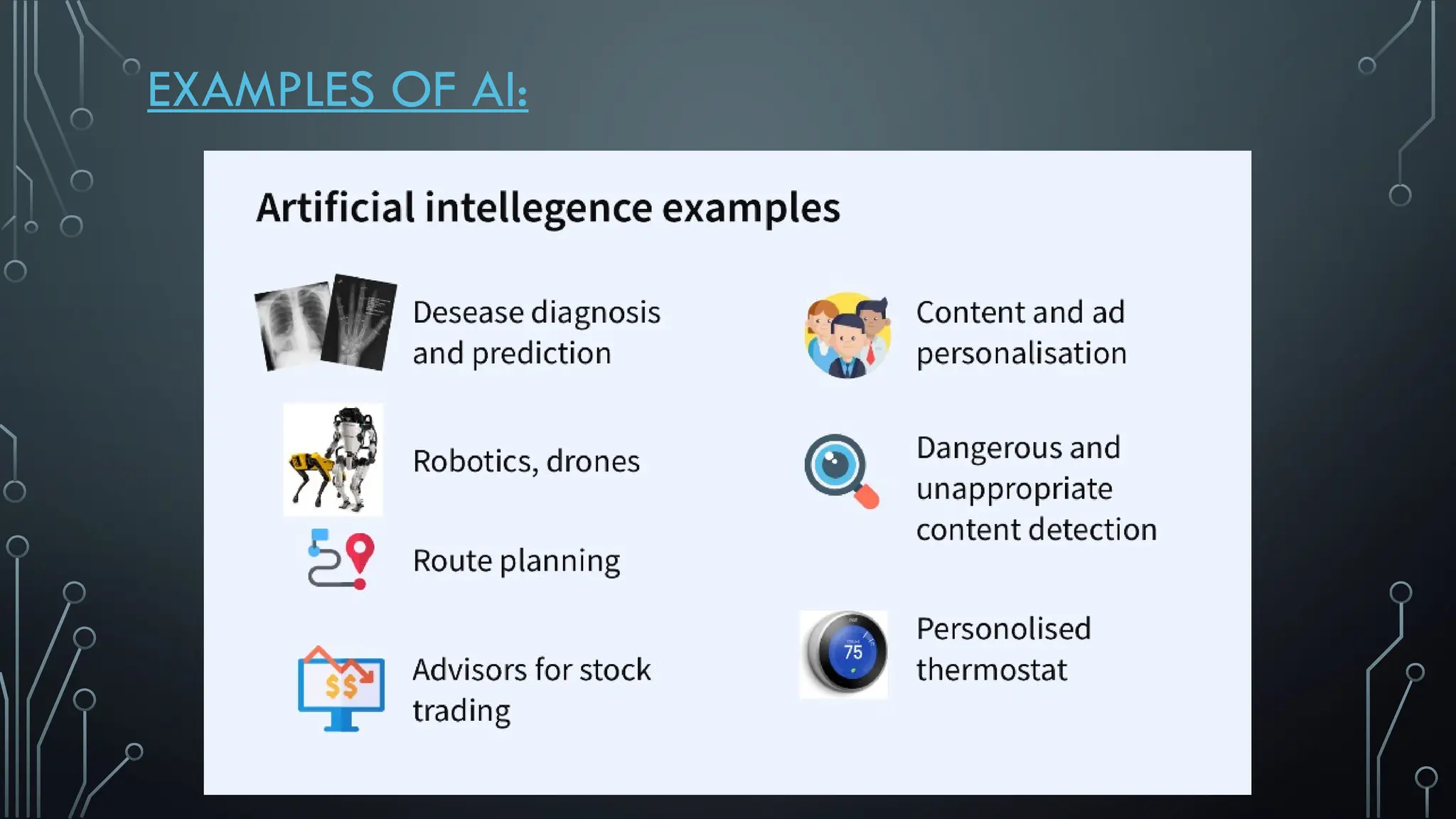
The document presents a comprehensive overview of artificial intelligence (AI), covering its definition, early history, types, workings, current status, challenges, future prospects, benefits, and global risks. It highlights the evolution of AI from theories posed by Alan Turing to its practical applications in various sectors. Despite potential dangers, the document concludes that AI's impact will largely depend on human usage, emphasizing its dual nature as a tool for both benefit and risk.