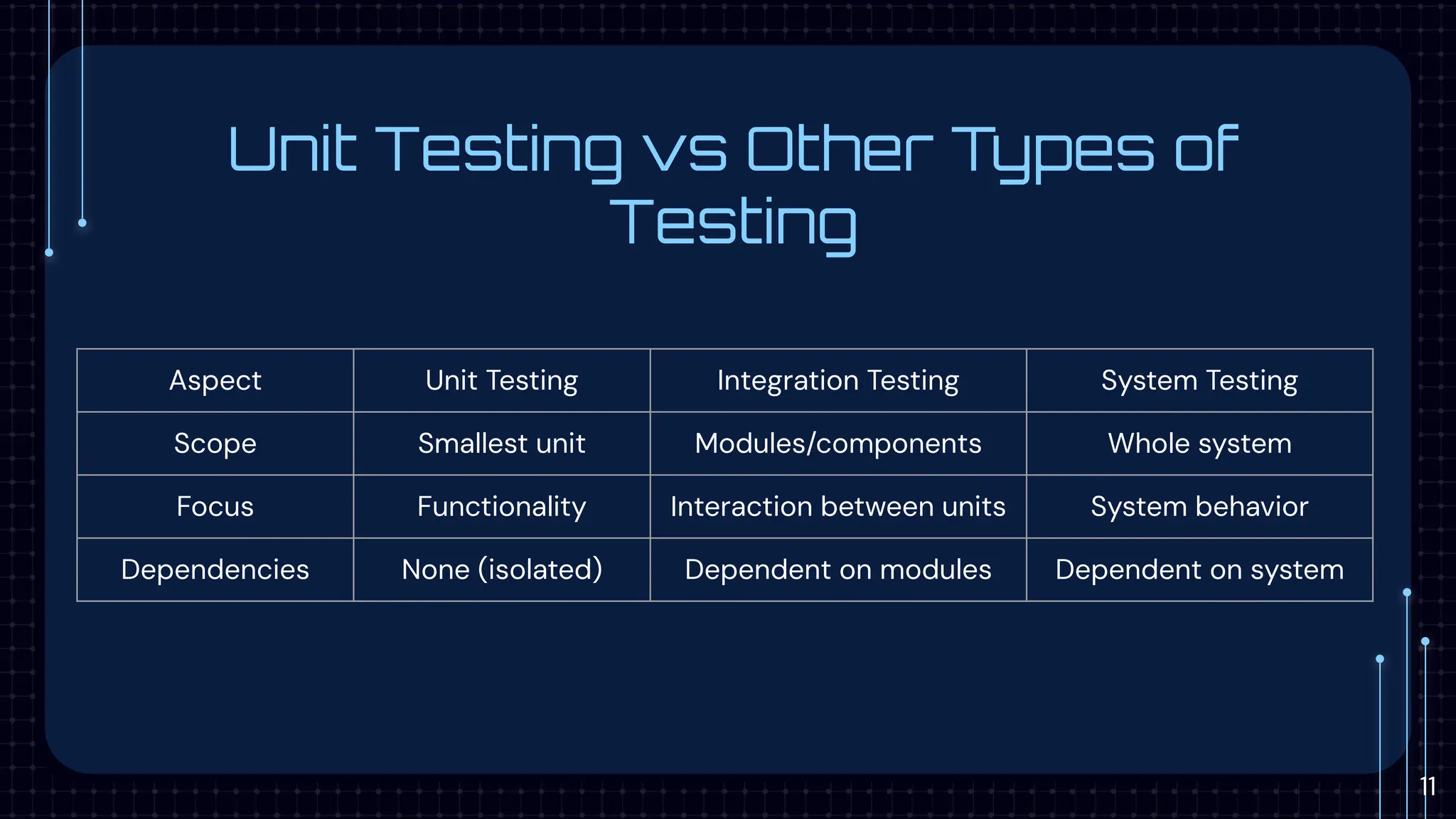
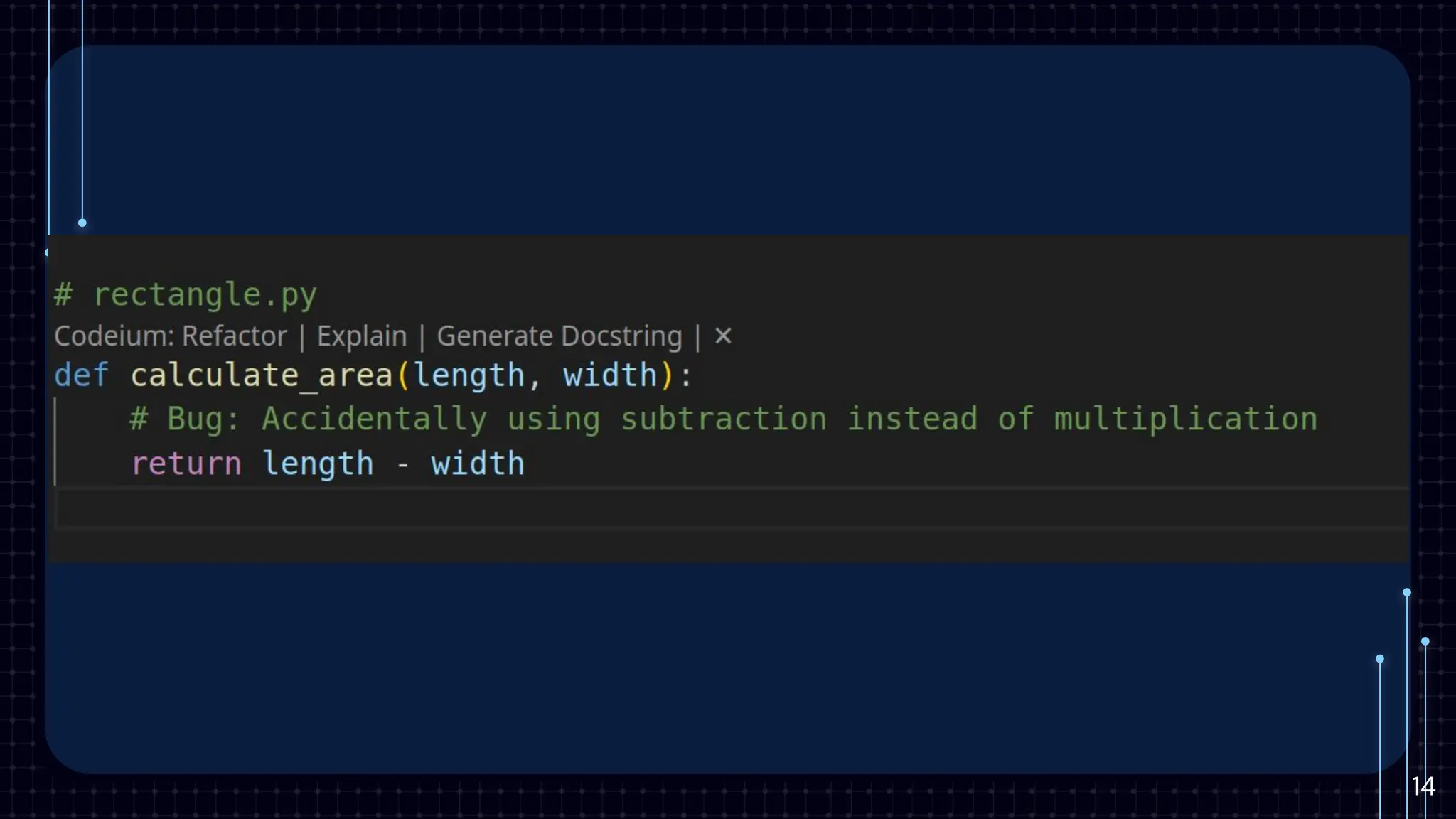
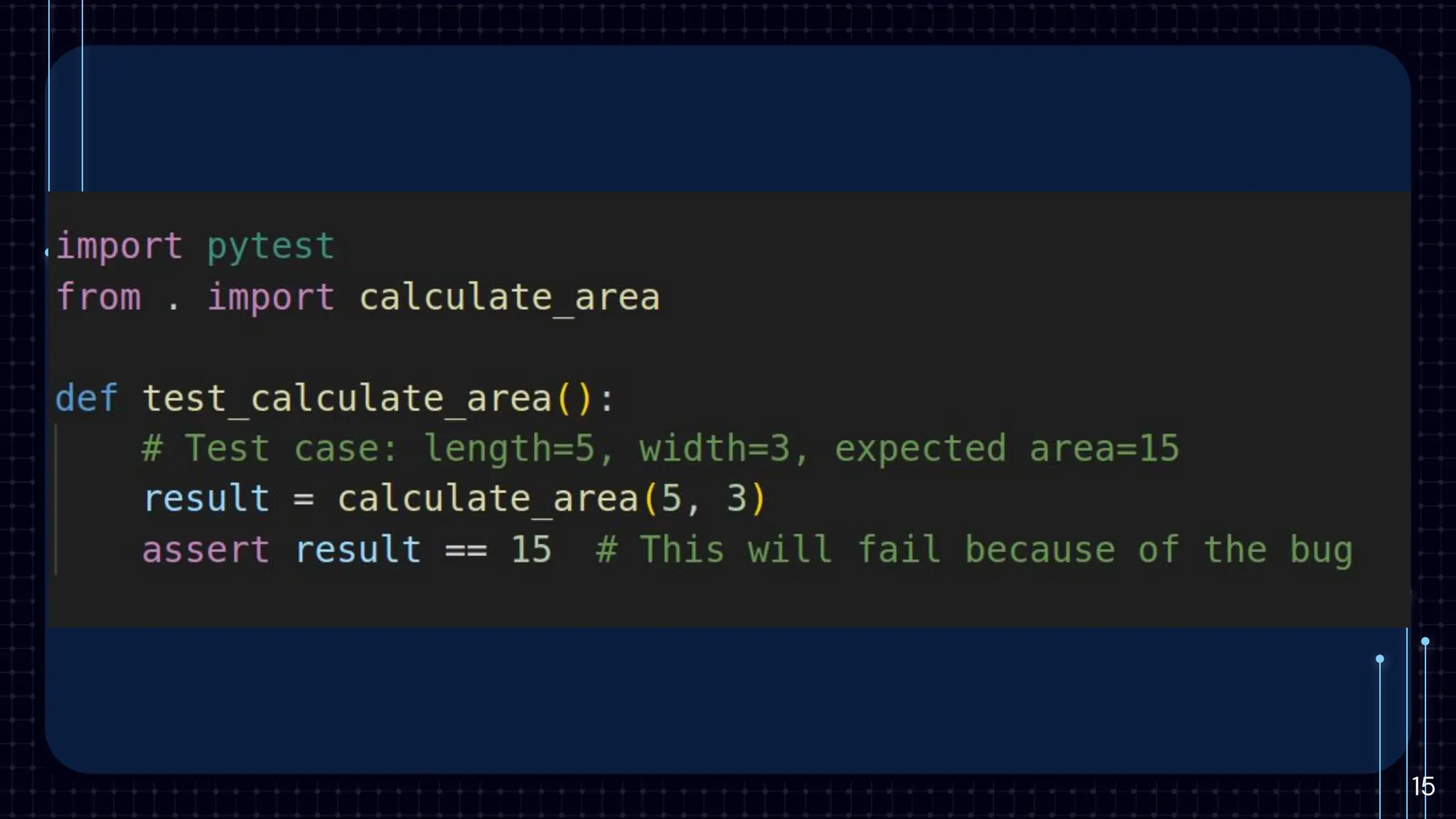
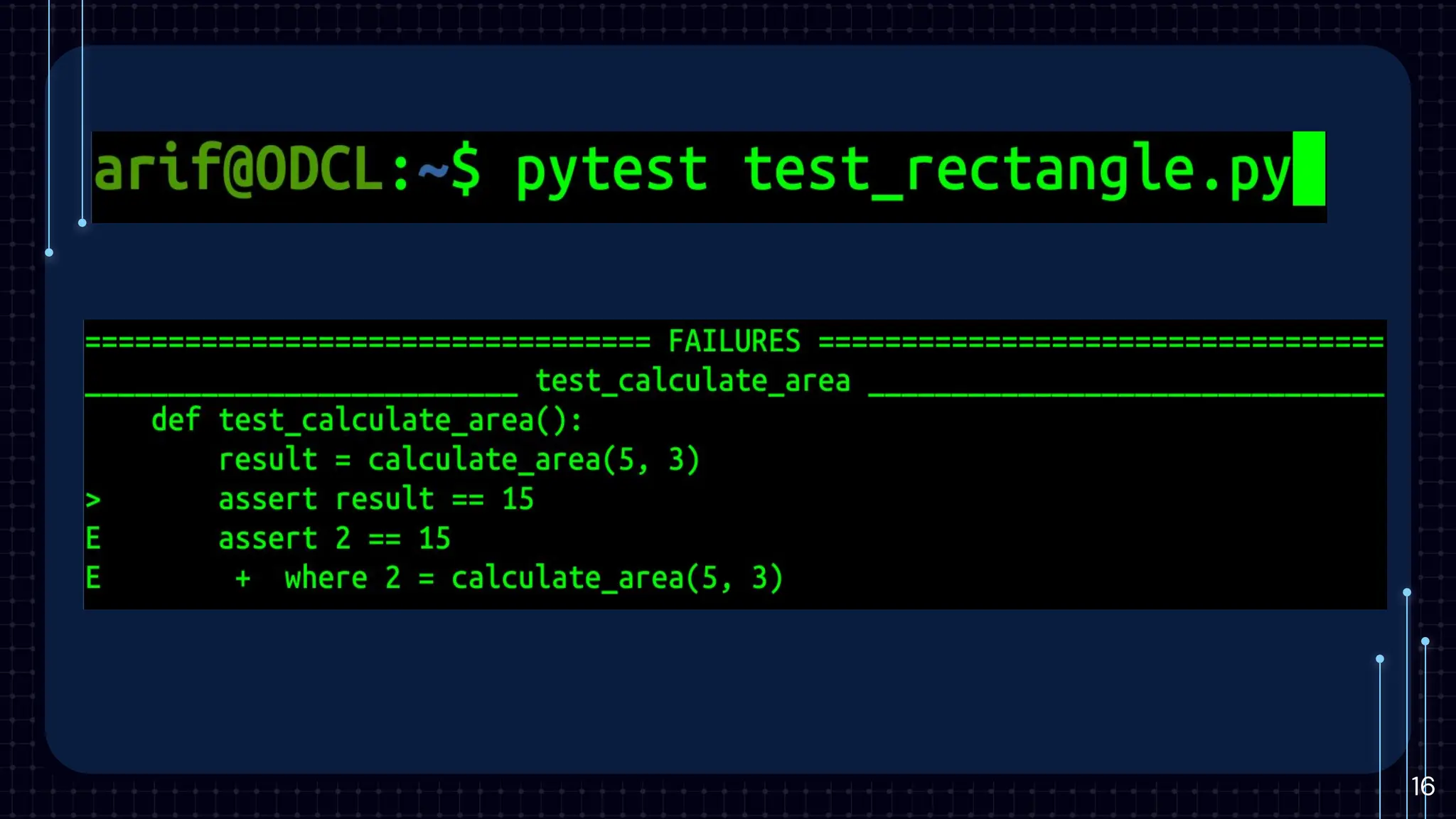
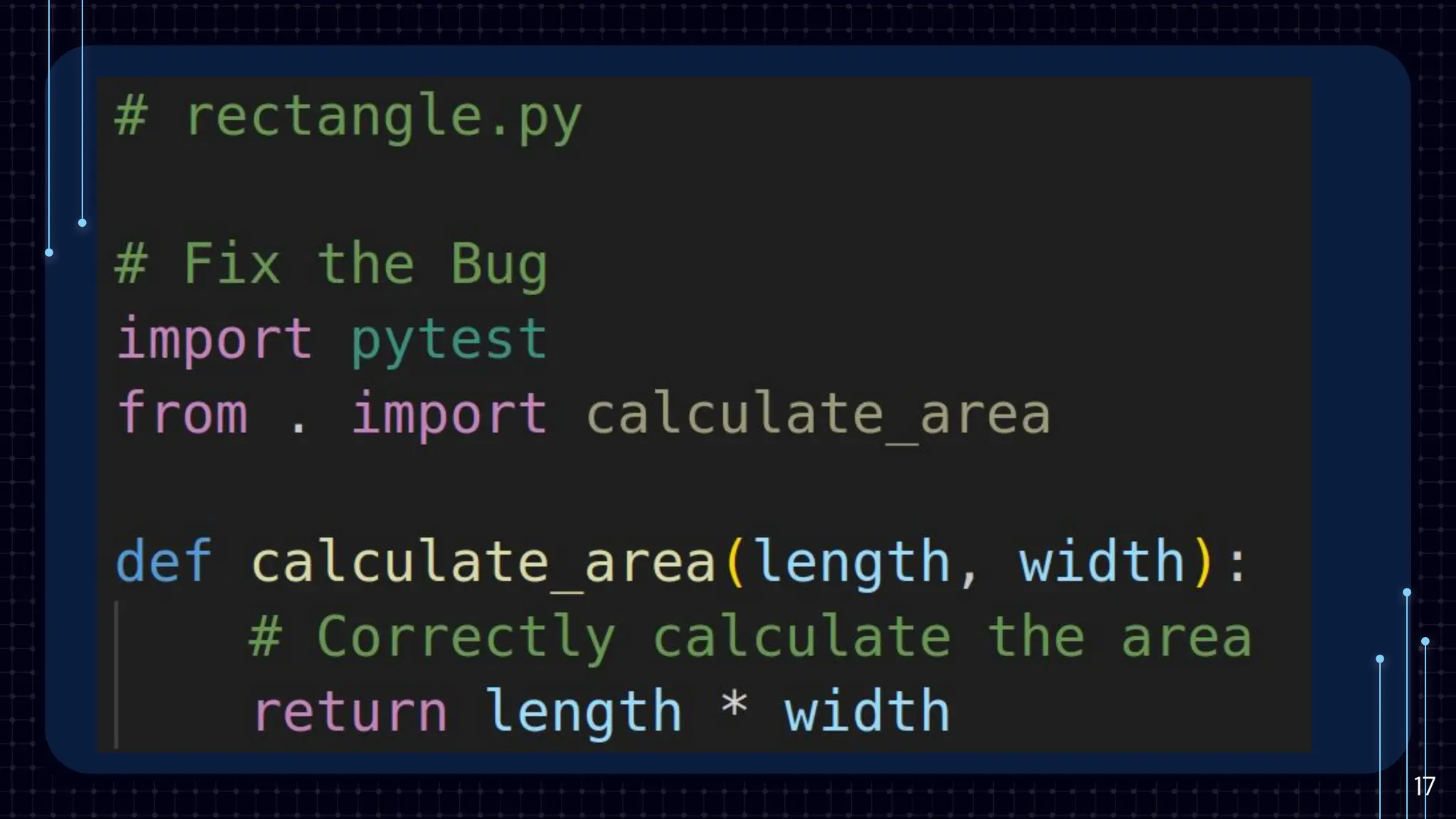
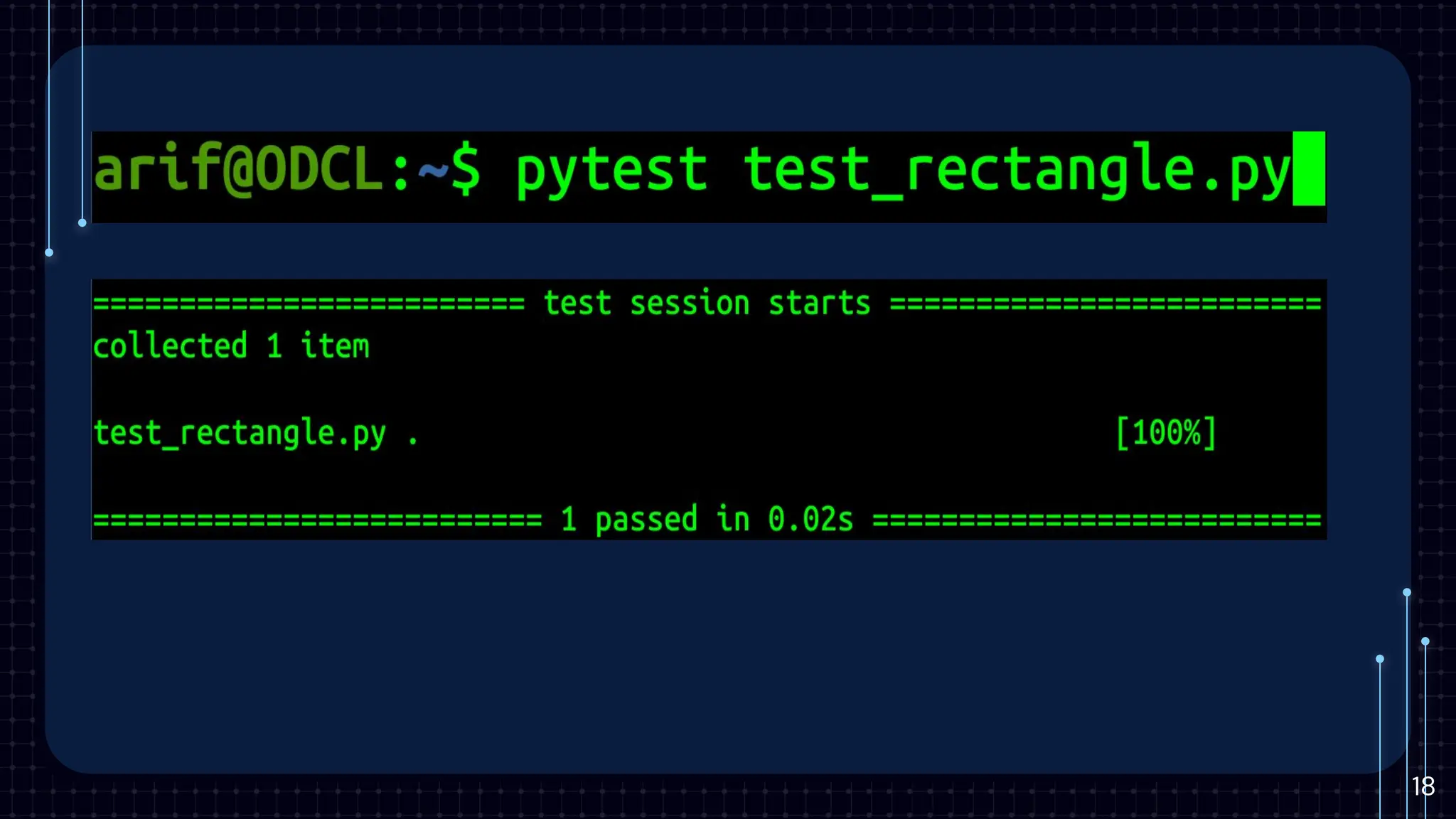
The document provides an introduction to unit testing, emphasizing its importance in enhancing code reliability and identifying bugs early. It covers key characteristics, best practices, common frameworks, and challenges associated with unit testing, alongside tools for measuring code coverage. Key takeaways highlight the benefits of unit tests in ensuring robust and maintainable code within the development workflow.