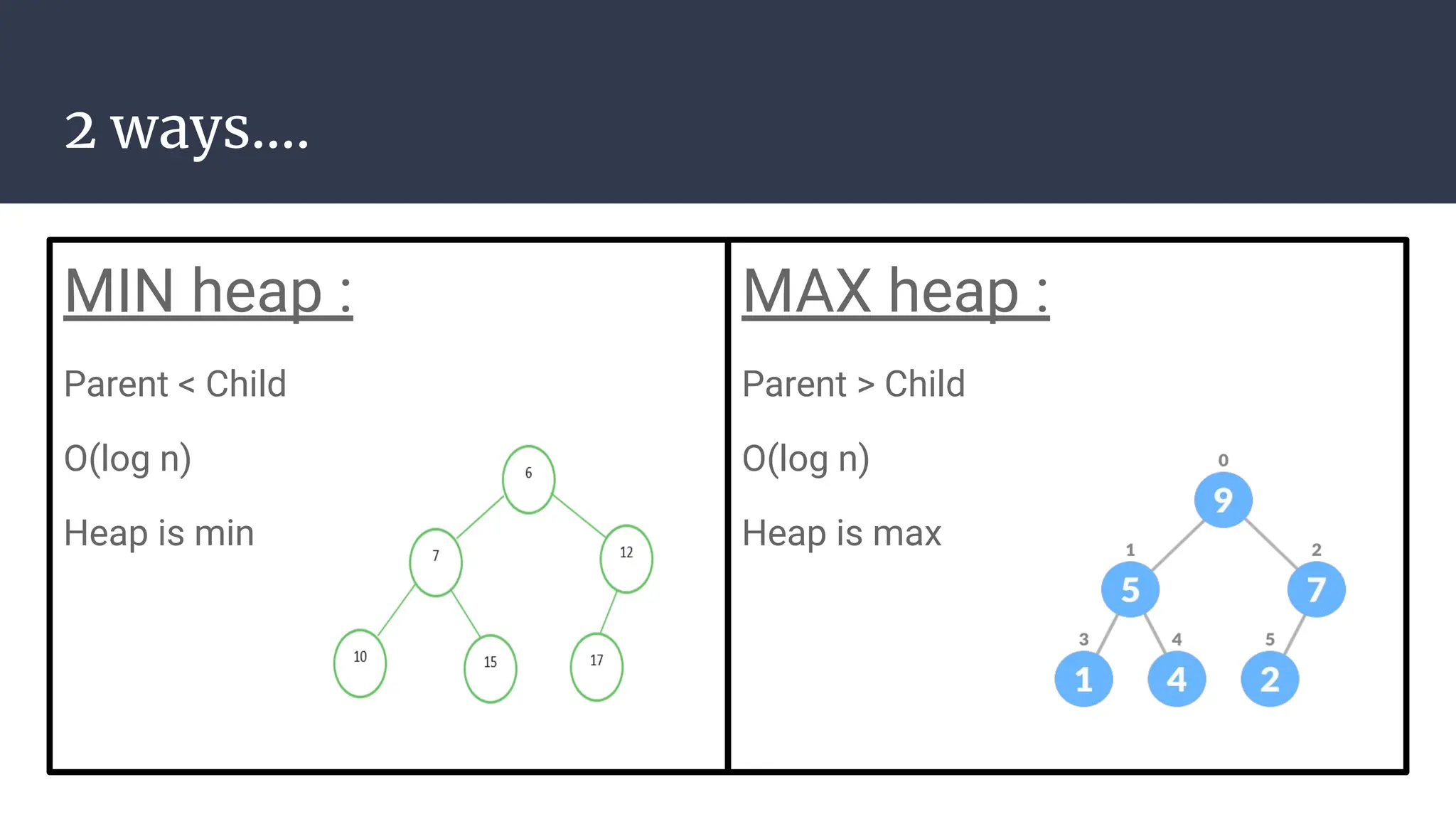
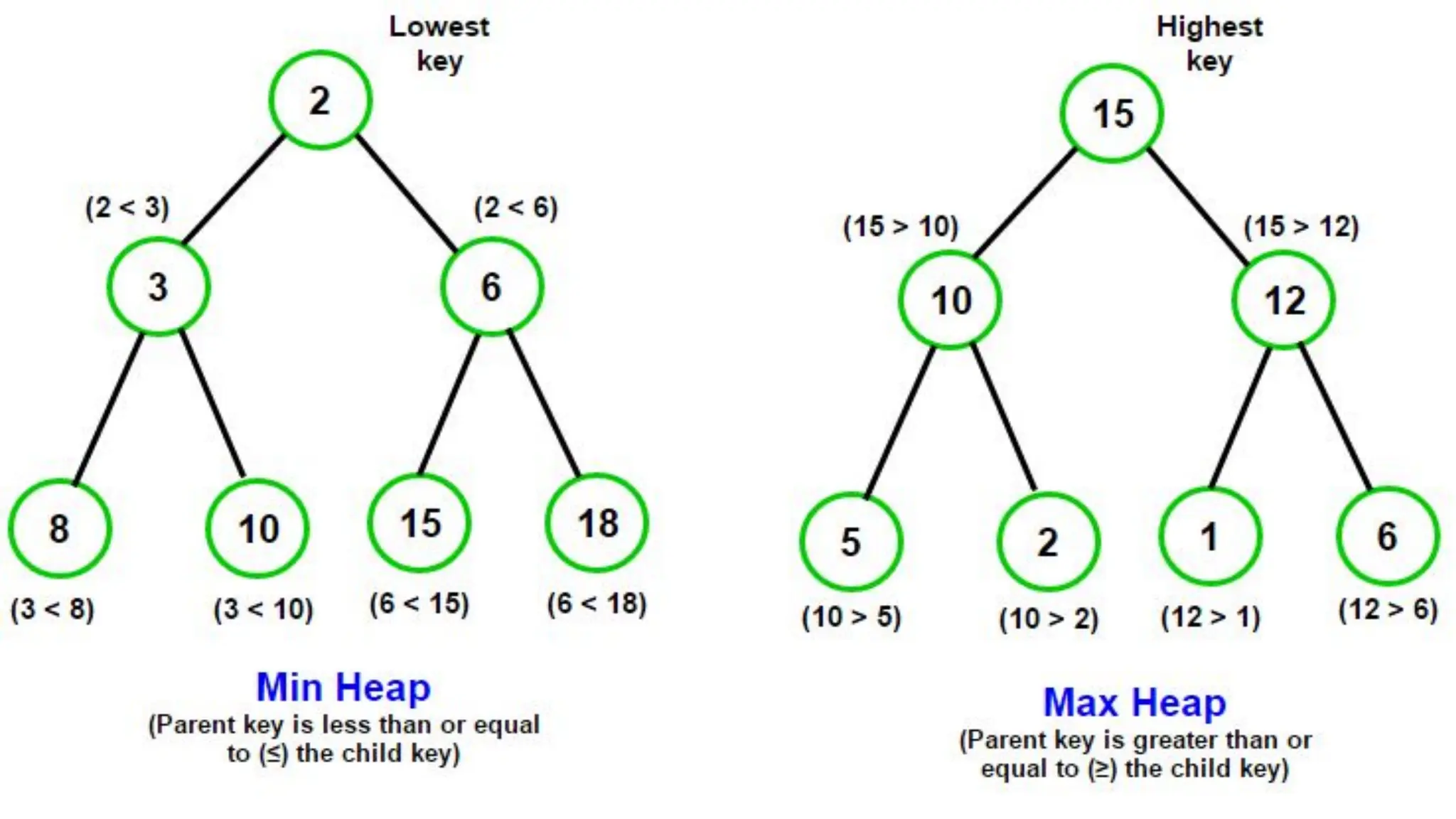
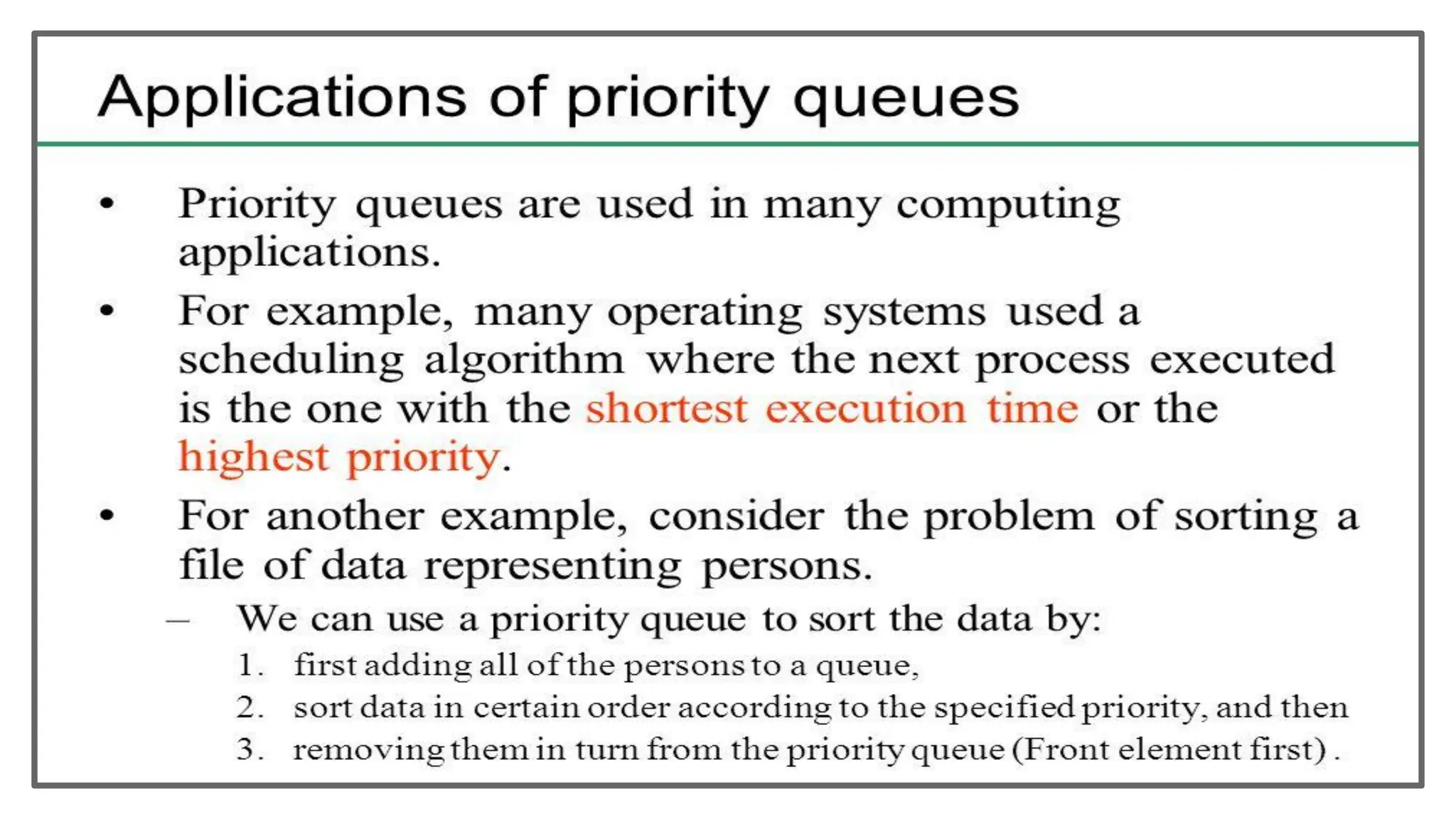
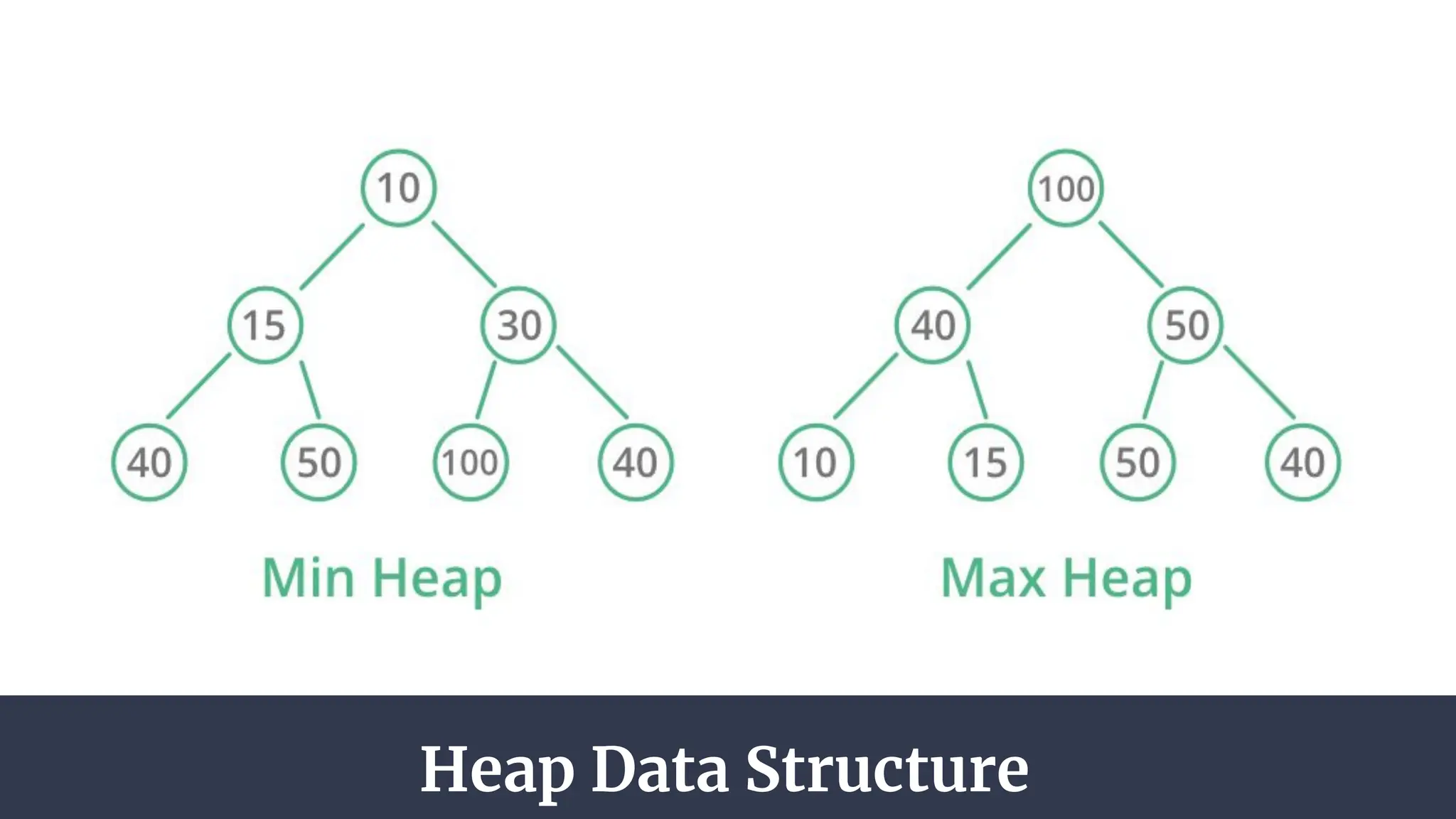
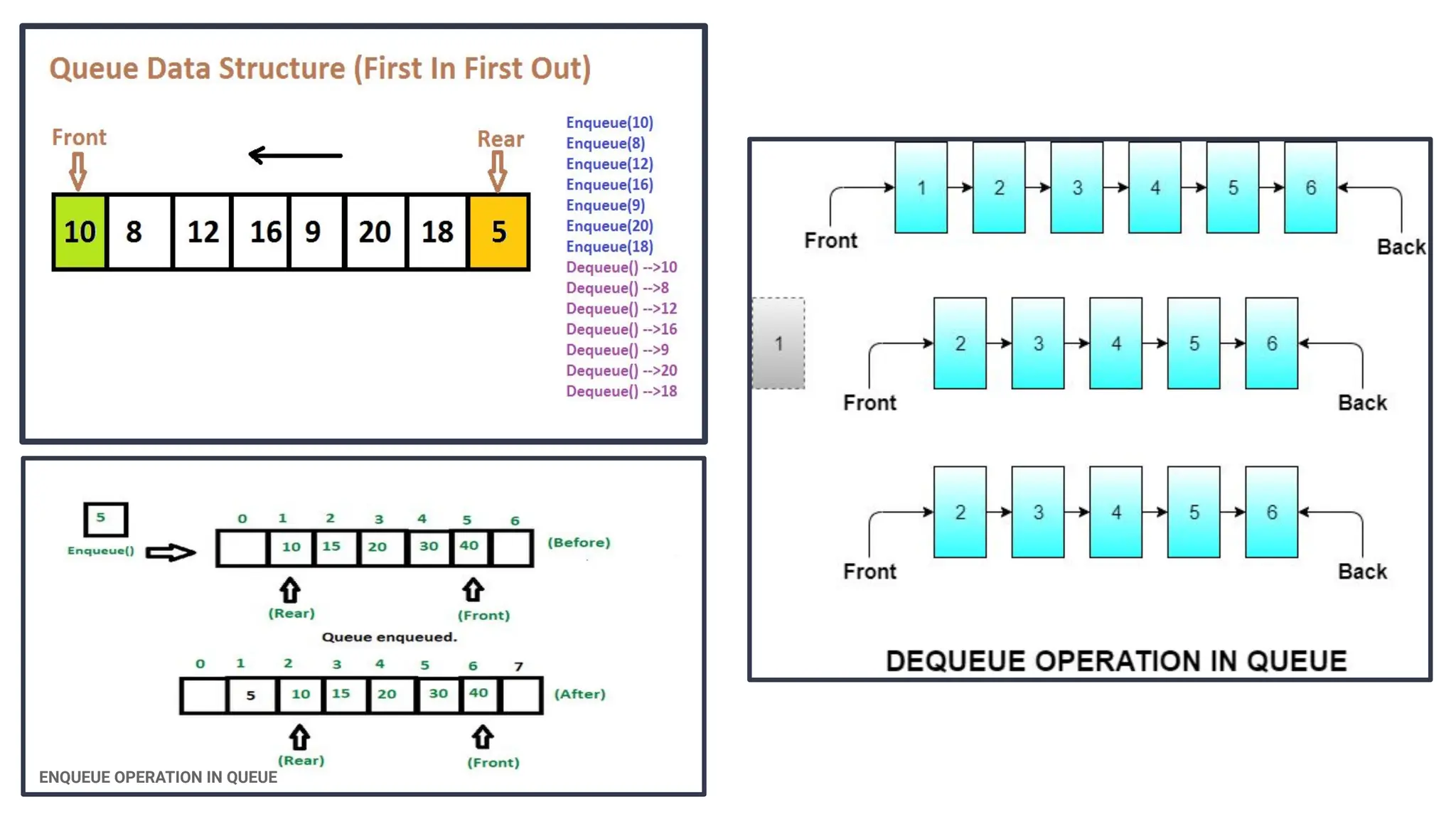
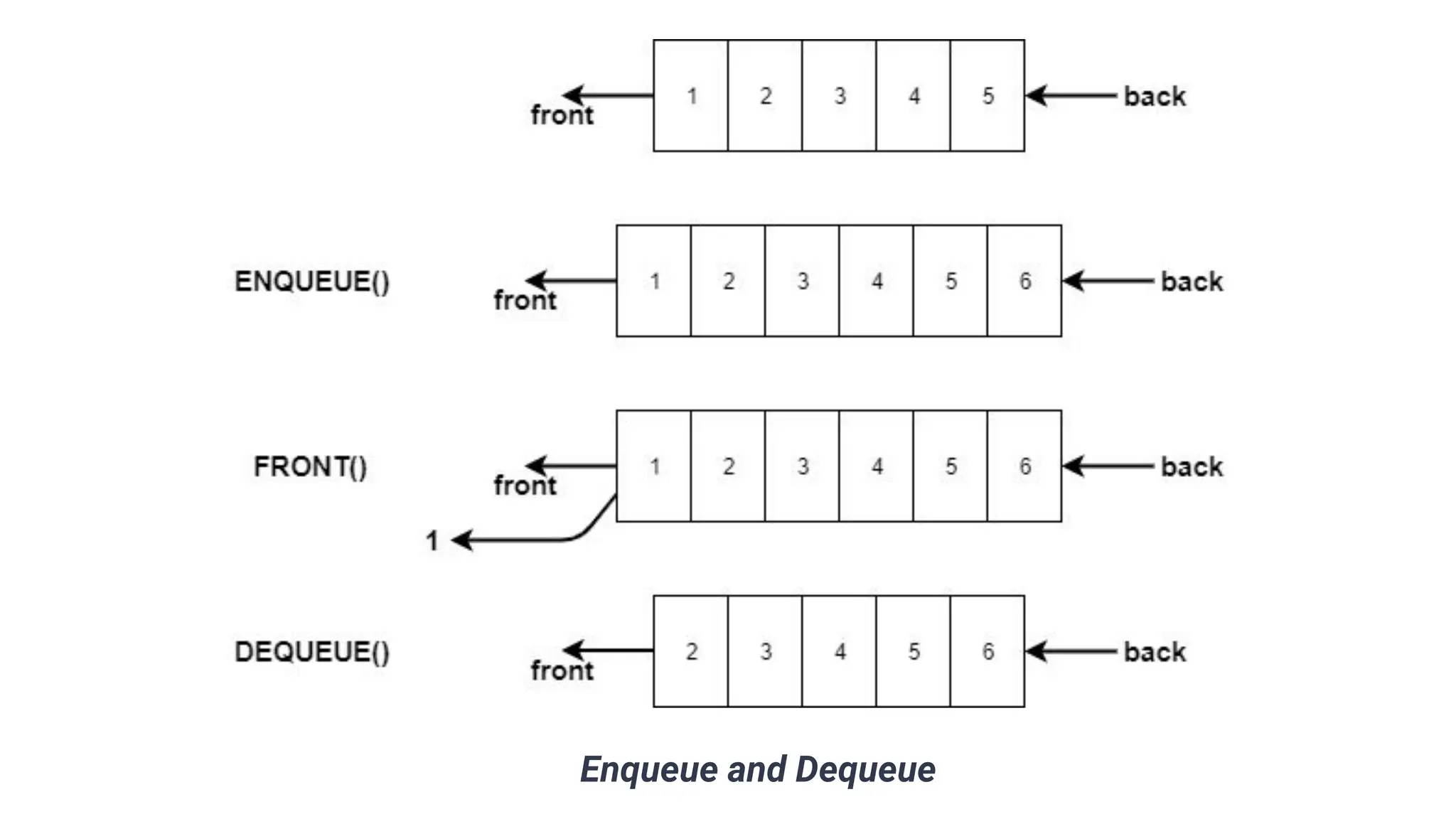
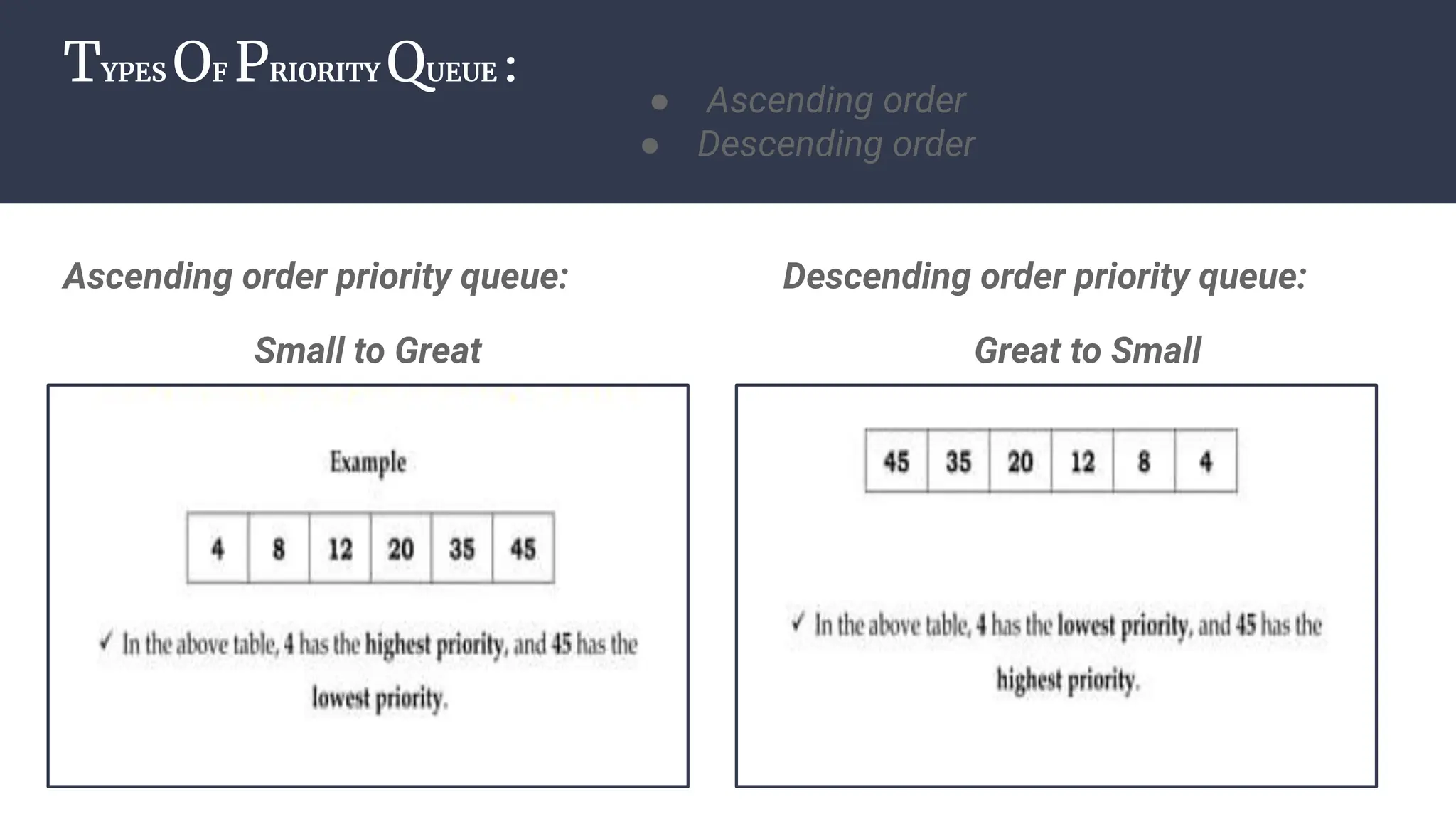
The document discusses priority queues implemented using heaps, distinguishing between min heaps and max heaps based on the priority of elements. It outlines basic operators for heap operations such as enqueue, dequeue, peek, isfull, and isempty, and specifies how elements are prioritized for deletion. The document also highlights the structure of heaps and the order of queues as either ascending or descending.