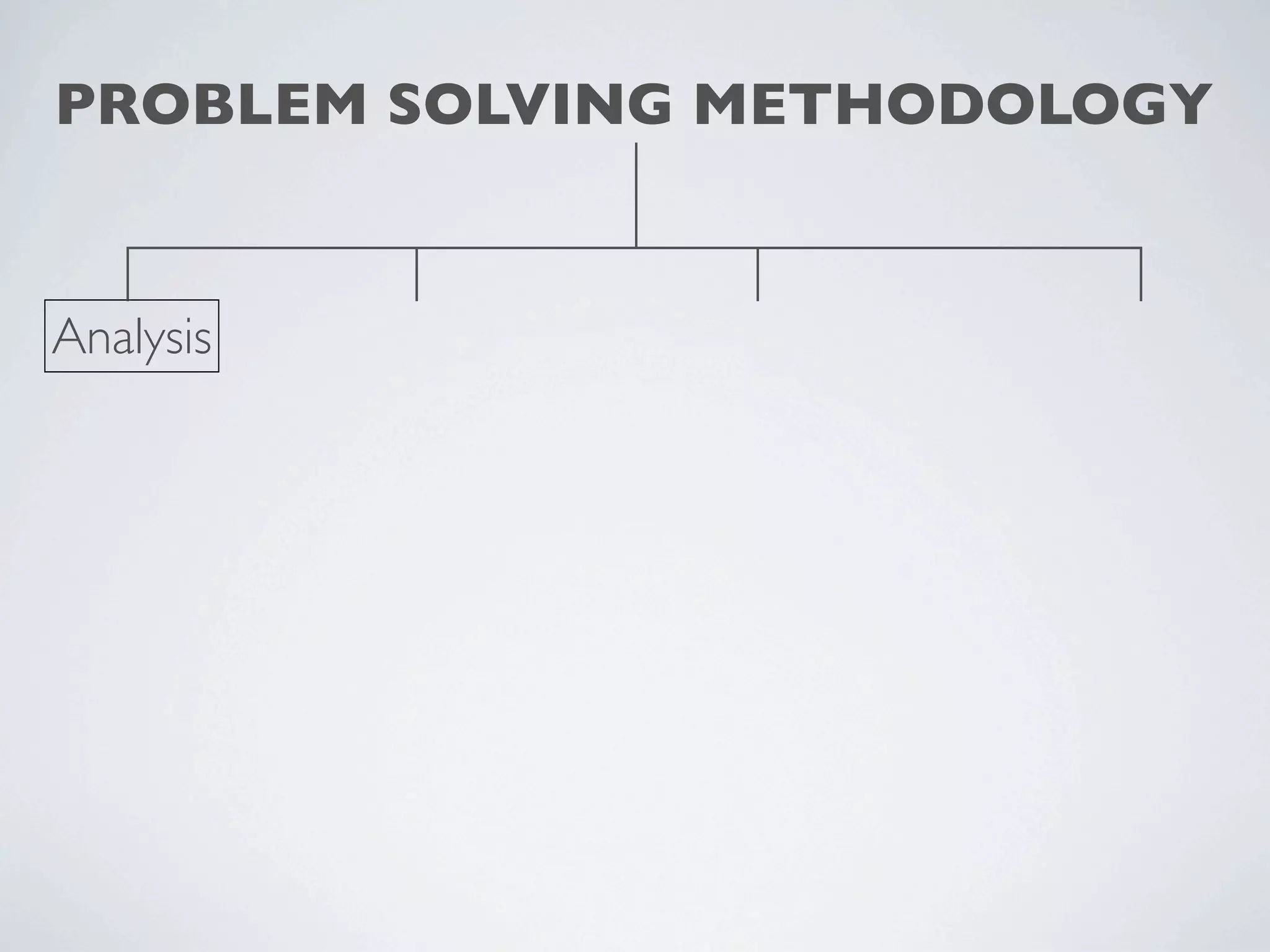
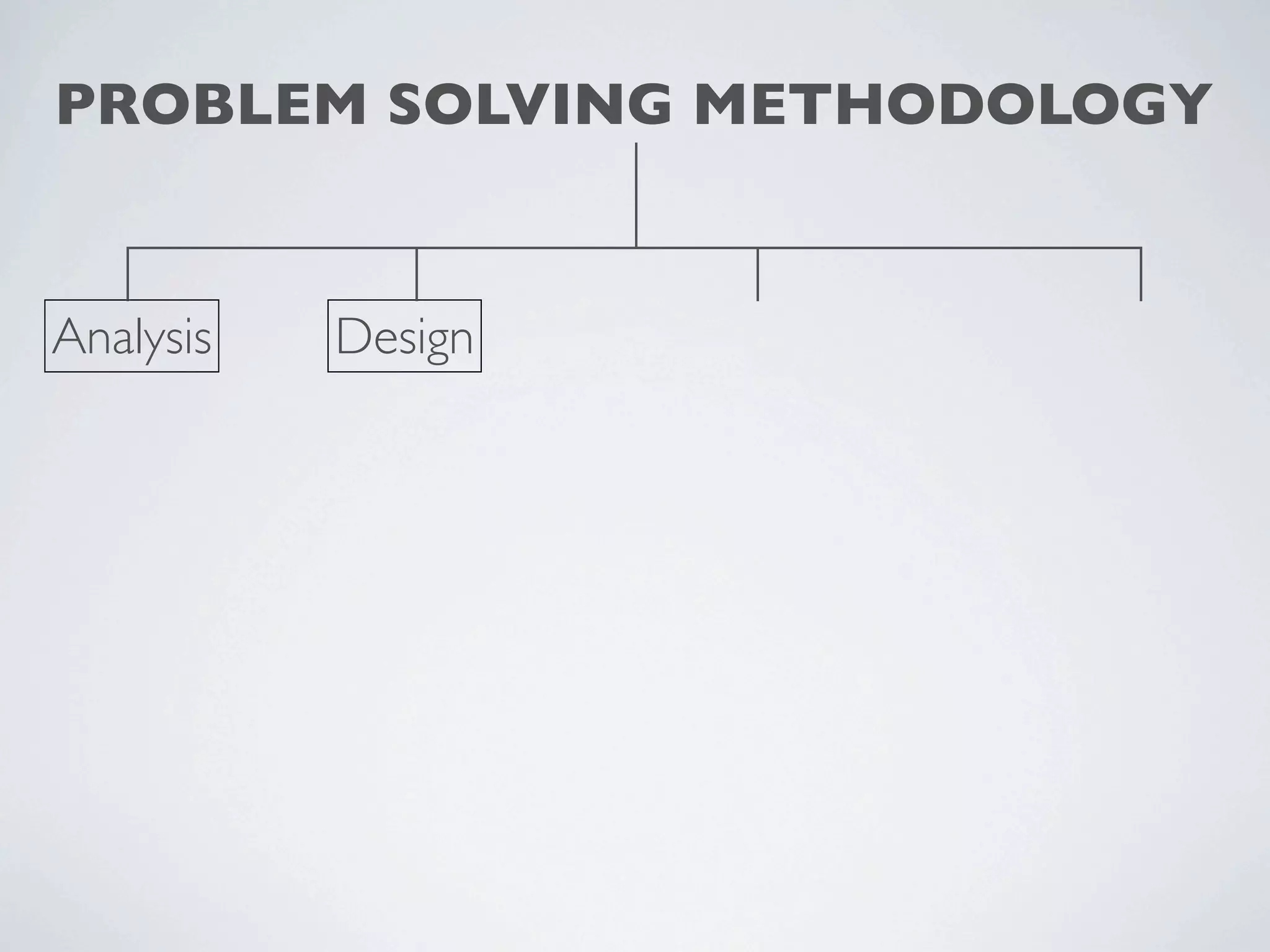
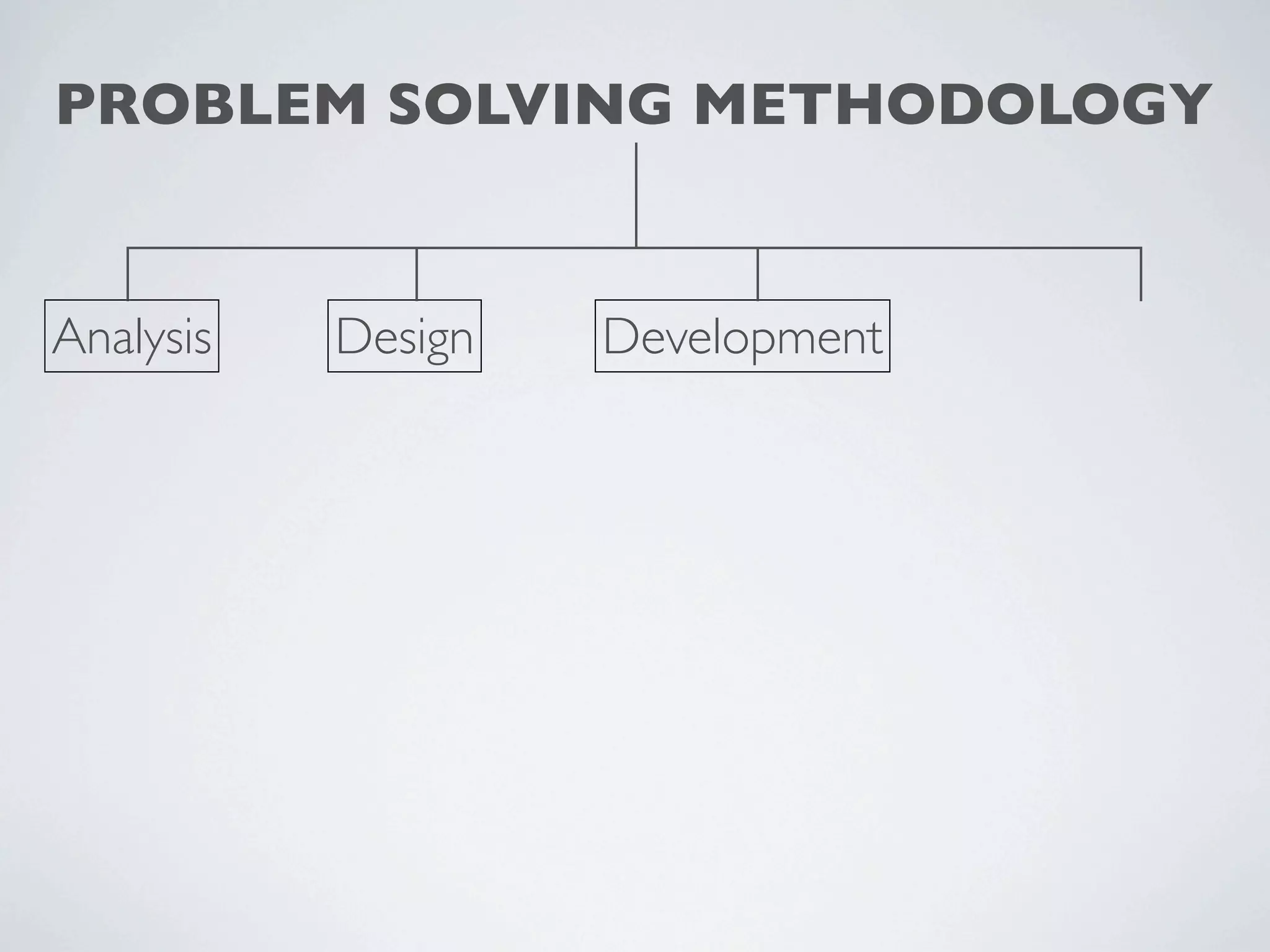
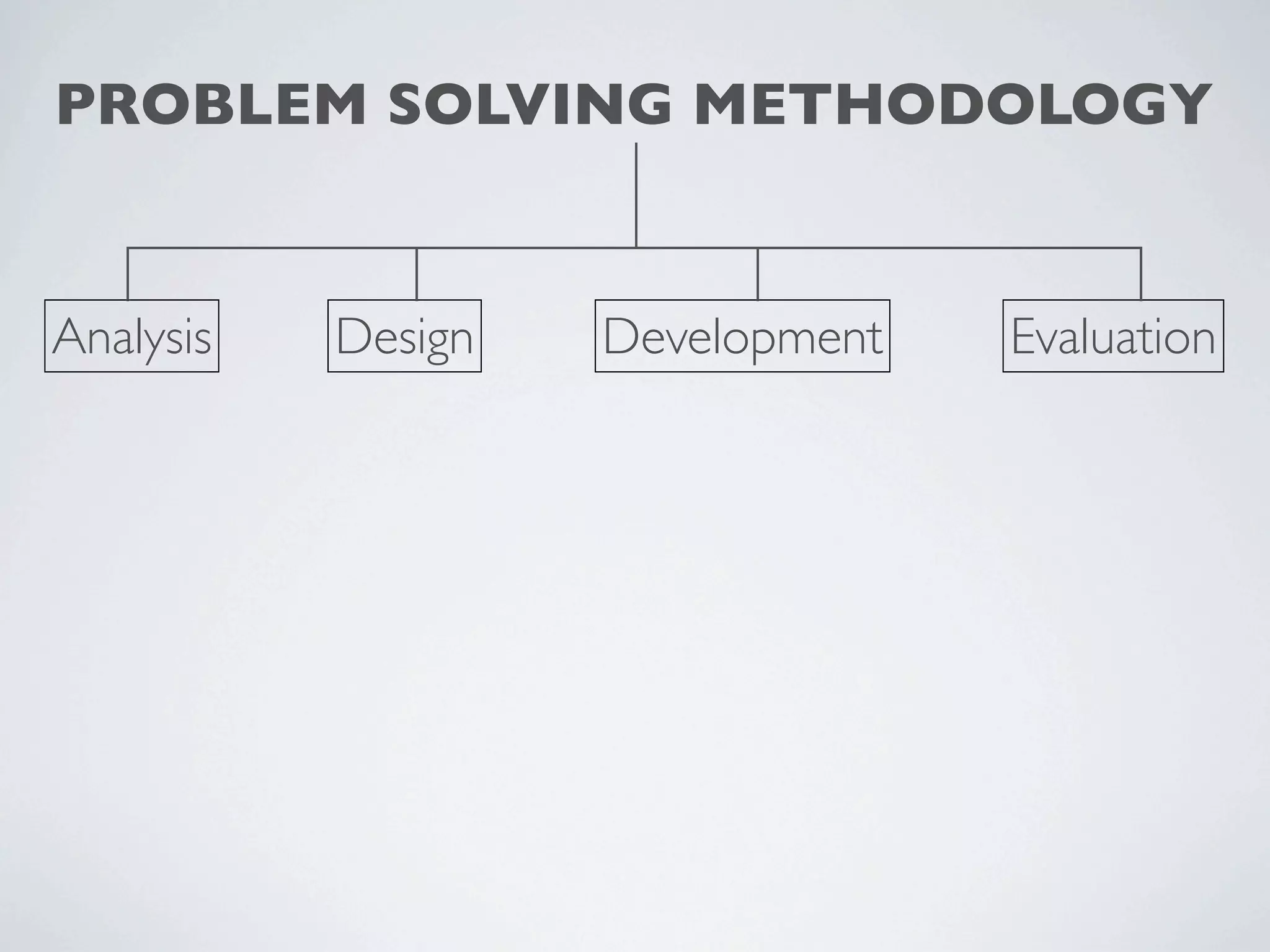
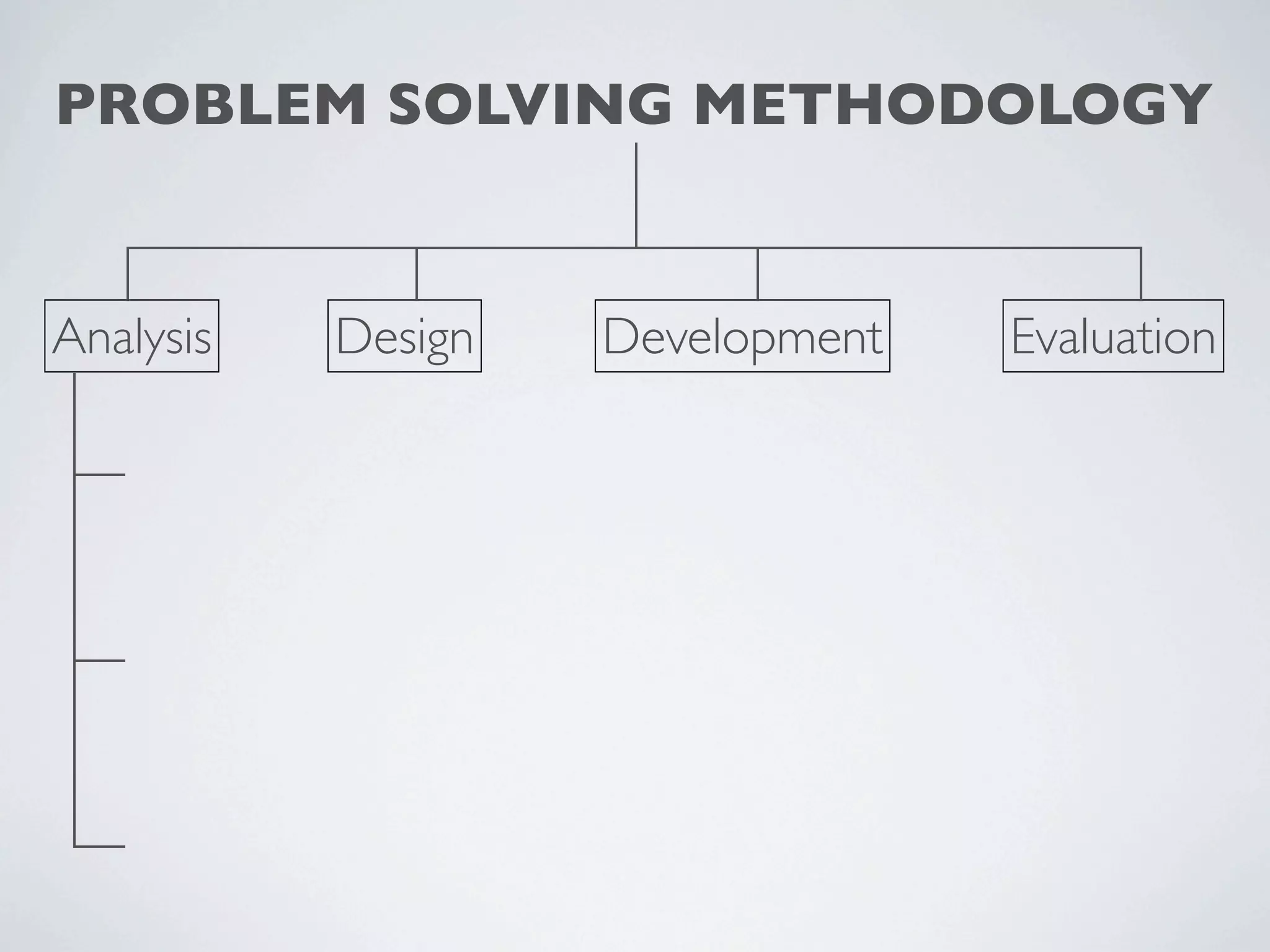
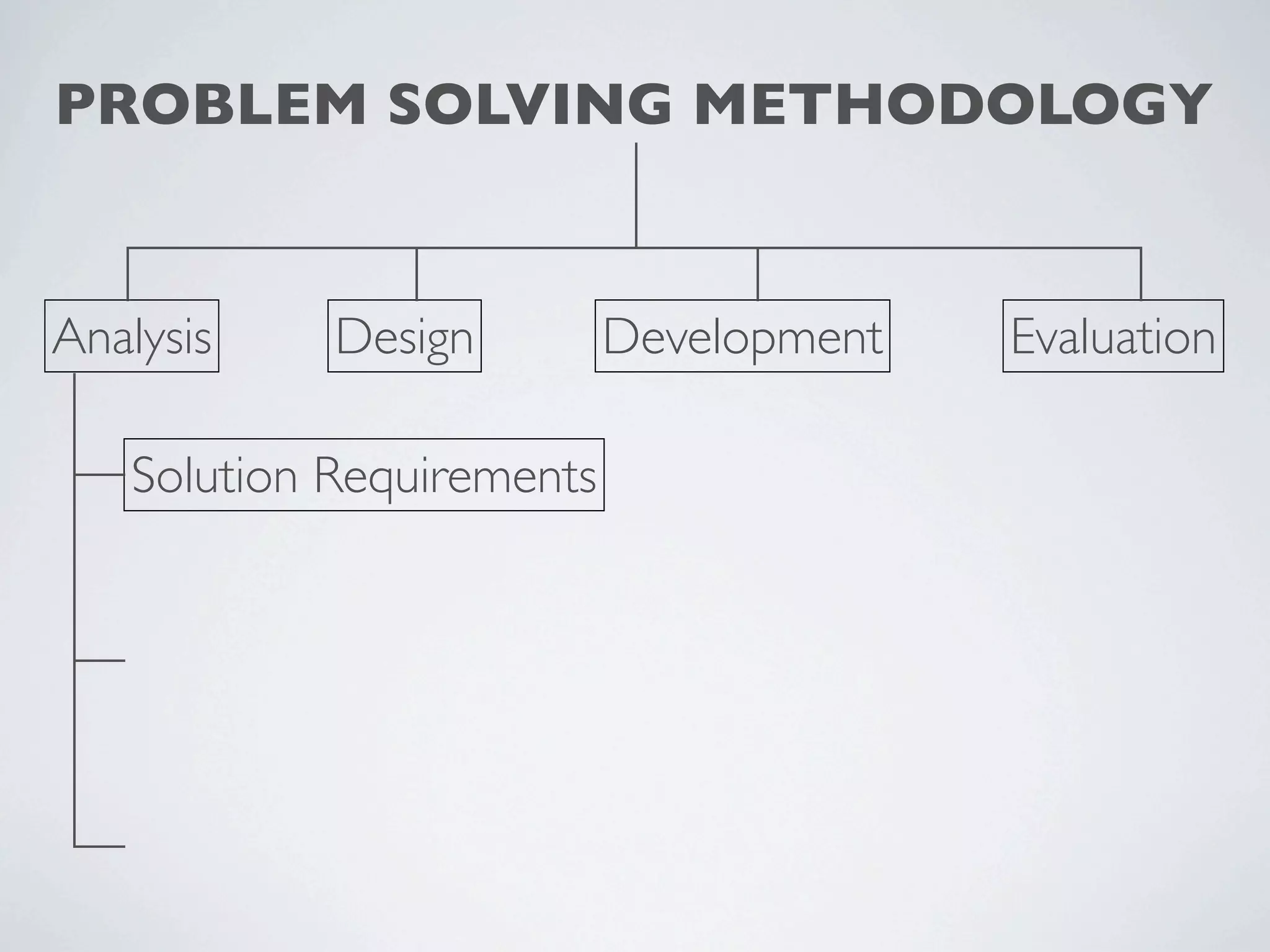
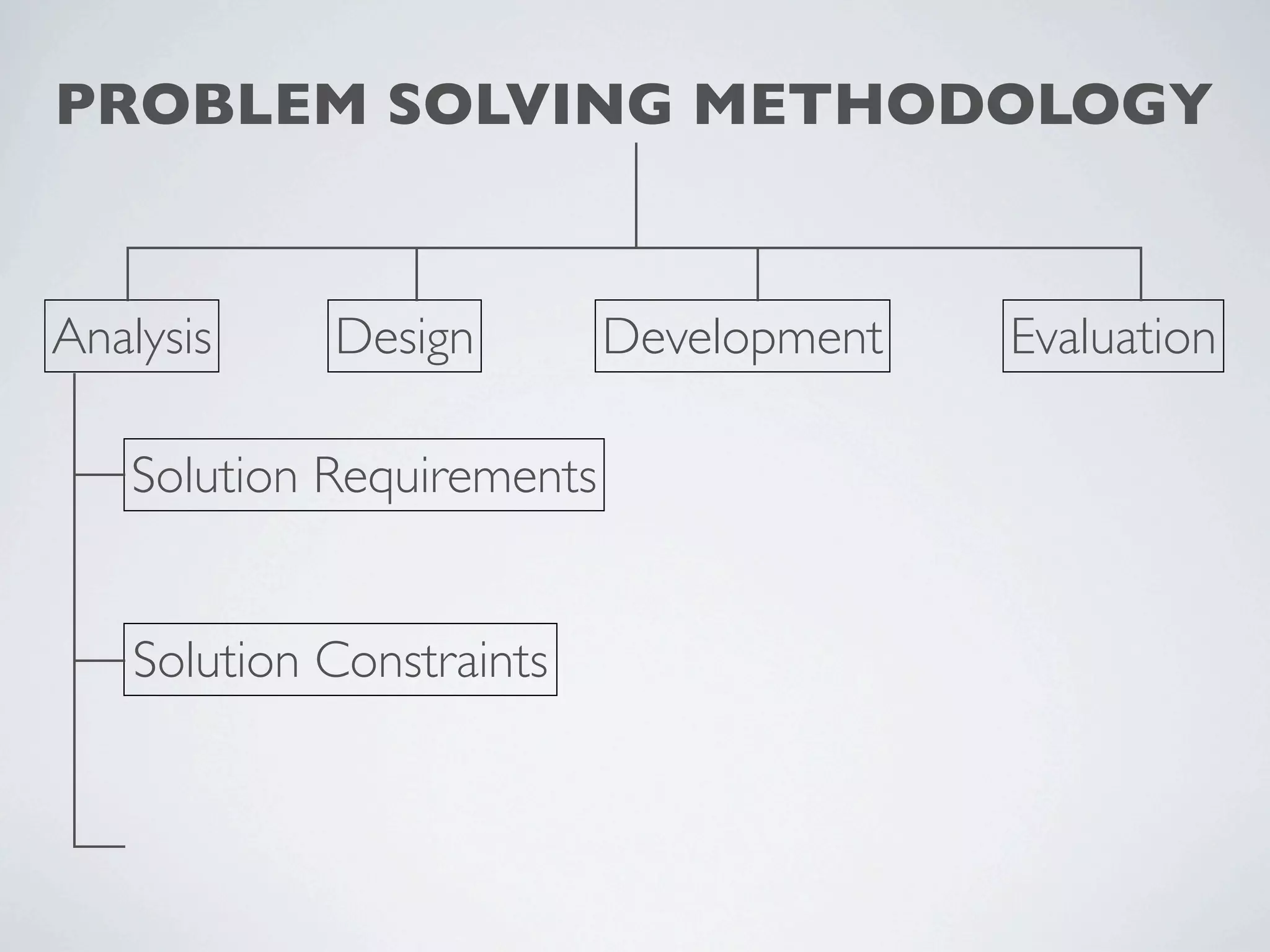
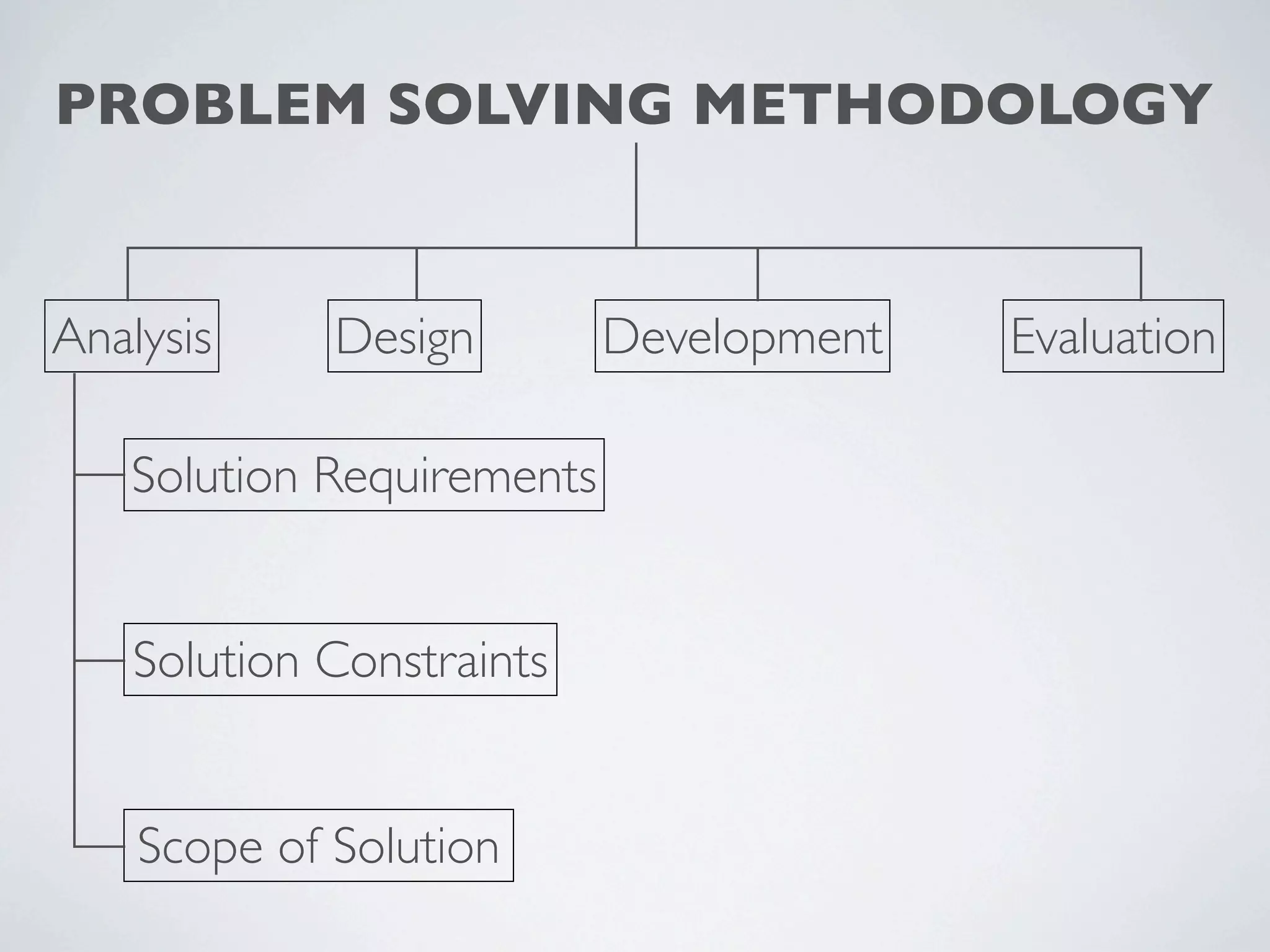
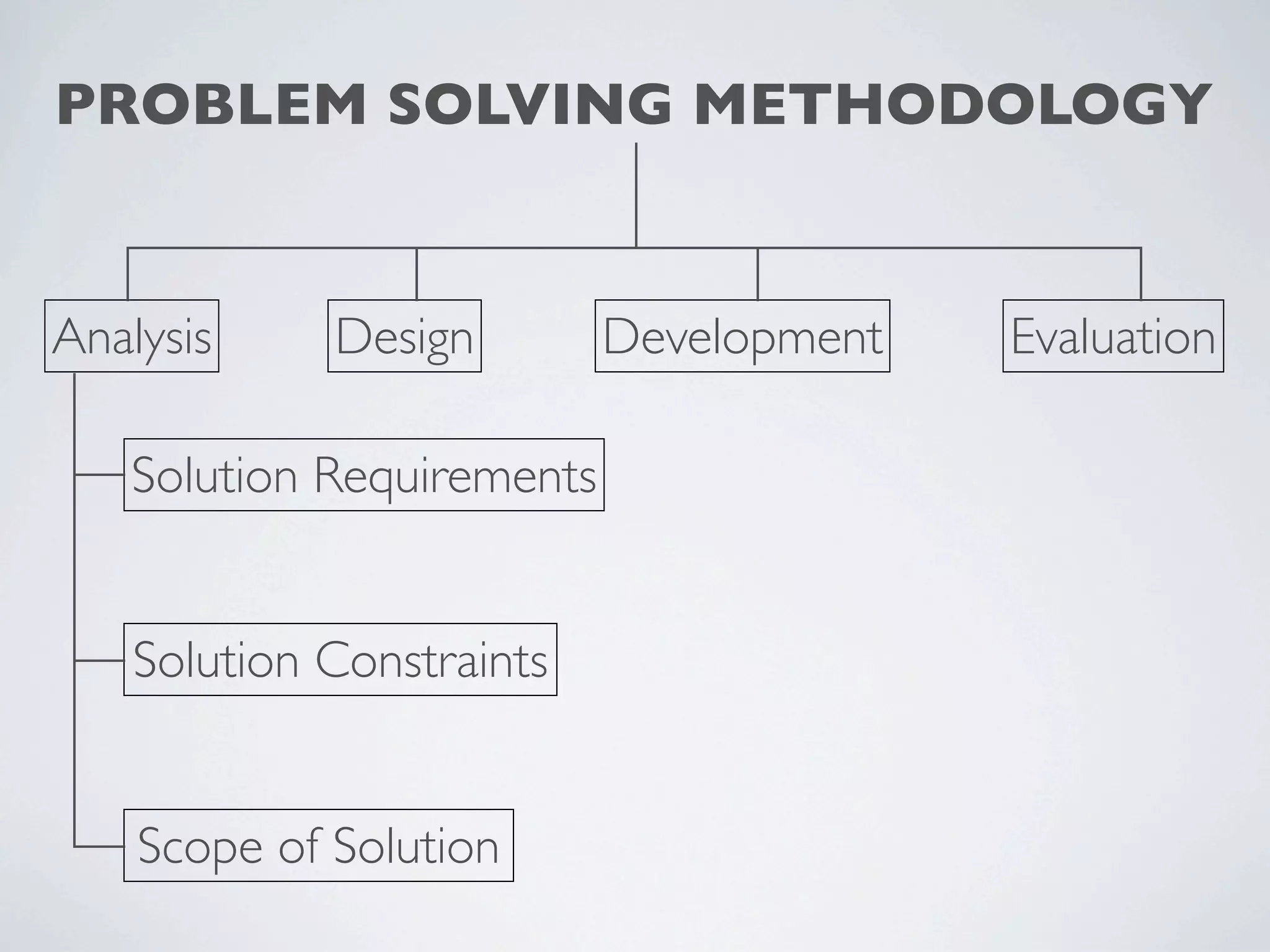
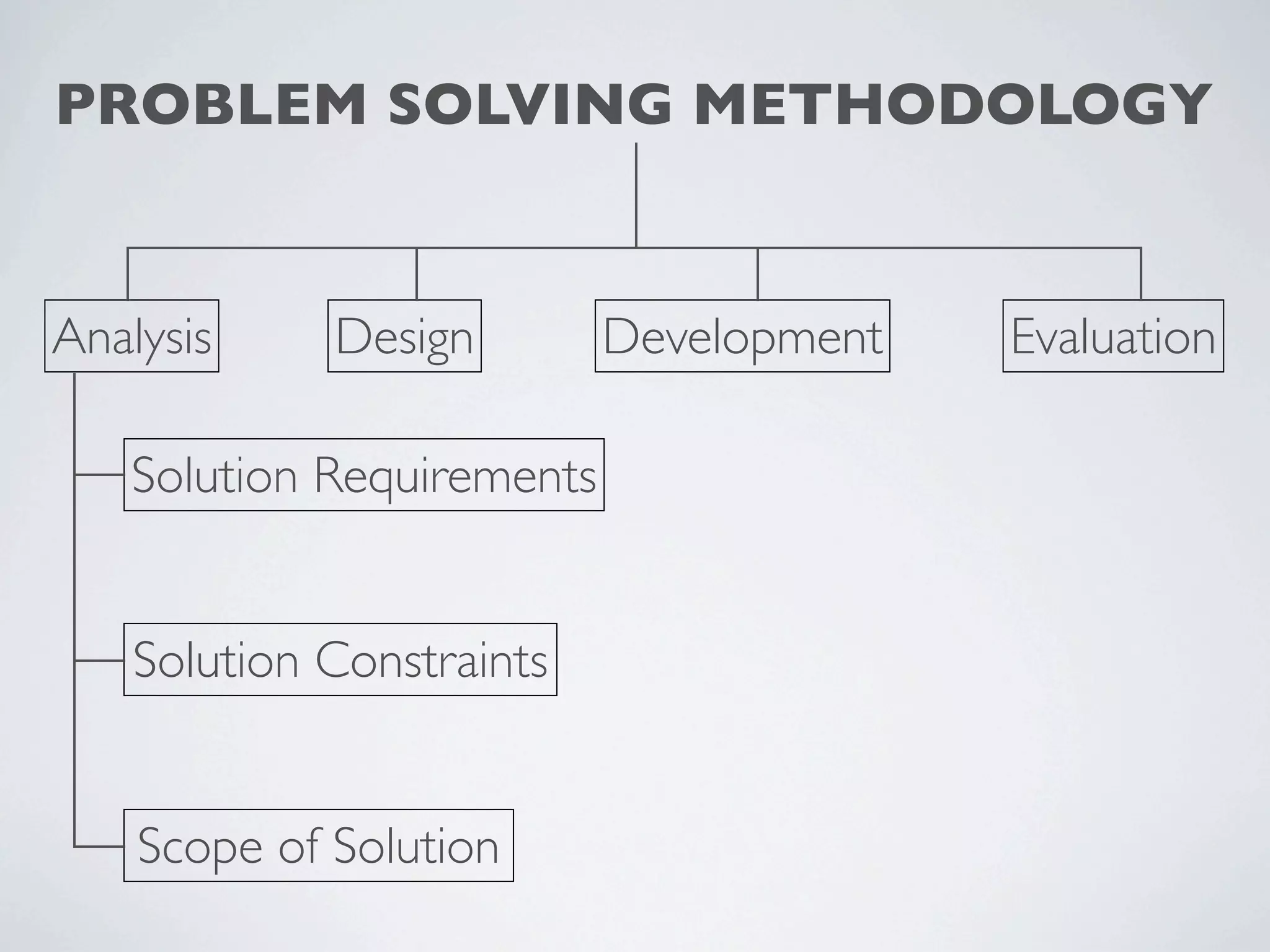
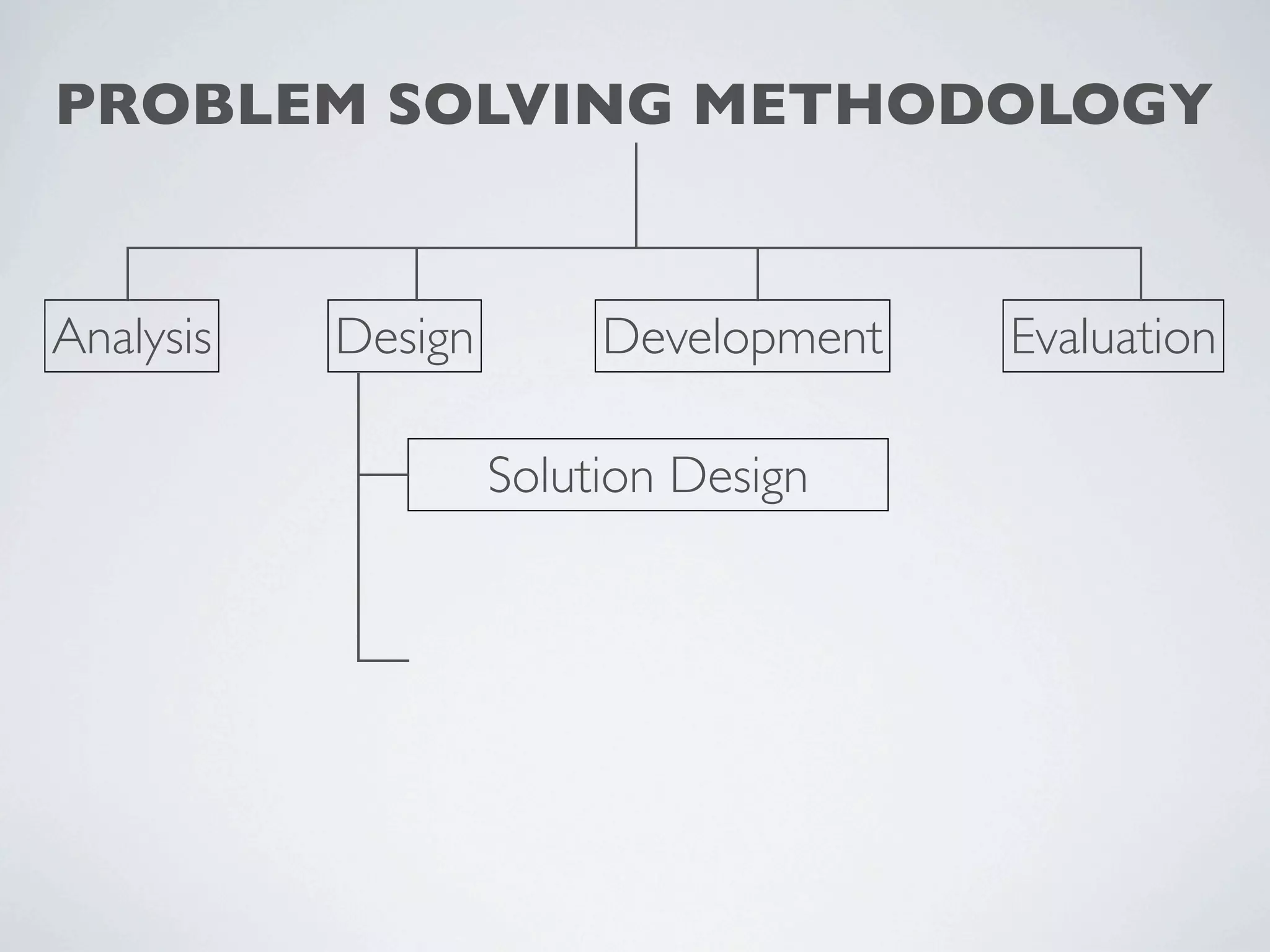
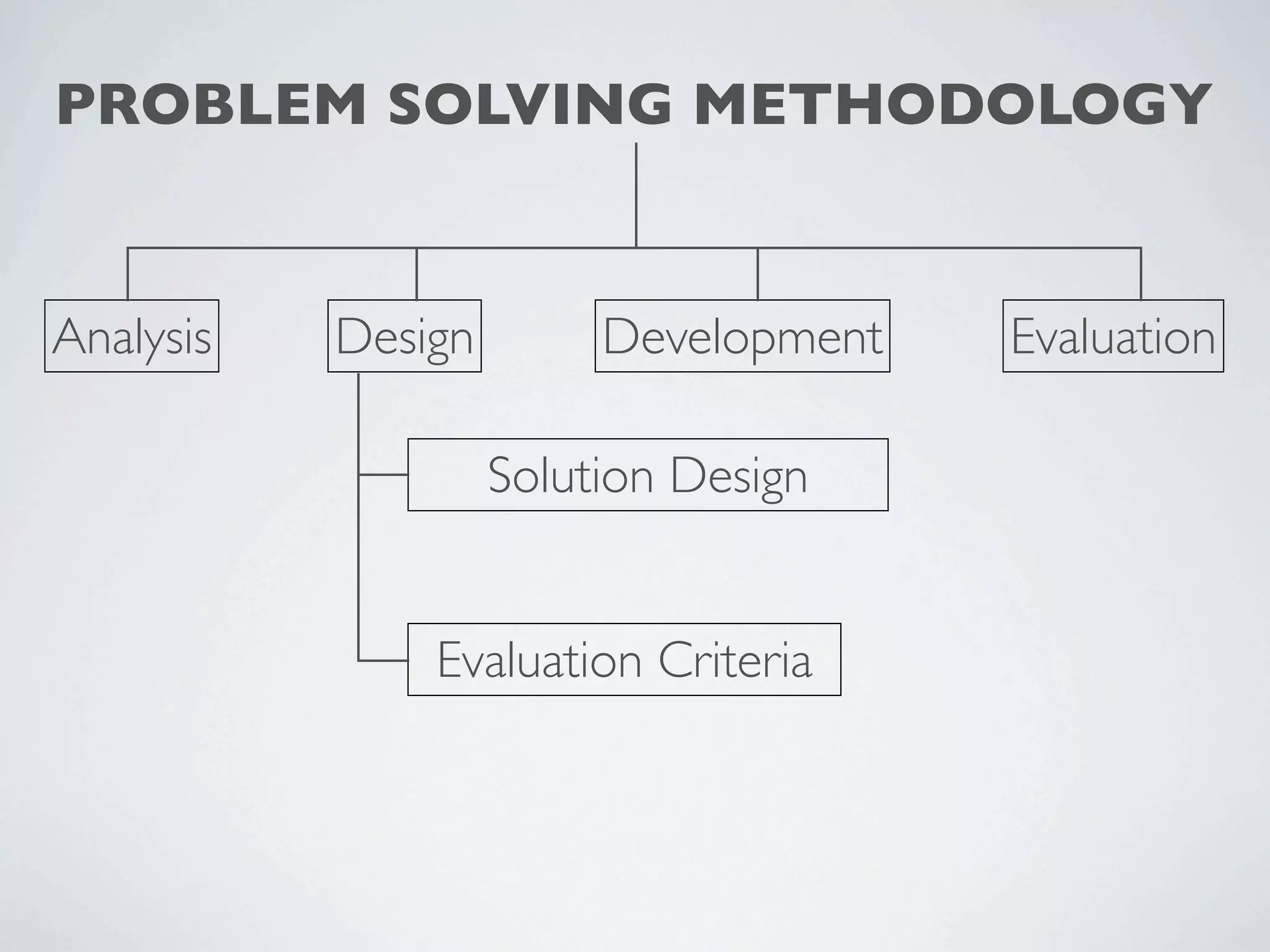
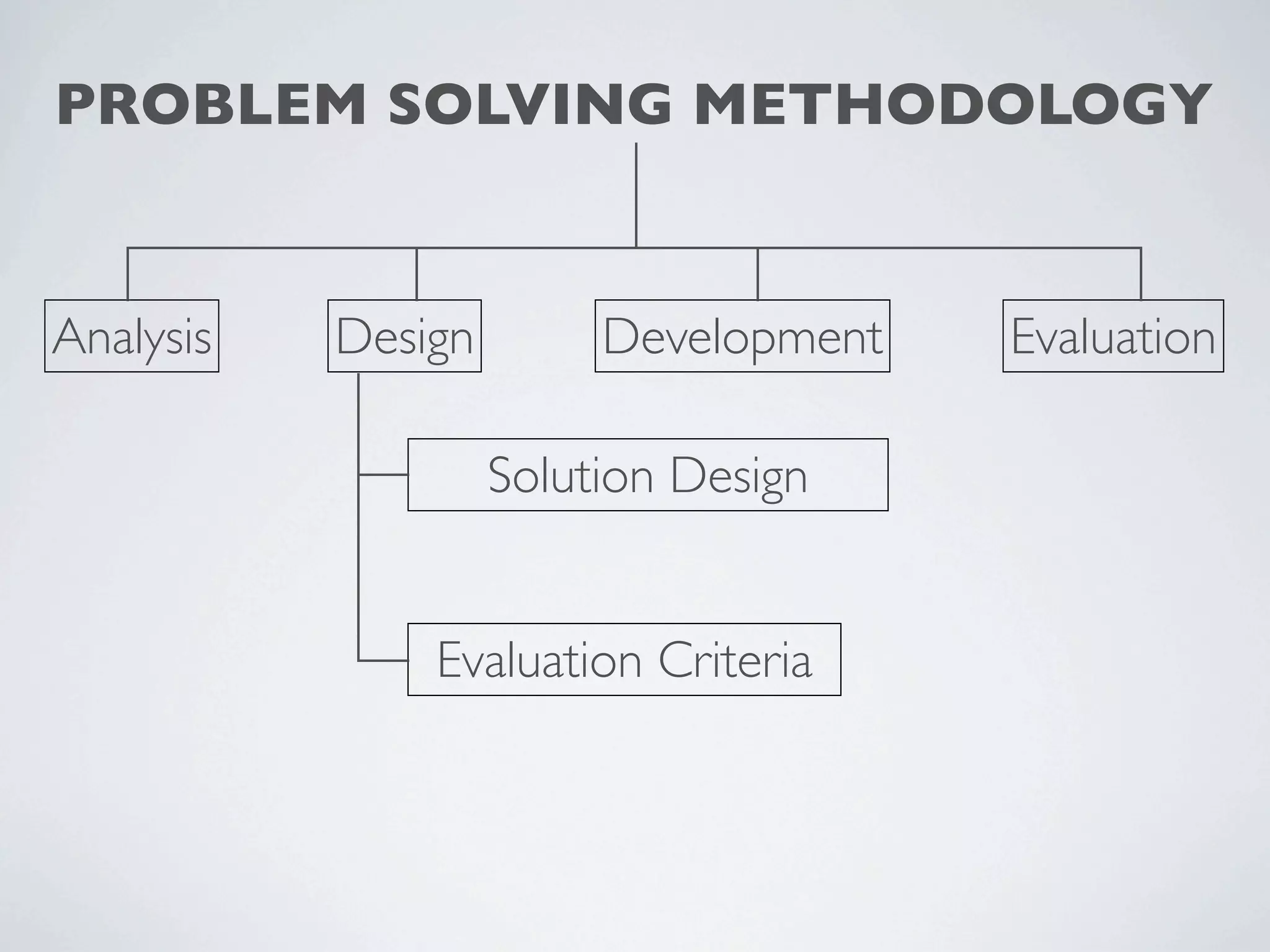
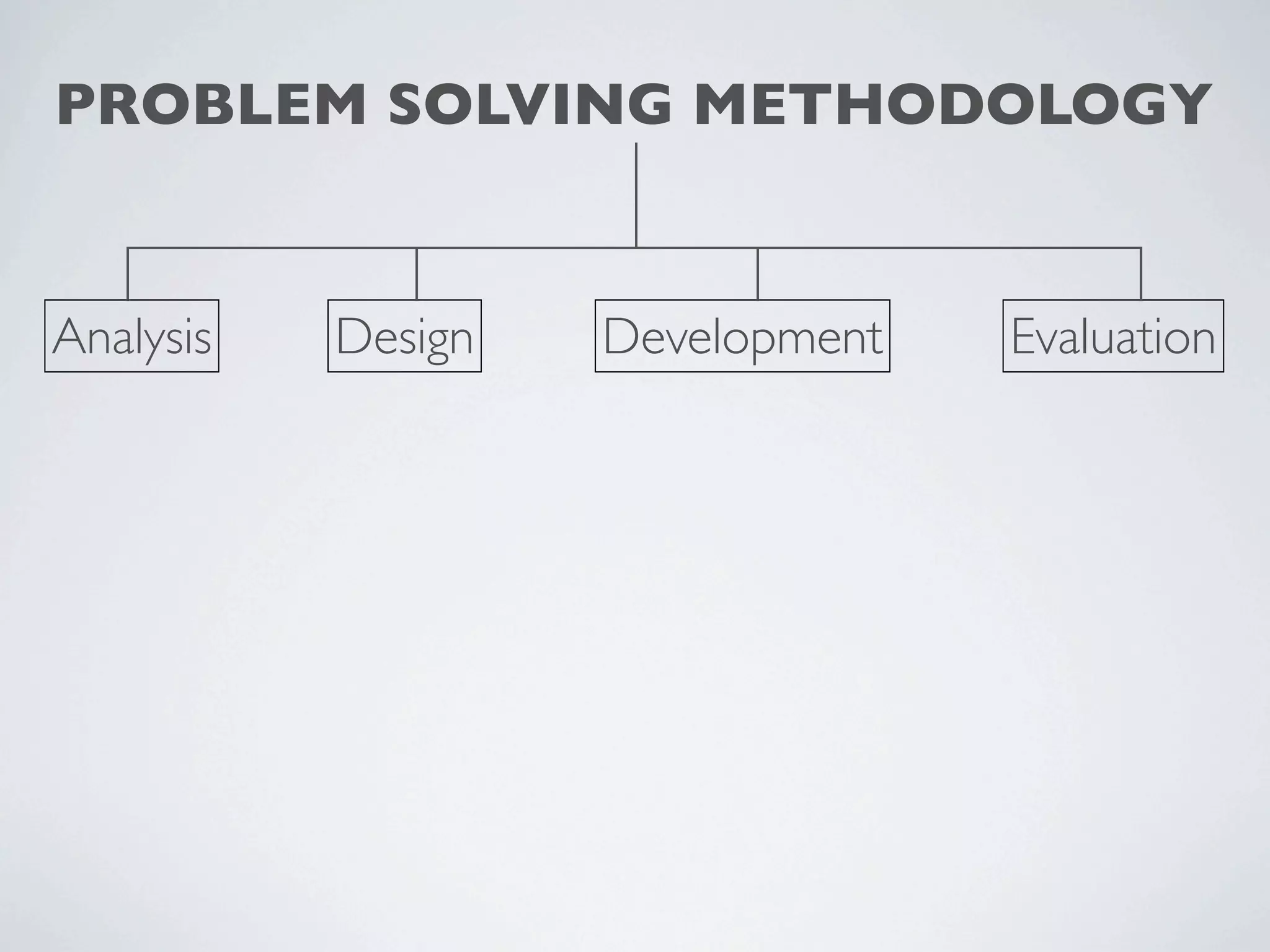
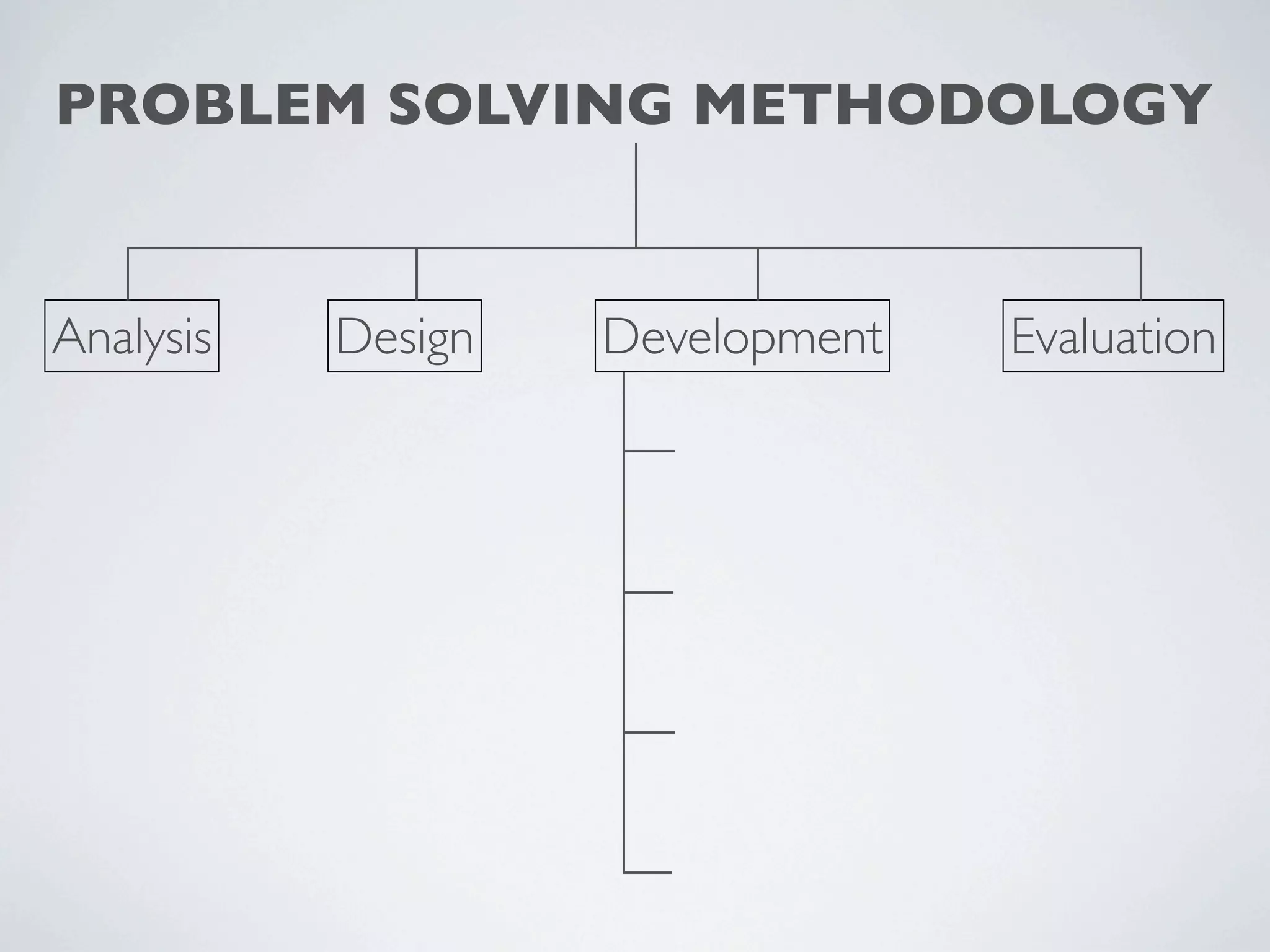
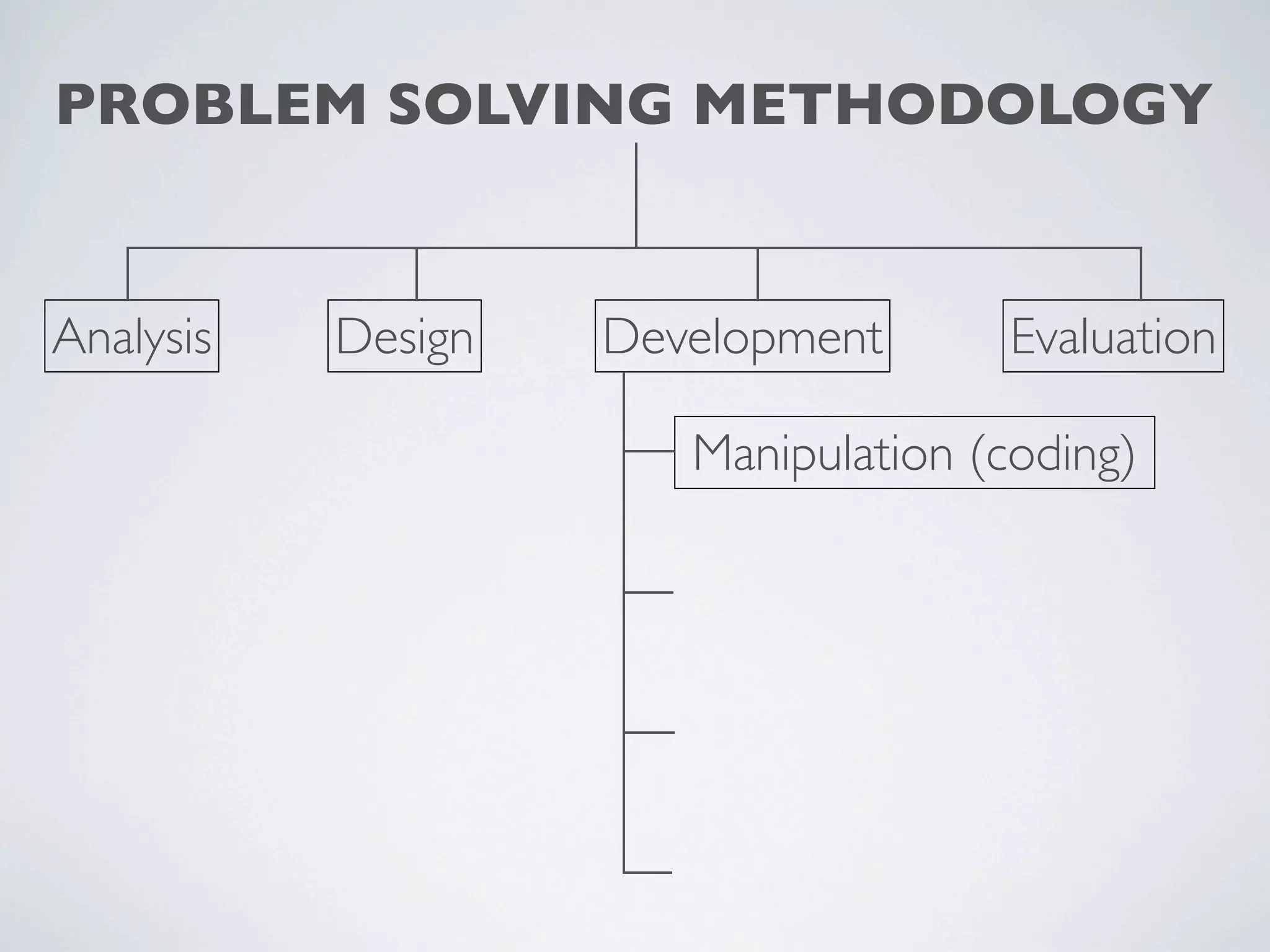
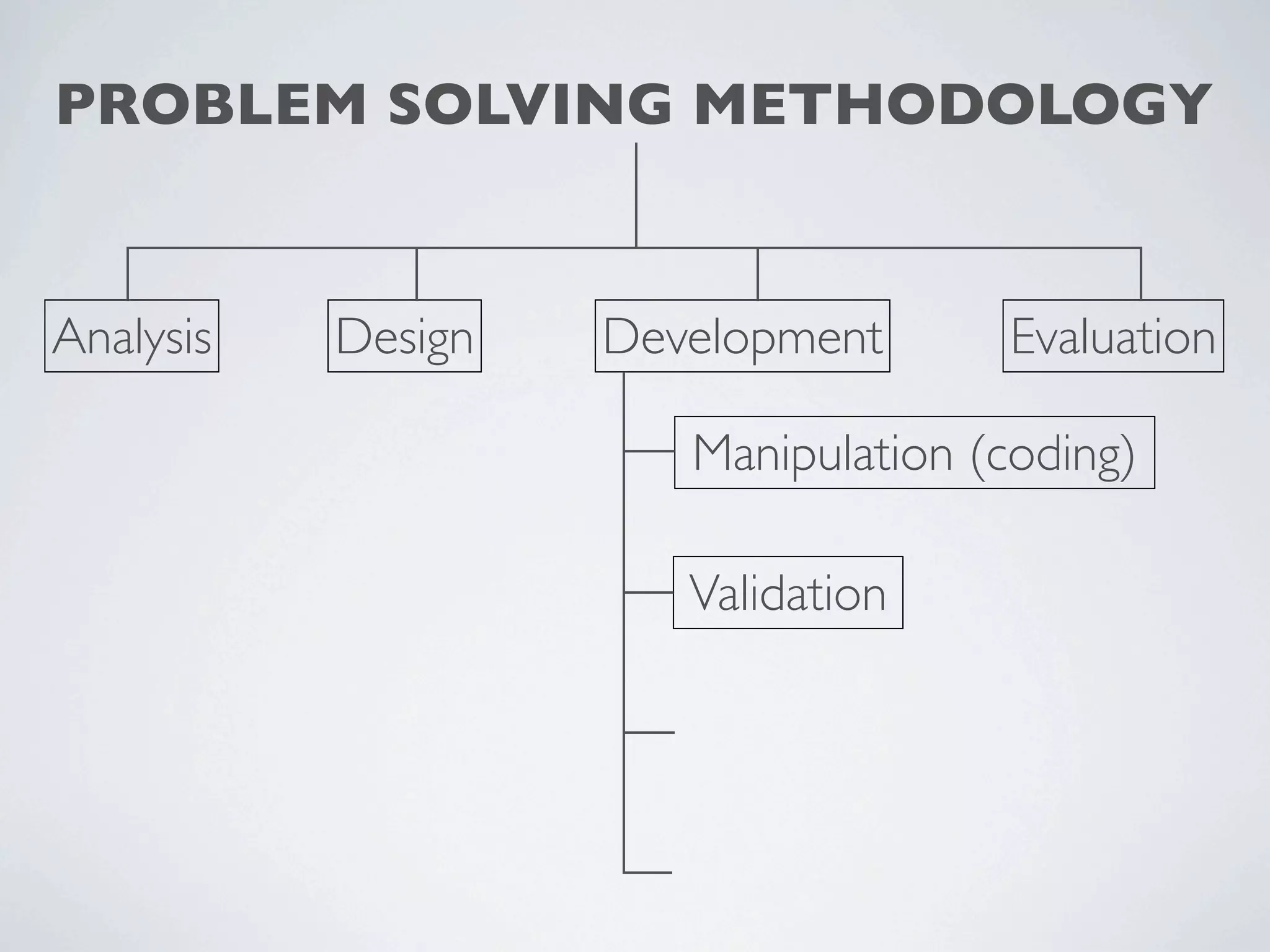
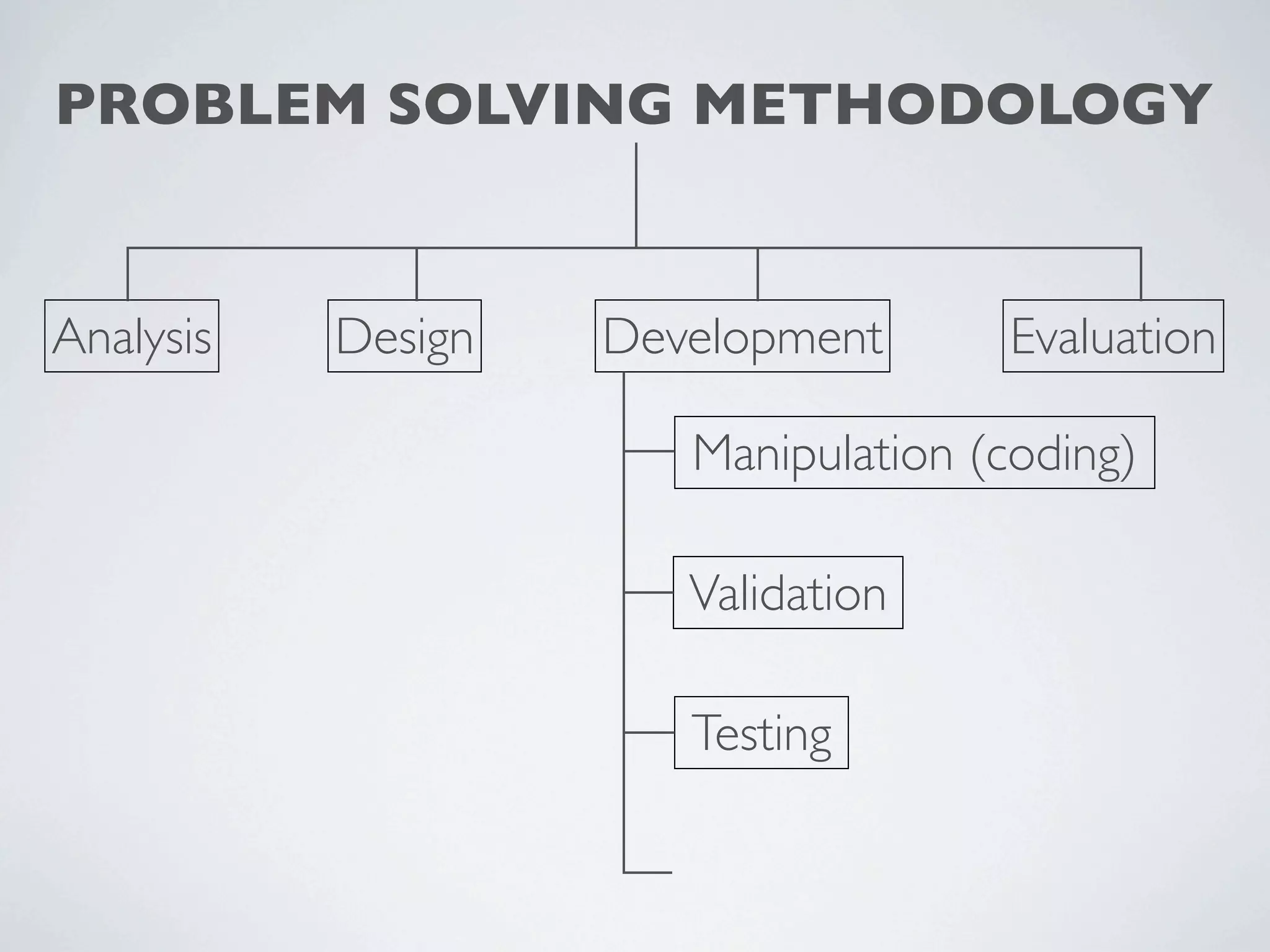
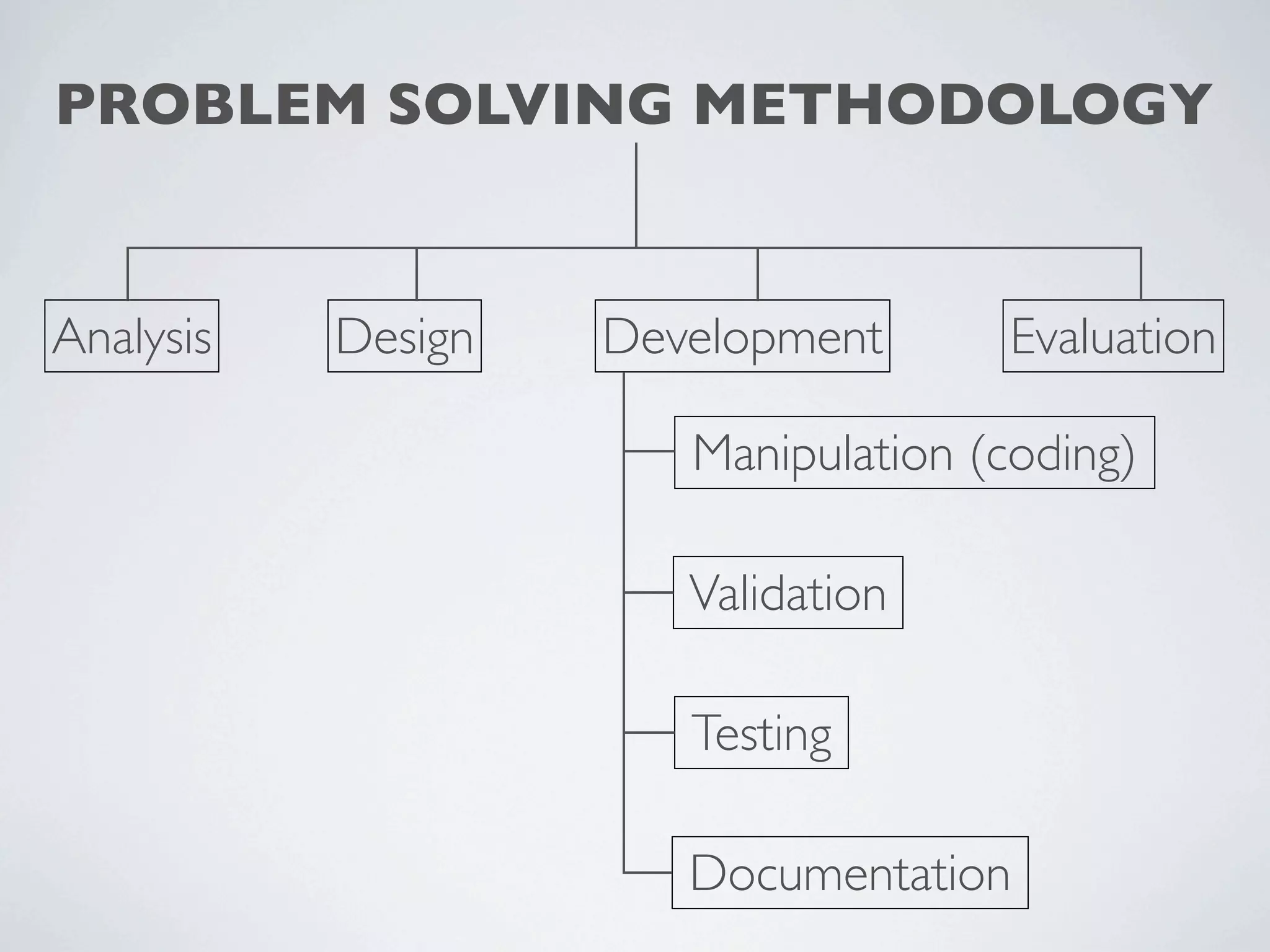
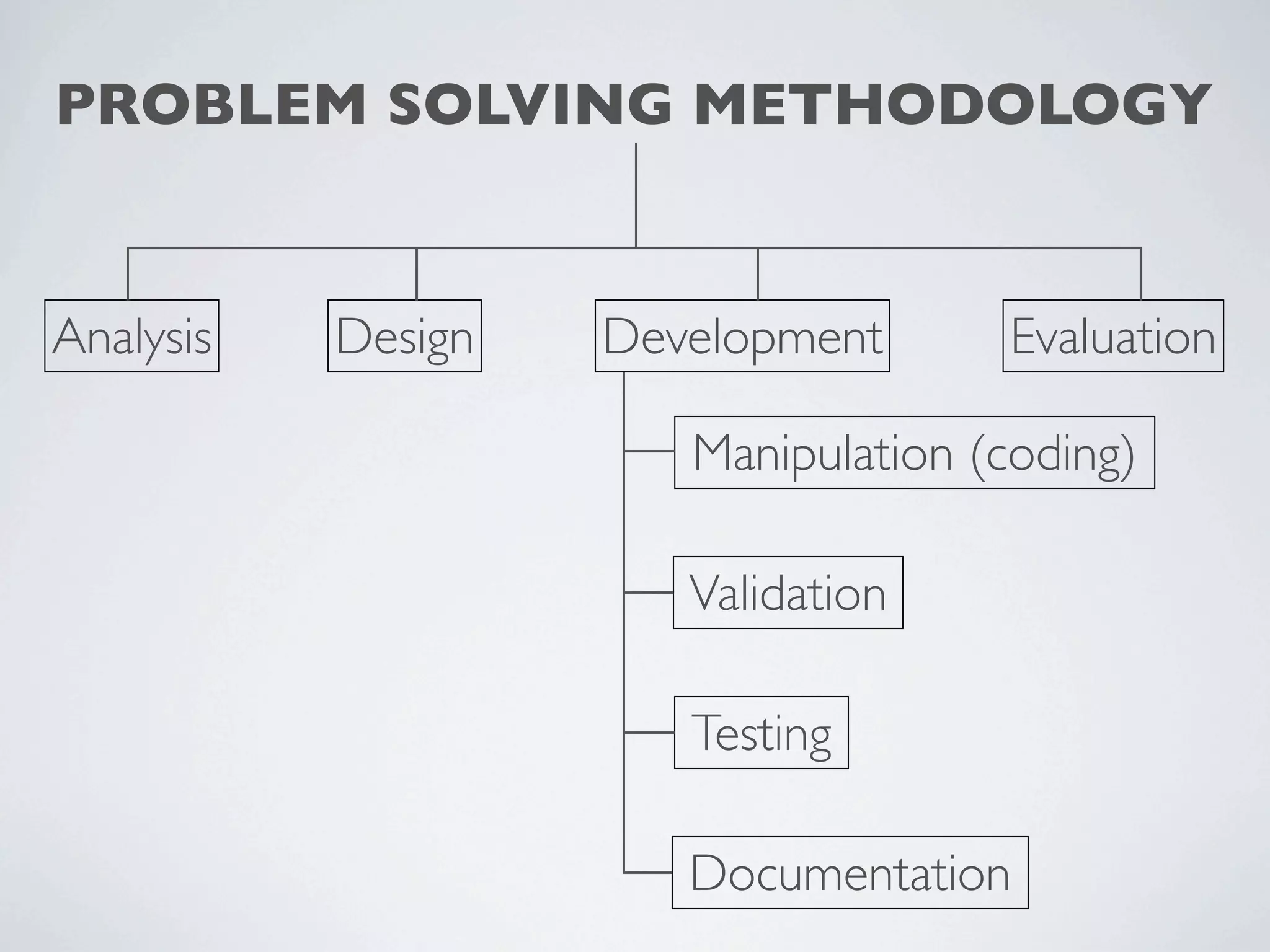
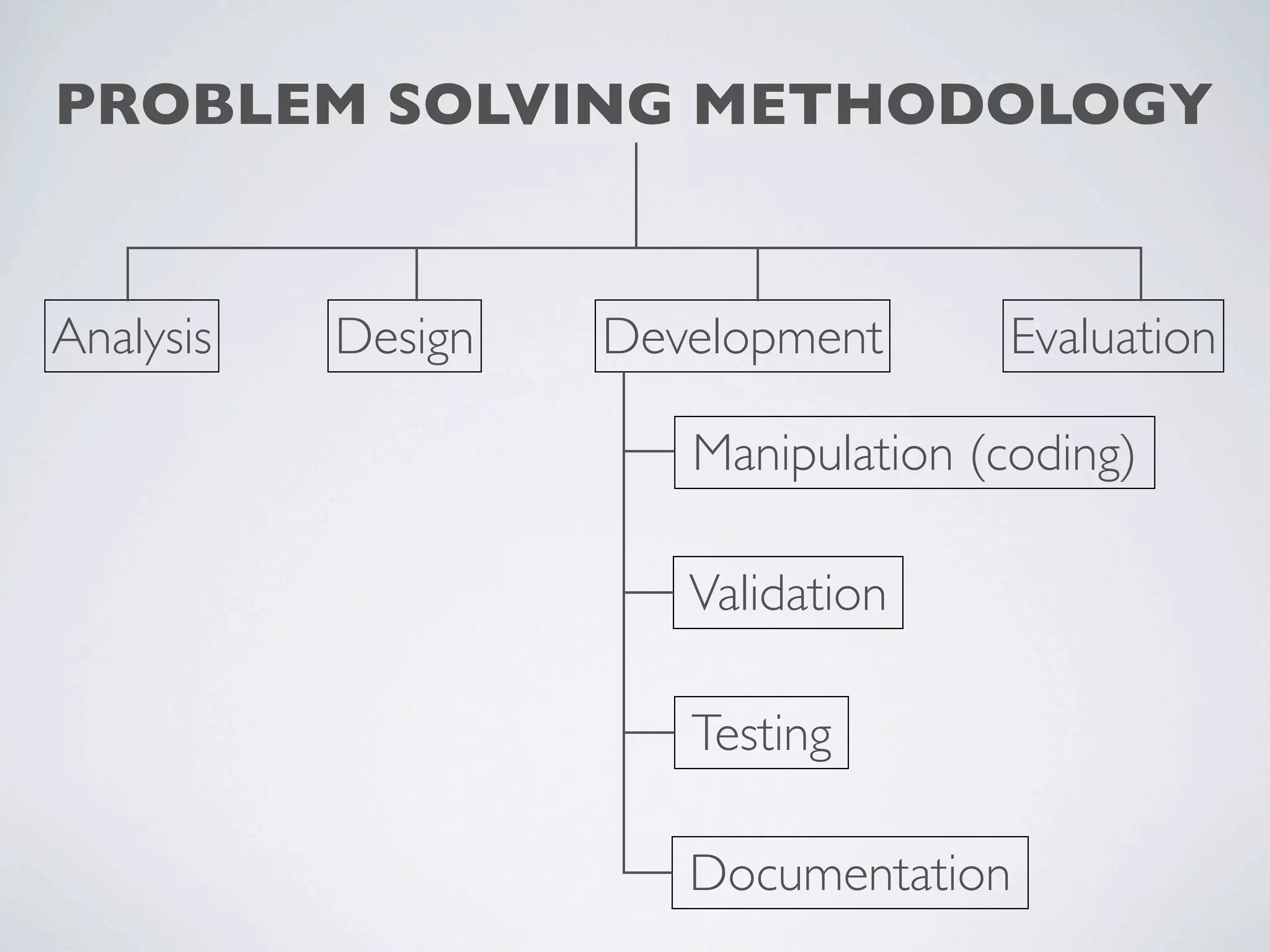
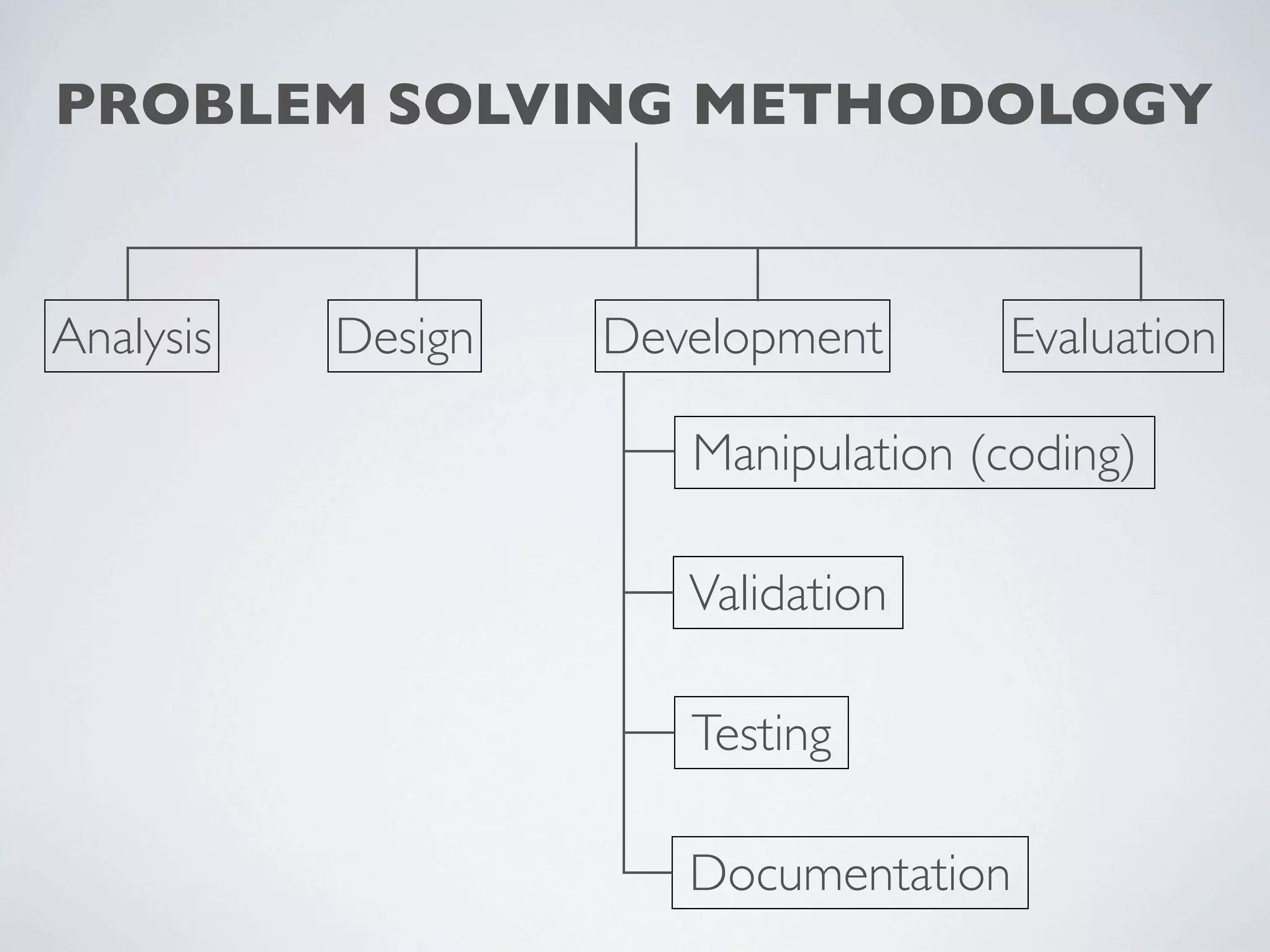
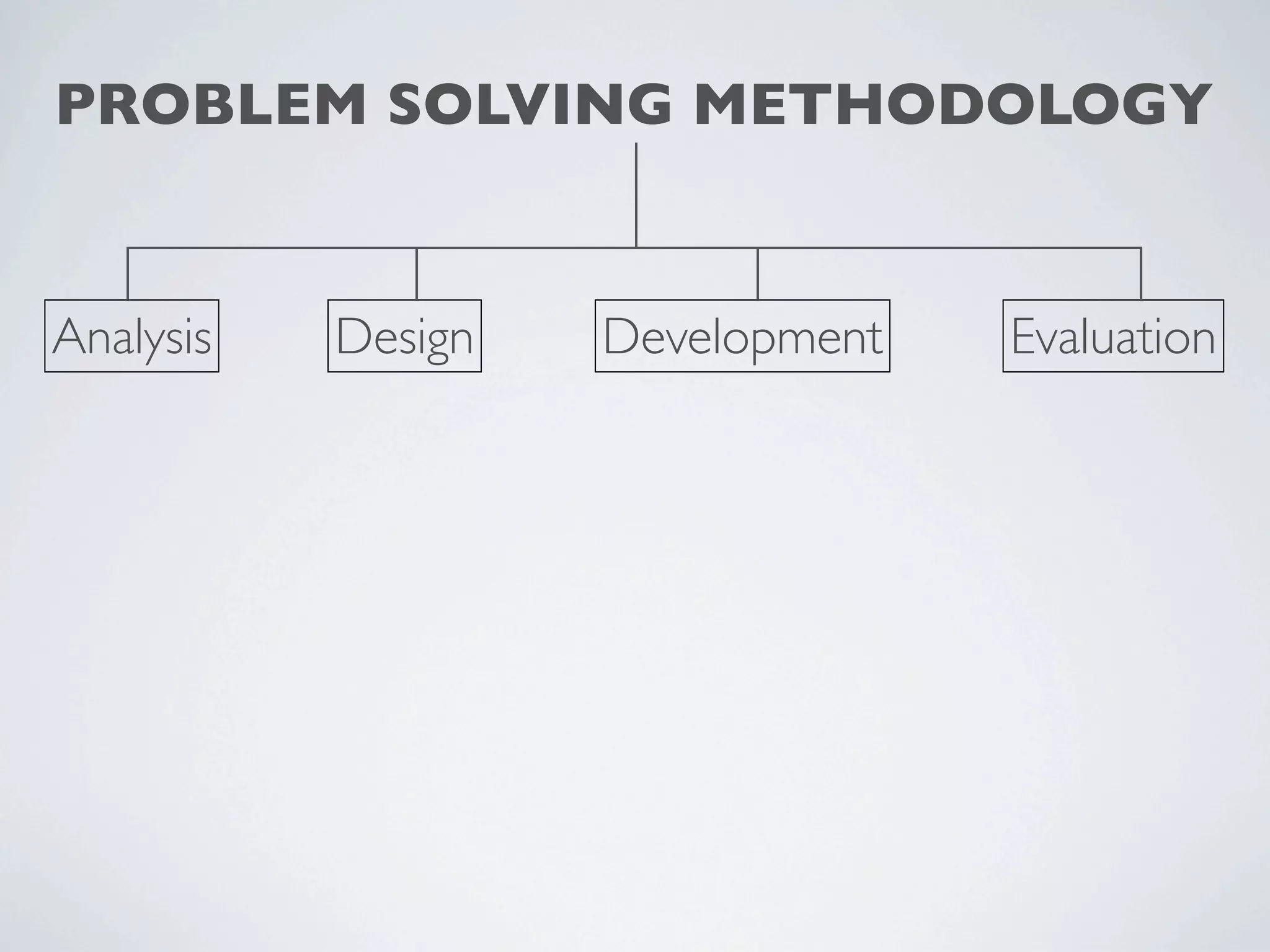
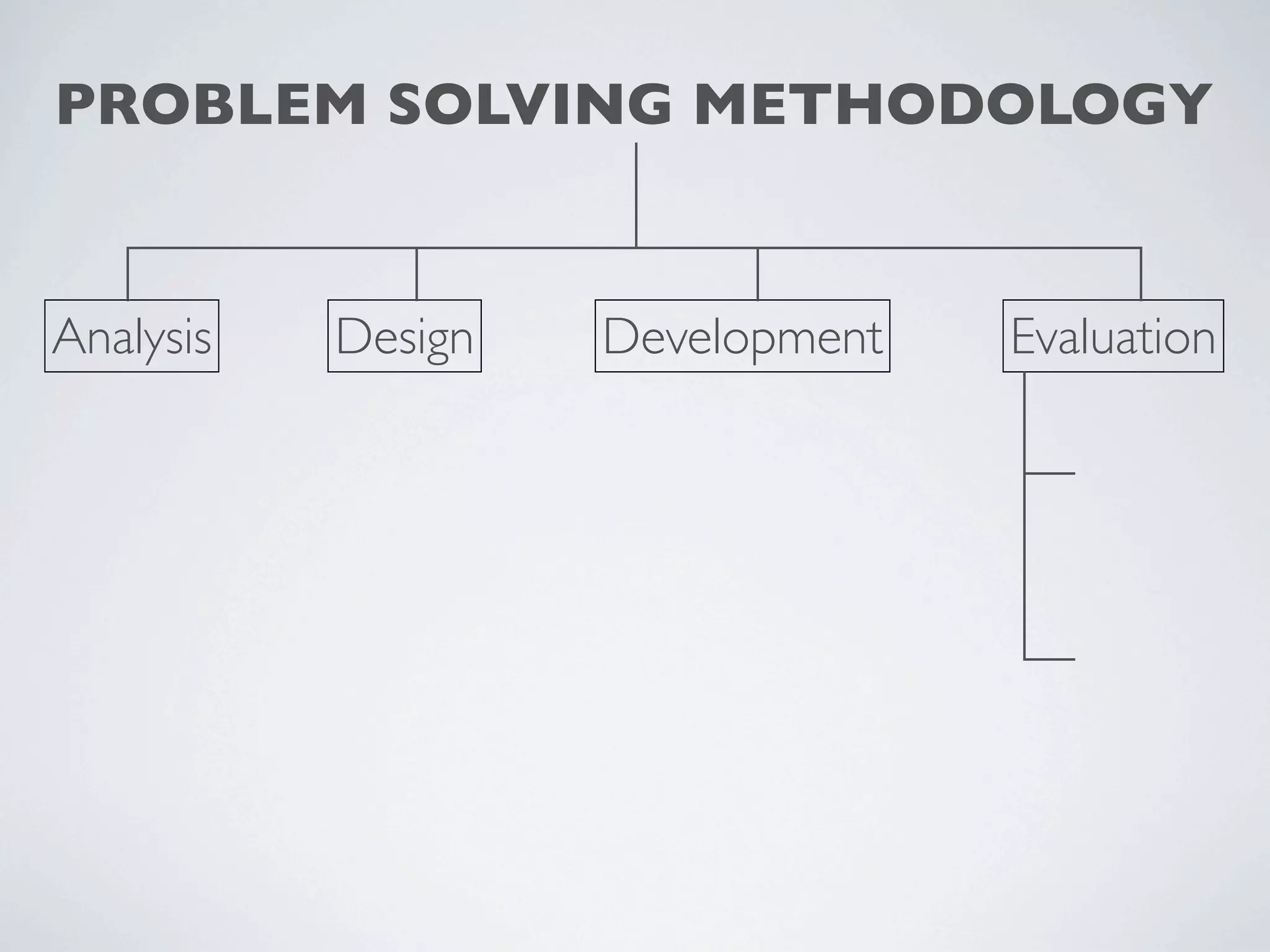
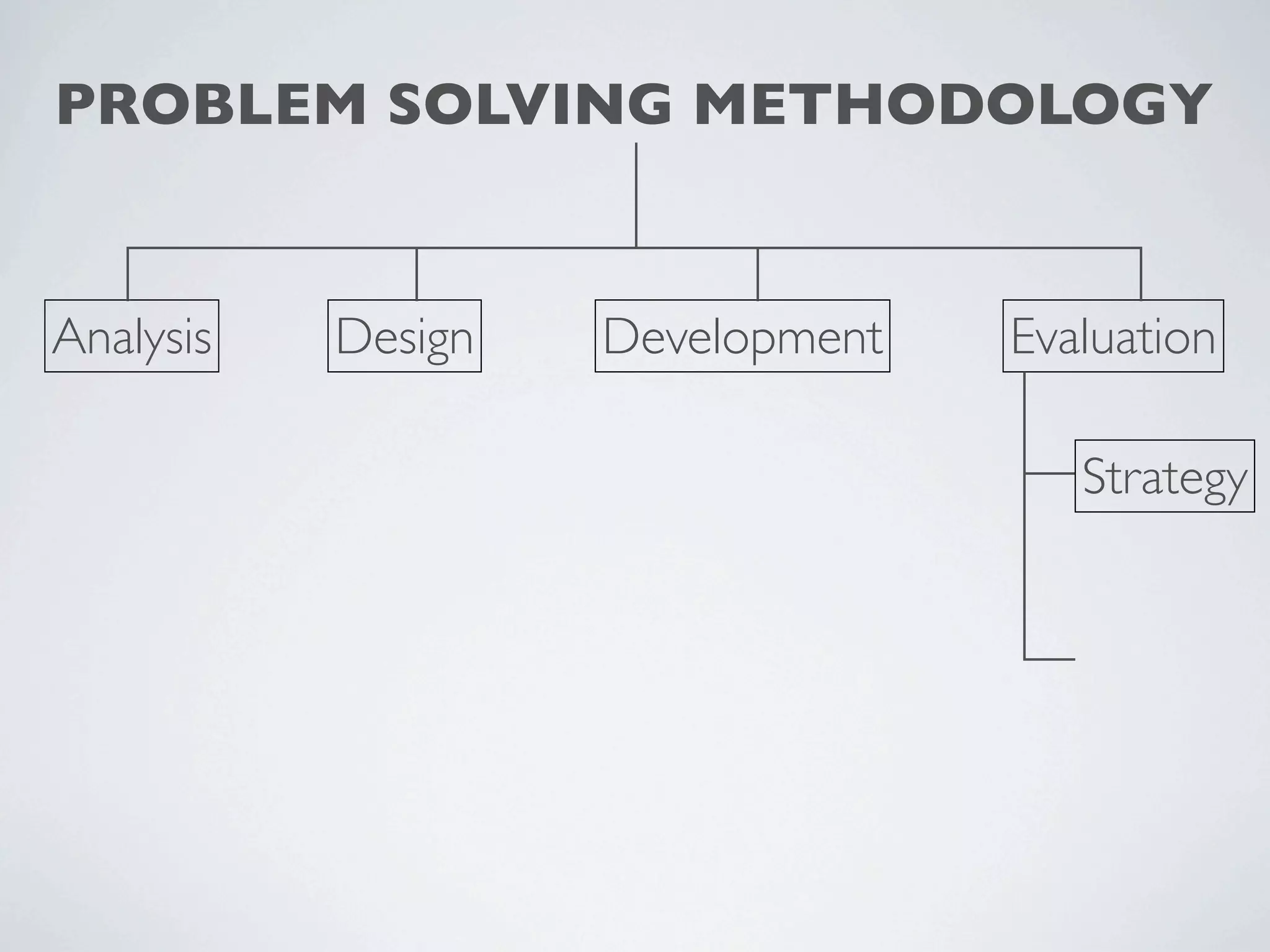
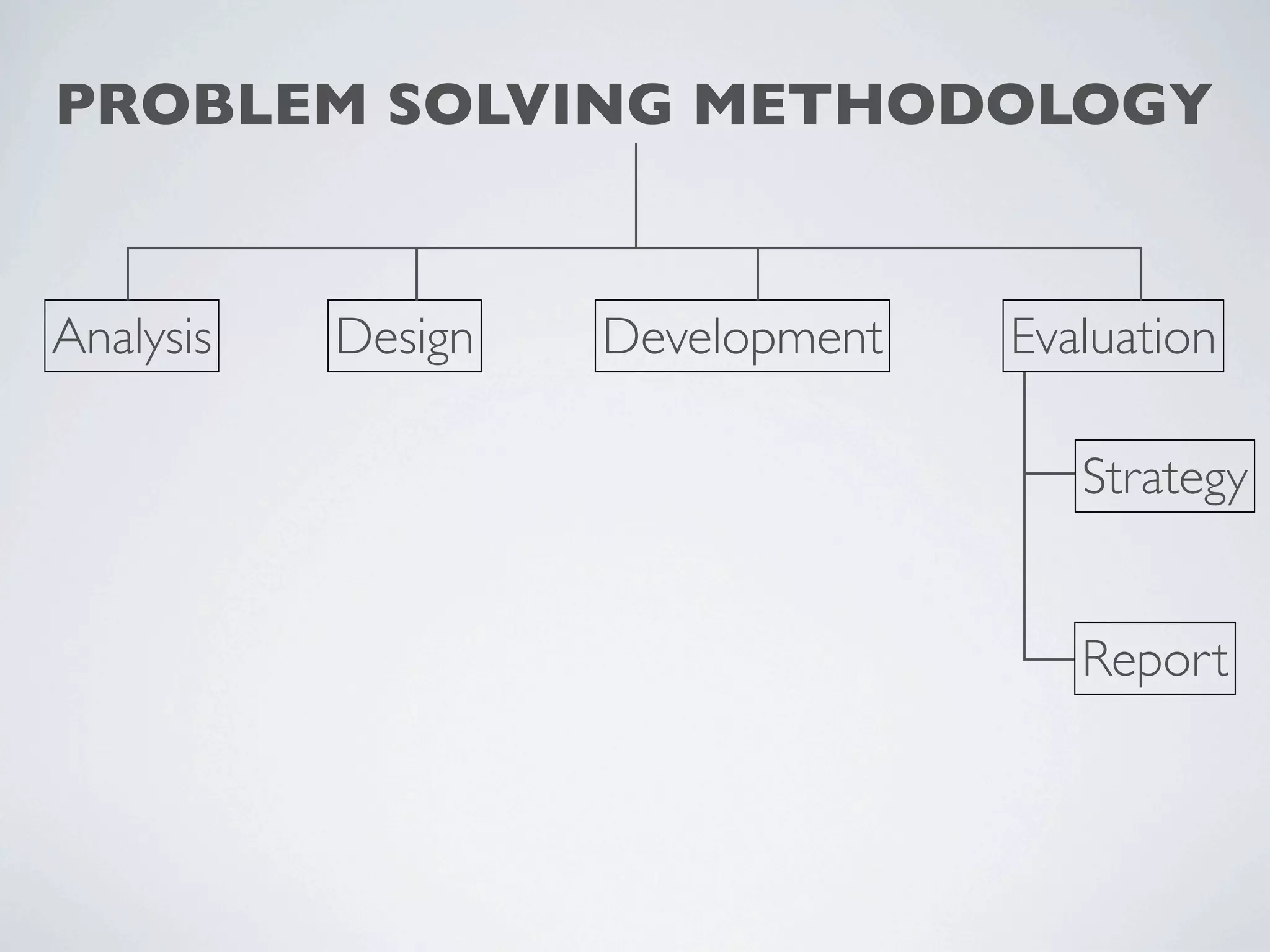
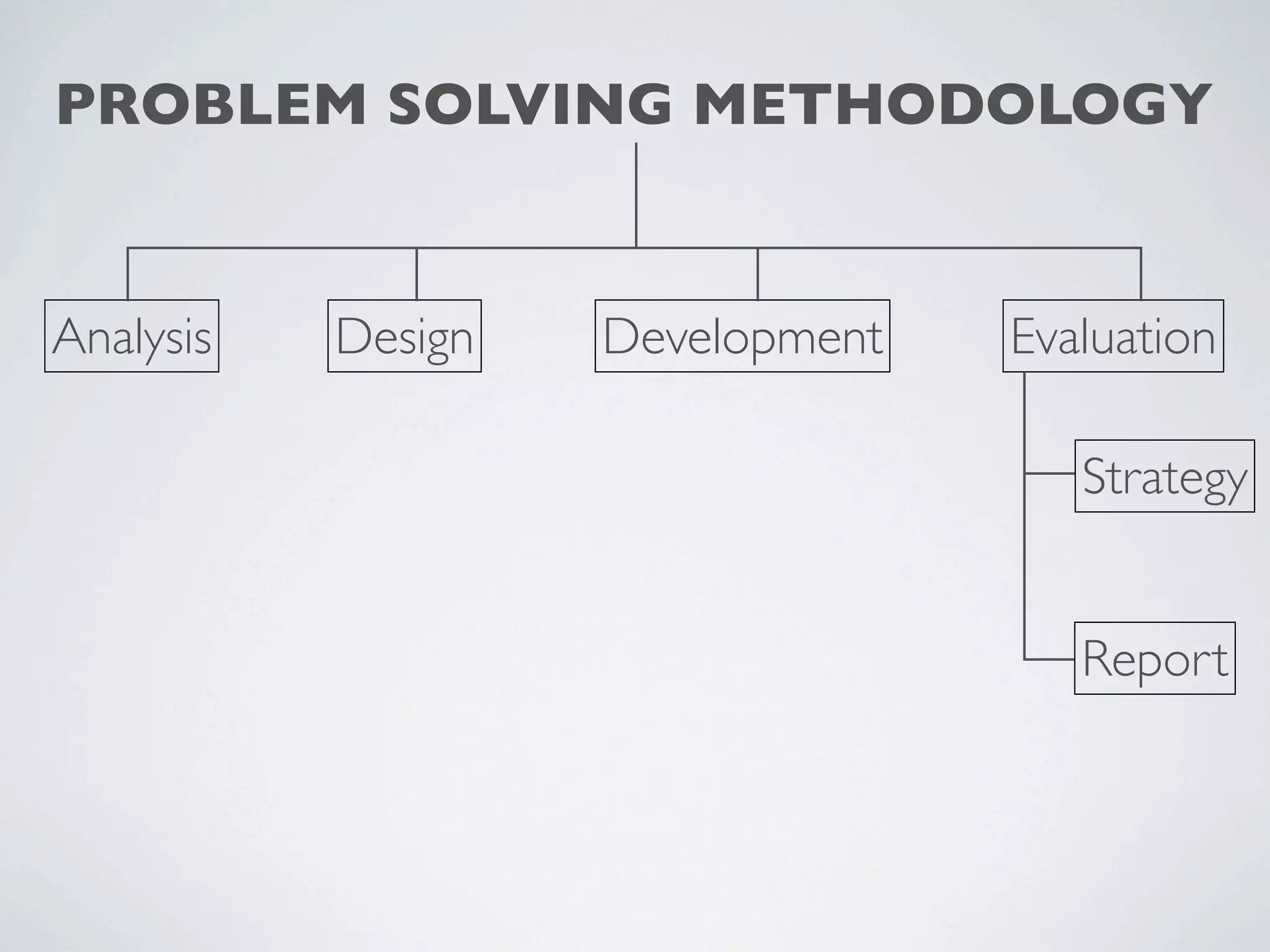
This document outlines a problem solving methodology consisting of analysis, design, development, and evaluation phases. In the analysis phase, the solution requirements, constraints, and scope are determined. The design phase involves planning the solution and establishing evaluation criteria. In development, the solution is coded, validated, tested, and documented. Finally, the evaluation phase consists of developing a strategy to evaluate the solution and reporting on how well it meets requirements.