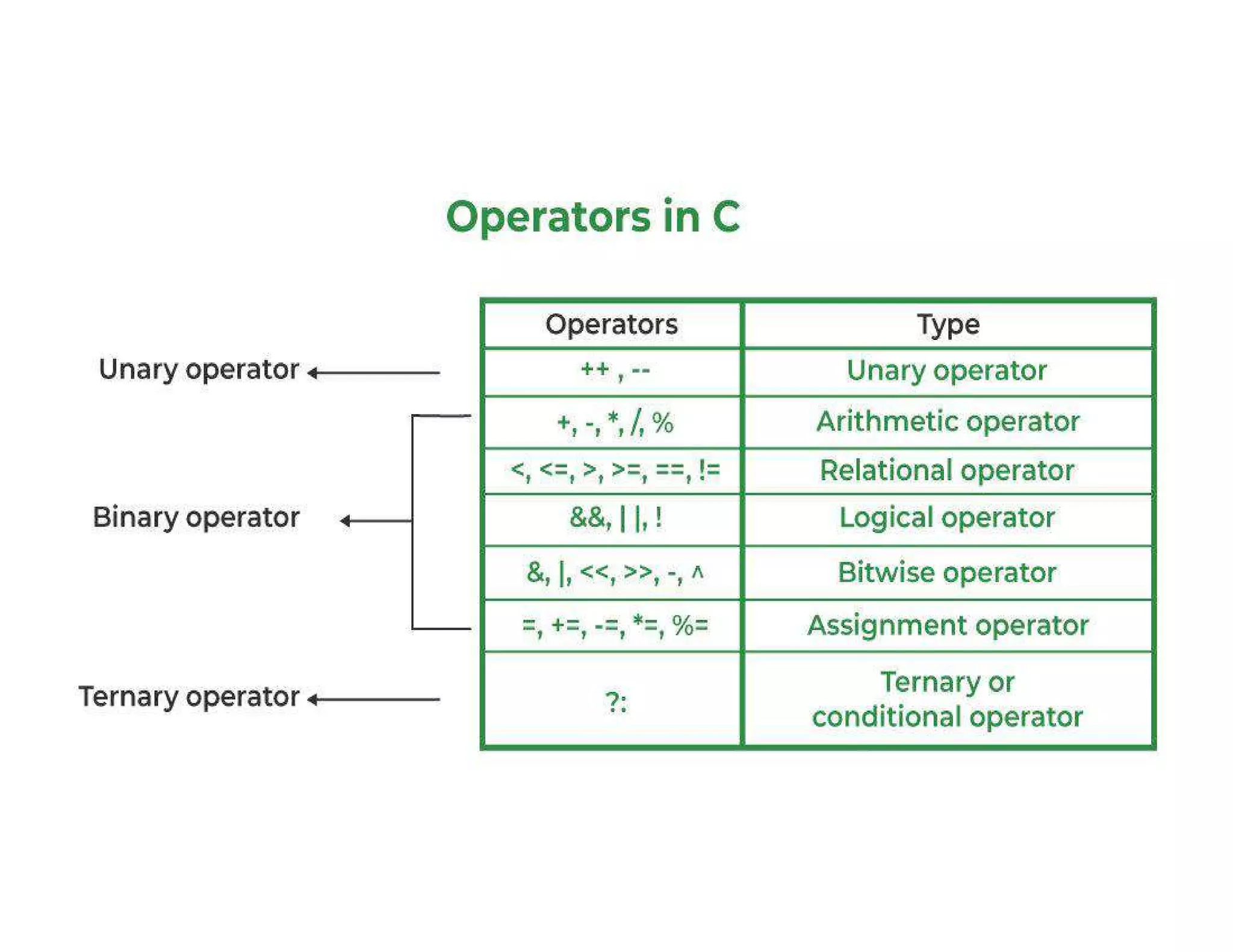
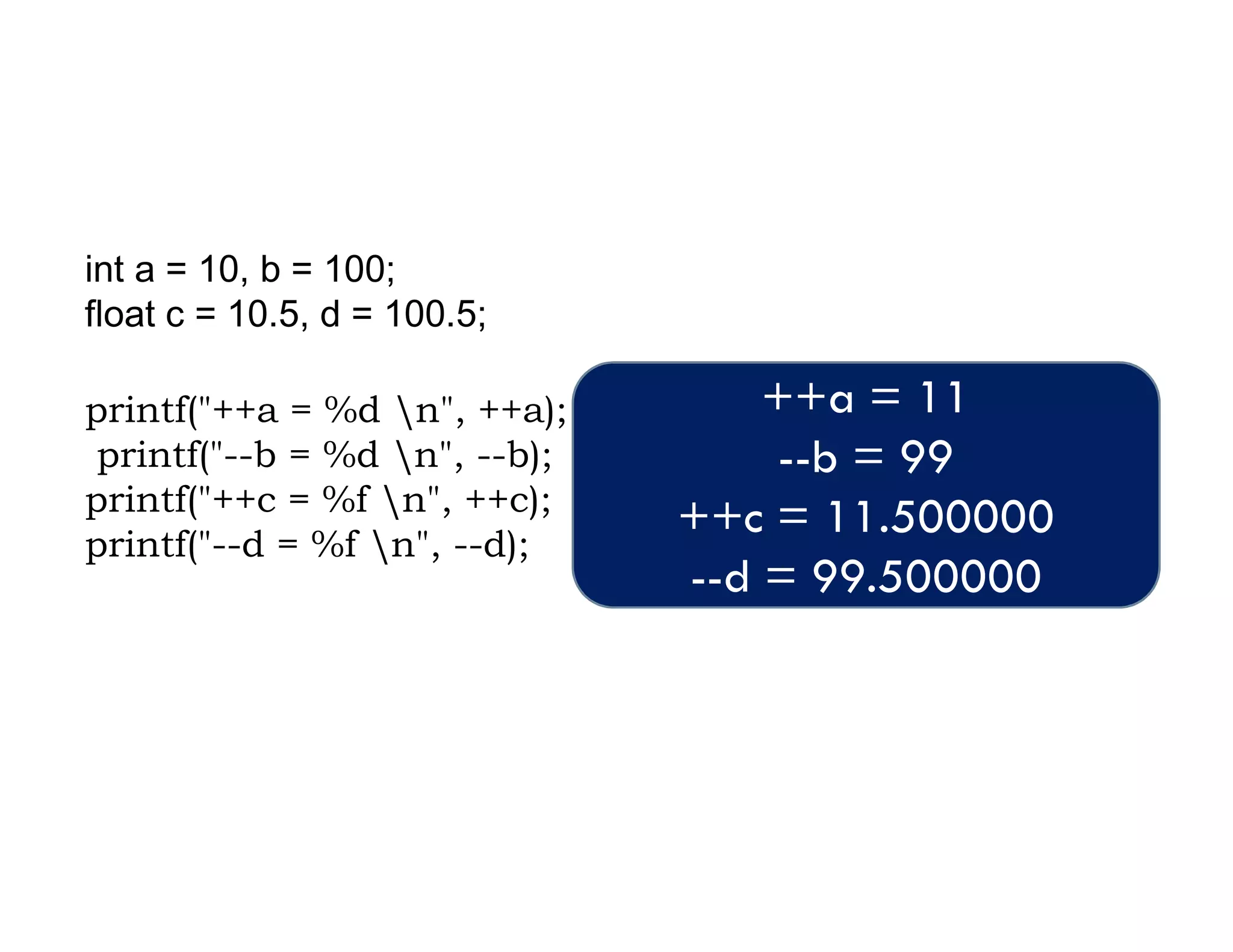
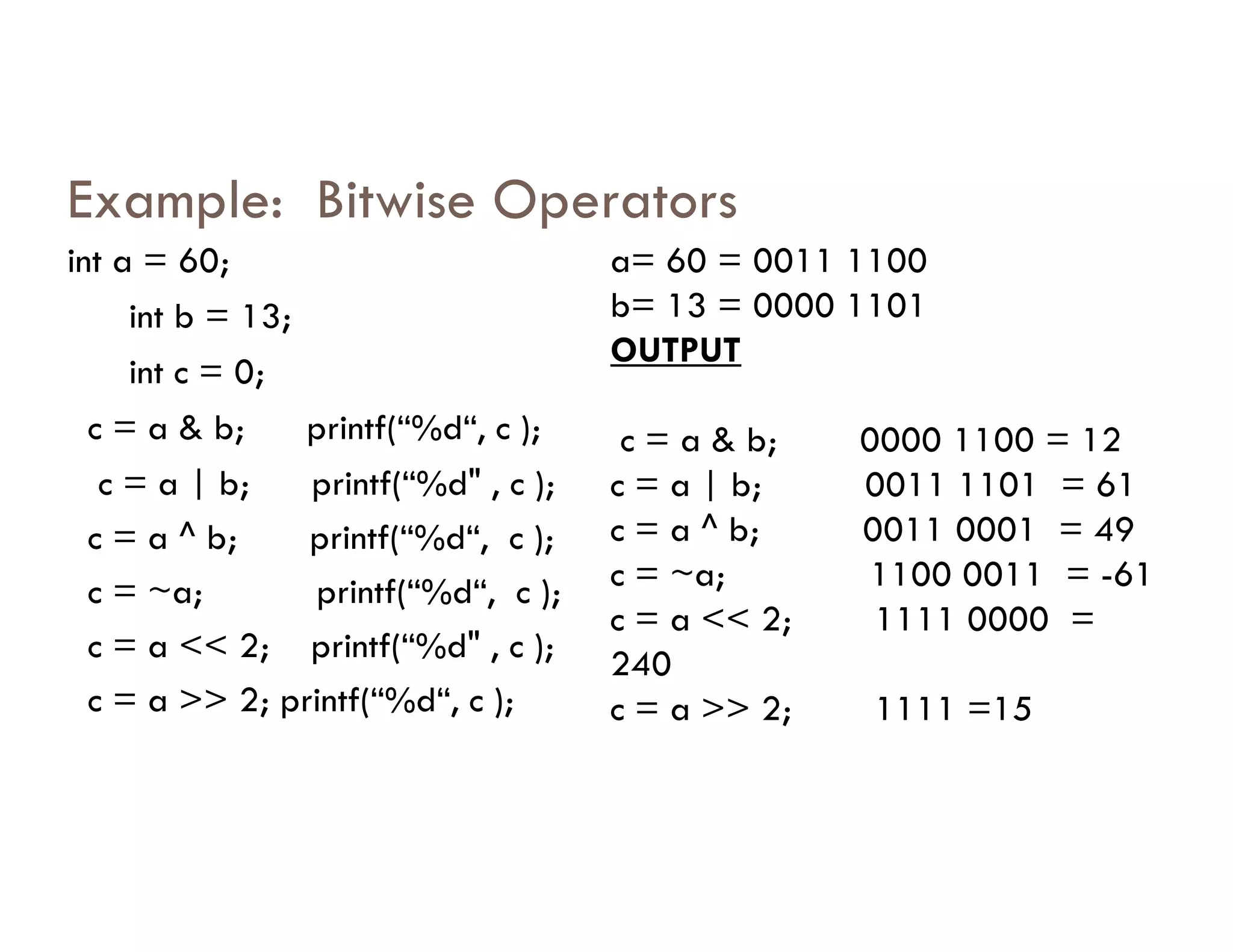
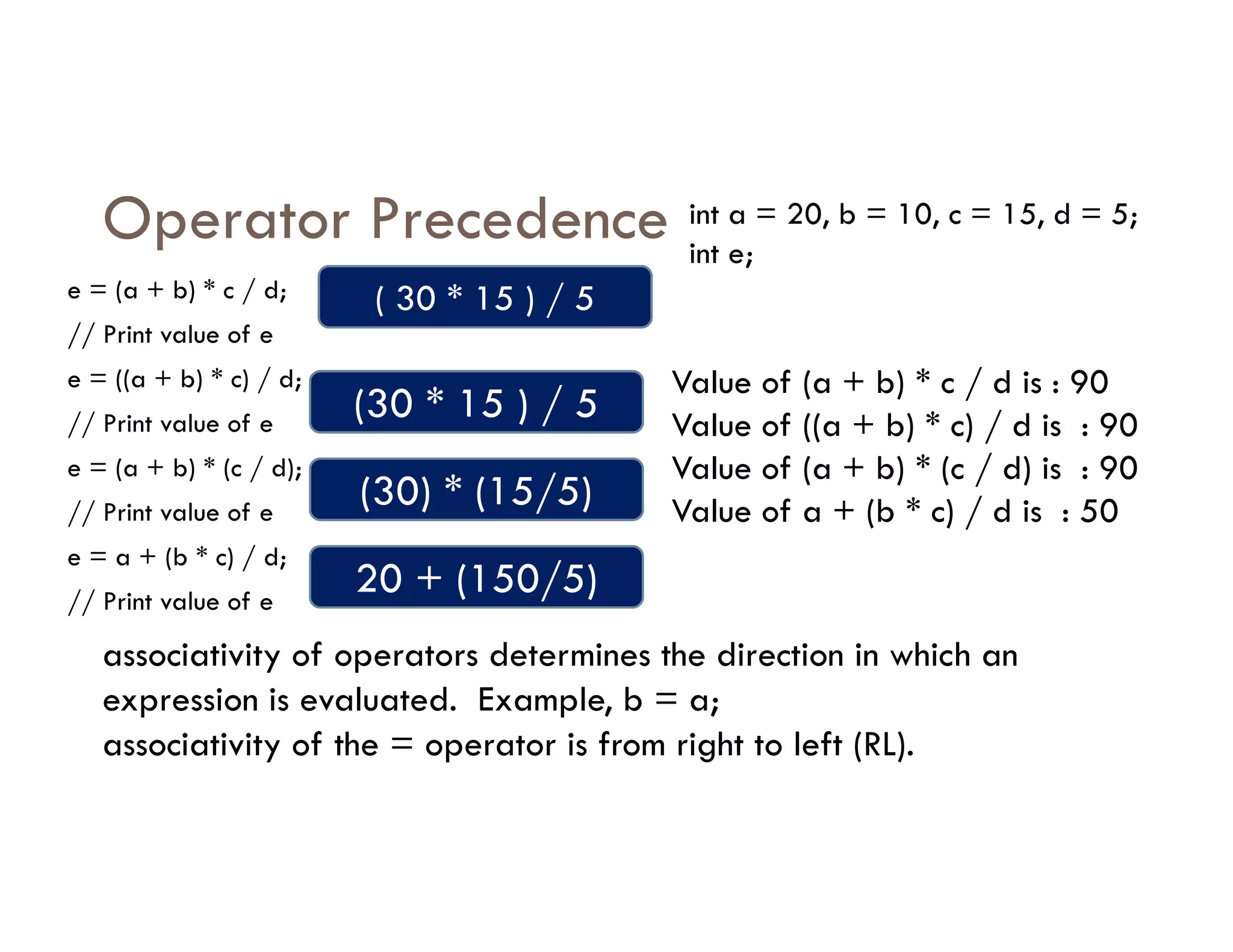
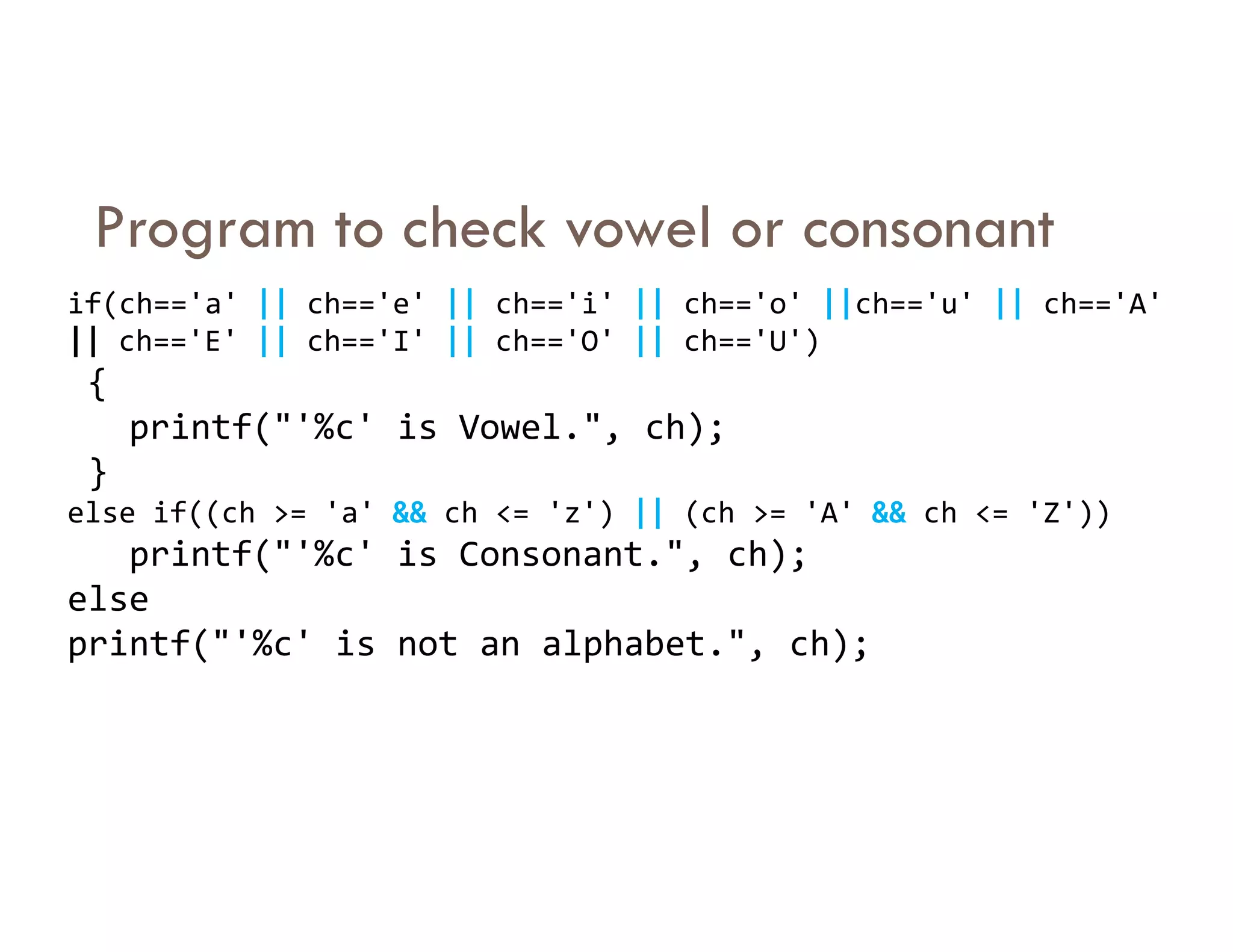
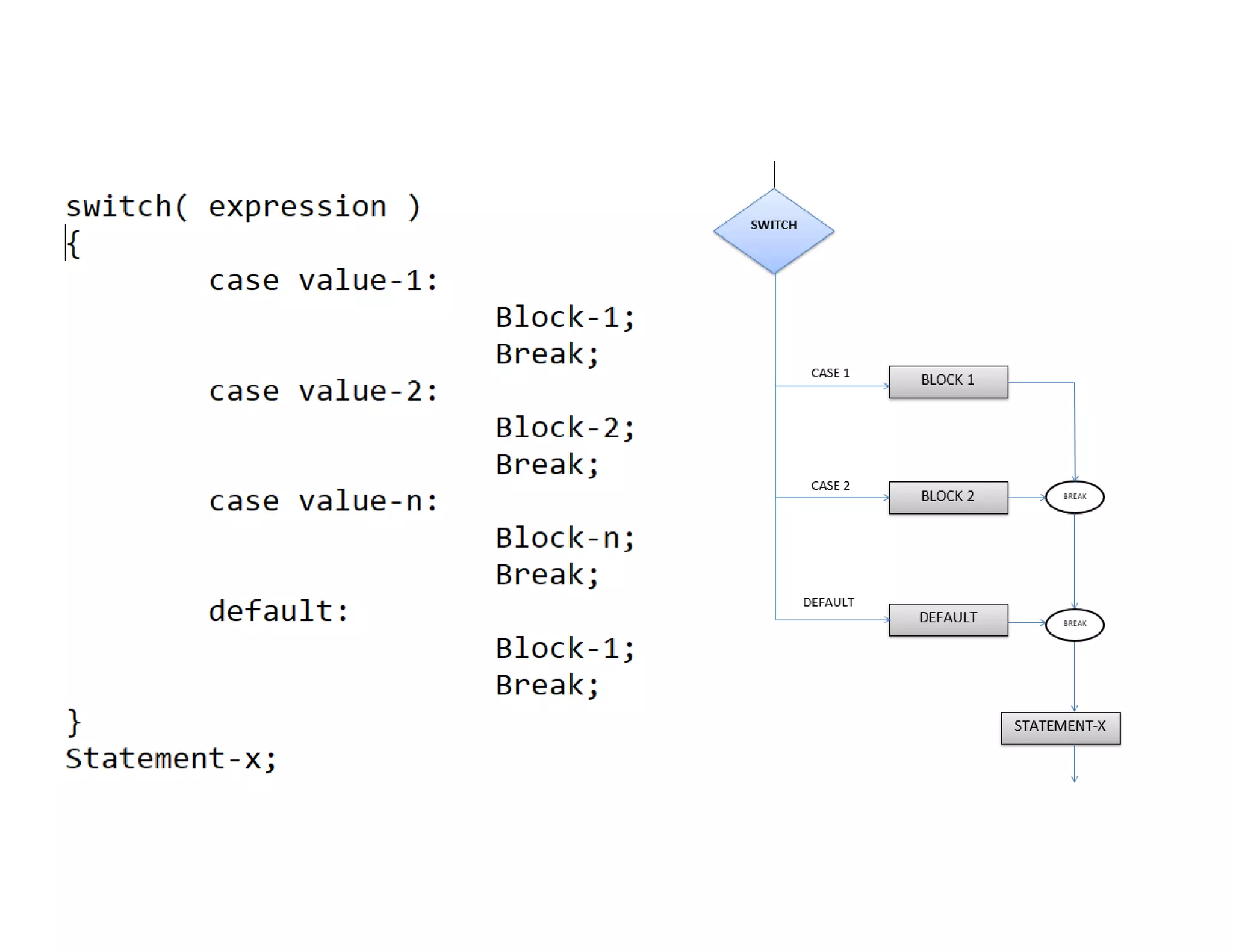
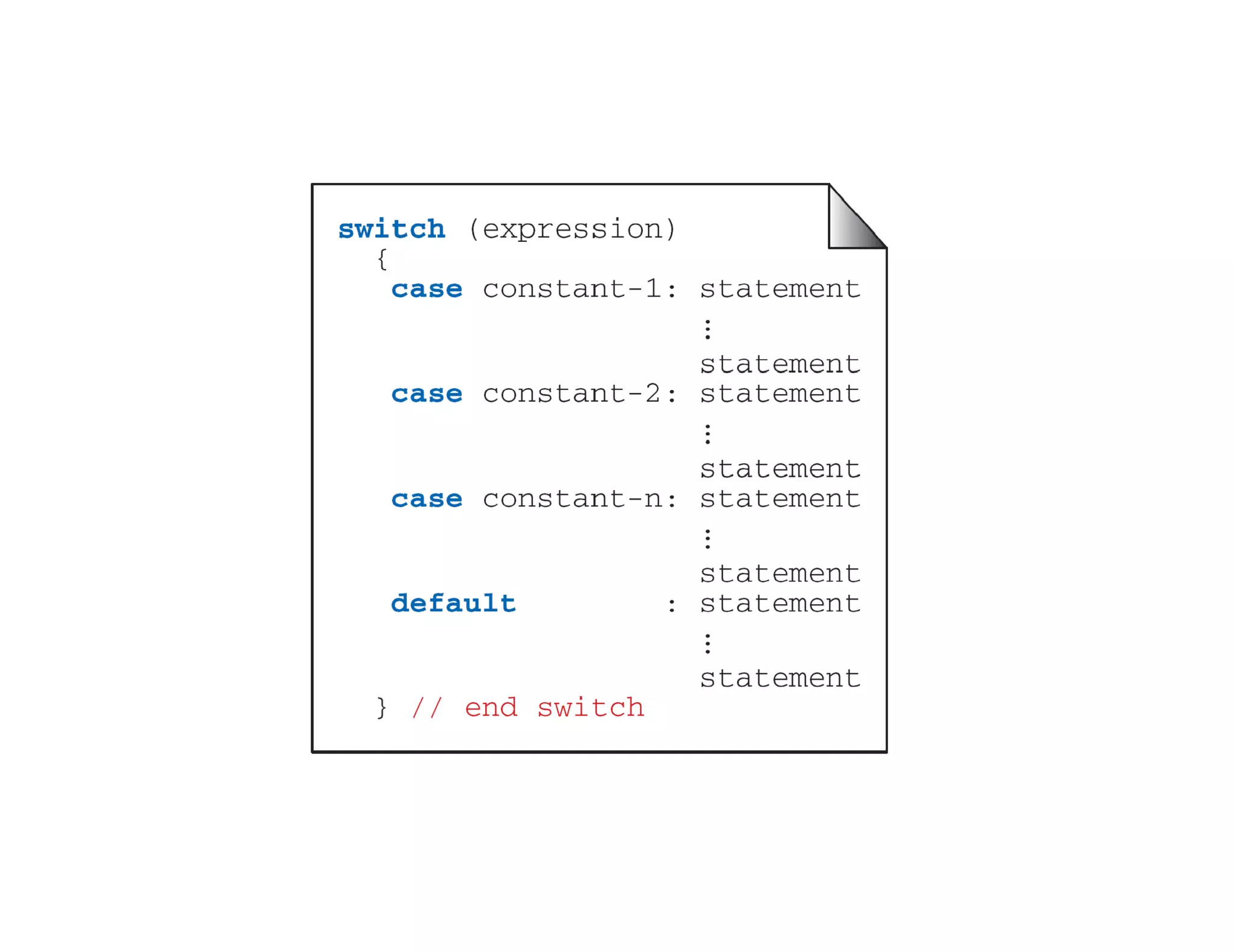
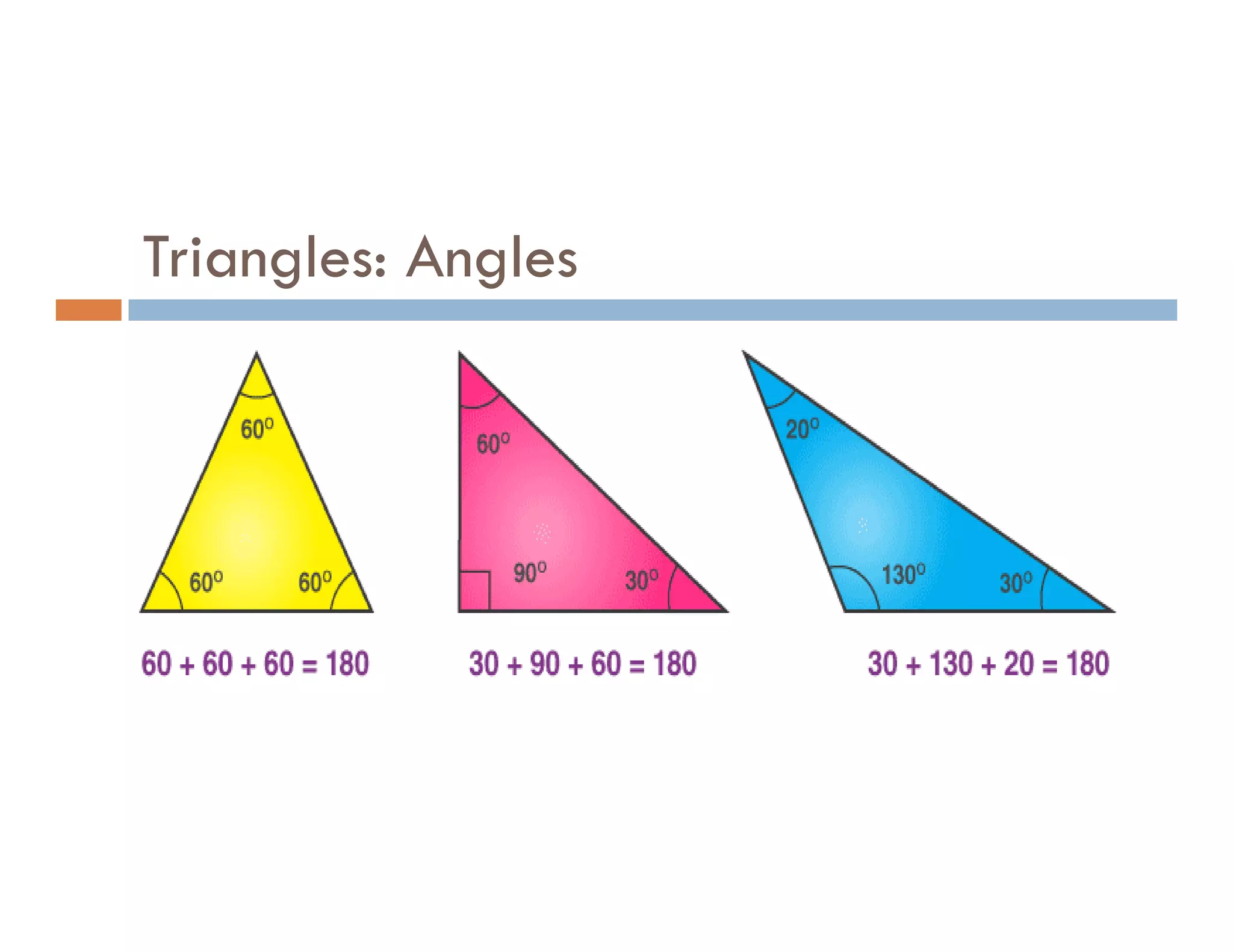
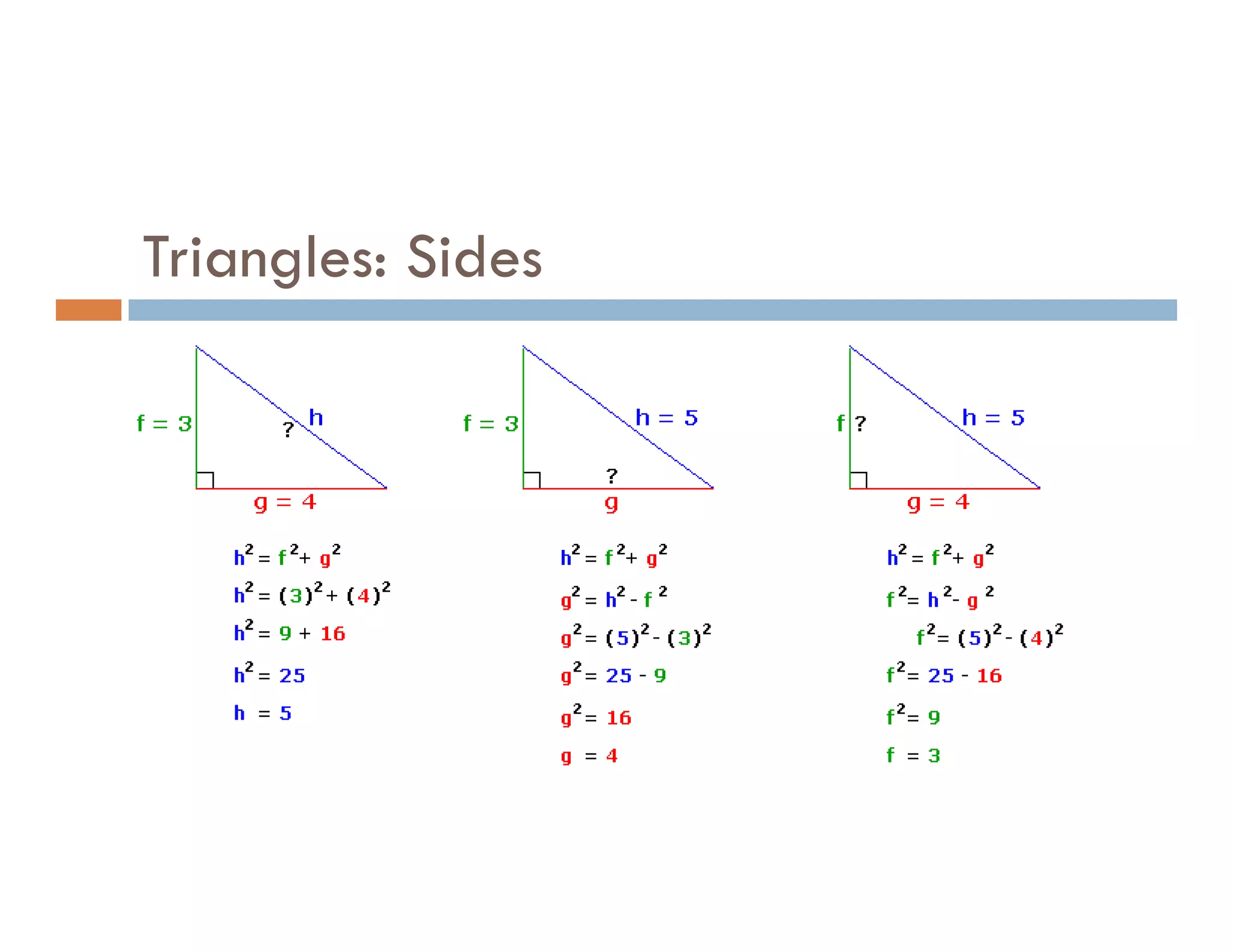
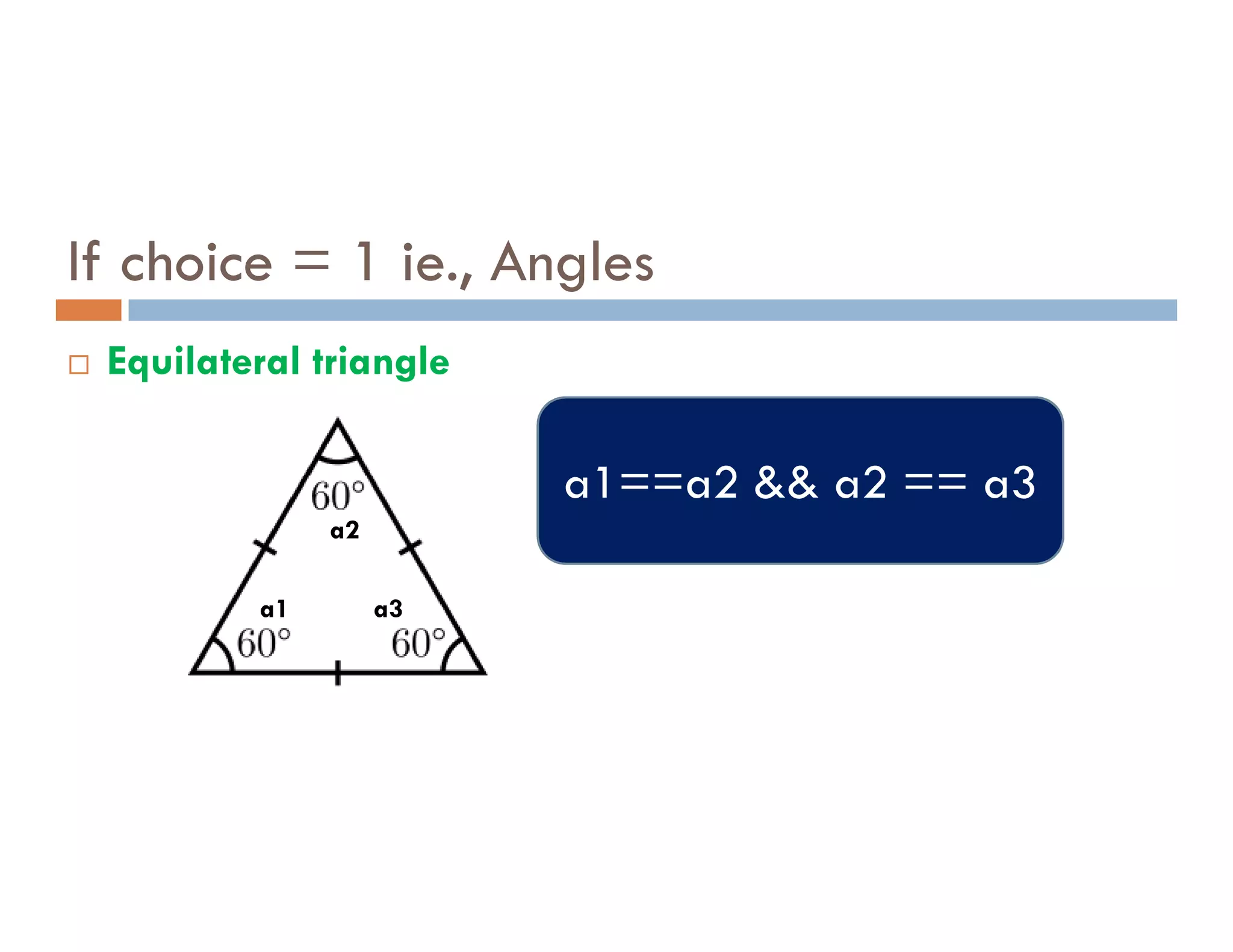
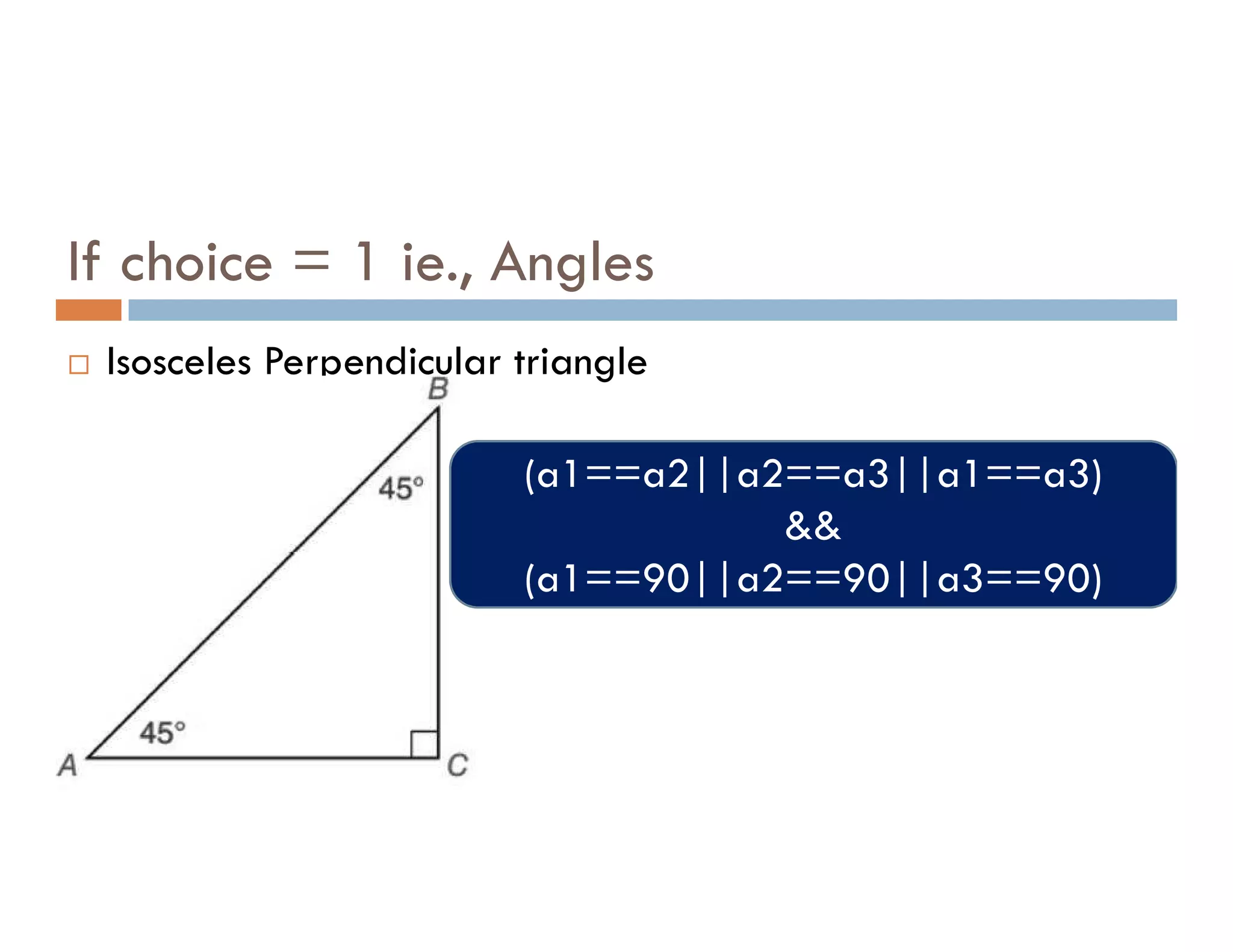
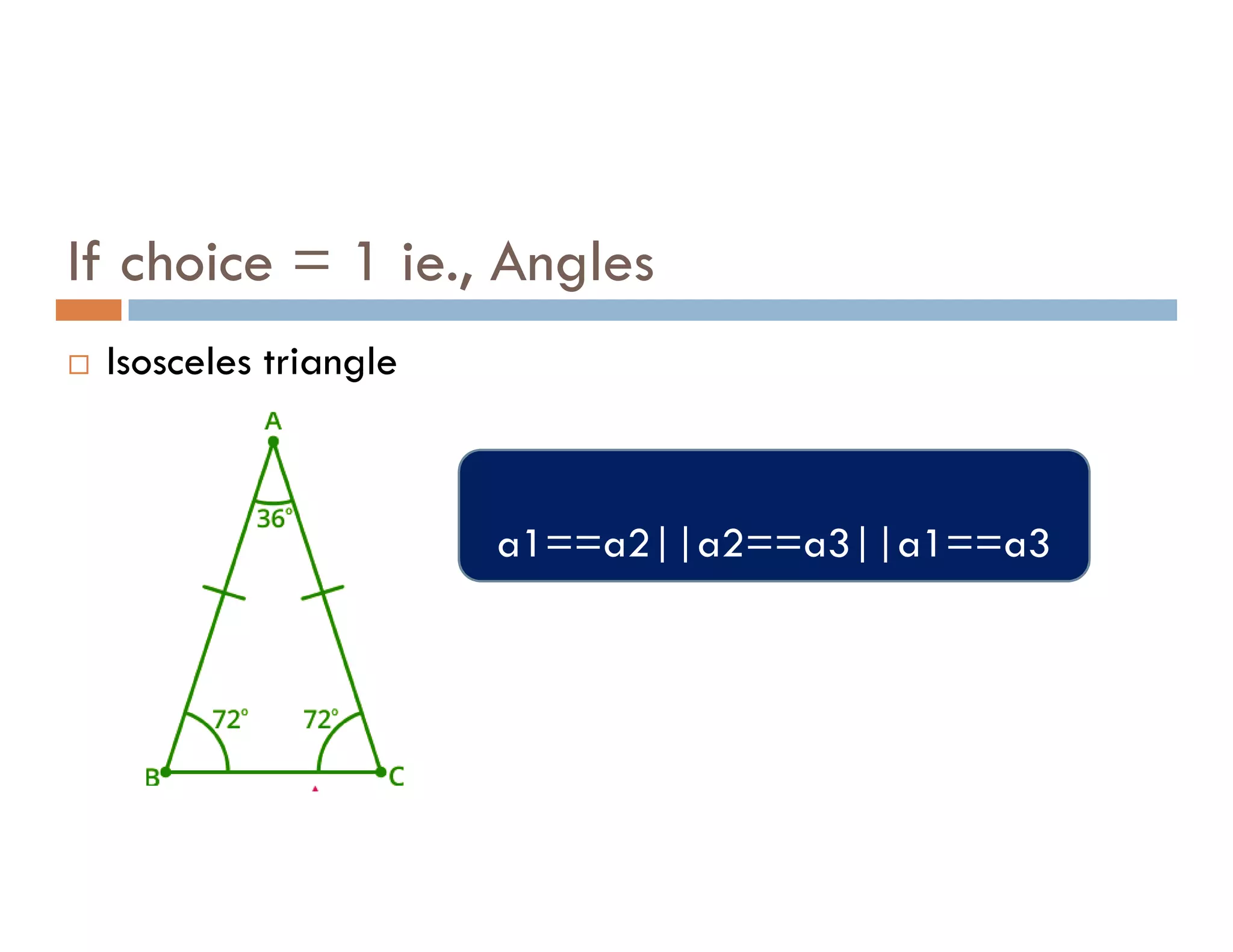
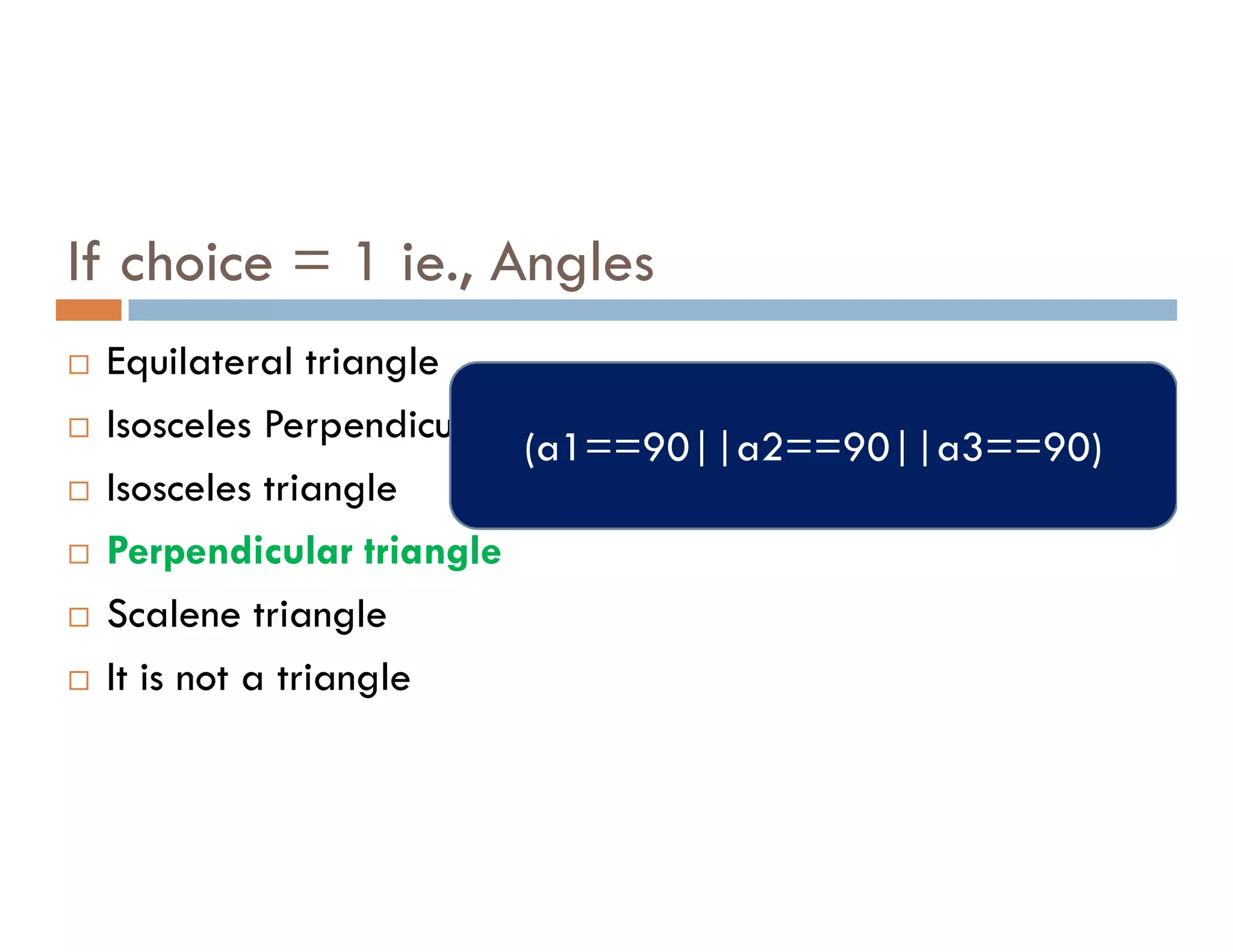
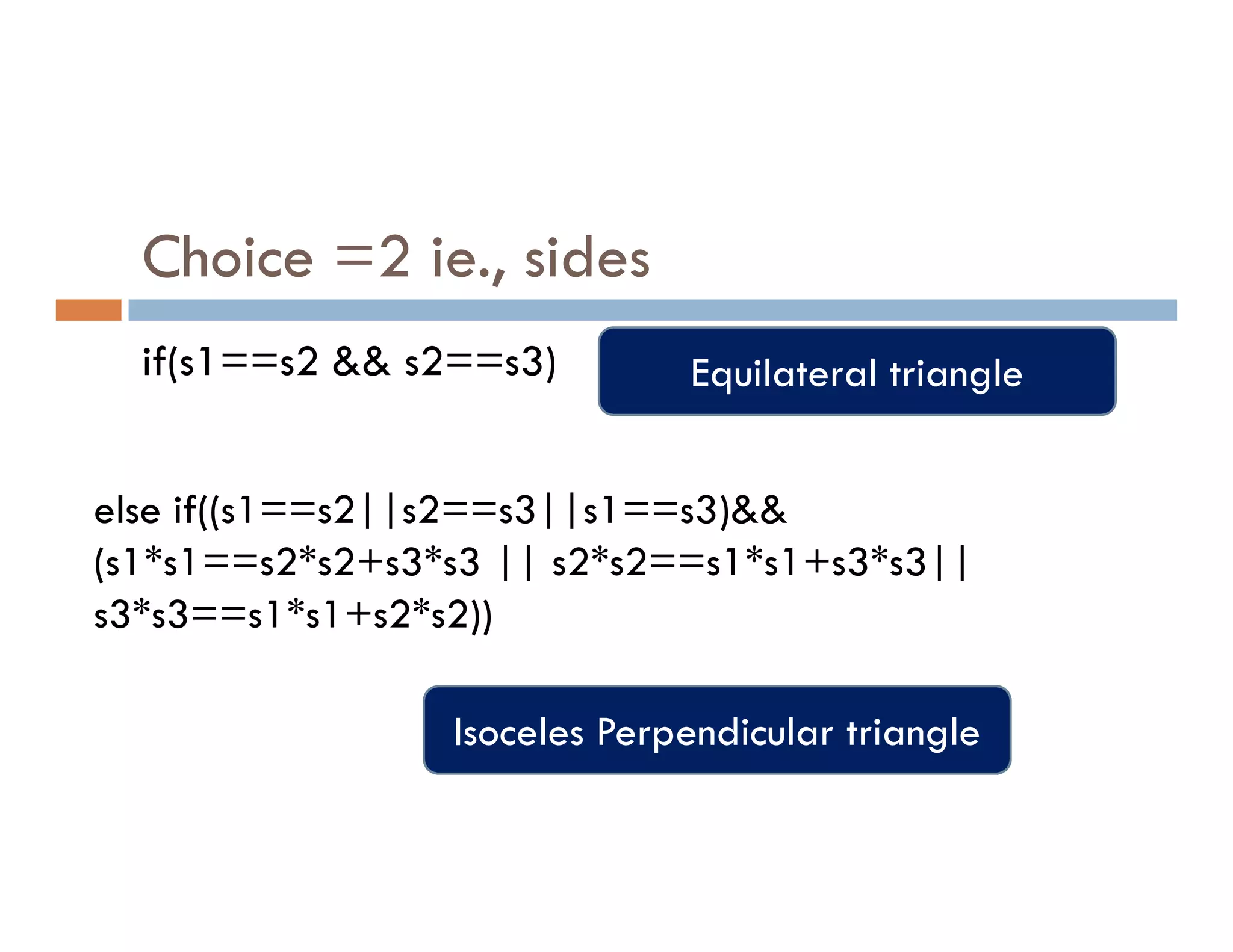
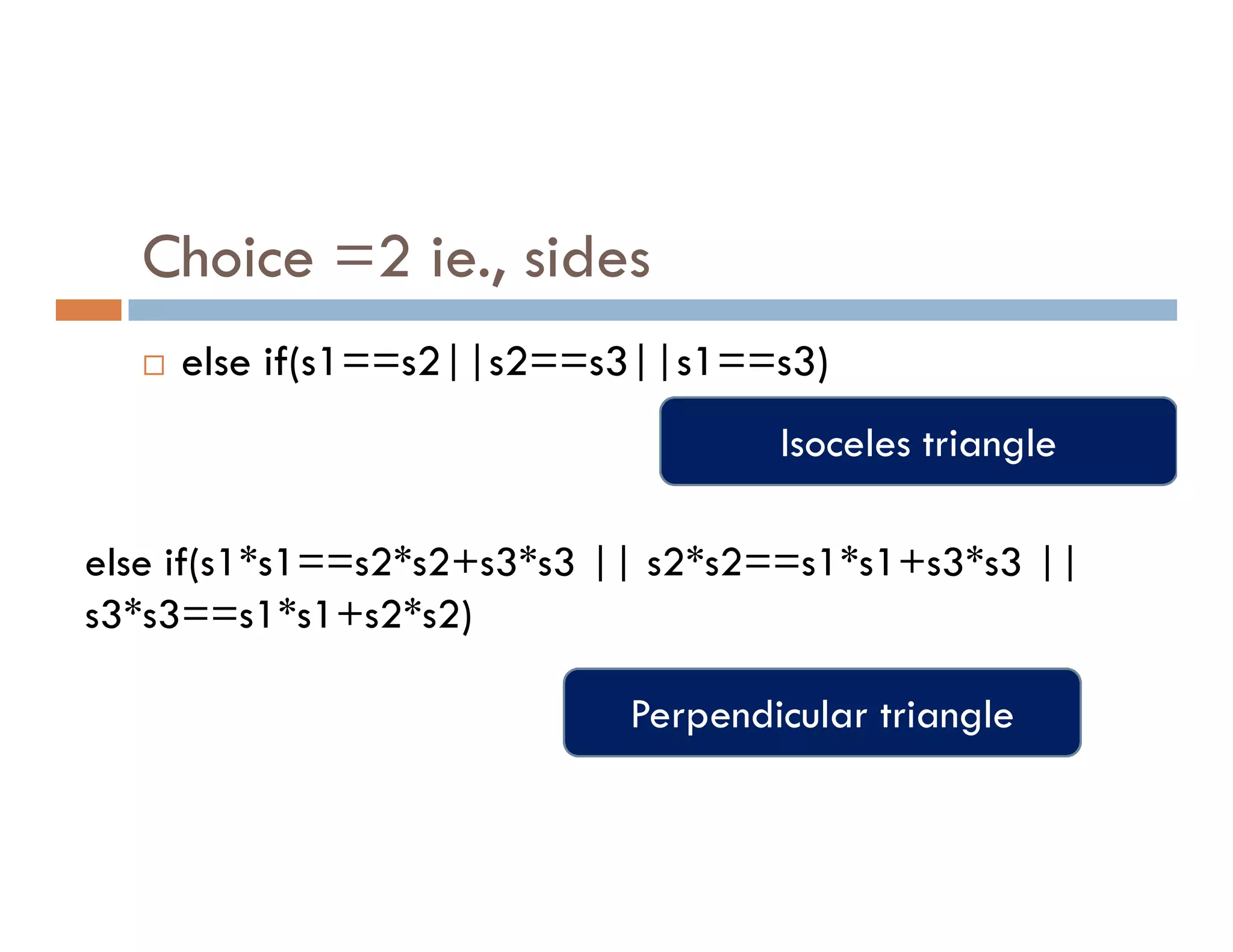
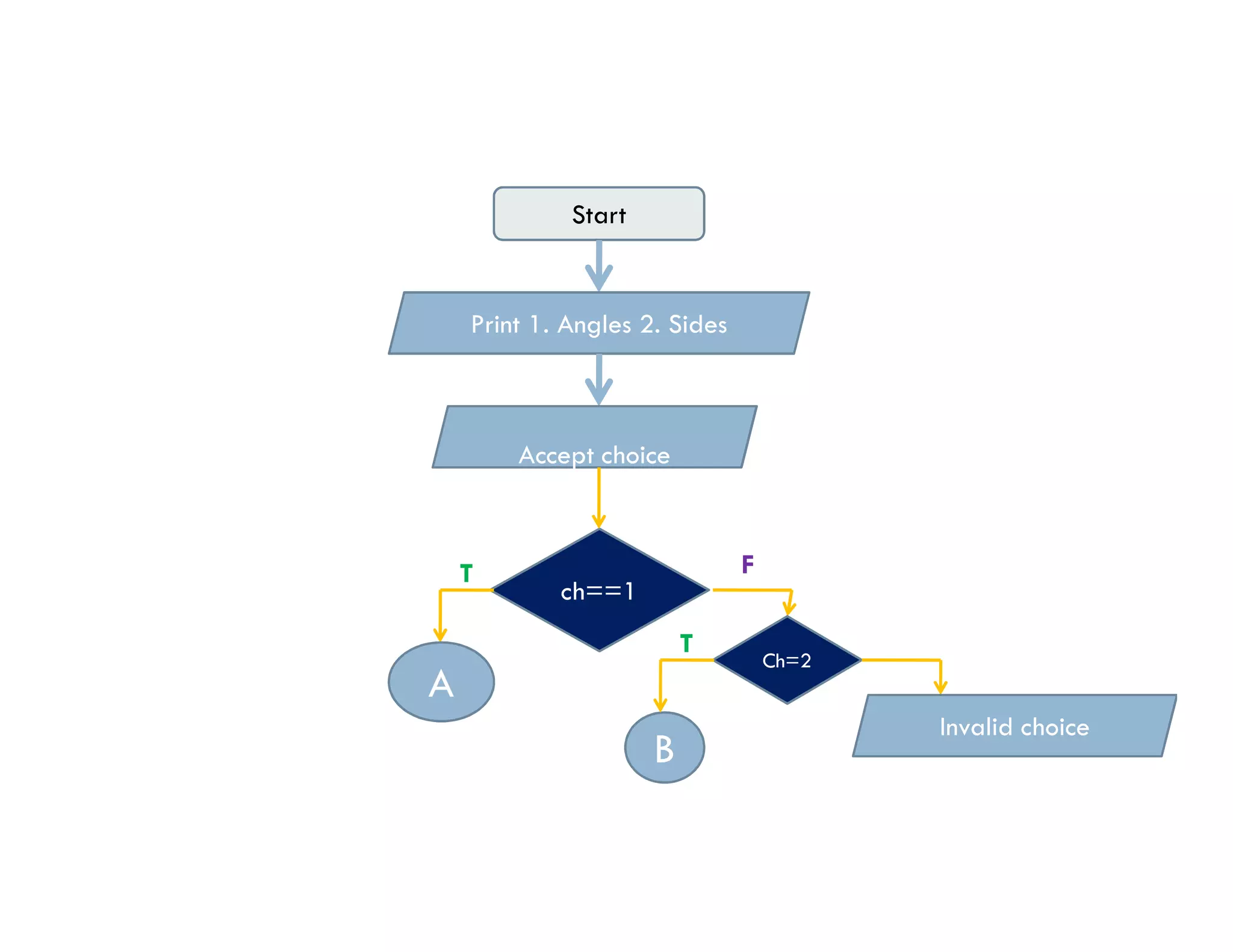
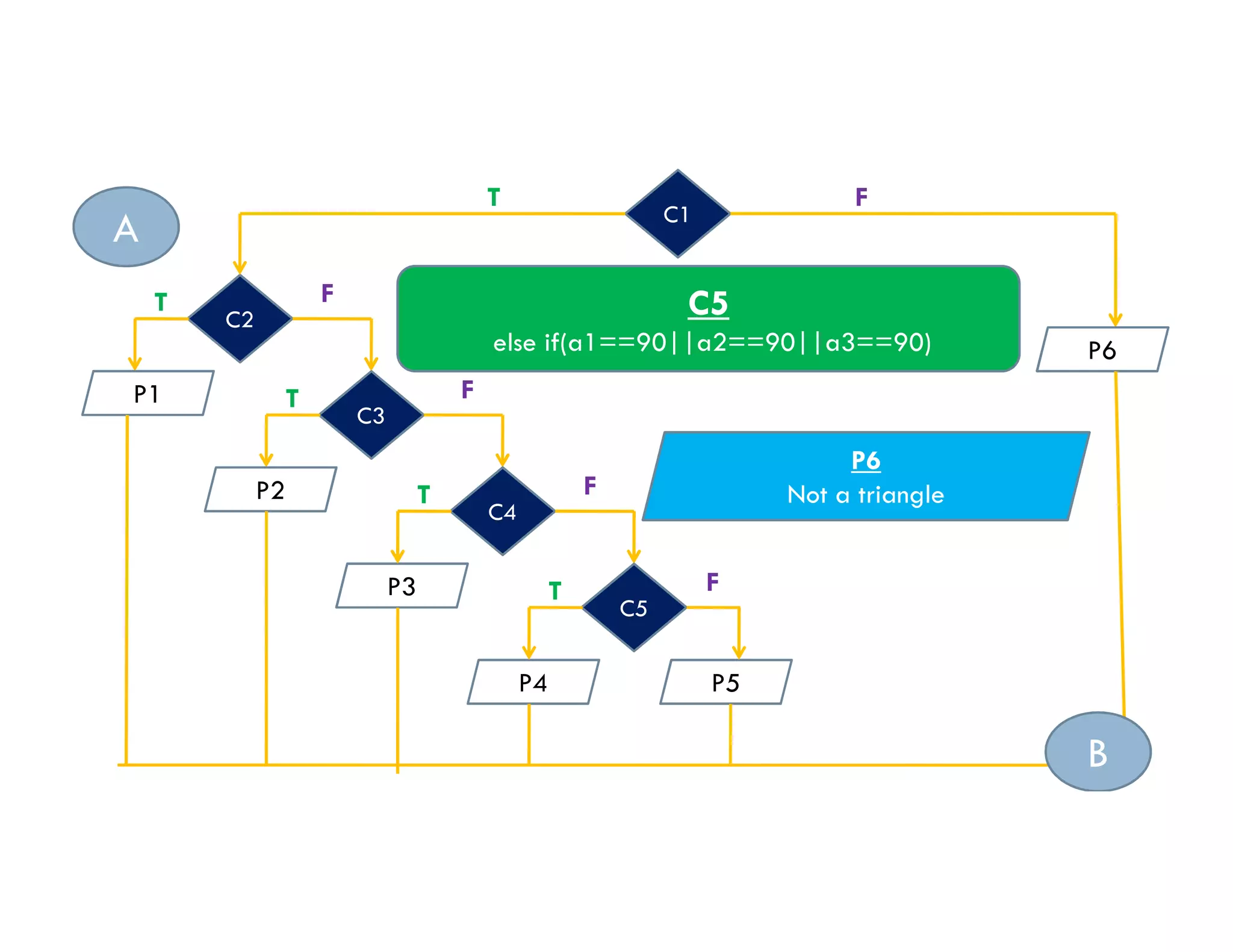
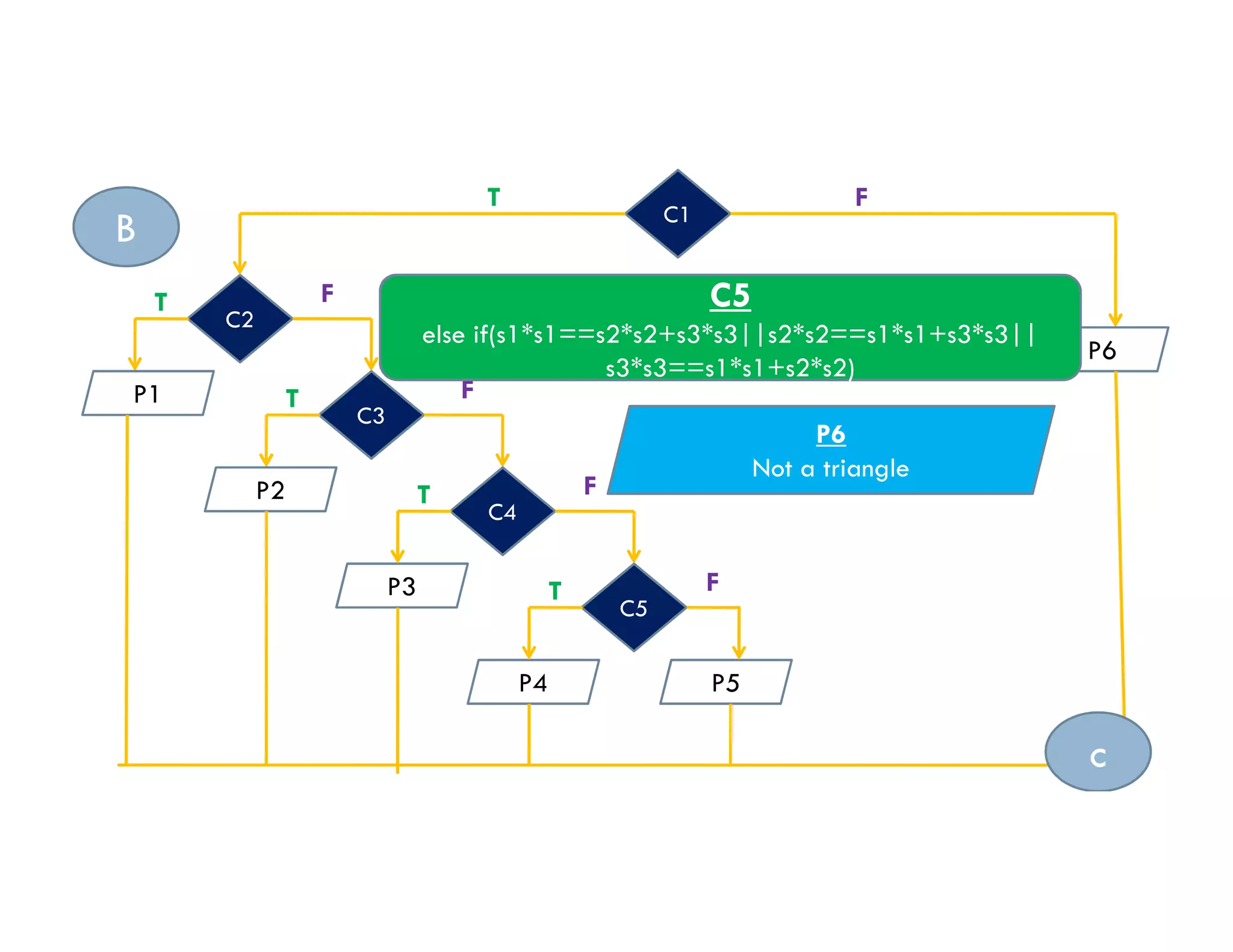
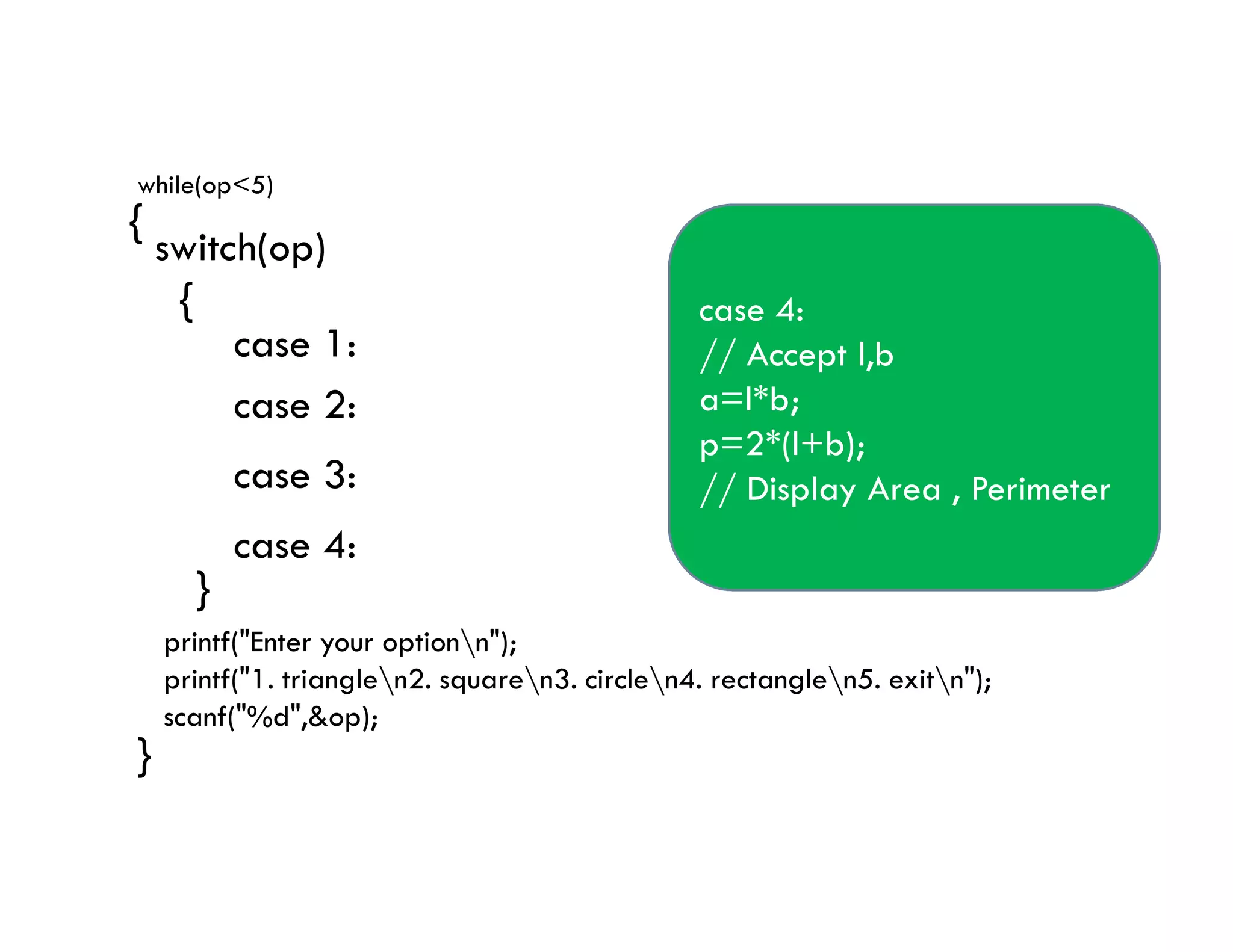
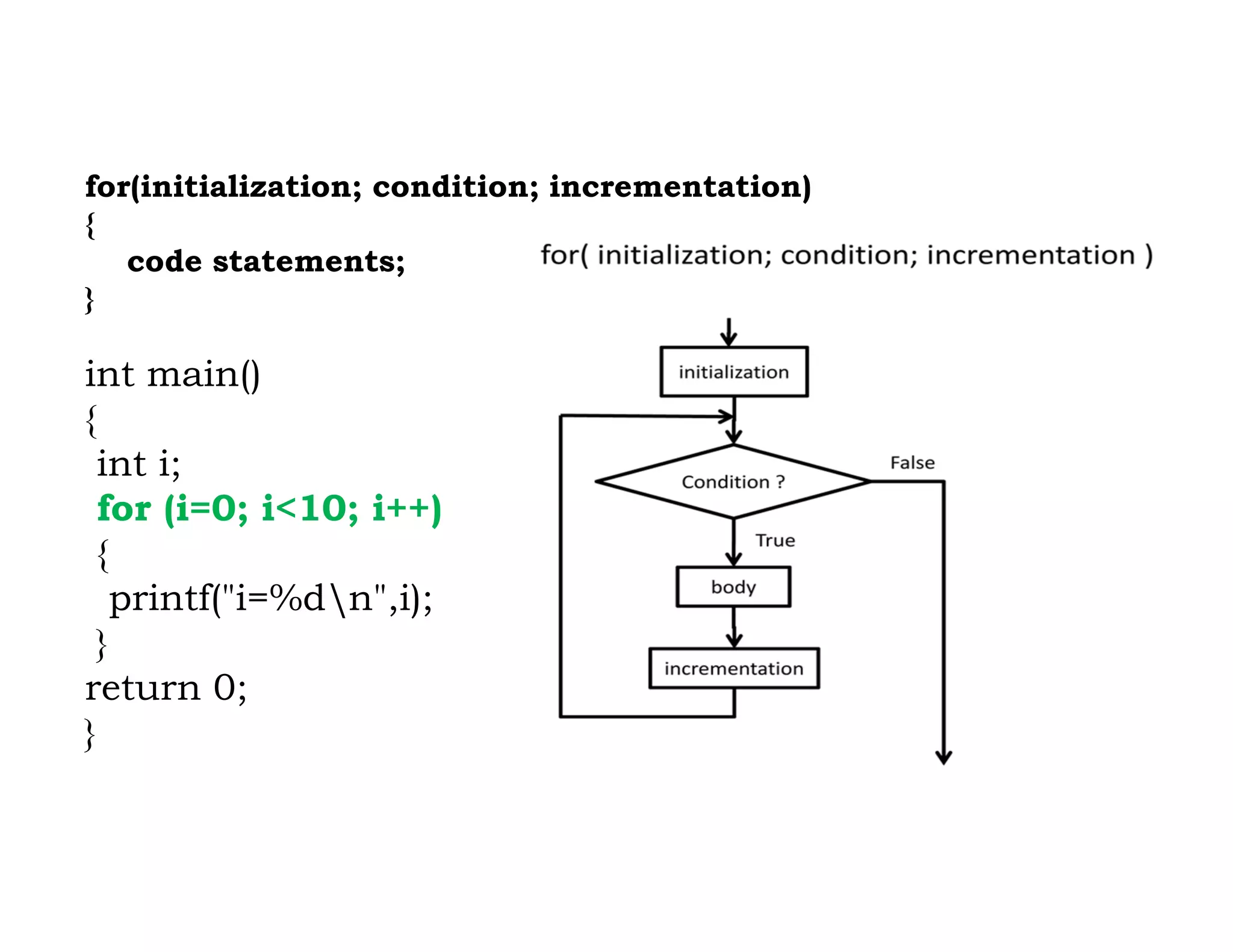
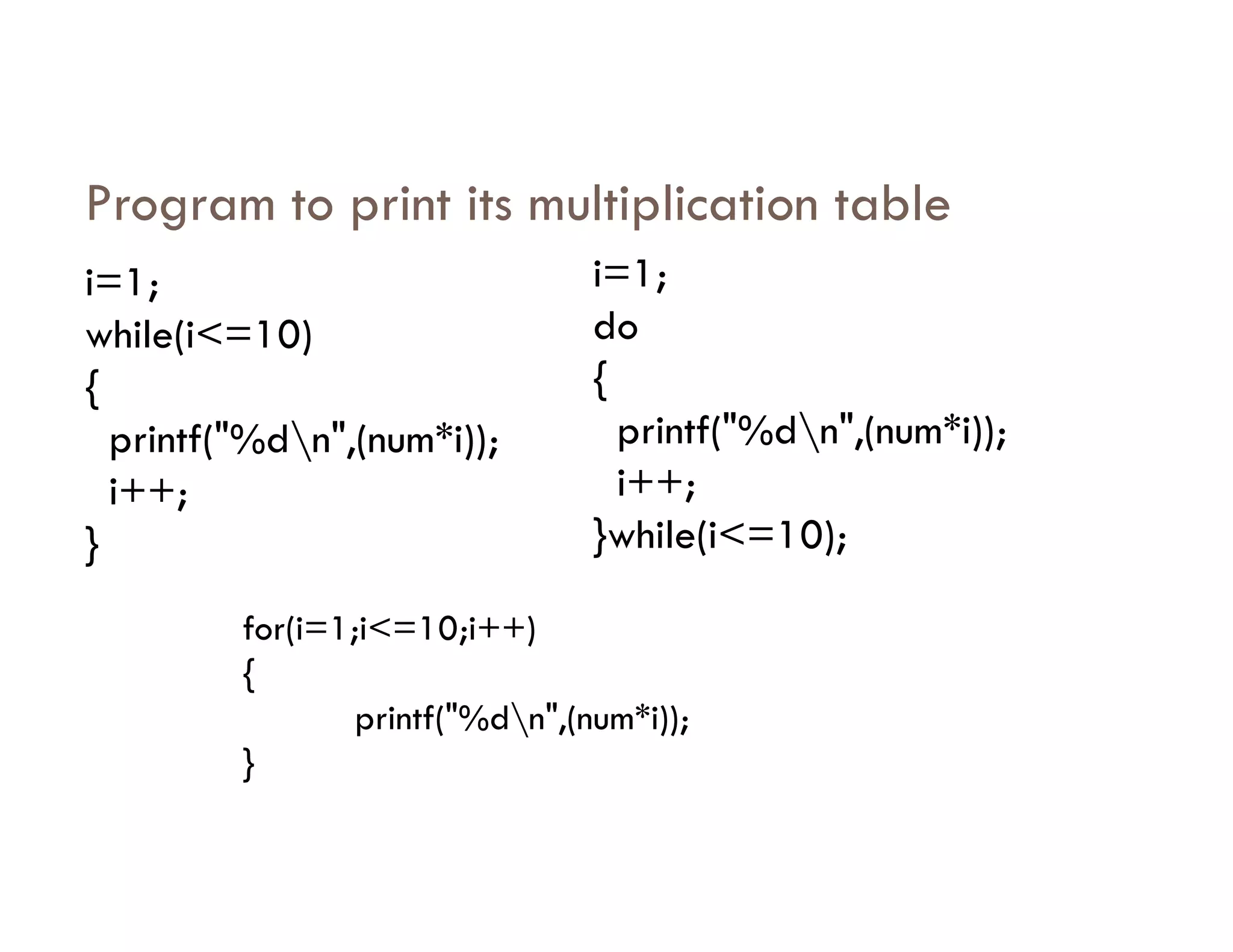
The document summarizes topics covered in a programming for problem solving (PPS) class, including control structures like if/else statements, loops, and switch cases. Example programs are provided to find the largest of three numbers, determine if a character is a vowel or consonant, and identify the type of triangle based on angle or side lengths. The last example uses nested if/else and switch statements to classify triangles as equilateral, isosceles, right-angled, or scalene depending on the problem constraints.




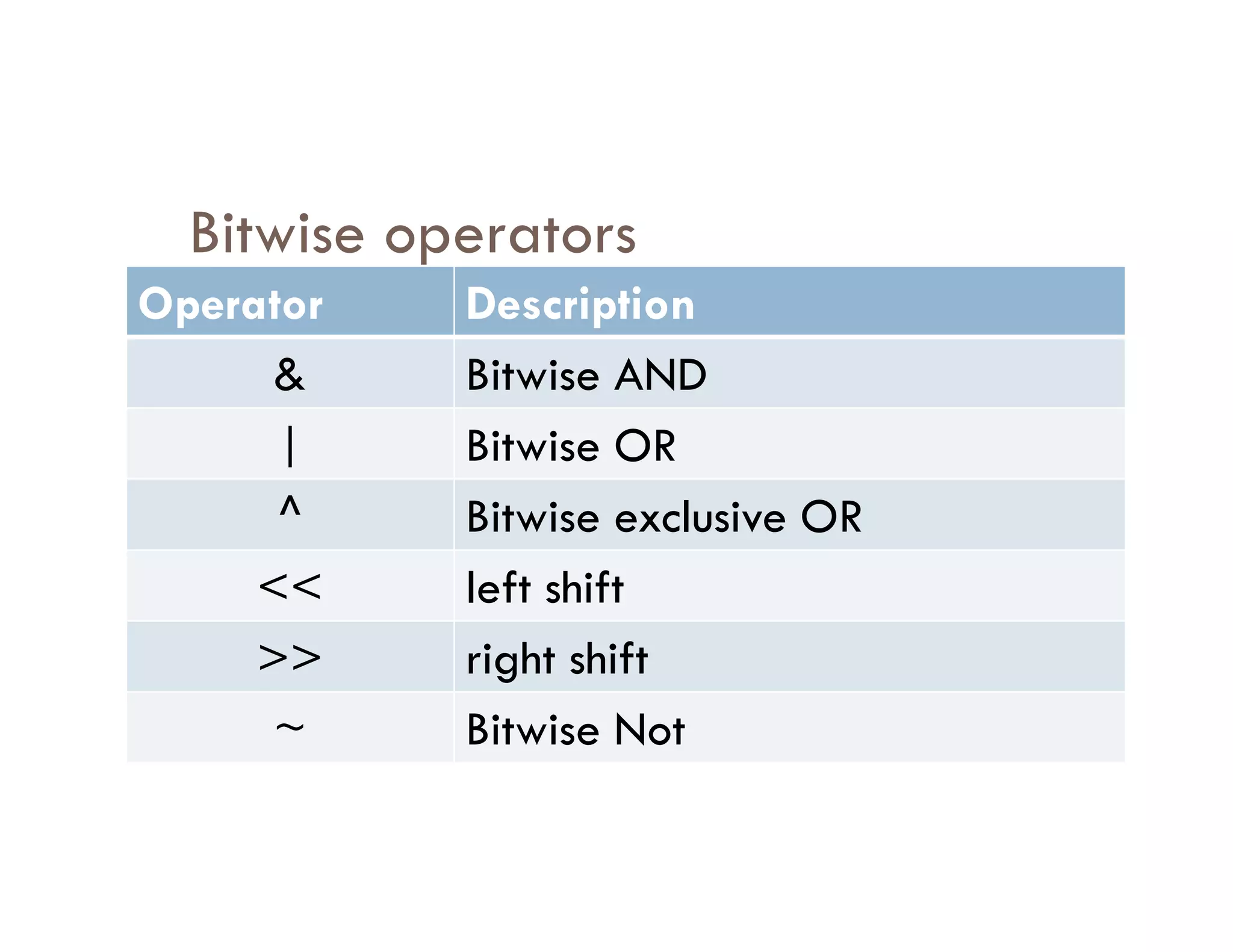
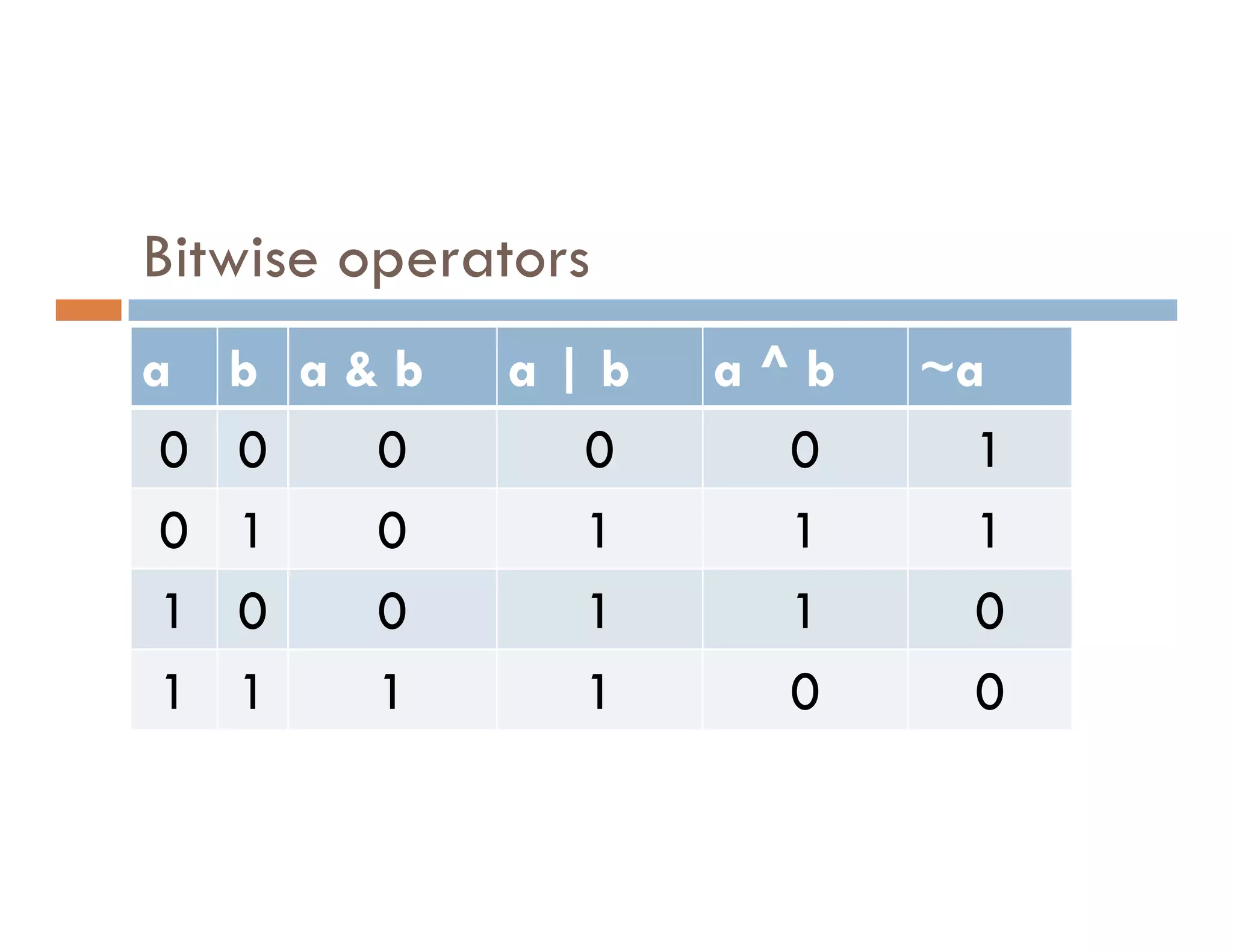


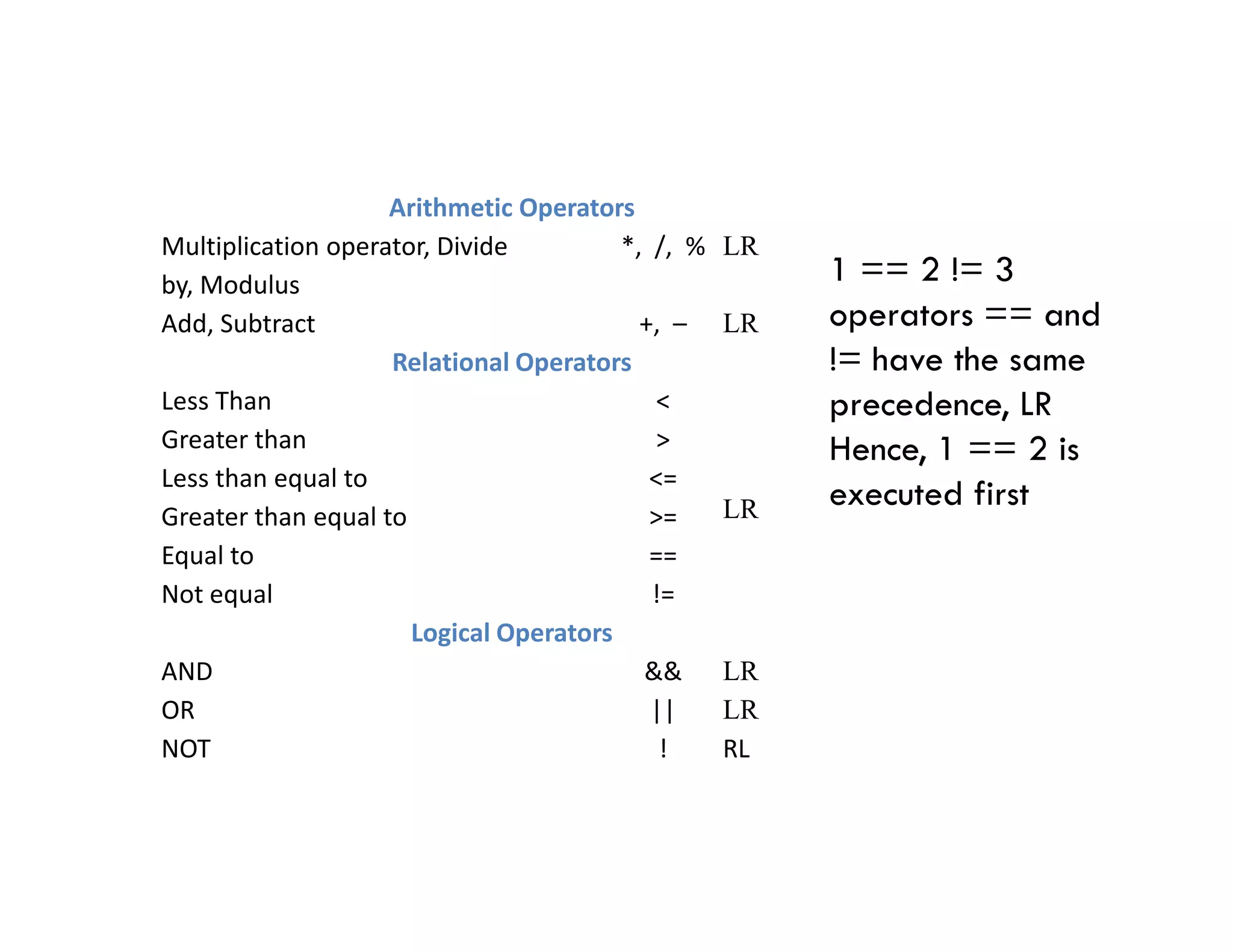
![Operator Description Associativity
()
[ ]
.
Parentheses (grouping)
Brackets (array subscript)
Member selection
Member selection via pointer
LR
++ --
+ -
Unary preincrement/predecrement
Unary plus/minus
+ -
! ~
(type)
*
&
sizeof
Unary plus/minus
Unary logical negation/bitwise
complement
Unary cast (change type)
Dereference
Address
Determine size in bytes
RL
= Assignment operator](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pps06dec2022updated-221205110938-180e2bea/75/Programming-for-Problem-Solving-14-2048.jpg)






































![Accept name from the user
Method 1
char name[20];
printf("Enter your name:");
Method 2
char name[20]
printf(“Enter your name:”)
printf("Enter your name:");
scanf("%s",name);
printf("Your name is: %s",name);
printf(“Enter your name:”)
gets(name);
printf(“Your name is:”);
puts(name);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pps06dec2022updated-221205110938-180e2bea/75/Programming-for-Problem-Solving-79-2048.jpg)
![Accept name from the user
Method 3
#define MAX_LIMIT 20
int main()
Method 4
char name[20];
printf("Enter your name:");
int main()
{
char name[MAX_LIMIT];
printf("Enter your name:");
fgets(name,MAX_LIMIT,stdin);
printf("Your name is: %s",name);
printf("Enter your name:");
scanf("%[^n]%*c",name);
printf("Your name is: %s",name);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pps06dec2022updated-221205110938-180e2bea/75/Programming-for-Problem-Solving-80-2048.jpg)