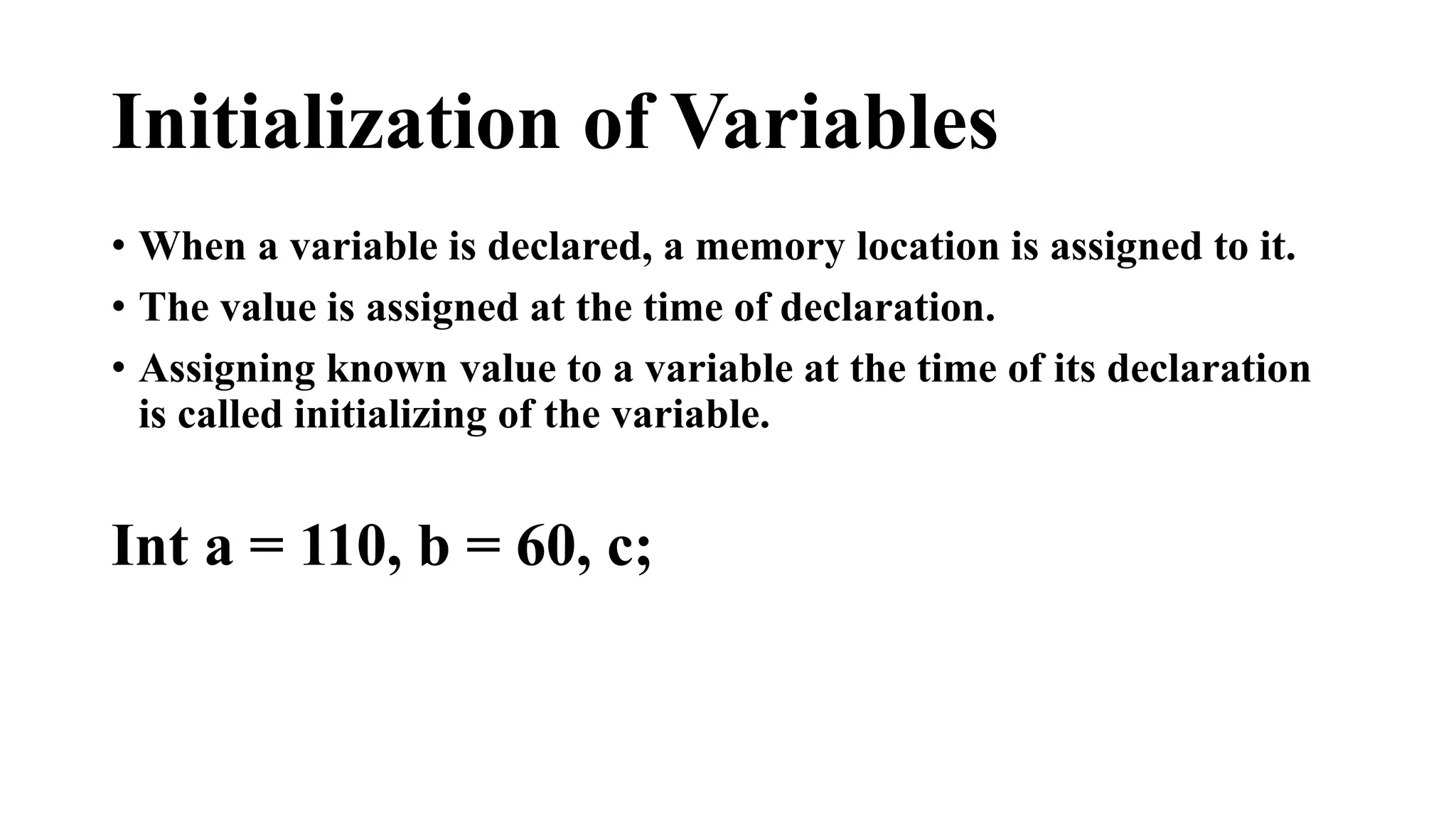
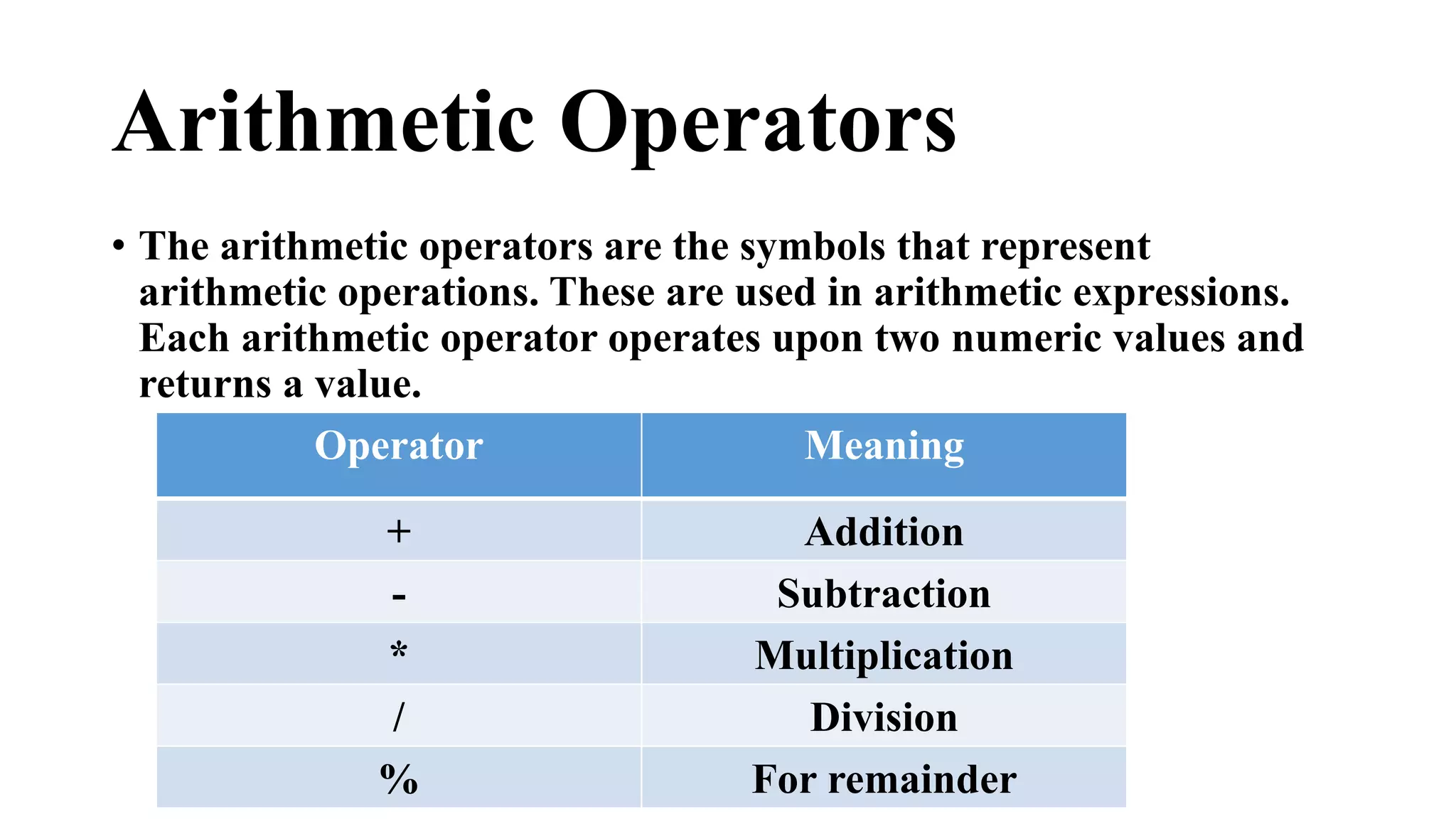
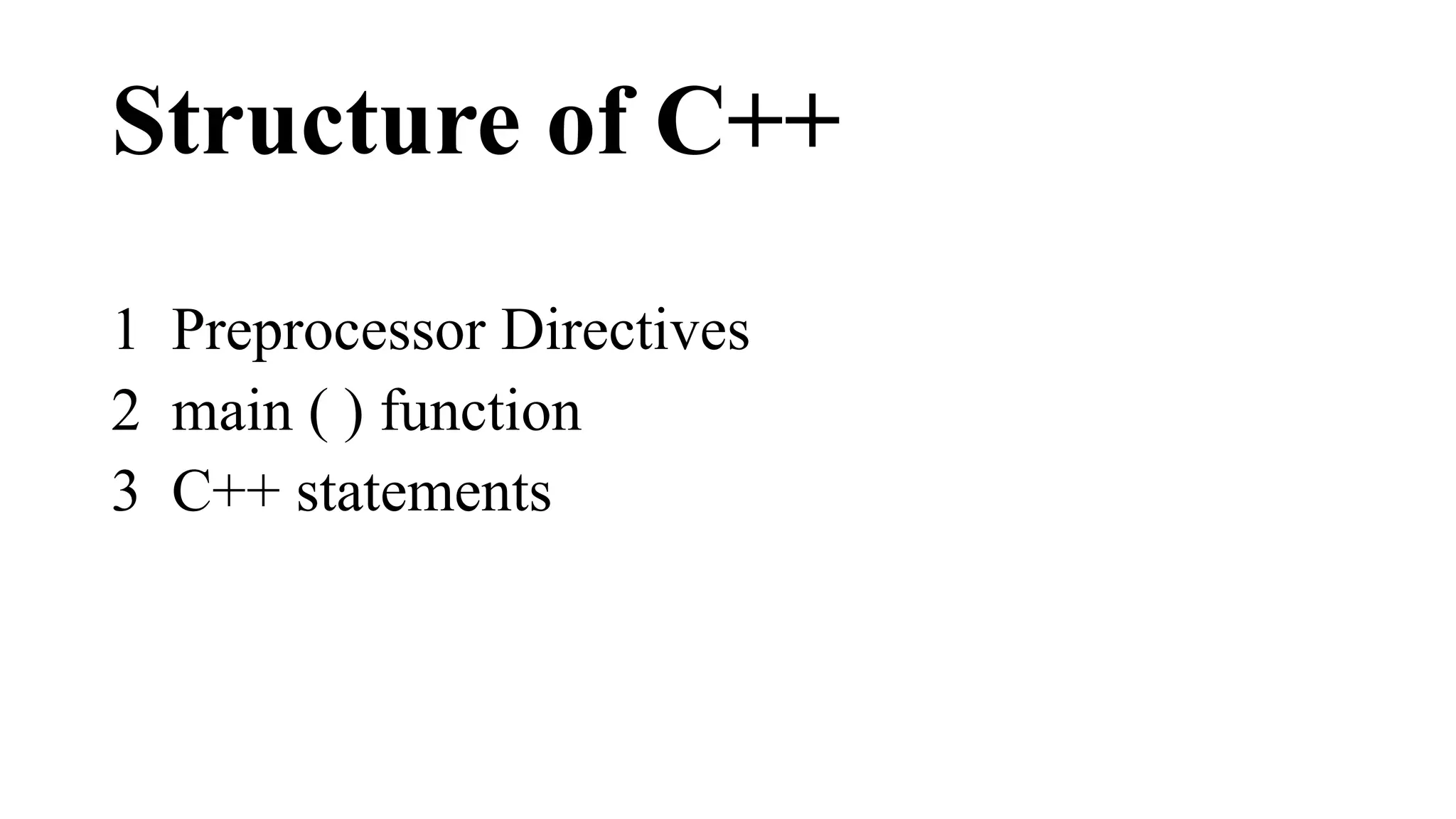
This document provides an overview of programming fundamentals and the history and structure of C++ programming. It discusses how BCPL and B led to the development of C in 1972. C++ was then created in the 1980s as an extension of C to support object-oriented programming. The document outlines the structure of a C++ program, including the preprocessor, main function, statements, variables, data types, and arithmetic operators. It also describes how a C++ program is compiled from source code to an executable file.











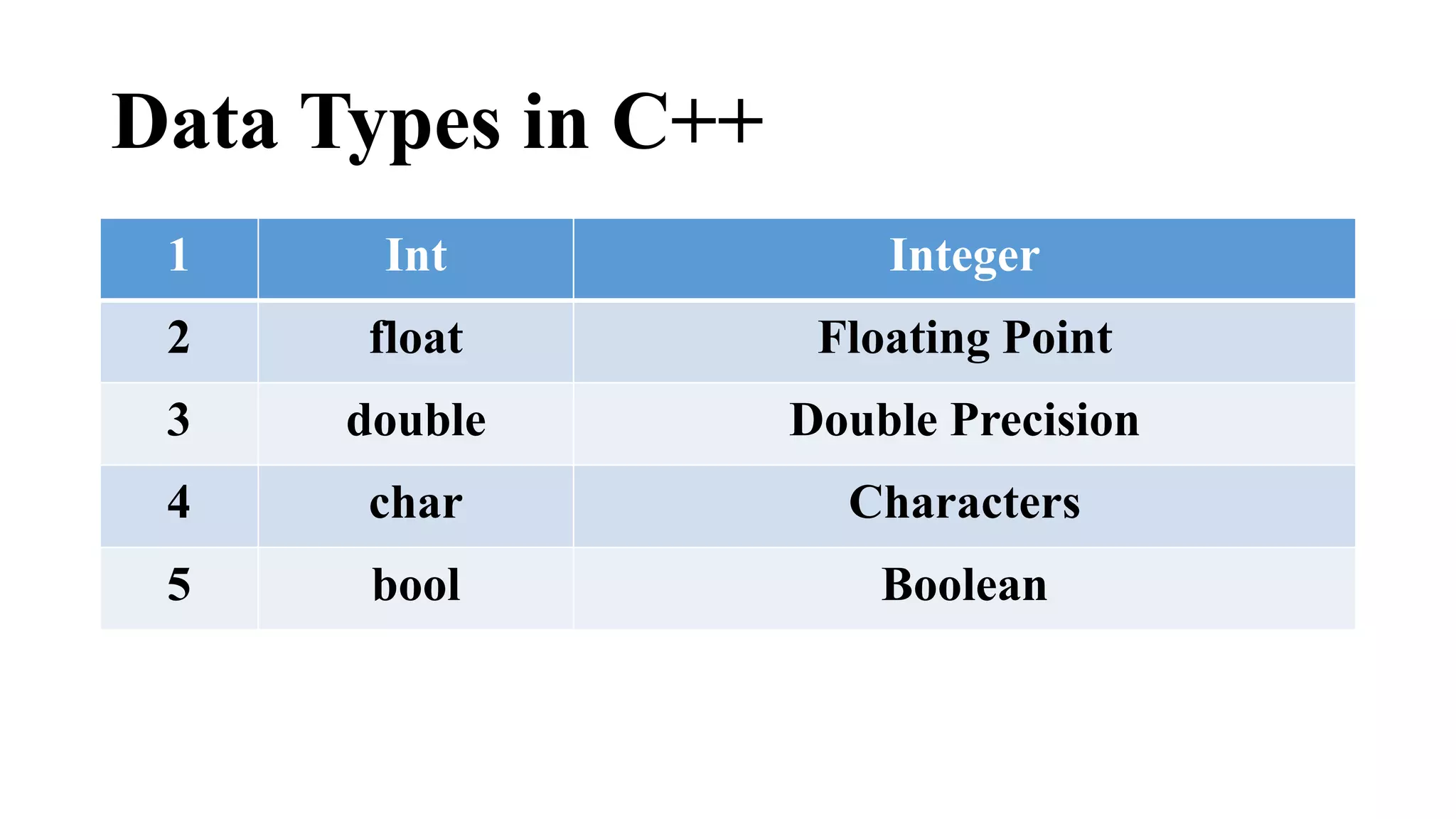
![Declaration of Variables
• Assigning the name and data type that a variable can hold is called the declaration
of the variable.
• All variables that are used in a program are declared using variable declaration
statement.
• Syntax :
• Type list of variables;
Type = int, float etc
Variables = abc, xyz, s,e etc
Int abc, xyz, d, s;
float b;
char num [15];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pfslidelectureno-141122071922-conversion-gate01/75/Programming-Fundamental-Slide-lecture-no-2-Section-E-14-2048.jpg)