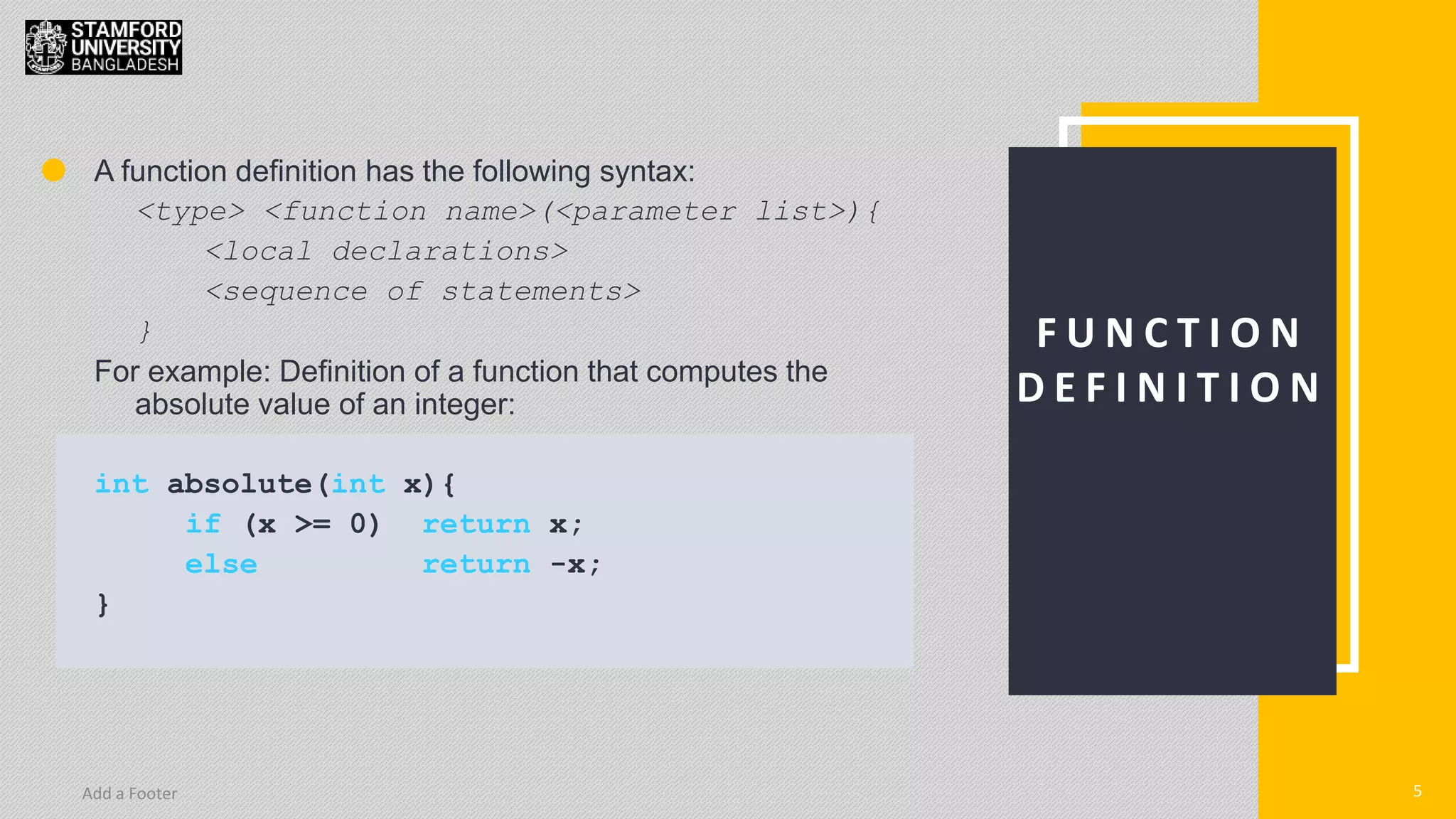
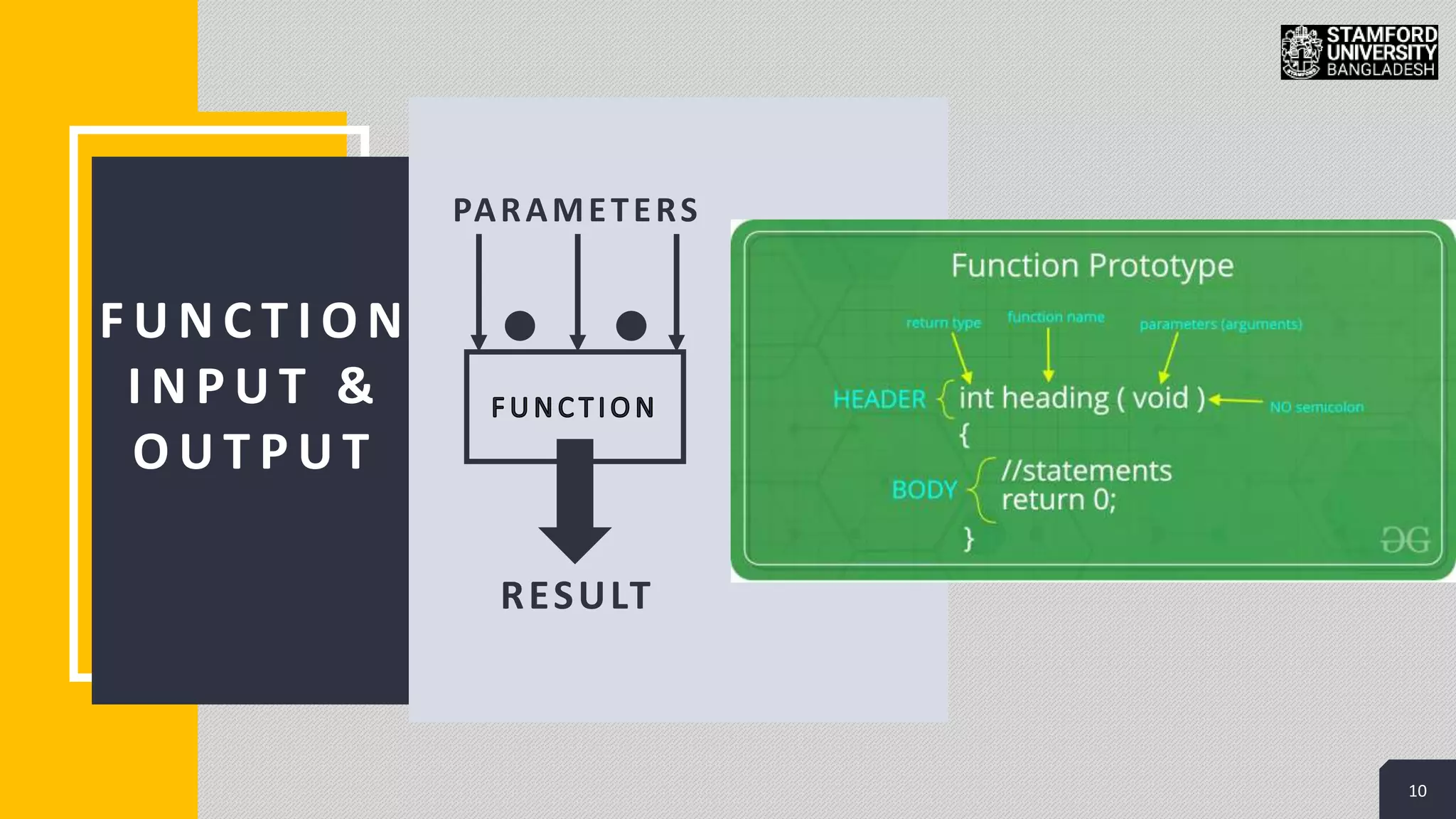
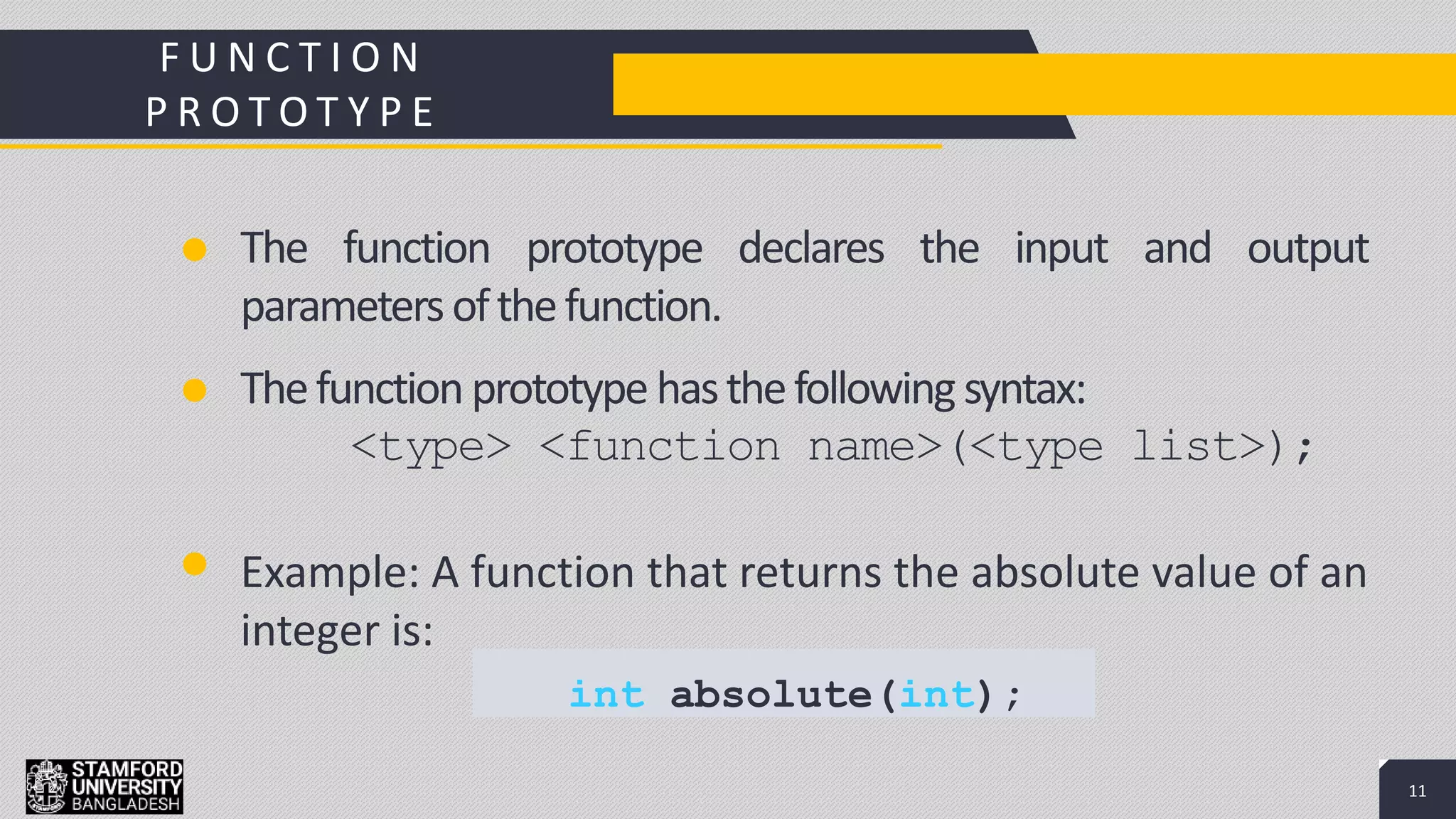
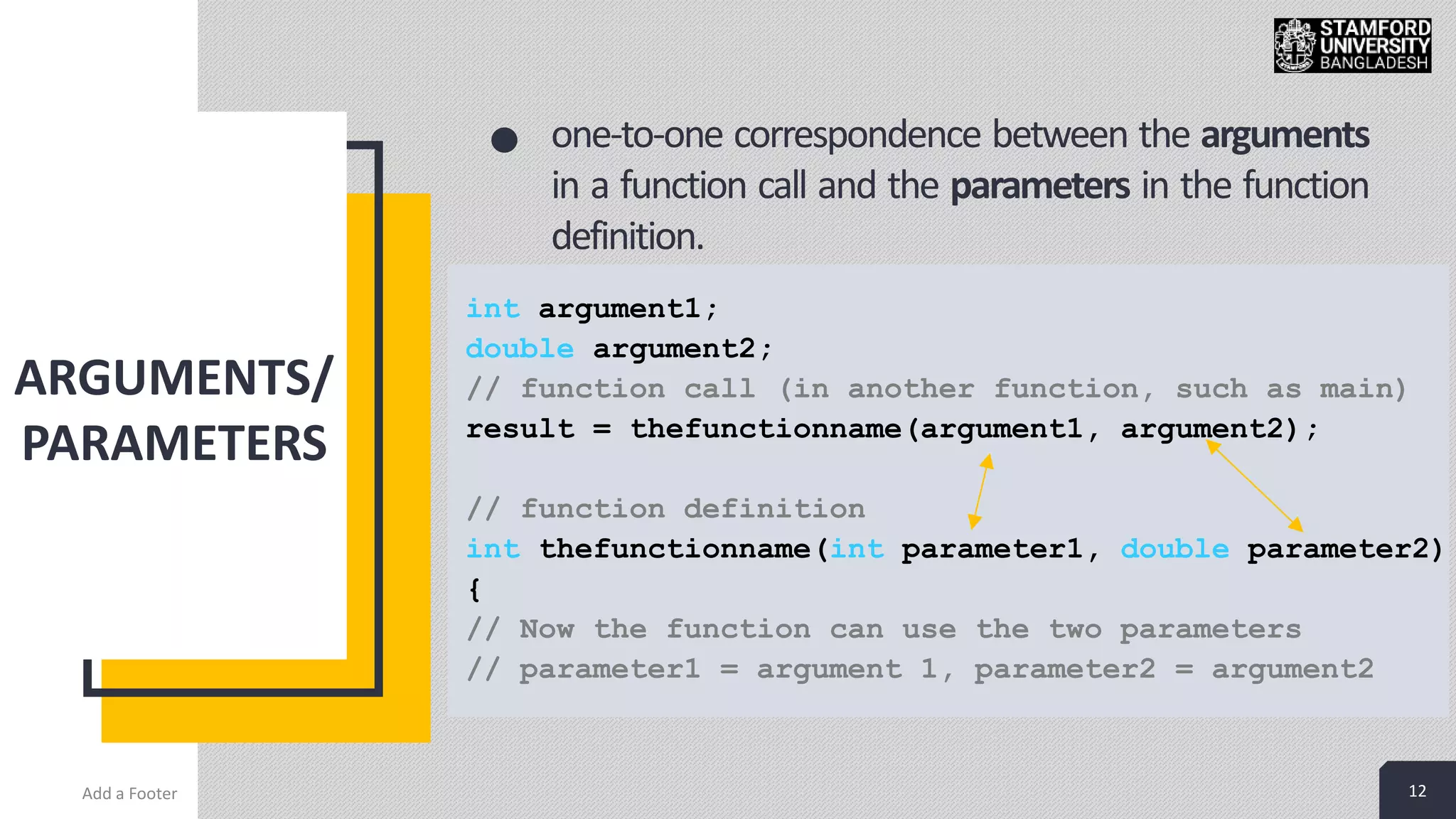
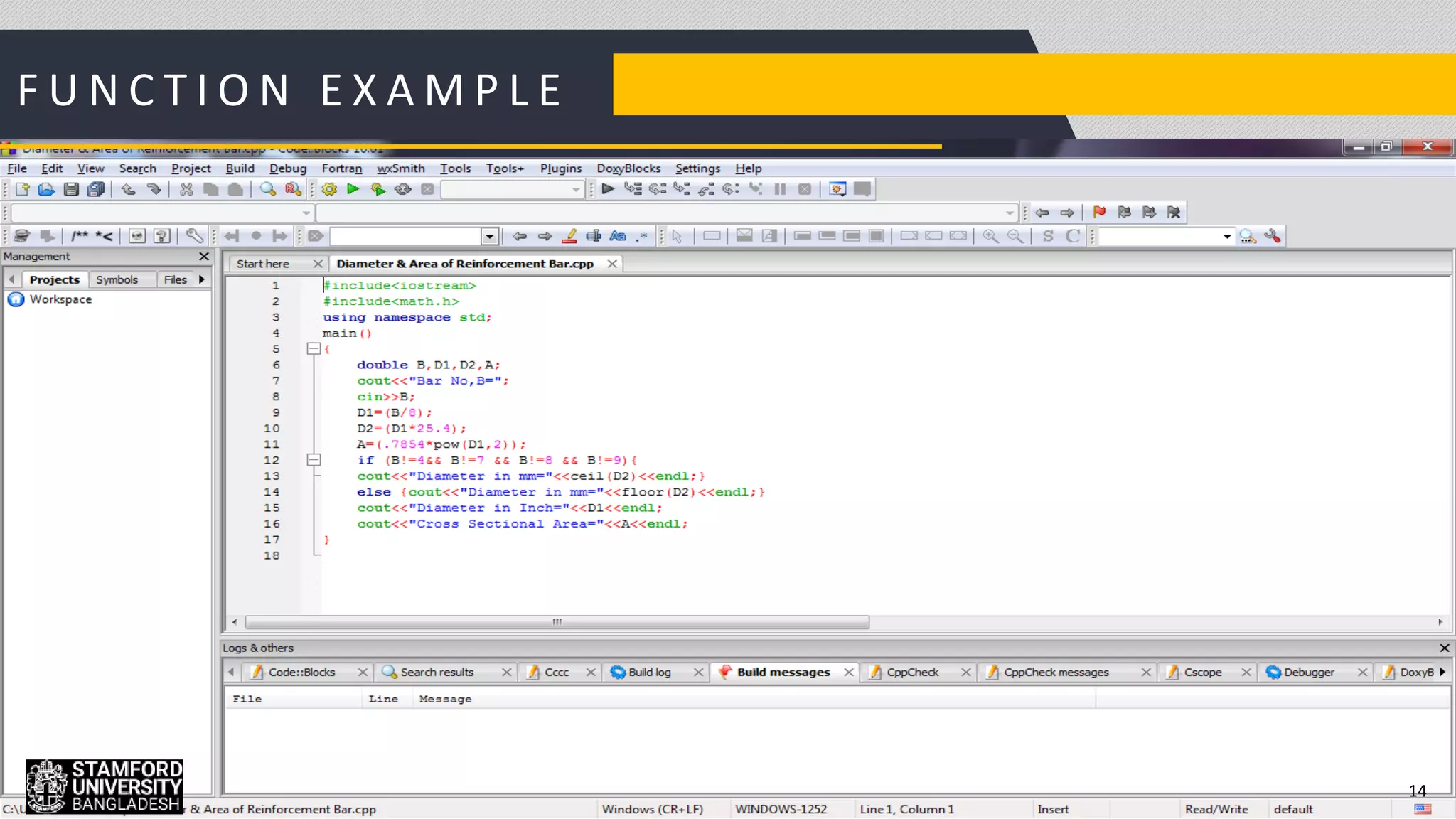
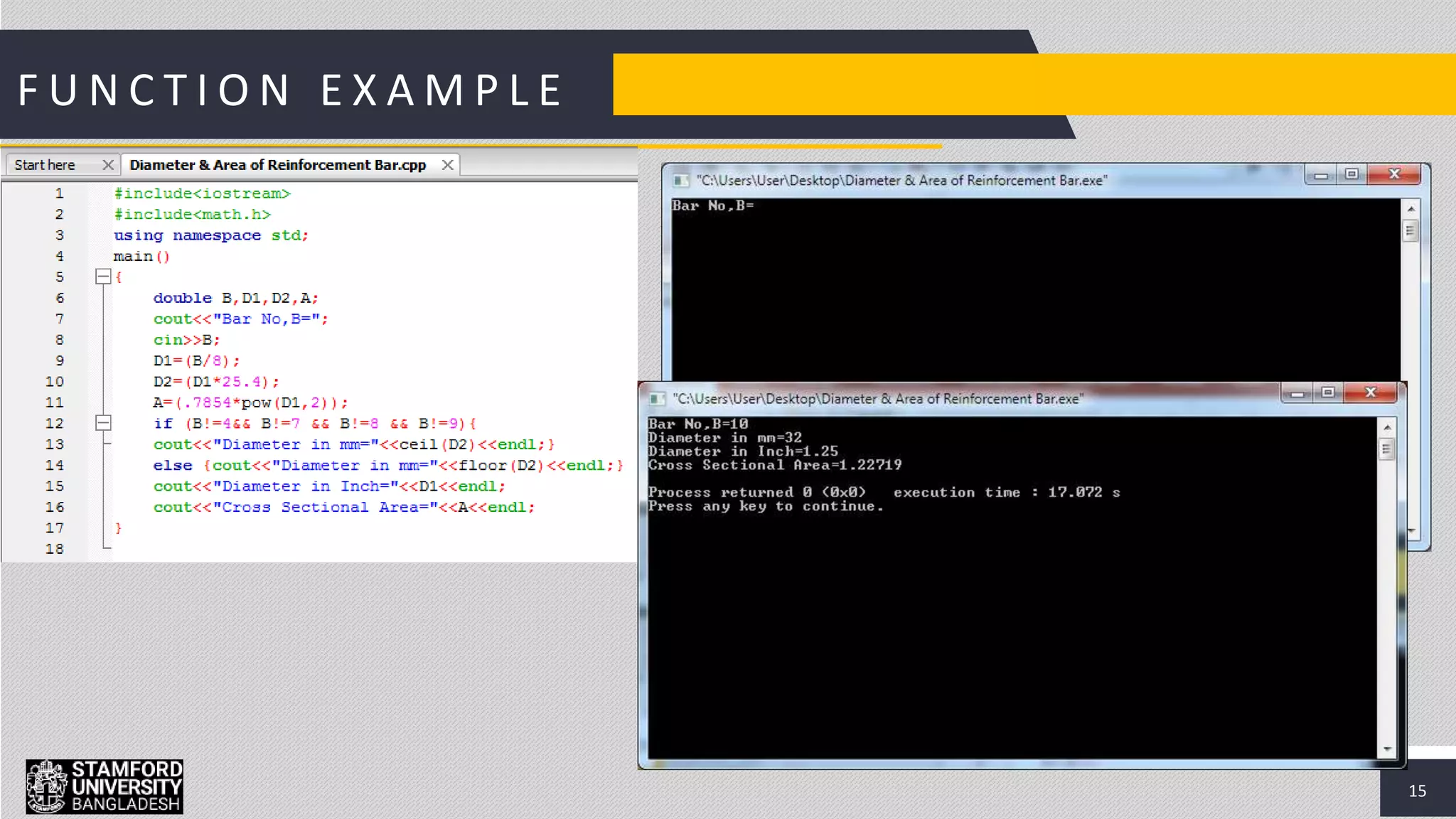
This document discusses functions in C/C++ programming. It explains that functions allow complex problems to be broken down into smaller parts or tasks. Functions separate the concept or logic of a program from its implementation. They make programs easier to understand and allow code to be reused by calling the same function multiple times. The document also covers function definitions, prototypes, parameters, arguments, return types and provides examples of built-in library functions.