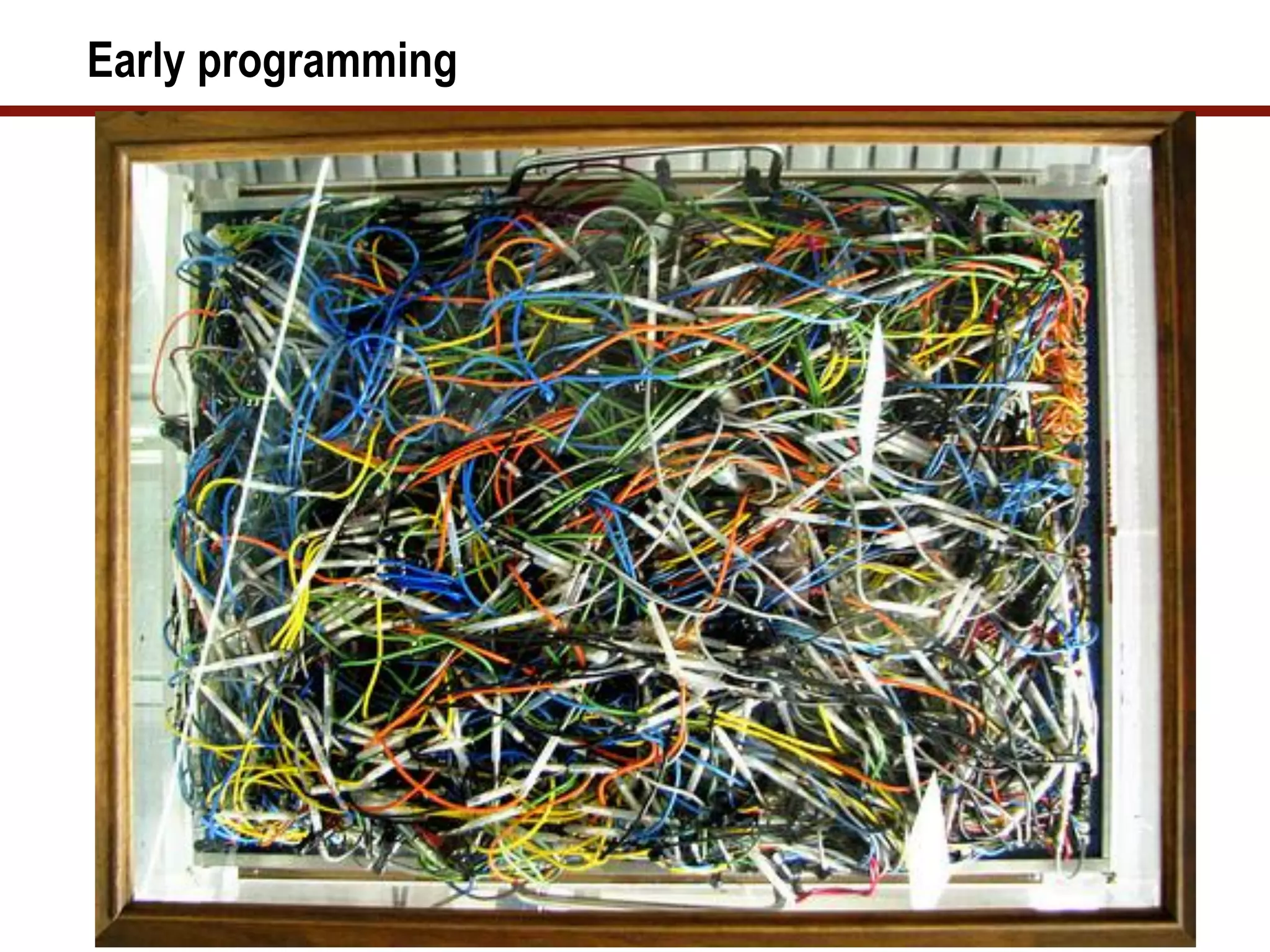
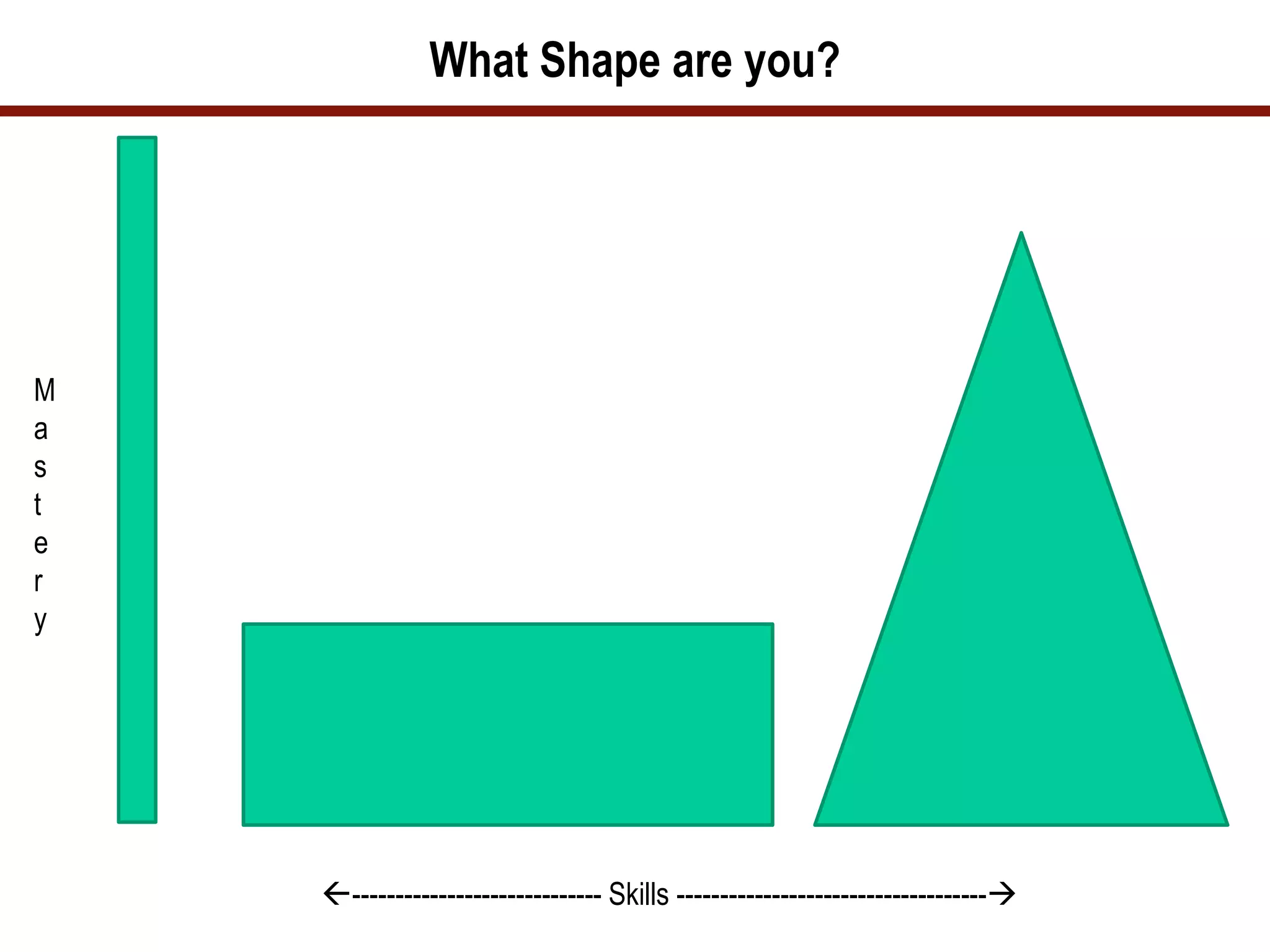
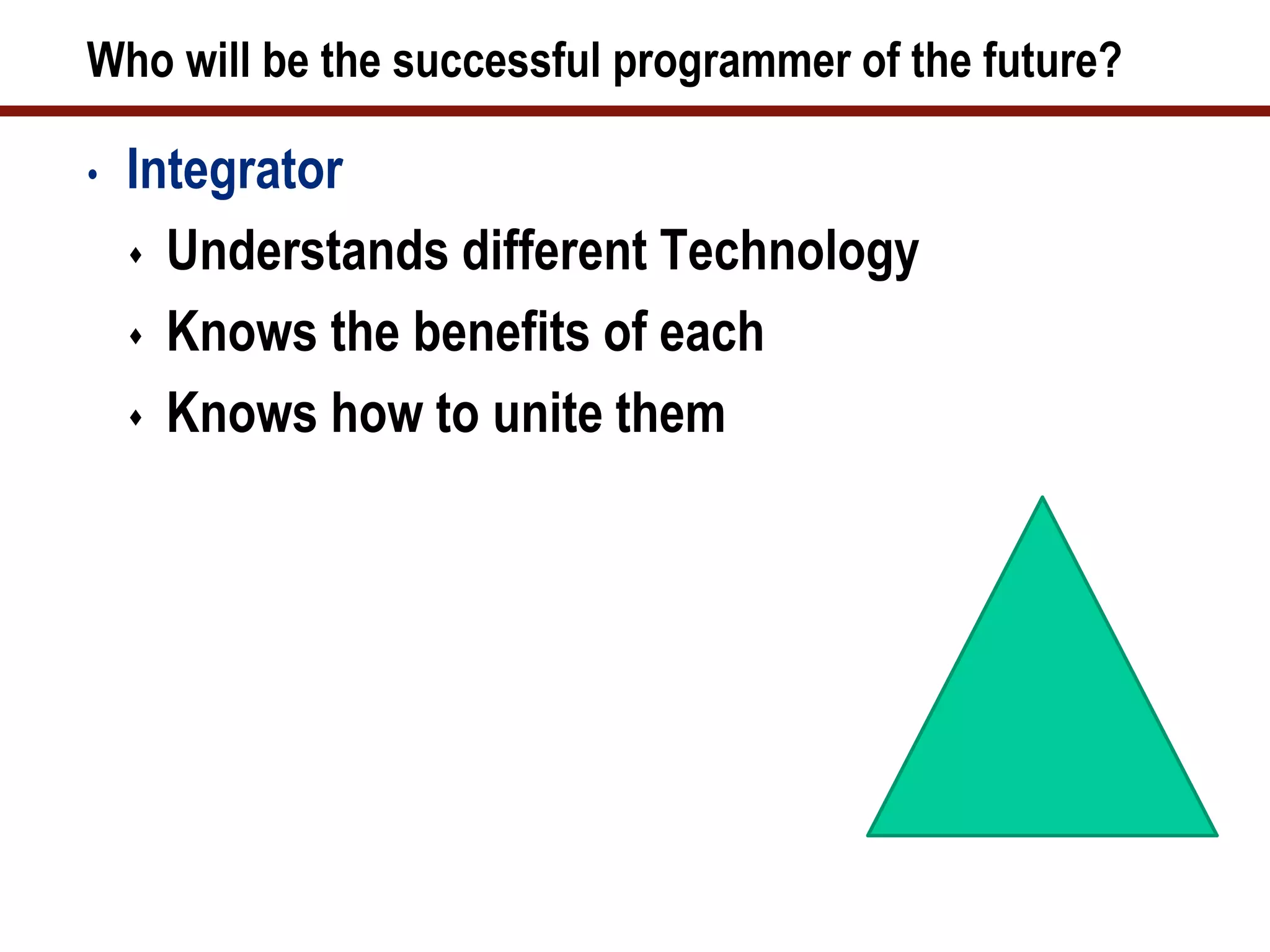
The document provides a history of computer programming from the 19th century to modern times. It discusses early programming languages and machines like the Analytical Engine, ENIAC, and EDVAC. It then outlines the evolution of programming languages through each decade from the 1950s to the 2000s. The document emphasizes that programming skills require constant learning and adapting to new technologies. Successful programmers of the future will need to integrate different technologies and understand business needs.