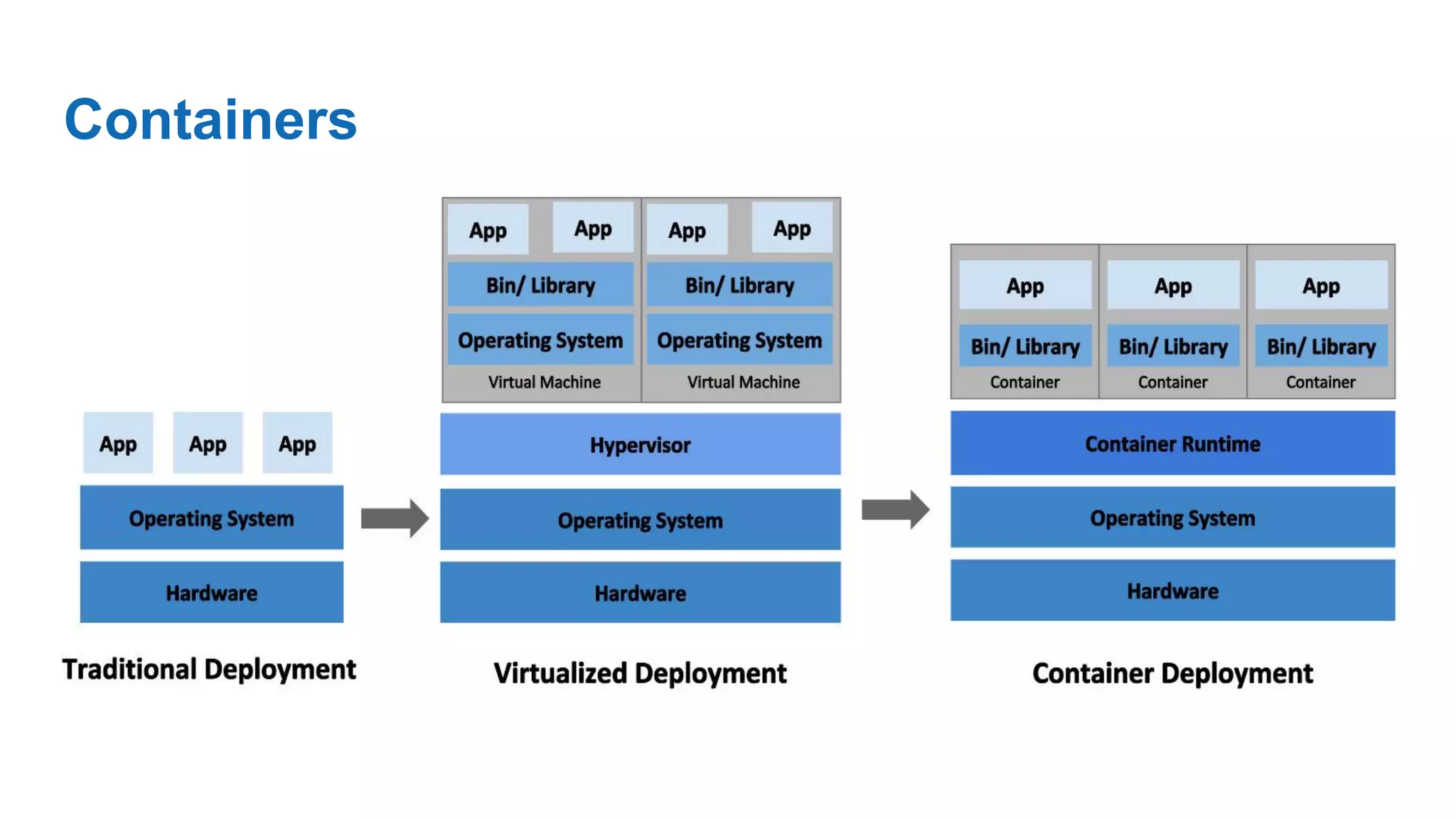
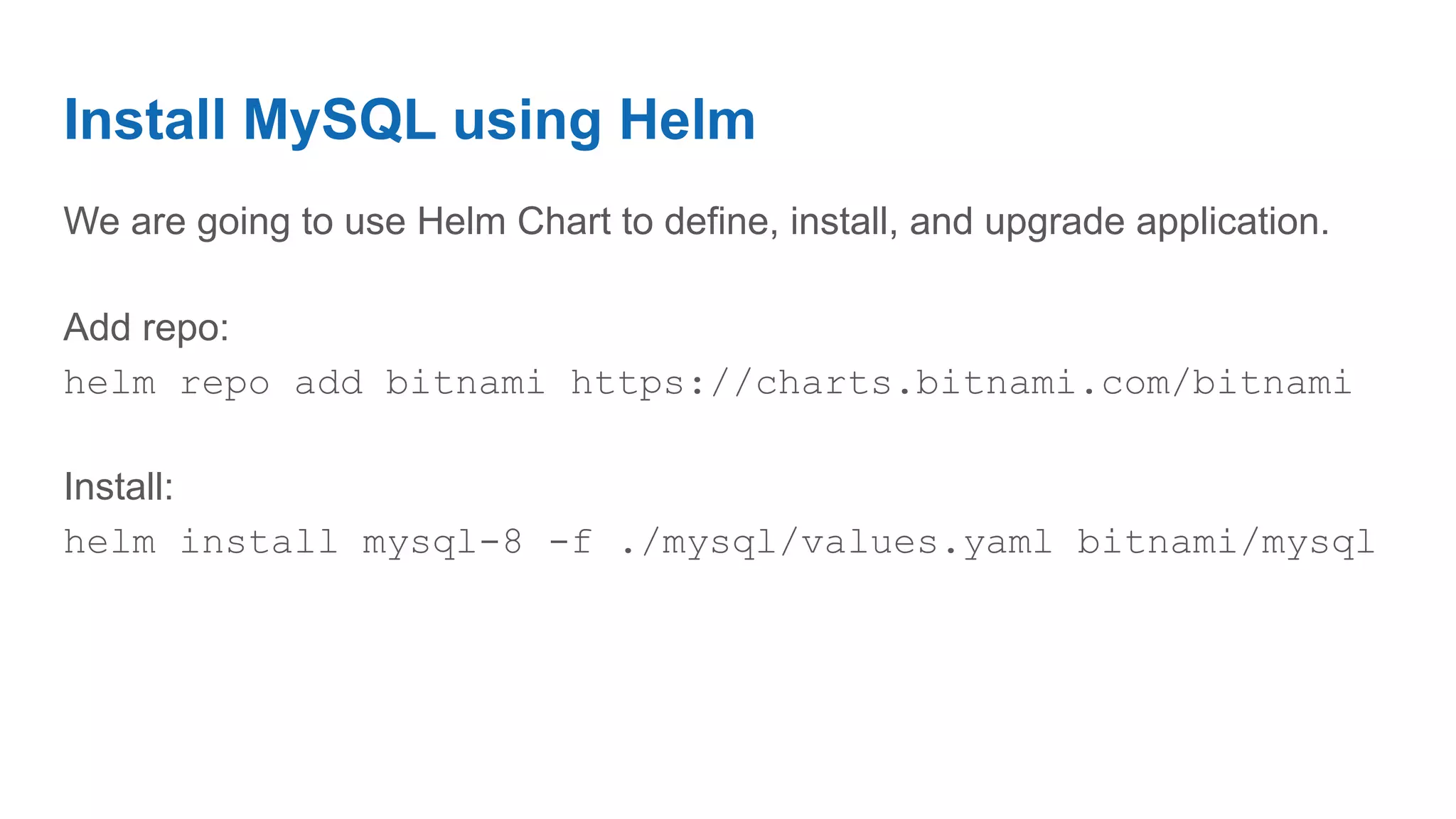
Kubernetes is an open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. It allows you to group hosts, schedule containers, enable communication between containers, associate containers to storage, and ensure high availability and scalability. The demo uses Minikube to run a single-node Kubernetes cluster locally, installs Helm package manager, and deploys a MySQL database cluster on Kubernetes with replication and load balancing using Helm charts. It also shows how to connect to and upgrade the MySQL deployment.