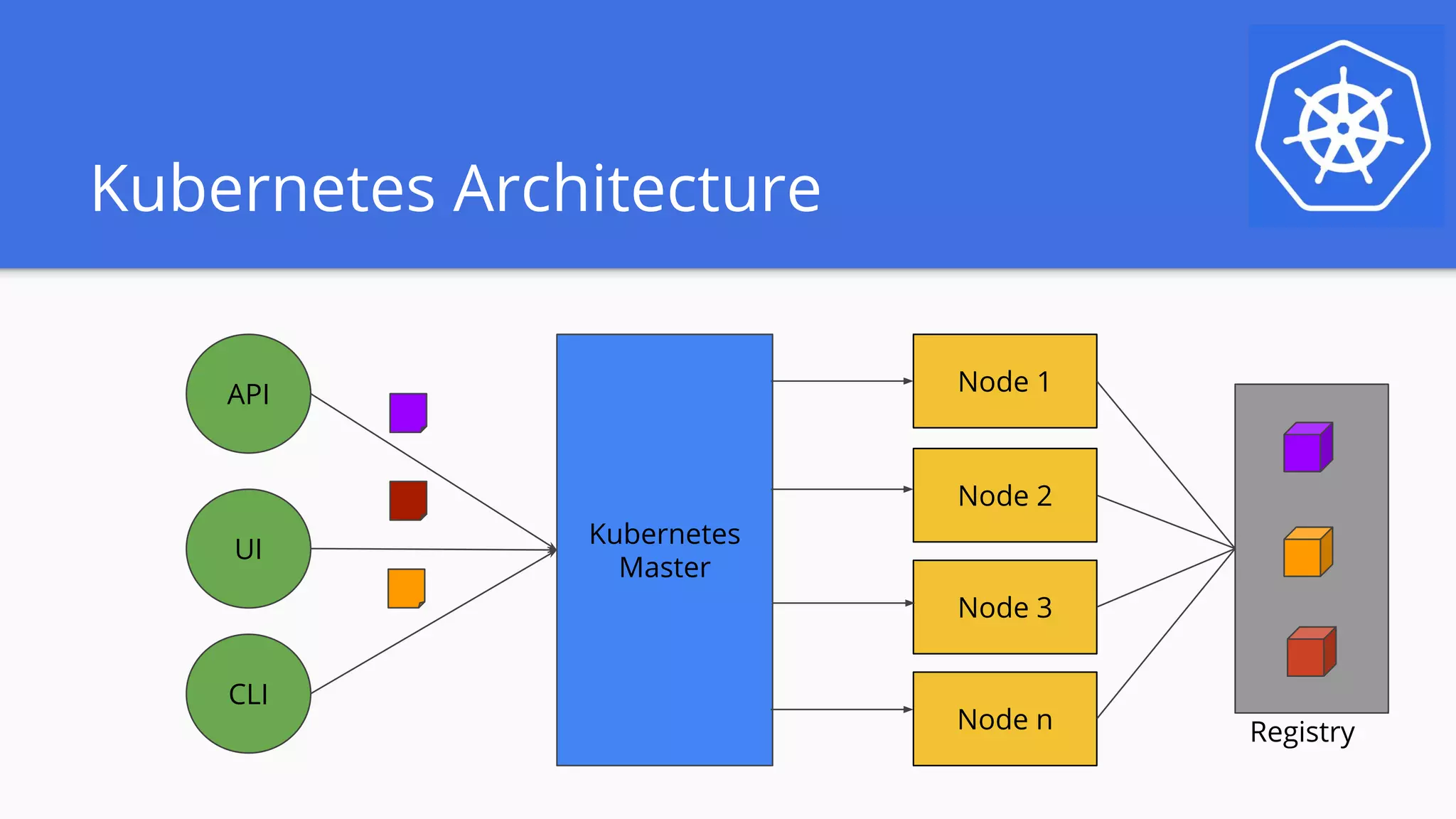
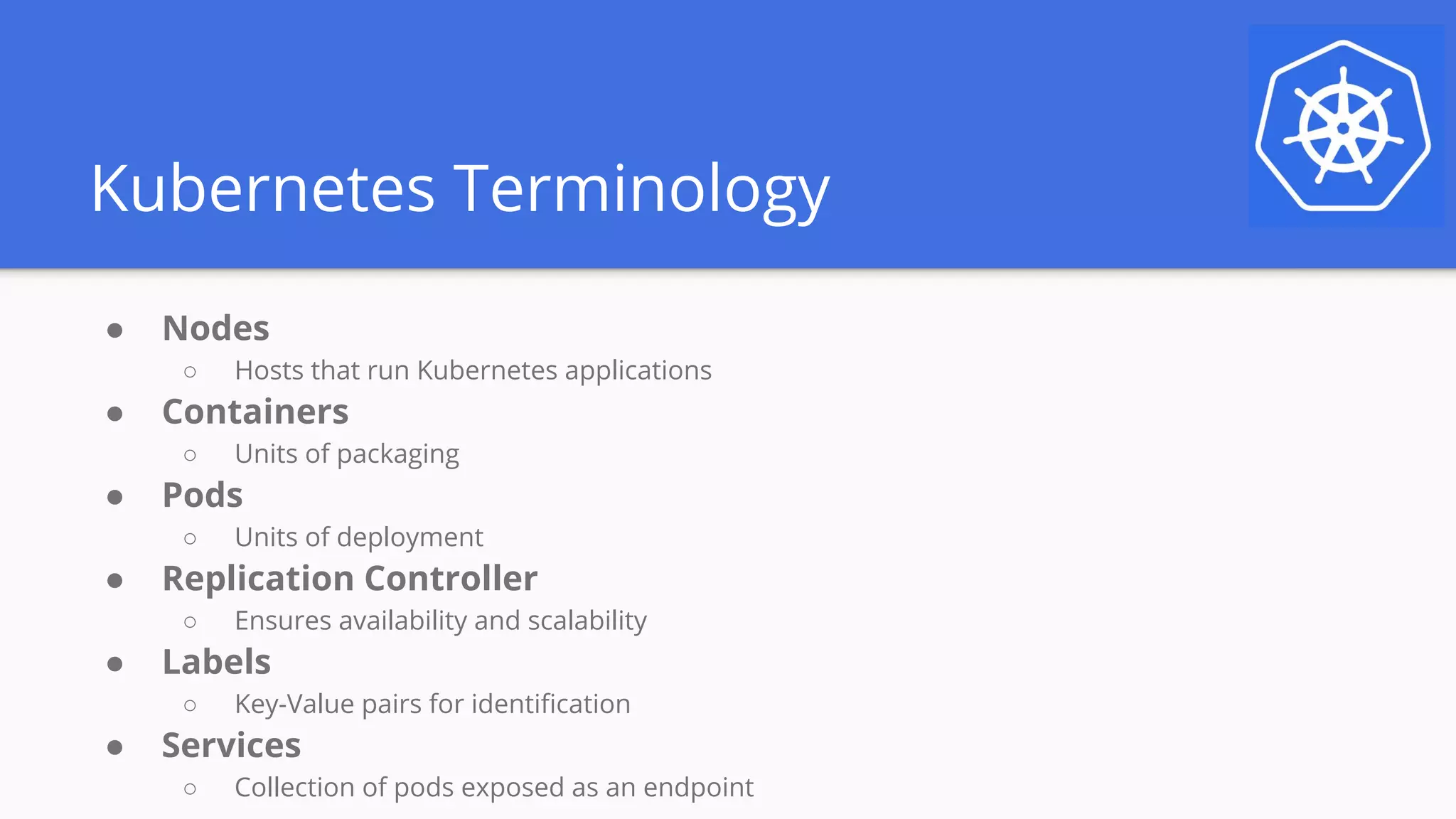
The document announces a monthly webinar series aimed at helping participants get started with Kubernetes, featuring insights from industry experts and covering key concepts such as container orchestration and Kubernetes architecture. Attendees will receive $100 Google Cloud Platform credits and have the opportunity to win subscriptions to an ebook library. The webinar will also provide practical guidance on setting up a development environment and deploying applications using Kubernetes.