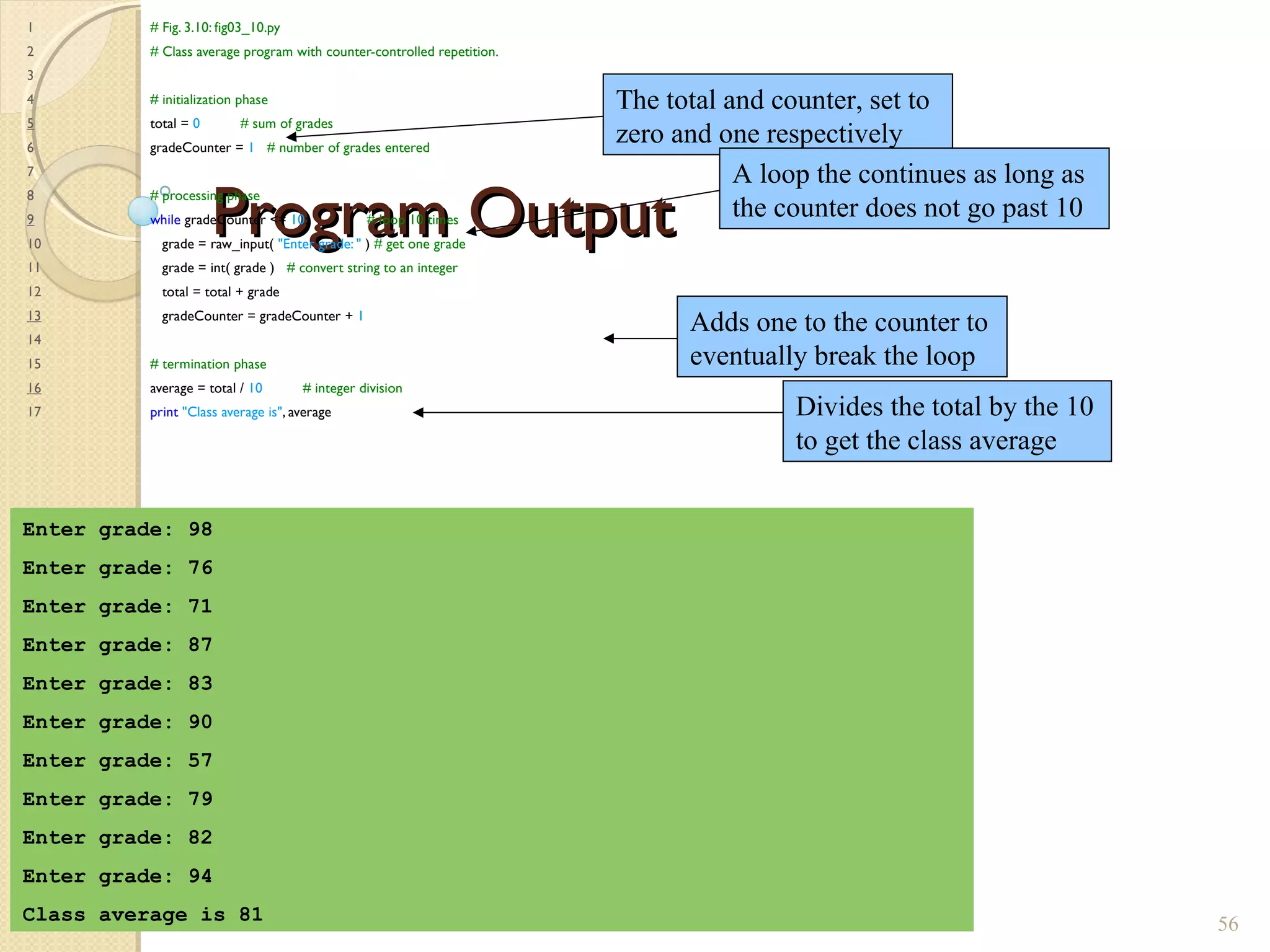
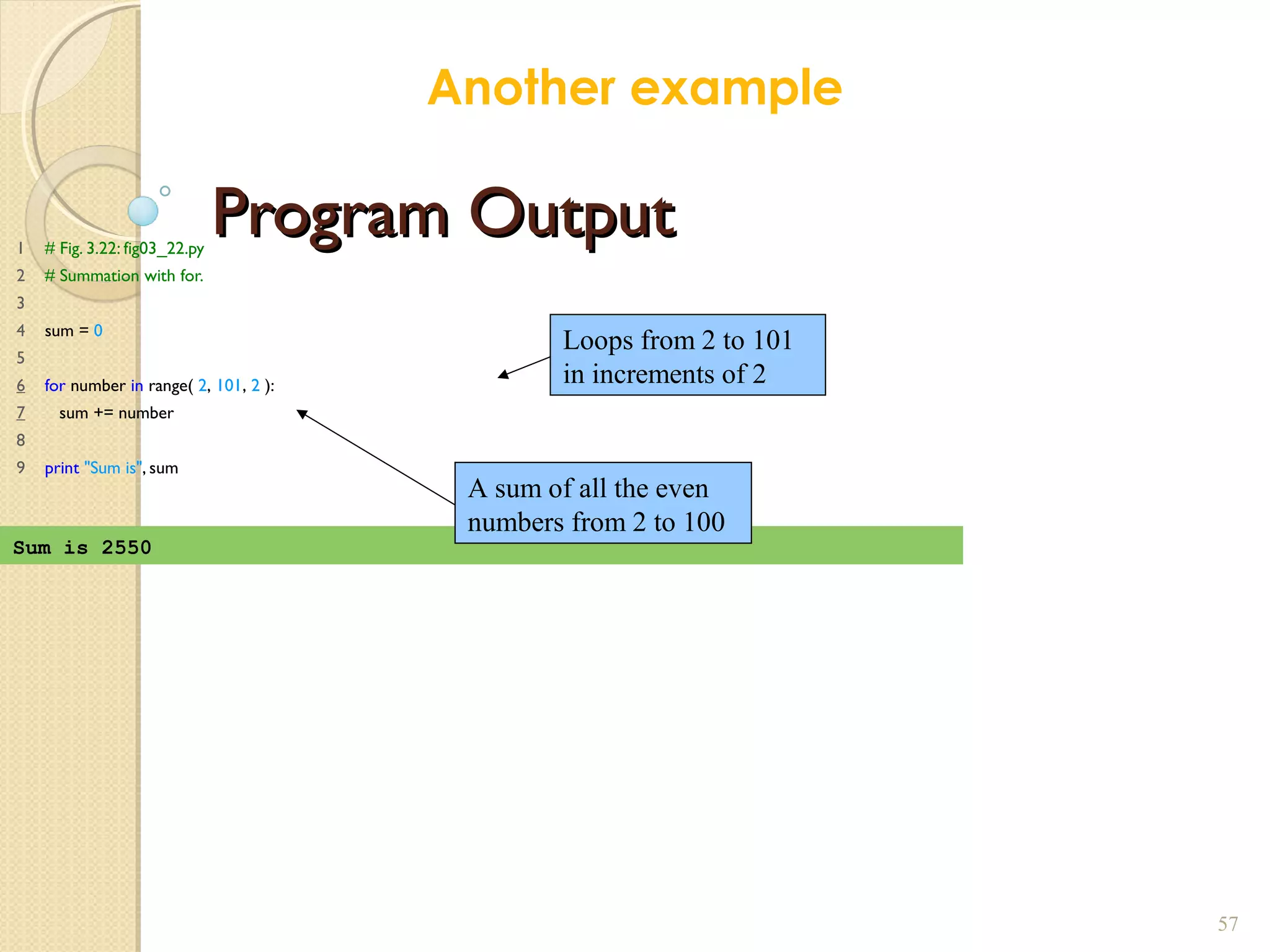
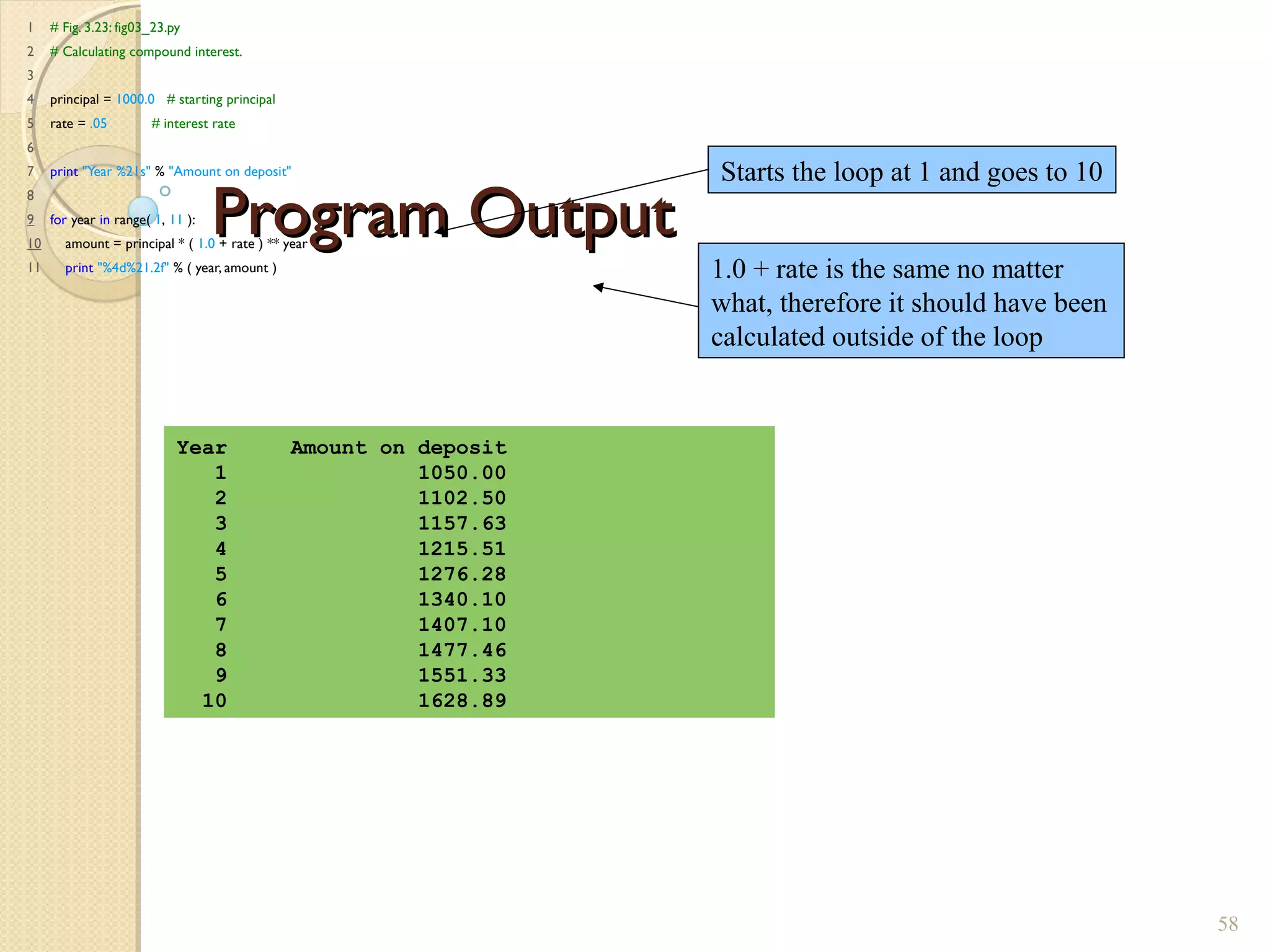
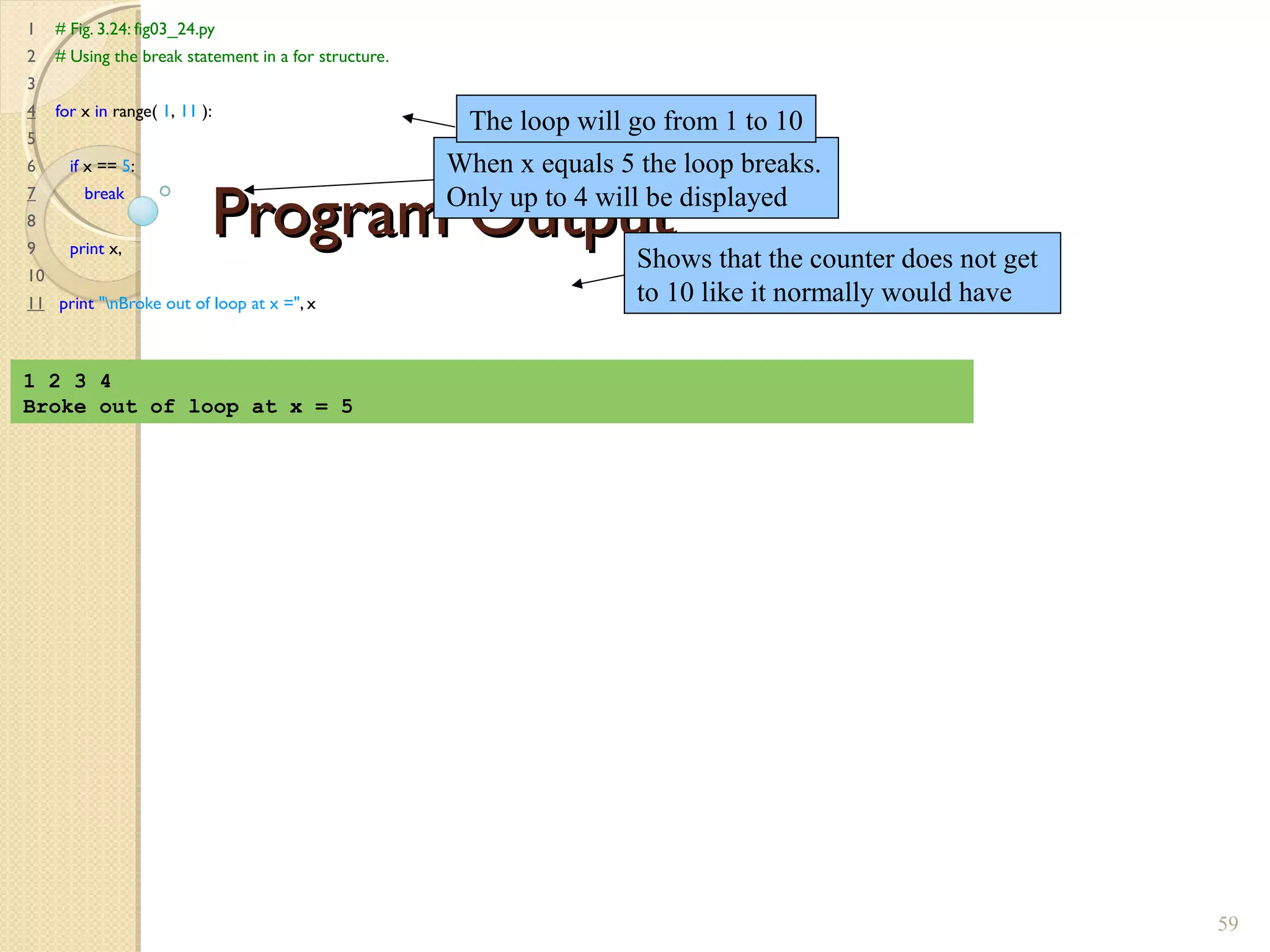
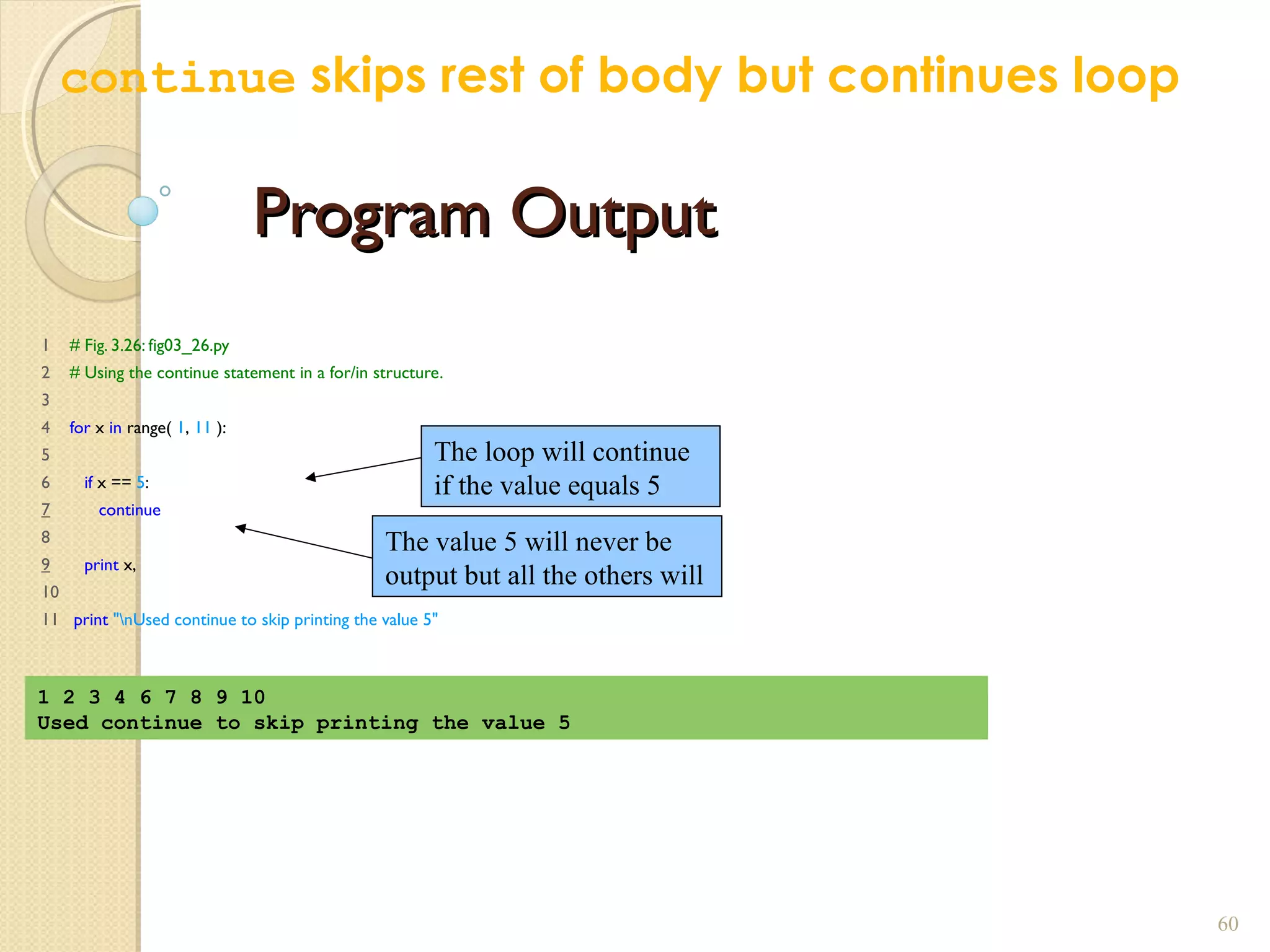
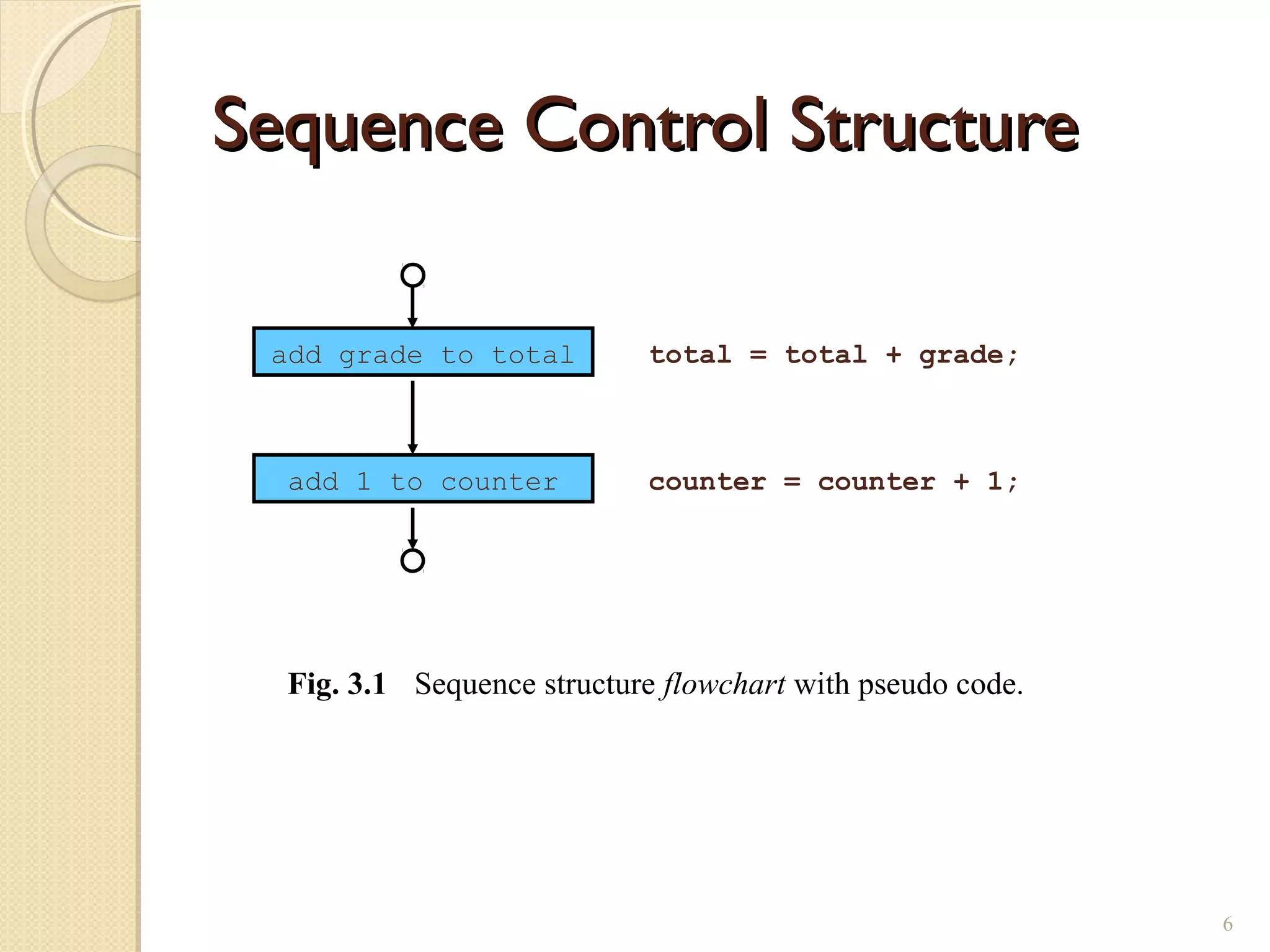
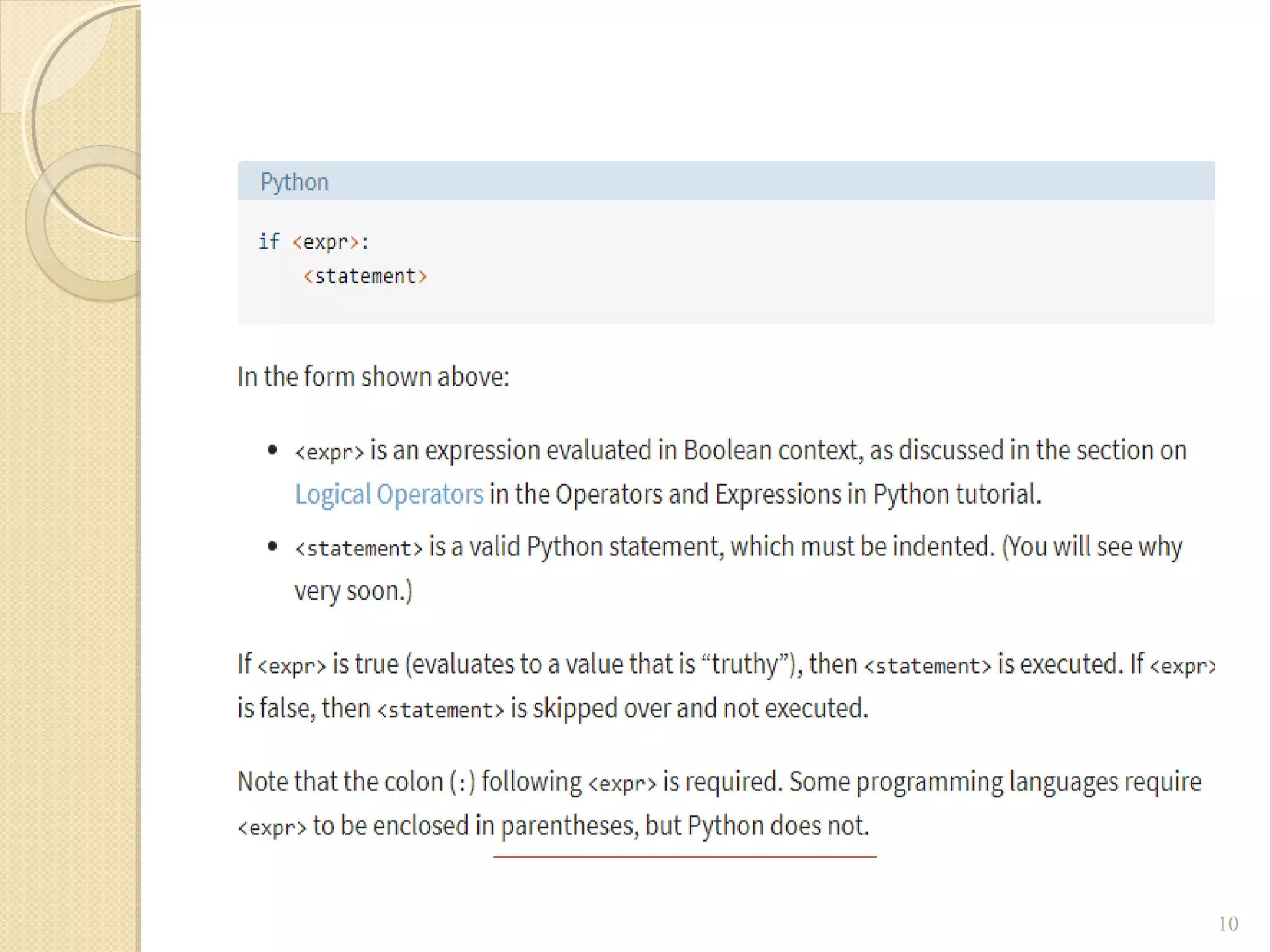
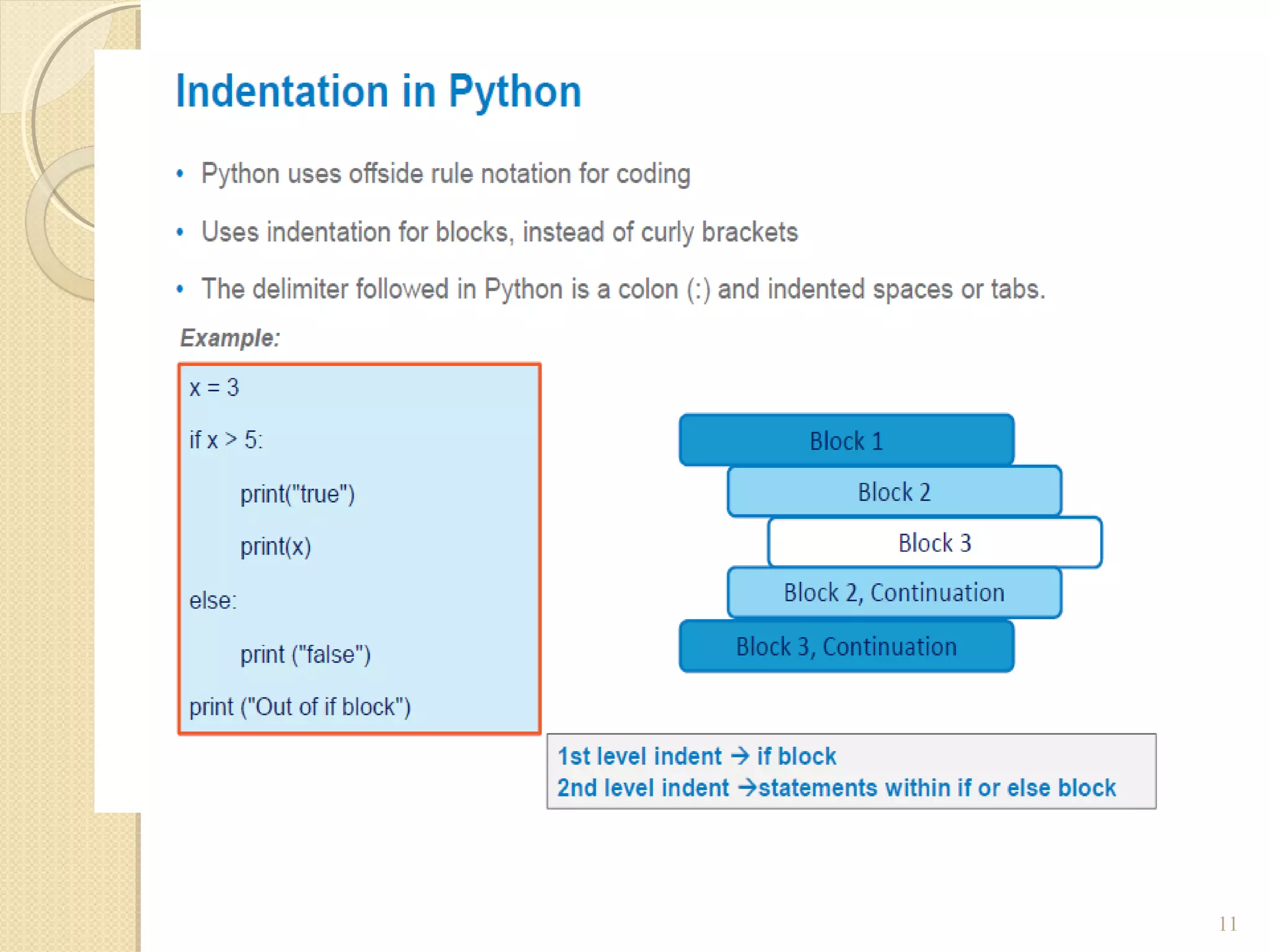
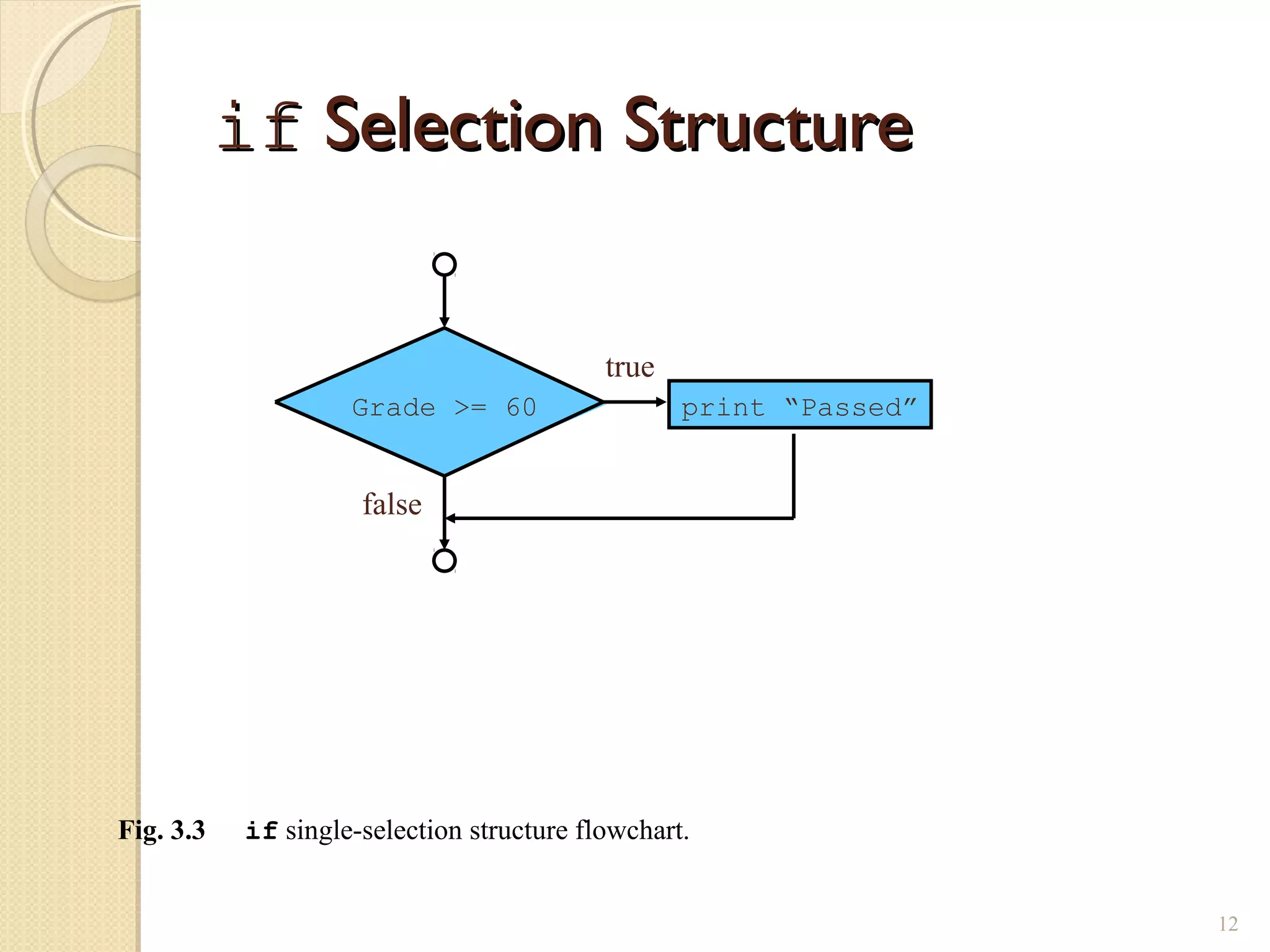
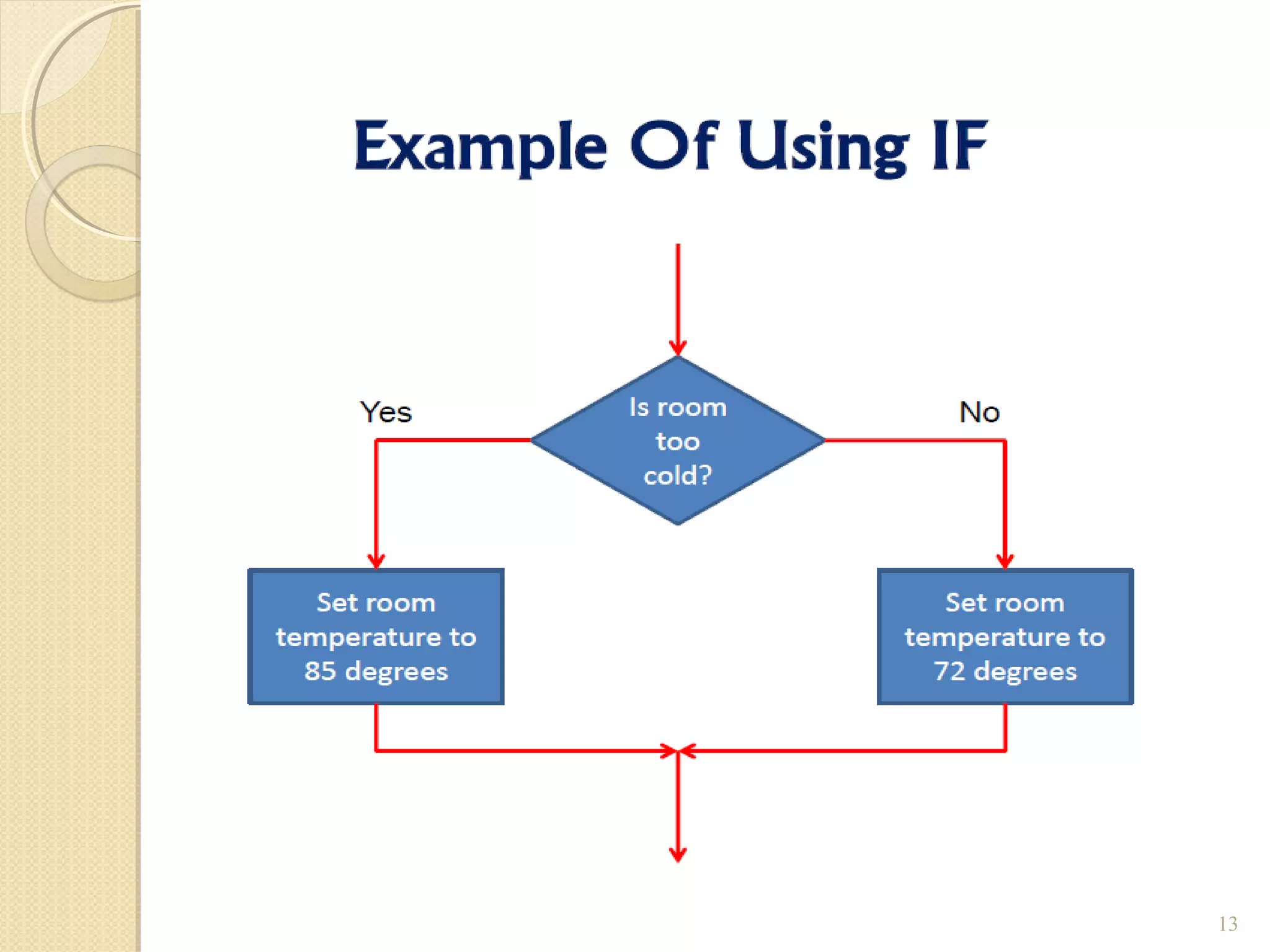
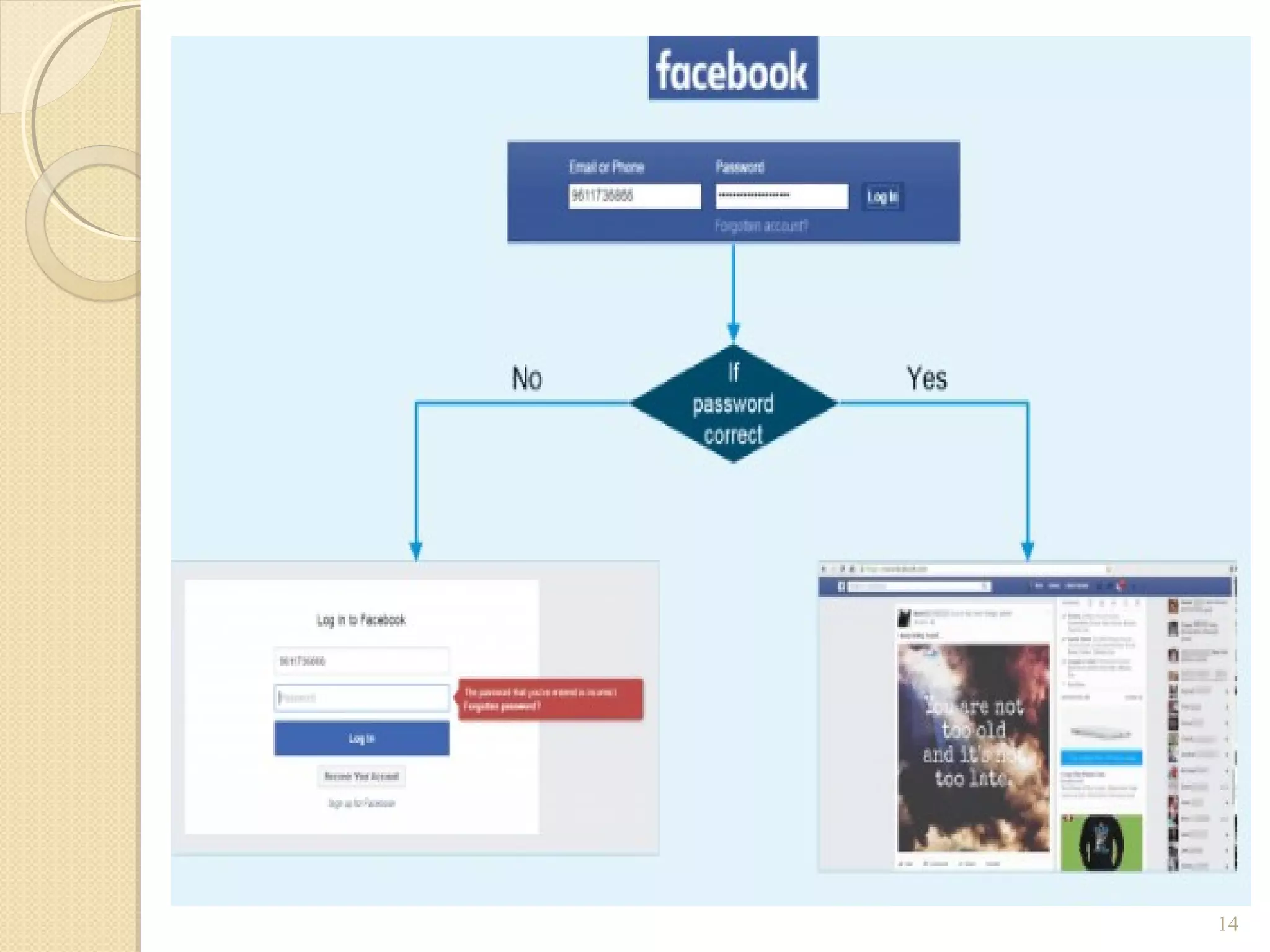
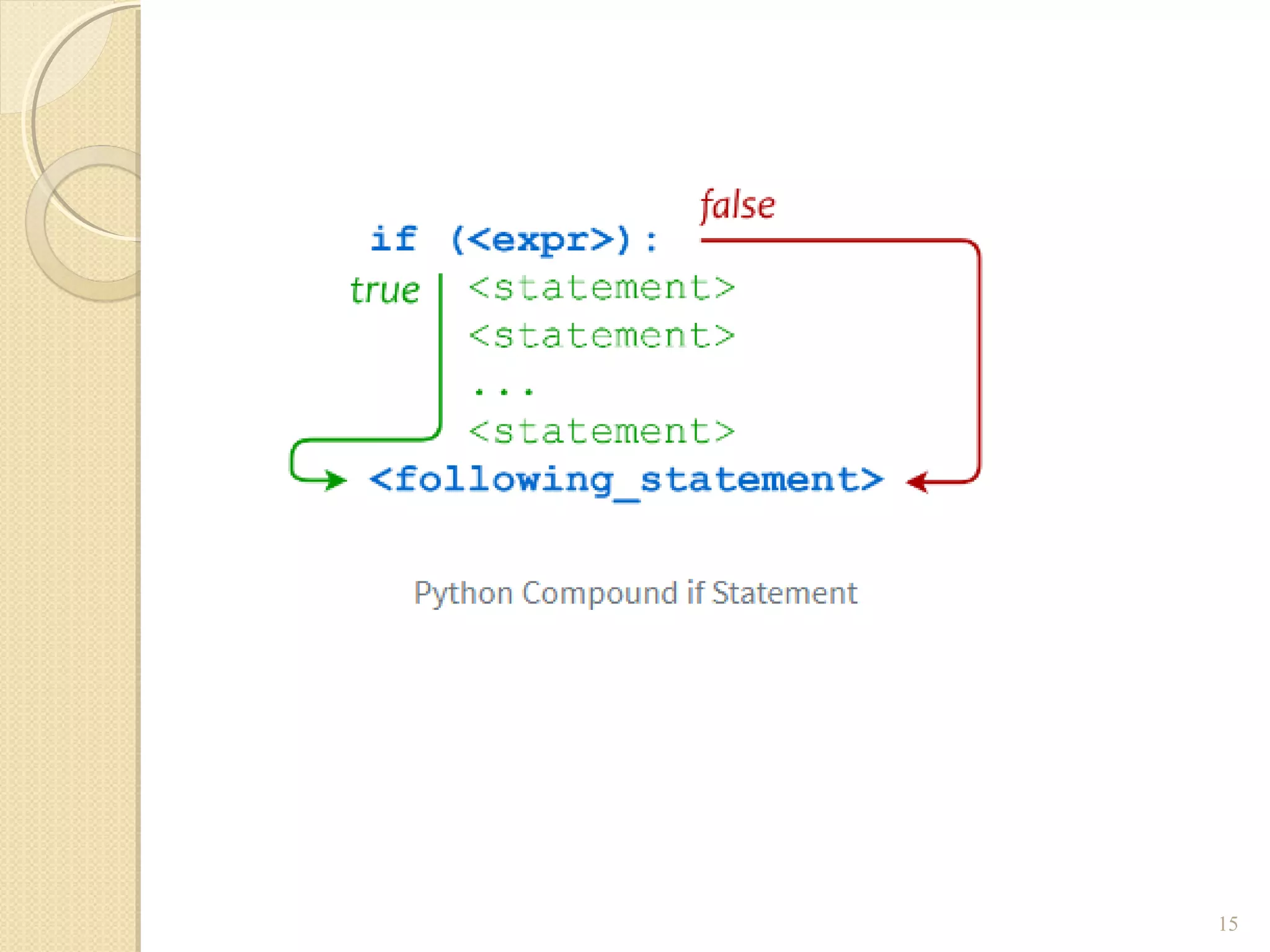
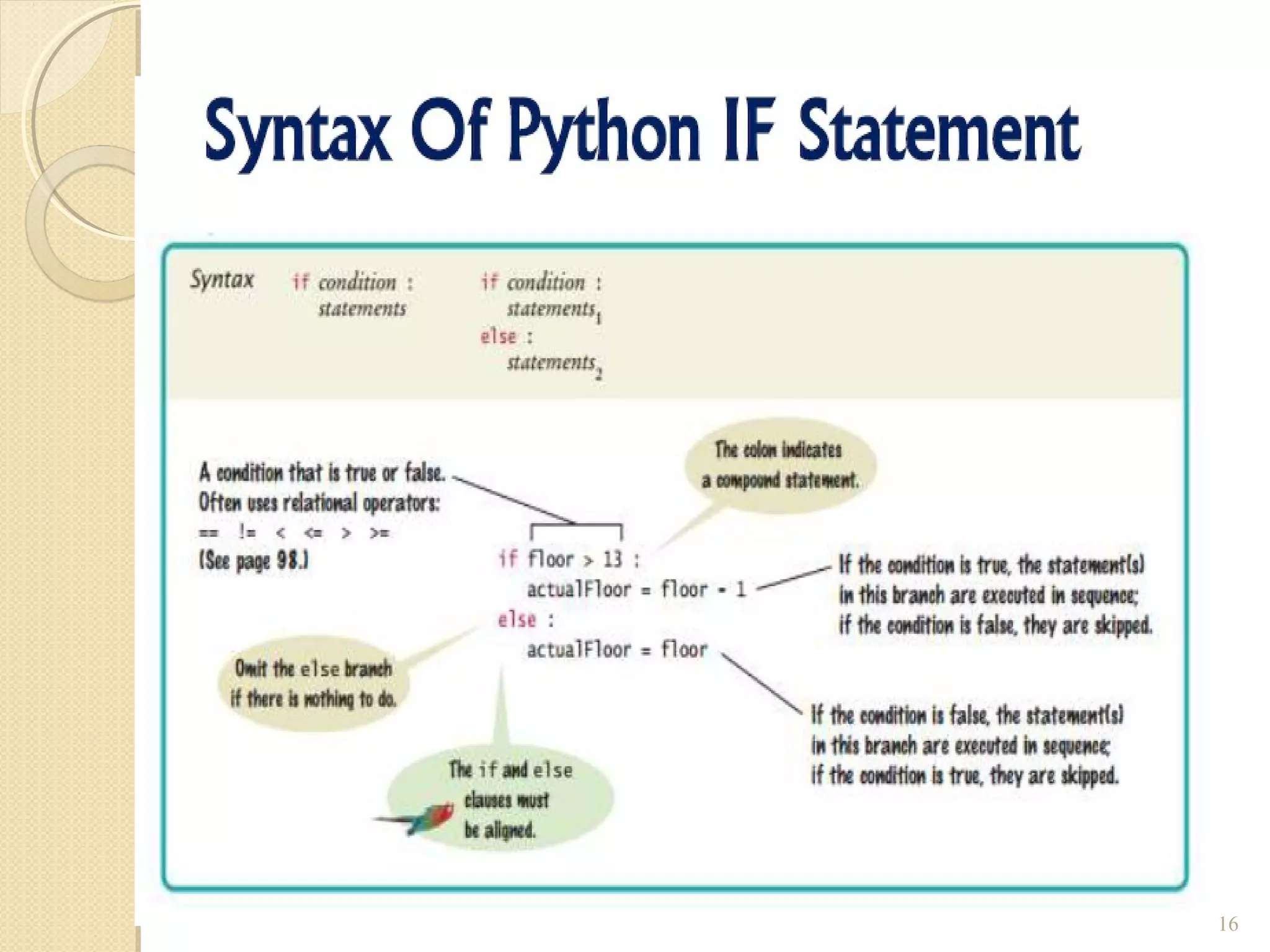
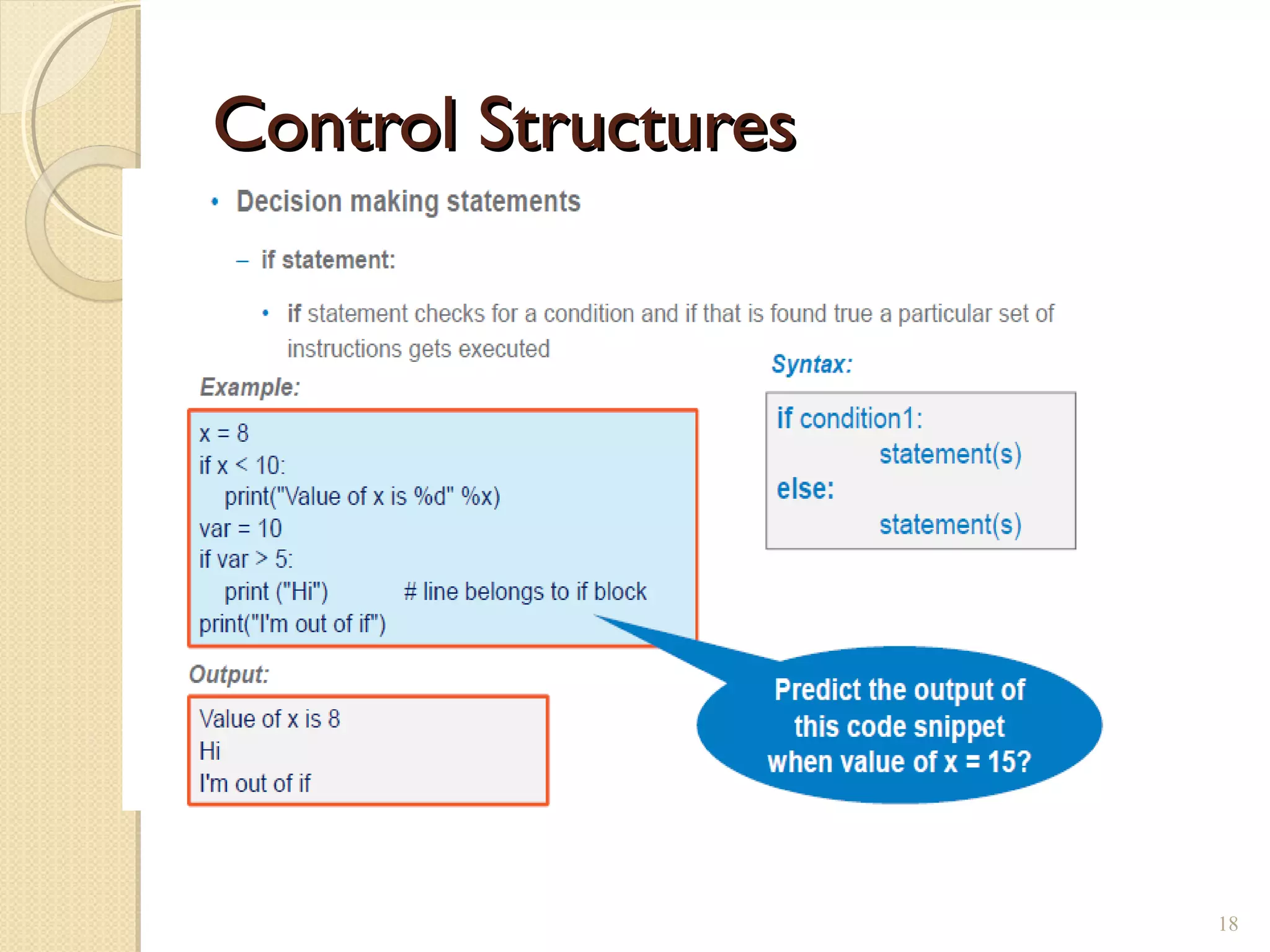
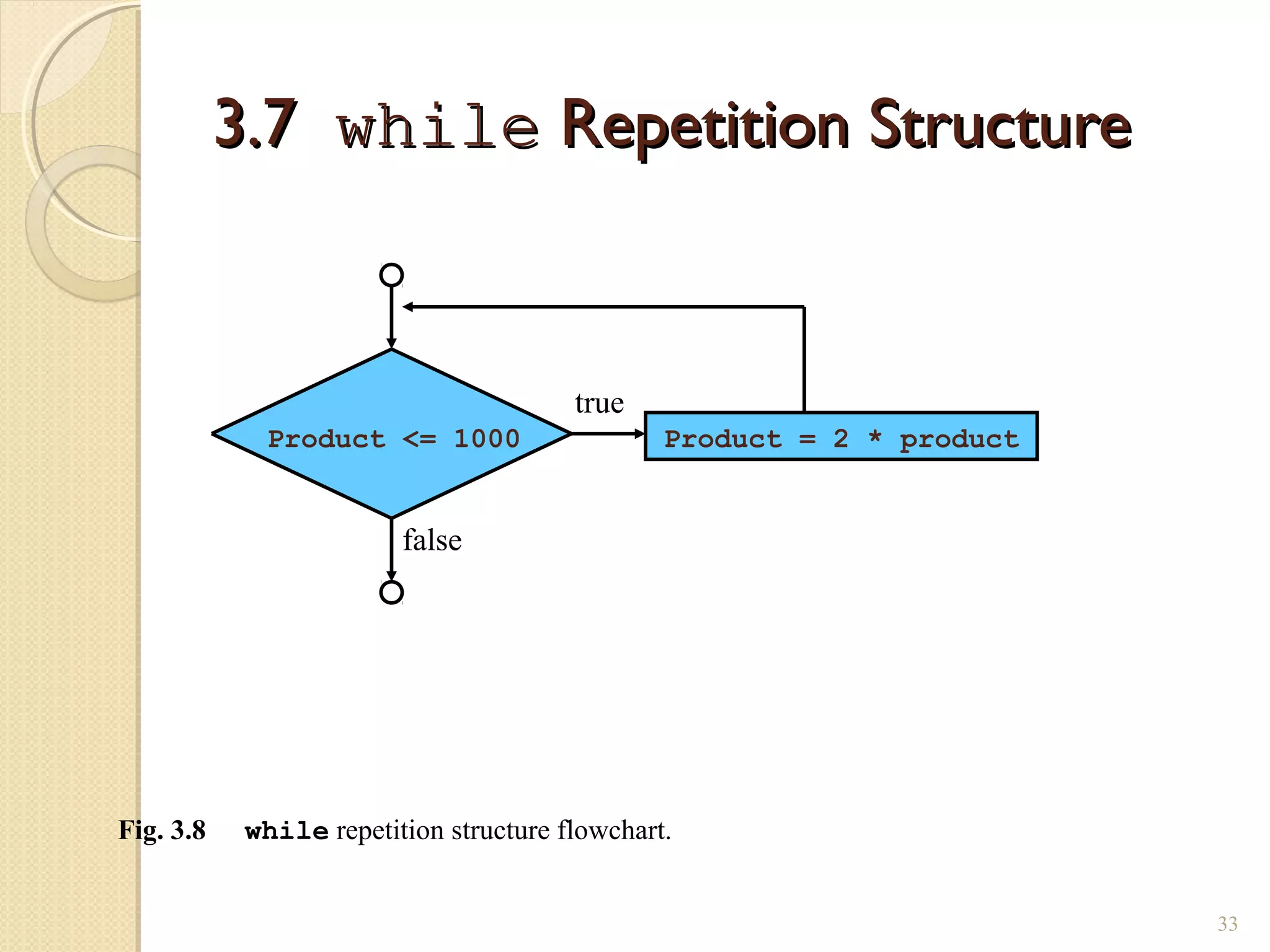
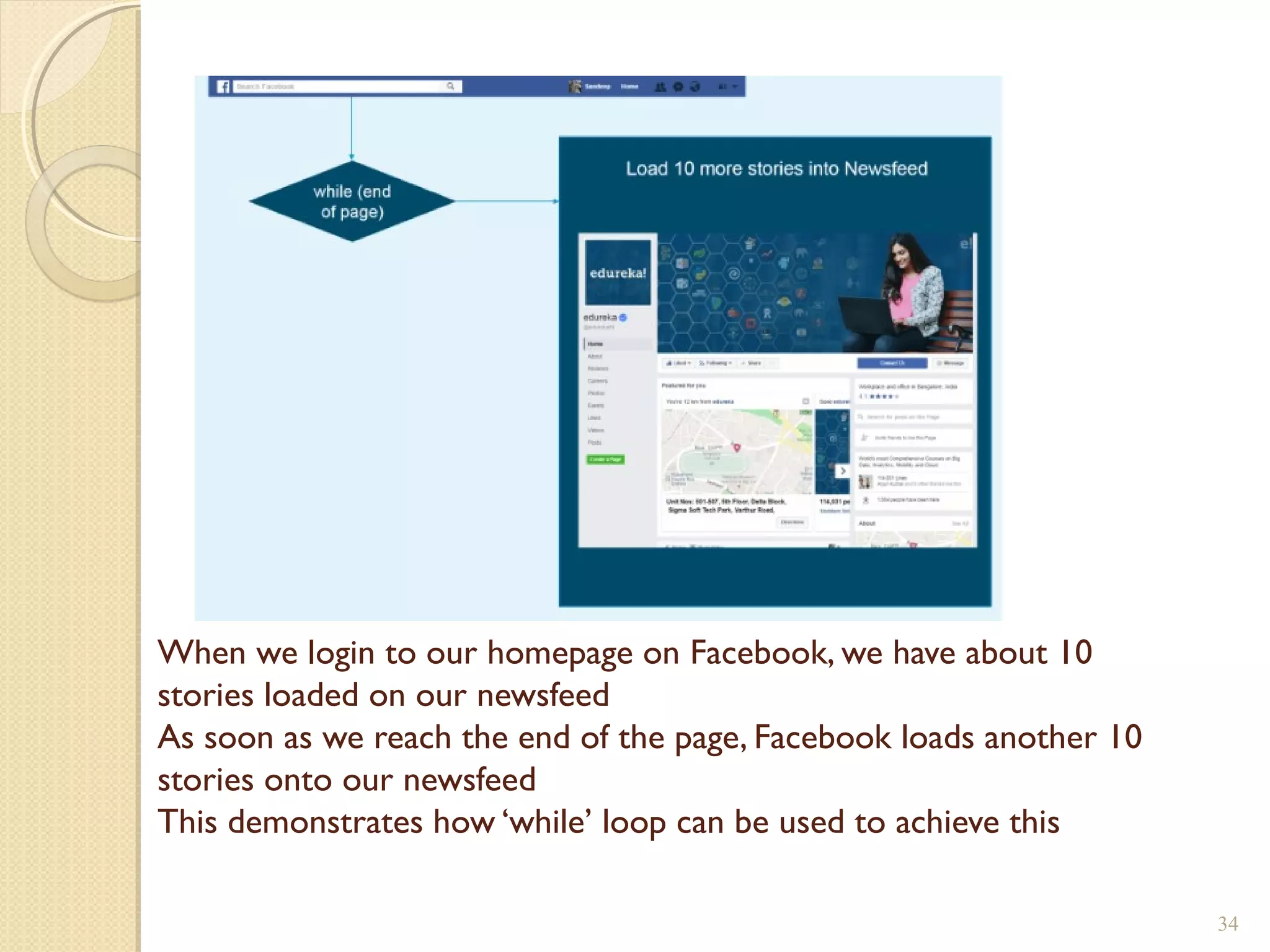
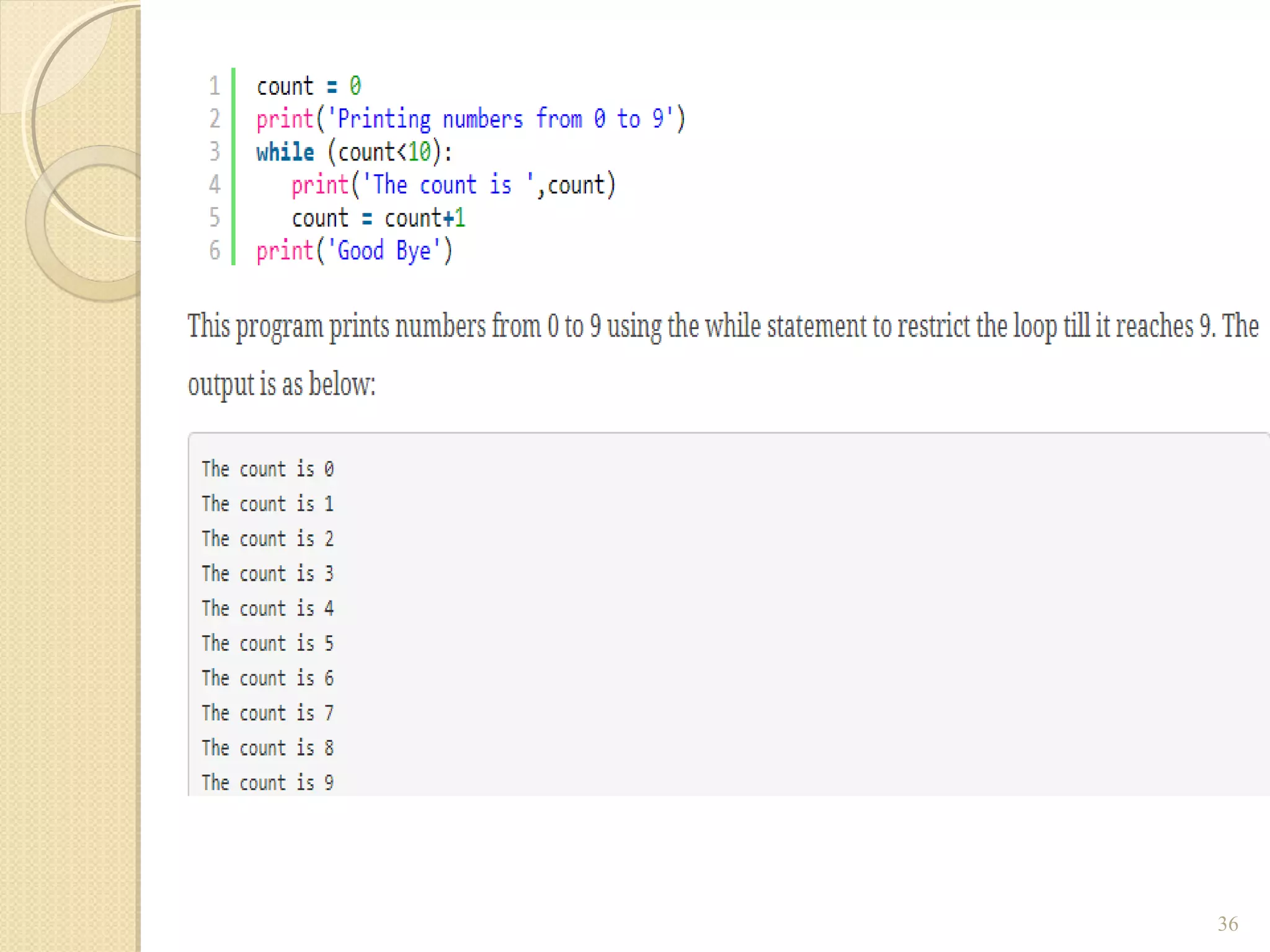
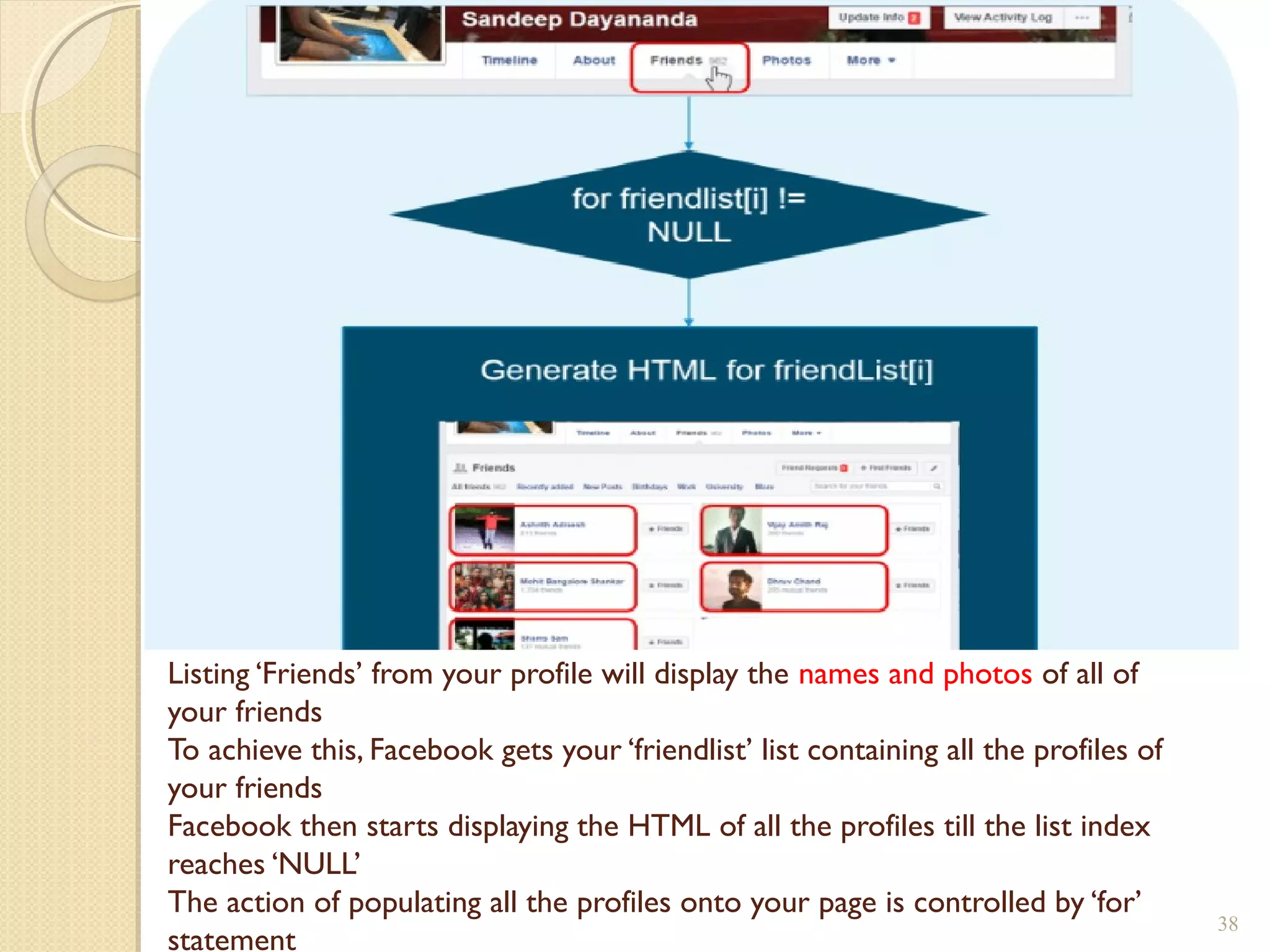
The document provides an overview of control structures in Python, detailing three main types: sequential, decision (if/else), and repetition (while/for). It includes examples of how to implement these structures and discusses the importance of logical operators and augmented assignment in programming. Additionally, it explains practical applications like checking conditions and performing calculations through iterations.








![ >>> if x and y: # Falsy
... print('yes')
...
>>> if 'aul' in 'grault': # Truthy
... print('yes')
...
yes
>>> if 'quux' in ['foo', 'bar', 'baz']: # Falsy
... print('yes')
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlstructures-190308111358/75/Python-Control-structures-20-2048.jpg)


















![Expression values?Expression values?
49
Python 2.2b2 (#26, Nov 16 2001, 11:44:11) [MSC 32 bit (Intel)] on win32
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> if 0:
... print "0 is true"
... else:
... print "0 is false"
...
0 is false
>>> if 1:
... print "non-zero is true"
...
non-zero is true
>>> if -1:
... print "non-zero is true"
...
non-zero is true
>>> print 2 < 3
1
Expressions have integer values. No true, false like in Java.
0 is false, non-0 is true.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlstructures-190308111358/75/Python-Control-structures-49-2048.jpg)



![keywordkeyword passpass : do nothing: do nothing
55
Python 2.2b2 (#26, Nov 16 2001, 11:44:11) [MSC 32 bit (Intel)] on win32
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> if 1 < 2:
... pass
...
Sometimes useful, e.g. during development:
if a <= 5 and c <= 5:
print “Oh no, both below 5! Fix problem”
if a > 5 and c <= 5:
pass # figure out what to do later
if a <= 5 and c > 5:
pass # figure out what to do later
if a > 5 and c > 5:
pass # figure out what to do later](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/controlstructures-190308111358/75/Python-Control-structures-55-2048.jpg)