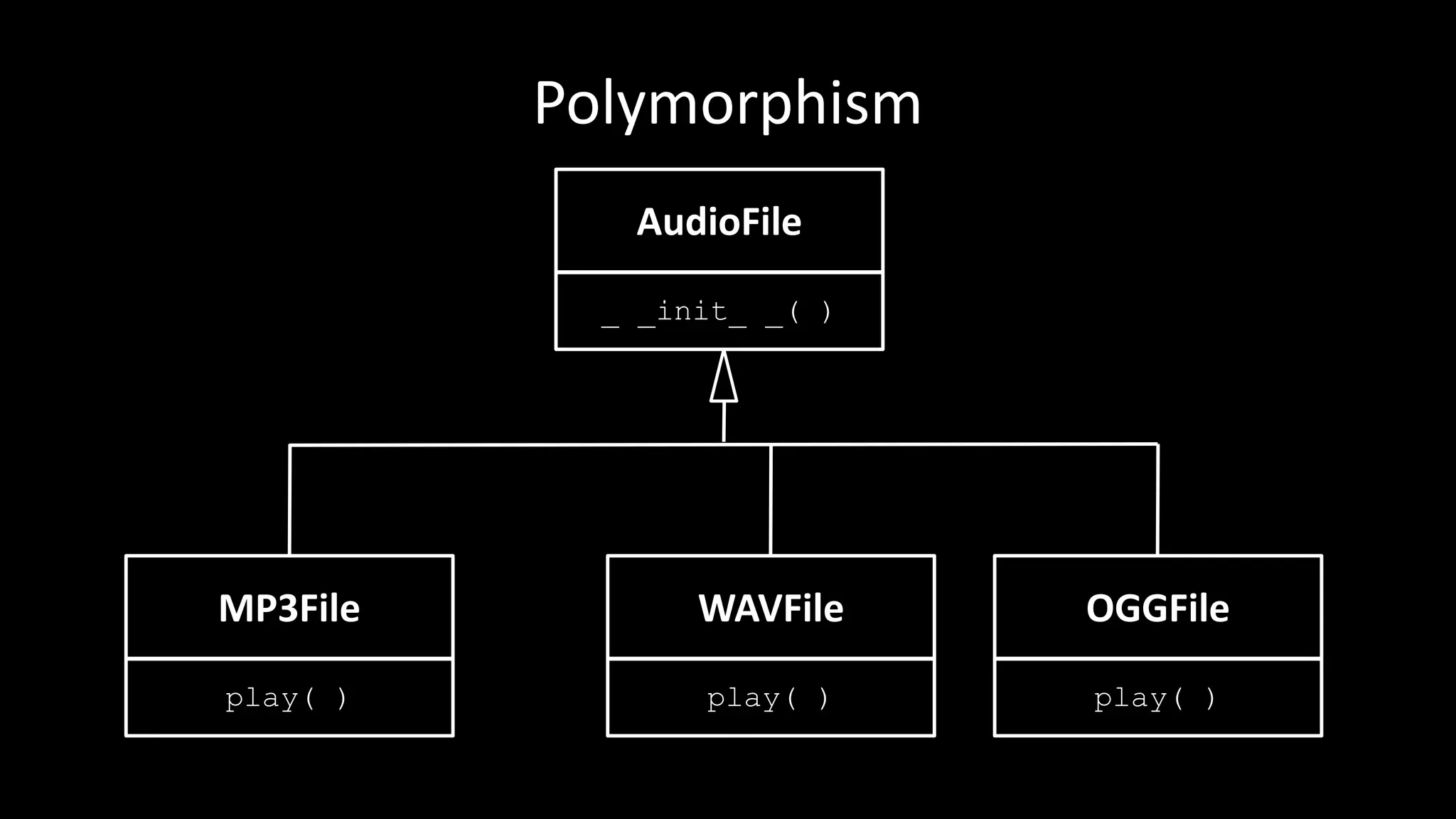
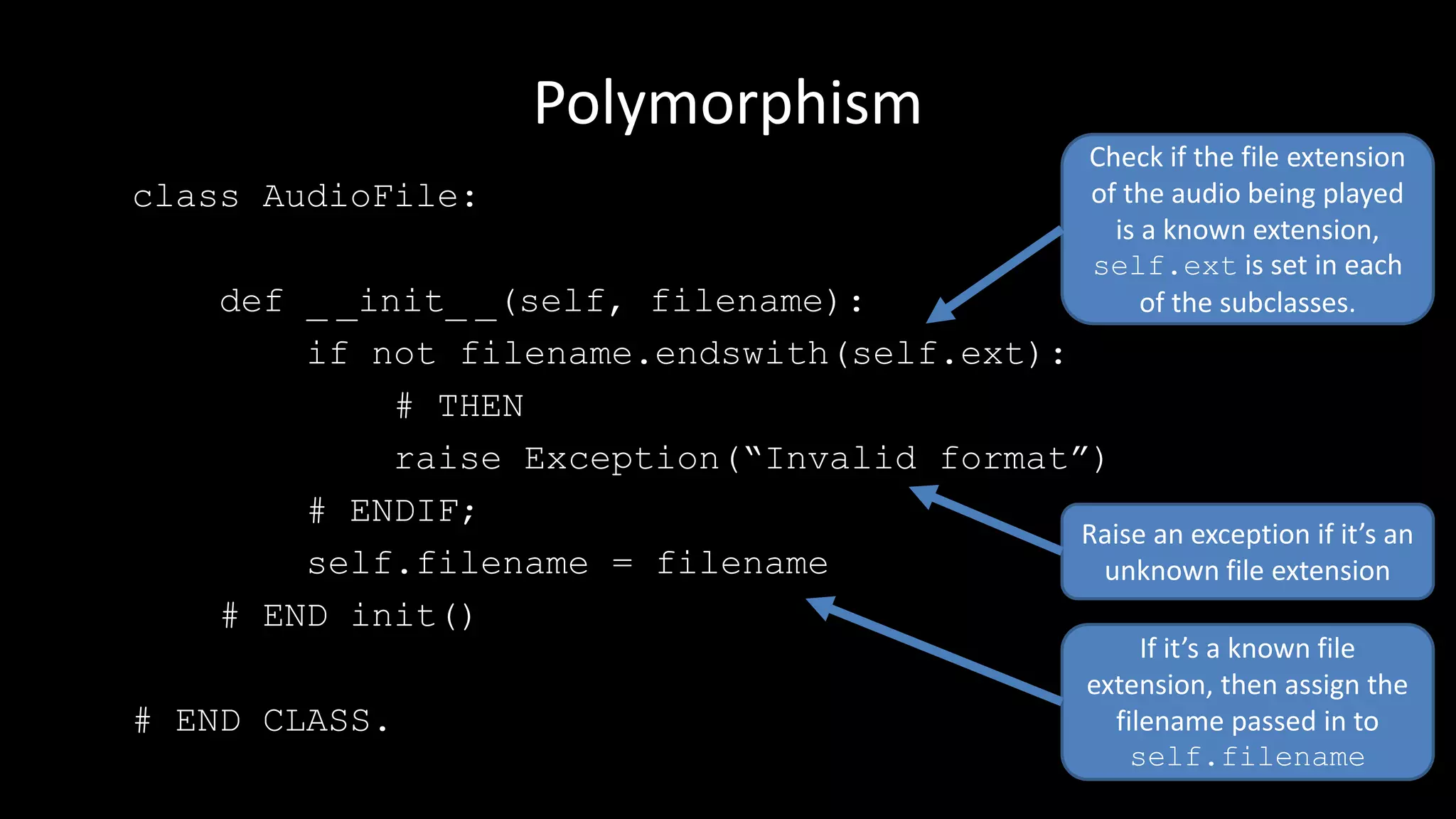
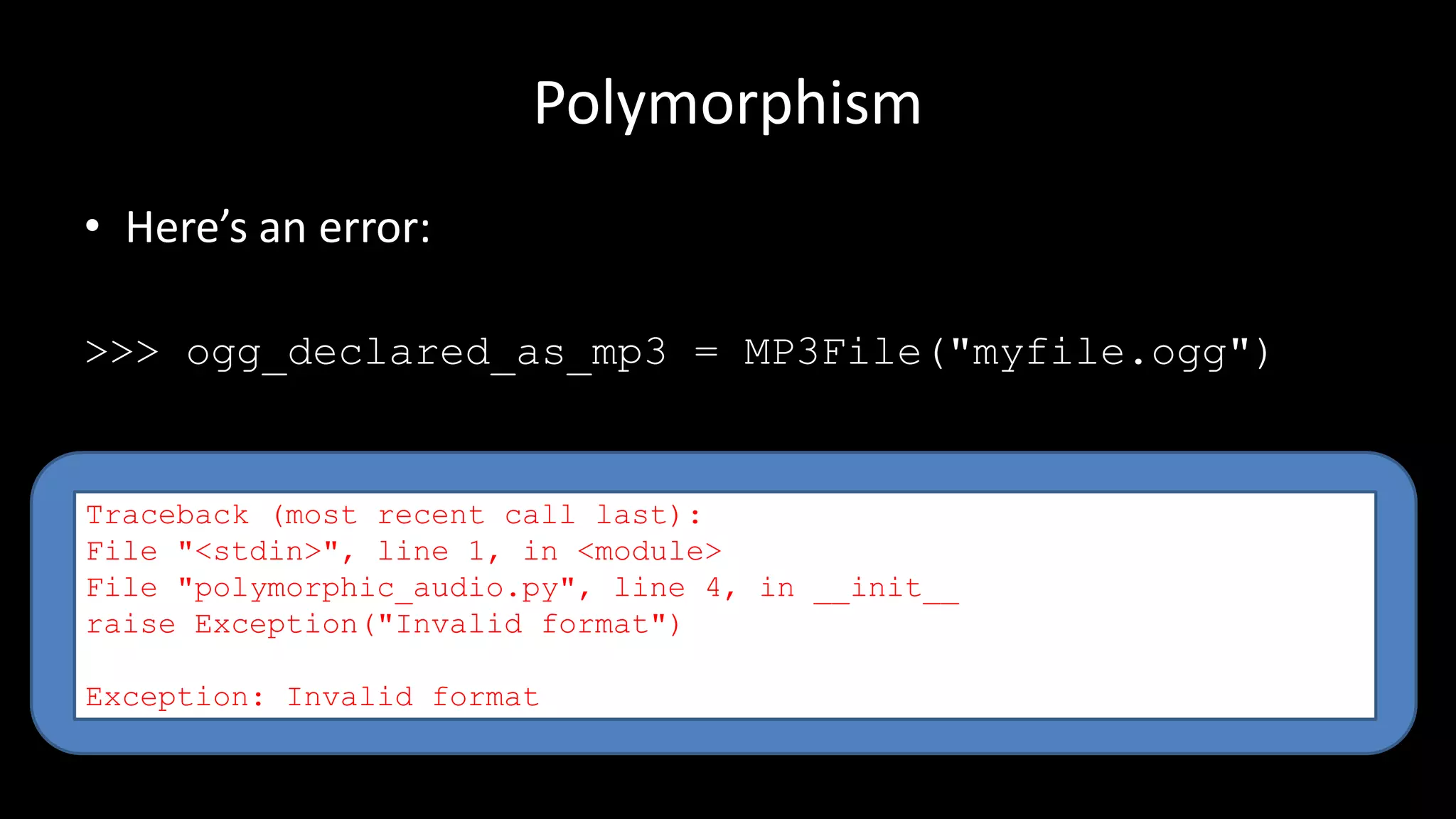
Polymorphism allows the same method name to perform different actions depending on the object type. The document discusses polymorphism in the context of playing different audio file types (e.g. MP3, WAV, OGG). It defines an AudioFile parent class with subclasses for each file type that override the play() method. This allows calling play() on any audio file object while the correct playback logic is handled polymorphically based on the file's type.